What Is Swift Code For Bank? Discover the answer at WHAT.EDU.VN, where we simplify international banking. We help you understand swift codes, their purpose, and how they facilitate secure global financial transactions. Explore international money transfers and bank identifier codes with our resources.
1. Understanding SWIFT Codes: The Key to Global Banking
A SWIFT code, also known as a BIC (Bank Identifier Code), is a standard format used for international money transfers. It acts as a unique identifier for banks and financial institutions worldwide. Think of it as a global address for banks, allowing them to securely communicate and process transactions across borders. This system ensures that your money arrives at the correct destination quickly and efficiently. The swift network is critical for international payments.
 Swift code ensures secure international money transfers
Swift code ensures secure international money transfers
2. The Meaning Behind SWIFT: Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication
SWIFT stands for the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication. This organization owns and manages the BIC system, providing a secure and reliable platform for financial institutions to exchange information and process payments. It is the backbone of international banking, facilitating trillions of dollars in transactions every day. SWIFT has revolutionized international payments.
3. SWIFT Codes: More Than Just Payment Processing
While SWIFT is primarily known for facilitating international payments, its role extends beyond simply transferring money. It also serves as a messaging system for banks, allowing them to securely exchange information about various financial transactions. This includes everything from trade finance to treasury operations. Swift is integral to modern finance.
4. SWIFT Code Synonyms: Understanding the Different Names
You might encounter SWIFT codes referred to by different names, including:
- SWIFT ID
- BIC code
- ISO 9362
These terms all refer to the same unique identifier for a bank or financial institution. Understanding these synonyms can help you navigate the world of international banking with greater ease. Understanding swift codes is important.
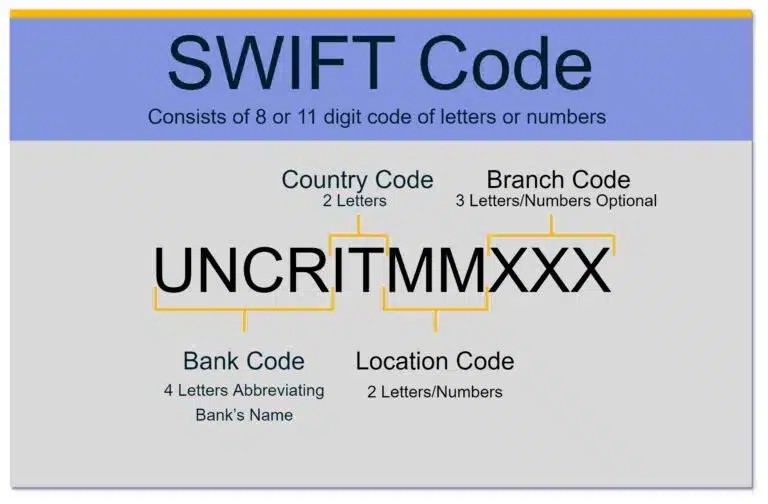
5. Decoding the SWIFT Code Format: A Detailed Breakdown
A SWIFT code is typically an 8- or 11-character alphanumeric code, structured as follows:
- Bank code (4 letters): Represents the bank’s name abbreviation.
- Country code (2 letters): Indicates the country where the bank is located.
- Location code (2 letters or numbers): Identifies the bank’s head office location.
- Branch code (3 letters or numbers): Specifies a particular branch of the bank (optional; if omitted, the code refers to the bank’s head office).
Understanding this format can help you decipher a SWIFT code and verify its accuracy. Swift codes have a standard format.
6. SWIFT Code Example: UniCredit Banca in Milan
Let’s take the example of UniCredit Banca in Milan, Italy. Its SWIFT code is UNCRITMMXXX. Here’s how it breaks down:
- UNCR: Bank code for UniCredit.
- IT: Country code for Italy.
- MM: Location code for Milan.
- XXX: Indicates the head office, as there is no specific branch code.
This example illustrates how a SWIFT code provides a clear and concise identifier for a specific bank and its location. Swift codes pinpoint a location.
7. When Do You Need a SWIFT Code? Essential Scenarios
You’ll typically need a SWIFT code when sending or receiving money internationally, particularly for wire transfers and SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area) payments. It ensures that the funds are routed to the correct bank and account. A swift code is needed for international transactions.
8. The Versatility of SWIFT: Serving a Wide Range of Institutions
The SWIFT network serves a diverse range of institutions, including:
- Banks
- Corporations
- Foreign exchange brokers
- Clearing systems
- Asset management companies
- Money brokers
- Non-bank financial institutions
- Treasury market participants
- Depositories
Its widespread adoption highlights its importance in the global financial ecosystem. Swift connects many institutions.
9. How SWIFT Facilitates International Payments: The Messaging System
SWIFT doesn’t actually transfer money itself. Instead, it acts as a secure messaging system between banks. It transmits payment instructions from the sending bank to the receiving bank, ensuring that the funds are routed correctly. Swift sends payment instructions.
10. SWIFT and Intermediary Banks: Navigating Complex Transactions
In some cases, a SWIFT payment may require an intermediary bank. This is often necessary when the sending and receiving banks don’t have a direct relationship. The intermediary bank acts as a bridge, facilitating the transaction. Intermediary banks help with swift payments.
11. Nostro and Vostro Accounts: The Foundation of SWIFT Transfers
To facilitate SWIFT transfers, banks often open accounts with each other, known as Nostro and Vostro accounts.
- Nostro: An account a bank holds in a foreign location with another bank (Latin for “ours”).
- Vostro: An account other banks have with them (meaning “yours”).
These accounts enable direct and efficient transfers between banks that have established relationships. Nostro and Vostro accounts are vital.
12. Finding Your SWIFT Code: Easy Methods to Locate It
You can typically find your SWIFT code on:
- Bank account statements
- Online banking portals
- Your bank’s website
- By contacting your bank directly
You can also use online SWIFT code search tools. Finding your swift code is simple.
13. Validating Your SWIFT Code: Ensuring Accuracy
Before initiating a transaction, it’s crucial to verify the SWIFT code using a SWIFT code checker. This helps prevent errors and ensures that your funds reach the intended destination. Check your swift code online.
14. SWIFT Codes and Security: Why They Matter
SWIFT codes play a crucial role in ensuring the security of international financial transactions. By providing a standardized and verifiable identifier for banks, they help prevent fraud and money laundering. The swift network is secure.
15. Addressing Common Concerns: FAQs About SWIFT Codes
Let’s address some frequently asked questions about SWIFT codes:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Is a SWIFT code the same as a BIC? | Yes, BIC (Bank Identifier Code) is the umbrella term for a SWIFT code. |
| Does it cost money to use a SWIFT code? | Typically, yes, as international transfers usually involve fees. The exact cost depends on the banks involved, the destination country, and any intermediary banks. |
| What happens if you give the wrong SWIFT code? | In the best case, the transaction will be rejected and the funds returned. However, it could also lead to delays or the funds being sent to the wrong account. Always double-check the SWIFT code. |
| Is a SWIFT code like a routing number? | SWIFT codes are used for international transactions, while routing numbers are used for domestic transactions in the U.S. They serve a similar purpose of identifying banks, but they are distinct systems. |
| Is a SWIFT code the same as an IBAN? | No. A SWIFT code identifies a specific bank, while an IBAN (International Bank Account Number) identifies an individual account at that bank. You often need both to make an international transfer. |
| How long does a SWIFT transfer take? | SWIFT transfers typically take 1-5 business days, depending on the countries and banks involved. |
| Are SWIFT transfers safe? | Yes, SWIFT is a secure network with measures in place to prevent fraud and money laundering. However, it’s still important to be vigilant and double-check all information before sending money. |
| Can I track a SWIFT transfer? | Yes, most banks provide a tracking number or reference code that allows you to monitor the progress of your SWIFT transfer. |
| What are the alternatives to SWIFT? | Alternatives to SWIFT include other payment networks like SEPA (for Euro payments), CHAPS (for UK payments), and various online money transfer services like Wise (formerly TransferWise) and Remitly. |
| How can I avoid high SWIFT transfer fees? | Compare fees from different banks and money transfer services. Consider using alternative payment methods if they offer lower fees. Ensure you have accurate information to avoid delays and additional charges. |
16. SWIFT vs. IBAN: Understanding the Key Differences
The main difference between SWIFT and IBAN lies in what the codes convey. A SWIFT code identifies a specific bank, whereas an IBAN identifies an individual account. Both are often needed for international transfers. IBAN identifies bank accounts.
17. The Future of SWIFT: Adapting to a Changing World
SWIFT continues to evolve and adapt to the changing needs of the global financial landscape. It is constantly updating its systems and technologies to remain a leading provider of secure and reliable international payment services. Swift is continuously evolving.
18. The Benefits of Using SWIFT: Efficiency, Security, and Global Reach
The SWIFT network offers numerous benefits, including:
- Efficiency: Facilitates rapid and efficient international payments.
- Security: Provides a secure platform for financial transactions.
- Global Reach: Connects thousands of financial institutions worldwide.
- Standardization: Uses a standardized format for bank identification.
These benefits make SWIFT a crucial component of the global financial system. Swift offers global benefits.
19. Exploring Alternatives to SWIFT: Other Payment Networks
While SWIFT is the dominant player in international payments, other networks exist, such as:
- SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area)
- CHAPS (Clearing House Automated Payment System)
- Faster Payments Service (FPS)
These networks may offer faster or cheaper alternatives for specific types of transactions. Understand swift payment alternatives.
20. How to Stay Safe When Using SWIFT: Protecting Yourself from Fraud
To protect yourself from fraud when using SWIFT:
- Always double-check the SWIFT code and account details before sending money.
- Be wary of phishing emails or other scams that attempt to obtain your financial information.
- Use strong passwords and keep your online banking credentials secure.
- Monitor your account activity regularly for any unauthorized transactions.
Staying vigilant can help you avoid becoming a victim of fraud. Stay safe when using swift.
21. SWIFT for Businesses: Streamlining International Transactions
For businesses that engage in international trade, SWIFT can be a valuable tool for streamlining payments and managing their finances. It allows them to send and receive money quickly and securely, reducing the risk of delays or errors. Swift streamlines international transactions.
22. SWIFT and Compliance: Meeting Regulatory Requirements
Financial institutions that use SWIFT must comply with various regulatory requirements, such as anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) regulations. These regulations help prevent illicit activities and ensure the integrity of the financial system. Swift complies with regulations.
23. The Role of SWIFT in International Trade Finance
SWIFT plays a crucial role in facilitating international trade finance. It enables banks to issue letters of credit, guarantees, and other financial instruments that support cross-border trade transactions. Swift aids international trade.
24. Understanding SWIFT Message Types: MT Codes
SWIFT uses a variety of message types, known as MT (Message Type) codes, to communicate different types of financial transactions. Examples include:
- MT103: Single Customer Credit Transfer
- MT202: Bank to Bank Transfer
- MT940: Customer Statement Message
Understanding these message types can provide insight into the specific nature of a SWIFT transaction. Swift uses a variety of message types.
25. SWIFT and Correspondent Banking: Building Global Networks
Correspondent banking relationships are essential for SWIFT to function effectively. Banks that don’t have a direct relationship with each other rely on correspondent banks to facilitate SWIFT transfers. Understand swift correspondent banking.
26. The Impact of Geopolitical Events on SWIFT: Sanctions and Restrictions
Geopolitical events can impact SWIFT, as countries may be sanctioned or restricted from using the network. This can have significant consequences for their economies and their ability to engage in international trade. Geopolitics impacts swift payments.
27. SWIFT and Fintech: Collaboration and Innovation
SWIFT is increasingly collaborating with fintech companies to develop innovative payment solutions. This includes exploring the use of blockchain technology and other emerging technologies to improve the speed and efficiency of international payments. Fintech influences swift operations.
28. SWIFT and Cross-Border Payments: Challenges and Opportunities
Cross-border payments face several challenges, including high costs, slow processing times, and lack of transparency. SWIFT is working to address these challenges and improve the overall cross-border payments experience. Swift improves cross-border payments.
29. SWIFT and Digital Currencies: Exploring the Future of Payments
As digital currencies gain traction, SWIFT is exploring their potential role in the future of payments. This includes investigating how digital currencies can be integrated into the SWIFT network to facilitate faster and cheaper cross-border transfers. Digital currencies may influence swift.
30. SWIFT and API Integration: Streamlining Connectivity
SWIFT is increasingly offering API (Application Programming Interface) integration to allow businesses to connect directly to the SWIFT network. This streamlines connectivity and makes it easier for businesses to initiate and manage international payments. Swift improves connectivity through APIs.
31. SWIFT and ISO 20022: Enhancing Data Standards
SWIFT is adopting the ISO 20022 messaging standard to enhance the quality and richness of data exchanged over the network. This will improve the efficiency and accuracy of financial transactions. Swift uses enhanced data standards.
32. SWIFT and Global Financial Inclusion: Reaching Underserved Communities
SWIFT is working to promote global financial inclusion by expanding access to financial services in underserved communities. This includes developing solutions that make it easier for individuals and businesses in these communities to send and receive money internationally. Swift promotes global financial inclusion.
33. SWIFT and the Fight Against Financial Crime: Preventing Money Laundering
SWIFT plays a critical role in the fight against financial crime by providing tools and technologies that help financial institutions detect and prevent money laundering. This includes monitoring transactions for suspicious activity and reporting it to the appropriate authorities. Swift prevents money laundering.
34. SWIFT and Cybersecurity: Protecting the Network from Threats
Cybersecurity is a top priority for SWIFT. The organization invests heavily in protecting its network from cyber threats and ensuring the security of financial transactions. Swift protects against cyber threats.
35. SWIFT and Real-Time Payments: Enabling Instant Transfers
SWIFT is working to enable real-time payments, allowing for instant transfers of funds between banks. This will significantly speed up the payment process and improve the overall customer experience. Swift enables real-time payments.
36. SWIFT and Blockchain Technology: Exploring New Possibilities
SWIFT is exploring the potential of blockchain technology to improve the efficiency and transparency of international payments. This includes investigating the use of blockchain for trade finance and other applications. Blockchain may influence swift.
37. SWIFT and Regulatory Compliance: Staying Ahead of the Curve
SWIFT is committed to staying ahead of the curve in terms of regulatory compliance. The organization works closely with regulators around the world to ensure that its systems and processes meet the highest standards. Swift maintains regulatory compliance.
38. SWIFT and Data Analytics: Gaining Insights from Transaction Data
SWIFT uses data analytics to gain insights from transaction data. This information can be used to improve the efficiency of the network, identify trends in financial activity, and detect potential fraud. Swift utilizes data analytics.
39. SWIFT and the Future of Banking: Transforming the Industry
SWIFT is playing a key role in transforming the banking industry. By providing a secure and reliable platform for international payments, it is enabling banks to offer new and innovative services to their customers. Swift transforms the banking industry.
40. Need Help with SWIFT Codes? Ask WHAT.EDU.VN!
Still have questions about SWIFT codes? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN, where you can ask any question and receive free answers from our community of experts. We’re here to help you navigate the complex world of international finance.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States.
Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890.
Website: what.edu.vn.
Don’t hesitate to reach out – we’re here to help you understand SWIFT codes and all things finance!