What Is The Best Move In Algebraic Chess Notation? Understanding chess notation is crucial for analyzing games and improving your strategy. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide clear explanations and resources to help you master this essential skill, ensuring you can confidently identify optimal moves. Explore strategic gameplay, piece placement and positional advantage.
1. Understanding Algebraic Chess Notation
Algebraic chess notation is a standardized method of recording and describing chess moves. It uses a combination of letters and numbers to identify each square on the chessboard. This notation is essential for studying chess games, solving puzzles, and communicating moves effectively. If you’re struggling to understand the best move in algebraic chess notation, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help. We offer free guidance and answers to all your chess-related questions.
1.1. Basics of Algebraic Notation
Each square on the chessboard is identified by a unique coordinate. Columns (files) are labeled a through h from left to right from White’s perspective, and rows (ranks) are numbered 1 through 8 from White’s perspective. Thus, each square is uniquely identified, such as a1, b2, c3, and so on.
1.2. Recording Moves
Moves are recorded by indicating the piece moved and the destination square. For example:
- Nf3 indicates that the knight moves to the square f3.
- e4 indicates that the pawn moves to the square e4 (pawns are notated without a letter).
- Rxa1 indicates that the rook captures a piece on the square a1.
- O-O indicates kingside castling.
- O-O-O indicates queenside castling.
1.3. Special Symbols
Several symbols are used to provide additional information about the move:
- x indicates a capture.
- + indicates a check.
- # indicates a checkmate.
- = indicates a pawn promotion.
- !! indicates a brilliant move.
- ! indicates a good move.
- ? indicates a mistake.
- ?? indicates a blunder.
2. Identifying the Best Move
The best move in algebraic chess notation refers to the optimal move in a given position that maximizes a player’s chances of winning or achieving a favorable outcome. Identifying this move requires a deep understanding of chess principles, strategic thinking, and tactical calculation.
2.1. Evaluating the Position
Before identifying the best move, it’s essential to evaluate the current position on the board. Consider the following factors:
- Material balance: Who has more pieces or pieces of higher value?
- King safety: Is your king vulnerable to attack?
- Piece activity: Are your pieces well-placed and actively participating in the game?
- Pawn structure: Are there any weak pawns or pawn islands?
- Control of key squares: Who controls the center and other important squares?
2.2. Calculating Variations
Chess is a game of calculation. To find the best move, you need to calculate the consequences of each possible move and anticipate your opponent’s responses. This involves visualizing the board several moves ahead and evaluating the resulting positions.
2.3. Strategic Considerations
Strategic considerations play a crucial role in determining the best move. These include:
- Developing your pieces: Bringing your knights and bishops into active positions.
- Controlling the center: Occupying or influencing the central squares.
- Creating weaknesses in your opponent’s position: Targeting weak pawns or squares.
- Improving your pawn structure: Avoiding isolated or doubled pawns.
- Planning long-term: Developing a plan for the game based on the position.
2.4. Tactical Motifs
Tactical motifs are short-term combinations of moves that can lead to immediate gains. Common tactical motifs include:
- Forks: A piece attacking two or more enemy pieces simultaneously.
- Pins: A piece that cannot move without exposing a more valuable piece to attack.
- Skewers: Similar to a pin, but the more valuable piece is attacked first, forcing it to move and exposing the less valuable piece.
- Discovered attacks: Moving a piece to reveal an attack by another piece.
- Sacrifices: Intentionally giving up material to gain a positional or tactical advantage.
3. Tools and Resources for Finding the Best Move
Several tools and resources can assist you in finding the best move in algebraic chess notation.
3.1. Chess Engines
Chess engines are computer programs that analyze chess positions and suggest moves. They use sophisticated algorithms to evaluate positions and calculate variations, often surpassing human players in tactical calculation. Some popular chess engines include Stockfish, Leela Chess Zero, and Komodo.
3.2. Chess Databases
Chess databases contain millions of chess games played by grandmasters and other strong players. By searching for similar positions in the database, you can see what moves have been played in the past and how the games unfolded. This can provide valuable insights and ideas for finding the best move.
3.3. Chess Analysis Software
Chess analysis software combines the capabilities of chess engines and chess databases. These programs allow you to analyze your own games, explore different variations, and learn from the games of others. Some popular chess analysis software includes ChessBase, Fritz, and Lucas Chess.
3.4. Online Chess Platforms
Online chess platforms such as Chess.com and Lichess.org offer a variety of tools and resources for finding the best move, including chess engines, databases, and analysis software. They also provide opportunities to play against other players, solve puzzles, and learn from instructional videos and articles.
4. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Finding the best move in algebraic chess notation can be challenging, and it’s easy to make mistakes. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
4.1. Not Considering All Possible Moves
When analyzing a position, it’s important to consider all possible moves, not just the ones that immediately come to mind. Overlooking a key move can lead to missed opportunities or even blunders.
4.2. Not Calculating Deep Enough
Chess is a game of calculation, and it’s essential to calculate variations deep enough to see the consequences of your moves. Short-sighted calculations can lead to tactical surprises and unfavorable outcomes.
4.3. Ignoring Strategic Considerations
While tactical calculation is important, it’s also essential to consider strategic factors such as piece activity, pawn structure, and control of key squares. Ignoring these factors can lead to a strategically inferior position, even if you avoid immediate tactical blunders.
4.4. Overvaluing Material
Material is important in chess, but it’s not the only factor to consider. Sacrificing material for a positional or tactical advantage can often be the best move. Overvaluing material can lead to missed opportunities and a passive, defensive game.
4.5. Not Learning from Mistakes
Everyone makes mistakes in chess, but it’s important to learn from them. Analyze your games to identify your mistakes and understand why they occurred. This will help you avoid making the same mistakes in the future and improve your chess skills.
5. Examples of Finding the Best Move
Let’s look at some examples of how to find the best move in algebraic chess notation.
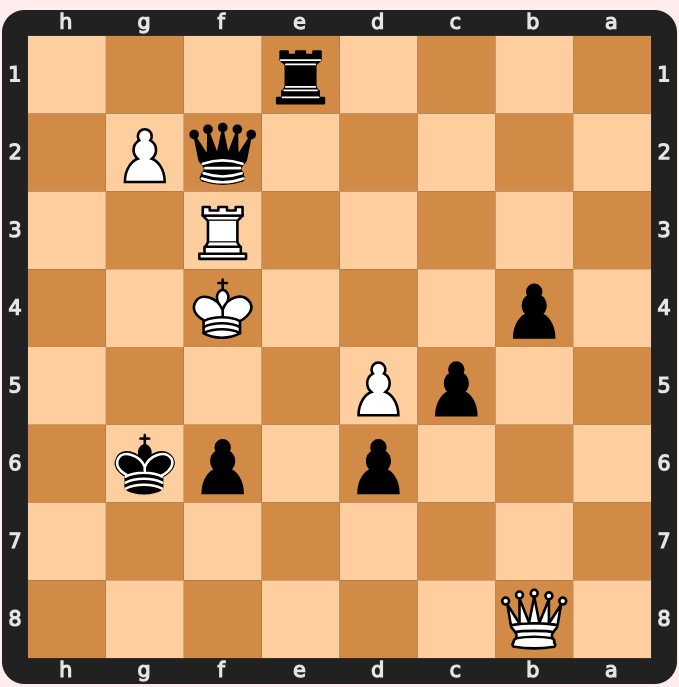
5.1. Example 1: Tactical Combination
In this position, White has a tactical combination that leads to a decisive advantage. Can you find the best move for White in algebraic chess notation?
The best move is Rd8+. This forces the black king to move and allows White to win a piece.
5.2. Example 2: Strategic Maneuvering
In this position, White can improve their position by strategically maneuvering their pieces. Can you find the best move for White in algebraic chess notation?
The best move is Rd8+, which puts pressure on Black’s position and prepares for a future attack.
5.3. Example 3: Endgame Technique
In this endgame position, White needs to find a precise sequence of moves to win. Can you find the best move for White in algebraic chess notation?
The best move is e3, which supports the pawn and prevents Black from advancing.
6. How WHAT.EDU.VN Can Help
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand that finding the best move in algebraic chess notation can be challenging. That’s why we offer a range of resources and services to help you improve your chess skills and make better decisions on the board.
6.1. Free Question Answering Service
Do you have a specific chess position that you’re struggling with? Our free question-answering service allows you to submit your questions and receive personalized advice from experienced chess players. Simply visit our website at WHAT.EDU.VN and submit your question.
6.2. Expert Analysis and Guidance
Our team of chess experts is available to provide detailed analysis and guidance on your games. Whether you’re looking for help with opening theory, middlegame strategy, or endgame technique, we can provide the support you need to reach your chess goals.
6.3. Community Support
Join our community of chess enthusiasts to connect with other players, share your games, and learn from each other. Our forums are a great place to ask questions, discuss chess topics, and find training partners.
6.4. Convenient and Accessible
Our services are available online, making it easy to access the help you need from anywhere in the world. Whether you’re at home, at school, or on the go, WHAT.EDU.VN is always there to support your chess journey.
7. Understanding Different Search Intentions
When users search for “what is the best move in algebraic chess notation,” they might have different intentions. Understanding these intentions helps in providing the most relevant and helpful information.
7.1. Beginner’s Guide to Chess Notation and Moves
Some users may be entirely new to chess and need a basic introduction to algebraic notation. They want to understand how moves are recorded and deciphered. This includes:
- Explanation of algebraic notation components (piece symbols, squares)
- Examples of common moves and notations
- Resources for learning more about chess basics
7.2. Understanding How to Evaluate the Best Move
Users might already understand algebraic notation but want to learn how to identify the best move in a given situation. This involves:
- Explanation of factors to consider when evaluating a position (material, king safety, piece activity)
- Tactical motifs and strategic considerations
- Examples of finding the best move in different scenarios
7.3. Advanced Strategy and Tactics
Experienced chess players might be looking for advanced strategies and tactics to improve their game. This includes:
- In-depth analysis of complex positions
- Discussion of advanced tactical motifs and strategic concepts
- Examples from grandmaster games
7.4. Troubleshooting Specific Positions
Some users might be stuck on a specific chess puzzle or game and need help finding the best move in that particular position. This involves:
- Providing a platform for users to submit their positions
- Offering personalized advice and analysis
- Connecting users with experienced chess players
7.5. Finding Resources and Tools
Users might be looking for resources and tools to help them find the best move, such as:
- Chess engines and analysis software
- Chess databases and online platforms
- Tutorials and instructional materials
8. Elevating Your Chess Game: A Comprehensive Guide
To truly excel in chess and consistently find the best moves, a multifaceted approach is essential. This includes mastering notation, understanding evaluation techniques, employing strategic thinking, and utilizing available resources.
8.1. Mastering Algebraic Notation
Algebraic notation is the language of chess, and fluency is crucial.
- Practice: Regularly transcribe games and puzzles into algebraic notation.
- Review: Frequently revisit the notation rules to reinforce your understanding.
- Apply: Use notation when analyzing your own games and studying master games.
8.2. Honing Evaluation Skills
Evaluating a chess position accurately is the foundation of finding the best move.
- Material Balance: Always start by assessing the material count for each side.
- King Safety: Evaluate the vulnerability of each king to potential attacks.
- Piece Activity: Determine how actively and effectively each piece participates in the game.
- Pawn Structure: Analyze pawn formations for weaknesses, strengths, and potential breakthroughs.
- Control of Key Squares: Identify which player controls the center and other strategically important squares.
8.3. Strategic Thinking
Strategic thinking involves formulating long-term plans and understanding the underlying principles of chess.
- Development: Prioritize developing your pieces to active squares.
- Center Control: Aim to control or influence the center of the board.
- Weaknesses: Identify and exploit weaknesses in your opponent’s position.
- Pawn Structure: Improve your pawn structure while weakening your opponent’s.
- Planning: Develop a coherent plan based on the specific characteristics of the position.
8.4. Tactical Acumen
Tactical motifs are the building blocks of many decisive combinations.
- Forks: Recognize and create opportunities for pieces to attack multiple targets simultaneously.
- Pins: Identify and exploit pins that restrict the movement of enemy pieces.
- Skewers: Utilize skewers to force the movement of valuable pieces, exposing weaker ones.
- Discovered Attacks: Set up discovered attacks that unleash hidden threats.
- Sacrifices: Be willing to sacrifice material for a positional or tactical advantage.
8.5. Leveraging Resources
Utilize available tools and resources to enhance your chess learning and analysis.
- Chess Engines: Employ chess engines to analyze positions and identify potential moves.
- Chess Databases: Study master games and explore opening theory using chess databases.
- Analysis Software: Utilize chess analysis software to dissect your own games and learn from your mistakes.
- Online Platforms: Engage with online chess platforms for playing, learning, and connecting with other players.
9. Advanced Techniques for Identifying Optimal Moves
Beyond the basics, several advanced techniques can help you pinpoint the best move with greater accuracy.
9.1. Candidate Moves
Before diving into calculations, identify a set of “candidate moves” – those that appear promising based on your initial evaluation. This narrows your focus and saves time.
9.2. The Process of Elimination
Evaluate each candidate move, looking for flaws or drawbacks. Systematically eliminate the weaker options until you are left with the most promising one.
9.3. Forcing Moves
Prioritize calculating forcing moves such as checks, captures, and threats. These moves often dictate the flow of the game and can lead to tactical opportunities.
9.4. Prophylaxis
Consider your opponent’s potential threats and try to neutralize them proactively. This involves anticipating their plans and taking measures to prevent them from achieving their goals.
9.5. The Principle of Two Weaknesses
Target two weaknesses in your opponent’s position simultaneously. This can stretch their resources and make it difficult for them to defend effectively.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is algebraic chess notation? | Algebraic notation is a standardized way of recording chess moves using letters and numbers to identify squares. |
| How do I read algebraic notation? | Each square is identified by a letter (a-h) for the file and a number (1-8) for the rank. Moves are recorded by indicating the piece and the destination square (e.g., Nf3). |
| What are the symbols used in algebraic notation? | Common symbols include x (capture), + (check), # (checkmate), O-O (kingside castling), and O-O-O (queenside castling). |
| How can I improve my chess evaluation skills? | Practice evaluating positions by considering material balance, king safety, piece activity, pawn structure, and control of key squares. |
| What are some common tactical motifs in chess? | Common tactical motifs include forks, pins, skewers, discovered attacks, and sacrifices. |
| How can chess engines help me find the best move? | Chess engines analyze positions and suggest moves using sophisticated algorithms, helping you identify tactical opportunities and strategic advantages. |
| Where can I find chess databases to study master games? | Chess databases like ChessBase and online platforms like Chess.com and Lichess.org offer vast collections of master games for study. |
| What are some common mistakes to avoid when finding the best move? | Avoid overlooking possible moves, not calculating deep enough, ignoring strategic considerations, overvaluing material, and not learning from your mistakes. |
| How can WHAT.EDU.VN help me improve my chess skills? | WHAT.EDU.VN offers a free question-answering service, expert analysis and guidance, community support, and convenient online access to help you reach your chess goals. |
| What if I’m stuck on a specific chess position and need help finding the best move? | WHAT.EDU.VN provides a platform to submit your specific positions and receive personalized advice and analysis from experienced chess players. |


11. The E-E-A-T Framework and Chess Expertise
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) is a framework Google uses to evaluate content quality. In the context of chess, demonstrating E-E-A-T is crucial for establishing credibility.
11.1. Experience
Real-world chess experience lends credibility to your advice.
- Playing Experience: Share your own experiences playing chess, including successes, failures, and lessons learned.
- Coaching Experience: If you have coached others, highlight your experience and the results your students have achieved.
- Tournament Experience: Discuss your participation in chess tournaments and your performance.
11.2. Expertise
Demonstrate your chess expertise through in-depth knowledge and analysis.
- Understanding of Chess Principles: Clearly explain complex chess concepts and strategies.
- Analysis of Games: Provide detailed analysis of chess games, highlighting key moves and strategic decisions.
- Knowledge of Chess History: Demonstrate familiarity with chess history, famous players, and important games.
11.3. Authoritativeness
Establish your authority in the chess world by referencing reputable sources and engaging with the chess community.
- Citing Reputable Sources: Back up your claims with references to established chess books, websites, and experts.
- Engaging with the Chess Community: Participate in chess forums, discussions, and events.
- Seeking Endorsements: Obtain endorsements from other chess experts or organizations.
11.4. Trustworthiness
Build trust with your audience by providing accurate, unbiased, and reliable information.
- Accuracy of Information: Ensure that all information you provide is accurate and up-to-date.
- Transparency: Be transparent about your sources and methods.
- Objectivity: Present information in an objective and unbiased manner.
12. Optimizing for Google Discovery
To increase the visibility of your chess content on Google Discovery, focus on creating visually appealing, engaging, and informative content.
12.1. High-Quality Images and Videos
Use high-quality images and videos to illustrate chess positions, tactics, and strategies. Visual content is more engaging and likely to be shared.
12.2. Compelling Headlines
Craft compelling headlines that capture the reader’s attention and accurately reflect the content of your article.
12.3. Engaging Introductions
Start your articles with engaging introductions that hook the reader and encourage them to continue reading.
12.4. Clear and Concise Writing
Write in a clear and concise style that is easy to understand. Avoid jargon and technical terms that may confuse readers.
12.5. Mobile Optimization
Ensure that your website is mobile-friendly and that your content is easily accessible on mobile devices.
13. Understanding YMYL and Chess Advice
YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) is a category of topics that Google considers to have a significant impact on a person’s life. While chess might not immediately seem like a YMYL topic, providing incorrect or misleading advice could have negative consequences for a player’s development and enjoyment of the game.
13.1. Responsible Advice
Always provide responsible and well-considered advice. Avoid making exaggerated claims or promising unrealistic results.
13.2. Tailored Guidance
Recognize that different players have different needs and goals. Tailor your advice to the specific circumstances of each individual.
13.3. Emphasis on Learning
Focus on helping players learn and improve their skills, rather than simply providing quick fixes or shortcuts.
13.4. Ethical Considerations
Promote ethical behavior in chess, such as fair play, respect for opponents, and adherence to the rules of the game.
14. The Importance of Continuous Learning
Chess is a game of continuous learning and improvement. Stay up-to-date with the latest developments in chess theory and practice, and never stop seeking new ways to enhance your skills.
14.1. Study Master Games
Regularly study master games to learn from the best players in the world. Pay attention to their opening choices, strategic plans, and tactical executions.
14.2. Analyze Your Own Games
Thoroughly analyze your own games to identify your mistakes and understand why they occurred. This is one of the most effective ways to improve your chess skills.
14.3. Solve Puzzles
Regularly solve chess puzzles to improve your tactical vision and calculation skills.
14.4. Seek Feedback
Seek feedback from other chess players and coaches. Constructive criticism can help you identify areas for improvement that you might not have noticed on your own.
14.5. Embrace Challenges
Embrace challenges and don’t be afraid to lose. Every loss is an opportunity to learn and grow as a chess player.
15. Maximizing Engagement and Shareability
To maximize the reach and impact of your chess content, focus on creating content that is both engaging and shareable.
15.1. Interactive Content
Create interactive content such as quizzes, puzzles, and polls to engage your audience and encourage them to participate.
15.2. Storytelling
Use storytelling to make your content more relatable and memorable. Share personal anecdotes, historical stories, or fictional scenarios to illustrate chess concepts and strategies.
15.3. Humor
Incorporate humor into your content to make it more entertaining and engaging. Chess doesn’t have to be serious all the time.
15.4. Visual Appeal
Pay attention to the visual appeal of your content. Use attractive layouts, fonts, and color schemes to make your content more visually appealing.
15.5. Social Sharing
Make it easy for readers to share your content on social media by including social sharing buttons.
16. Call to Action
Ready to elevate your chess game? Don’t struggle alone trying to find the best move! Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your chess questions for free. Our expert community is ready to provide fast, accurate answers and personalized guidance. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced player, WHAT.EDU.VN is your go-to resource for all things chess. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Your path to chess mastery starts now at what.edu.vn!