What Is The Biggest Religion In The World? Understanding global religious demographics involves examining faith adherence, religious beliefs, and the concept of religious population. Find out more about this topic on WHAT.EDU.VN, where answers are readily available. Delve into the world’s major faiths, including Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, and Buddhism, and gain a deeper understanding of religious statistics and religious demographics.
1. Understanding The Global Religious Landscape
The world’s religious landscape is constantly shifting, influenced by factors like birth rates, youth population sizes, religious conversions, and migration patterns. Understanding these dynamics provides valuable insights into how different religions grow and evolve over time. This overview will cover the major religious groups, their current sizes, and projected changes. If you have questions about religion or any other topic, don’t hesitate to ask on WHAT.EDU.VN for a free and quick answer.
1.1 Key Factors Influencing Religious Demographics
Several key factors influence the demographics of religious groups globally. These include:
- Fertility Rates: Higher fertility rates generally lead to faster population growth within a religious group.
- Youth Population: Religions with a larger youth demographic tend to grow more rapidly as these young individuals enter their reproductive years.
- Religious Switching: Conversion to and from different religions can significantly impact the size of religious populations.
- Migration: International migration patterns can shift the geographic distribution of religious groups.
Understanding these elements helps us comprehend the changing religious landscape of the world.
1.2 The Current Size of Major Religious Groups
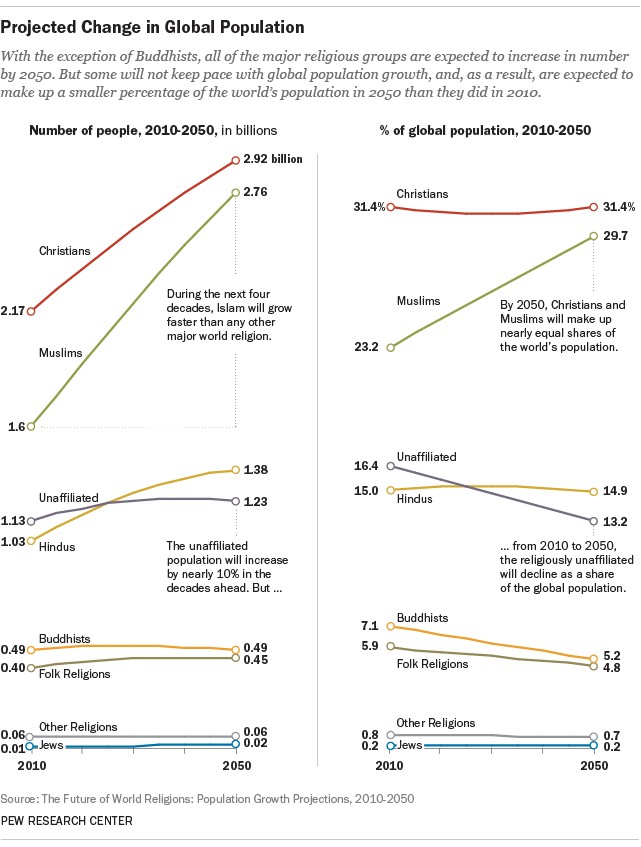
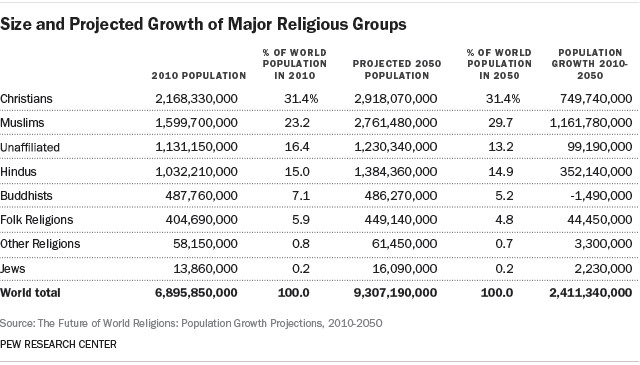
As of 2010, Christianity was the world’s largest religion, with approximately 2.2 billion adherents, making up 31% of the global population of 6.9 billion. Islam followed with 1.6 billion adherents, accounting for 23% of the world’s population. Other significant religious groups include Hinduism, Buddhism, and various folk religions. For more information on these trends and to ask any questions you may have, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
2. Christianity: The World’s Largest Religion
Christianity, with its origins in the teachings of Jesus Christ, encompasses a wide array of denominations and traditions. Its global presence is marked by a significant number of adherents across various continents.
2.1 Overview of Christianity
Christianity is based on the life, teachings, death, and resurrection of Jesus Christ, whom Christians believe to be the Son of God. The religion emphasizes love, forgiveness, and salvation through faith in Jesus.
2.2 Global Distribution and Number of Adherents
Christianity is widespread, with a substantial presence in Europe, the Americas, Africa, and Asia. As of 2010, there were approximately 2.2 billion Christians worldwide, making it the largest religion globally.
2.3 Factors Contributing to Christian Growth
The growth of Christianity is attributed to several factors, including:
- High Fertility Rates: Christian populations, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, have high fertility rates.
- Youth Population: A significant portion of Christians are under the age of 15, ensuring future growth.
- Migration: Migration patterns have contributed to the spread of Christianity to different regions.
3. Islam: The Fastest-Growing Major Religion
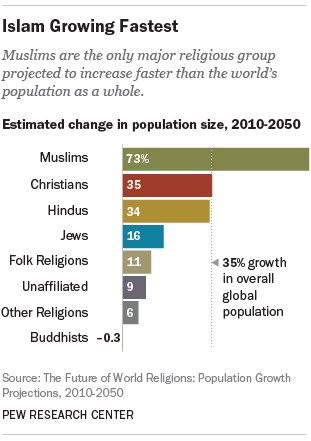
Islam, centered on the teachings of the Quran and the Prophet Muhammad, is the second-largest and fastest-growing major religion in the world. Its growth is fueled by high fertility rates and a youthful population.
3.1 Overview of Islam
Islam is based on the belief in one God, Allah, and the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad as revealed in the Quran. The religion emphasizes submission to God’s will and adherence to the Five Pillars of Islam.
3.2 Global Distribution and Number of Adherents
Islam has a significant presence in Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and Europe. As of 2010, there were approximately 1.6 billion Muslims worldwide, making it the second-largest religion globally.
3.3 Factors Contributing to Islamic Growth
The rapid growth of Islam is primarily due to:
- High Fertility Rates: Muslims have the highest fertility rate among major religious groups, averaging 3.1 children per woman.
- Youth Population: A large percentage of Muslims are under the age of 15, ensuring continued growth.
- Religious Switching: Modest net gains through religious conversion also contribute to Islamic growth.
4. Hinduism: Predominantly in India
Hinduism, primarily concentrated in India, is one of the world’s oldest religions. Its growth is closely tied to population trends in the Indian subcontinent.
4.1 Overview of Hinduism
Hinduism encompasses a diverse range of traditions, philosophies, and practices originating in the Indian subcontinent. It includes beliefs in dharma, karma, and reincarnation.
4.2 Global Distribution and Number of Adherents
Hinduism is mainly practiced in India and Nepal, with significant diaspora communities around the world. As of 2010, there were approximately 1 billion Hindus globally.
4.3 Factors Contributing to Hindu Growth
The growth of Hinduism is primarily driven by:
- High Fertility Rates: Hindu fertility rates are similar to the global average.
- Youth Population: A large percentage of Hindus are under the age of 15, contributing to population growth.
- Geographic Concentration: Predominantly located in India, where population growth is robust.
5. Buddhism: Stable Global Population
Buddhism, with its emphasis on mindfulness and enlightenment, is expected to maintain a relatively stable global population due to low fertility rates and aging populations in key Buddhist countries.
5.1 Overview of Buddhism
Buddhism is based on the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama, the Buddha, who sought enlightenment through meditation and mindfulness. The religion emphasizes the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path.
5.2 Global Distribution and Number of Adherents
Buddhism is primarily practiced in East and Southeast Asia, with a growing presence in the West. As of 2010, there were approximately 500 million Buddhists worldwide.
5.3 Factors Influencing Buddhist Population
The Buddhist population is expected to remain stable due to:
- Low Fertility Rates: Buddhists have some of the lowest fertility rates among major religious groups.
- Aging Populations: Many Buddhist countries, such as China, Thailand, and Japan, have aging populations.
- Minimal Religious Switching: Limited gains through conversion.
6. Other Religious Groups and the Unaffiliated
Besides the major religions, various other religious groups and the religiously unaffiliated also play a significant role in the global religious landscape. These groups have unique growth patterns and demographic characteristics.
6.1 Folk Religions
Folk religions, including African traditional religions, Chinese folk religions, and Native American religions, are projected to grow modestly. However, their growth rate is slower than the overall global population growth.
6.2 Judaism
Judaism, the smallest major religious group, is expected to grow slightly due to its relatively high fertility rates. However, it will remain a small percentage of the global population.
6.3 Other Religions
This category includes Baha’is, Jains, Sikhs, Taoists, and other smaller faiths. These religions are projected to grow slightly but will still represent a small fraction of the world’s population.
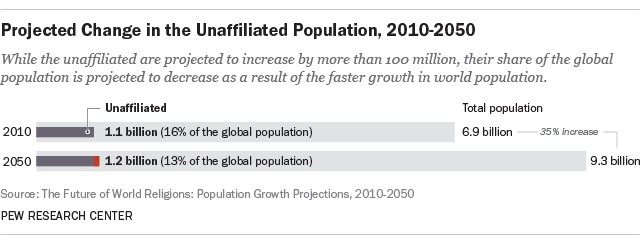
6.4 The Unaffiliated
The religiously unaffiliated, including atheists, agnostics, and those who do not identify with any particular religion, are projected to grow in absolute numbers but decline as a percentage of the global population.
7. Regional Variations in Religious Growth
Religious growth varies significantly across different regions of the world. Factors such as fertility rates, migration patterns, and religious switching contribute to these regional differences.
7.1 Sub-Saharan Africa
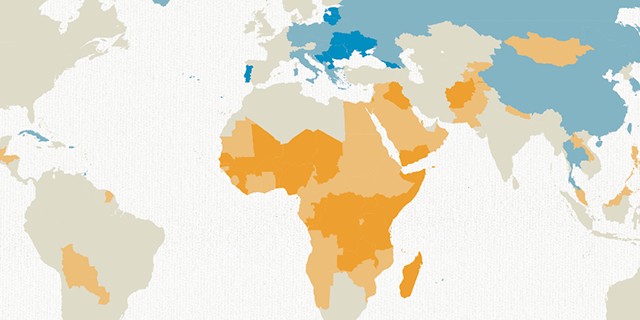
Sub-Saharan Africa is projected to experience the fastest overall religious growth. Both Christianity and Islam are expected to double in population due to high fertility rates in the region.
7.2 Middle East and North Africa
The Middle East and North Africa are also expected to experience faster-than-average growth, primarily driven by increases in the Muslim population.
7.3 Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to have a declining share of the world’s population. Religions heavily concentrated in this region, such as Buddhism and Chinese folk religions, will experience slower growth.
7.4 Europe
Europe is the only region where the total population is projected to decline. The Christian population is expected to shrink, while the Muslim population will increase due to migration and higher fertility rates.
7.5 North America
In North America, Muslims and followers of “other religions” are the fastest-growing religious groups. Christianity is projected to decline, while the unaffiliated population is expected to rise.
7.6 Latin America and the Caribbean
Christianity will remain the largest religious group in Latin America and the Caribbean. The religiously unaffiliated population is projected to grow in both absolute number and percentage terms.
8. Factors Influencing Religious Switching
Religious switching, or the change in religious affiliation, is an essential factor in understanding religious demographics. Conversion patterns are complex and vary significantly across different countries and regions.
8.1 Conversion to Christianity
Globally, Christianity is expected to experience net losses from religious switching. While some people convert to Christianity, a larger number are projected to leave the religion, primarily joining the ranks of the religiously unaffiliated.
8.2 Conversion to Islam
Islam is expected to experience modest net gains through religious switching. More people are projected to convert to Islam than leave the religion.
8.3 The Role of the Unaffiliated
The unaffiliated are expected to add more people through religious switching than they lose. This trend is particularly evident in Europe and North America.
9. The Impact of Migration on Religious Demographics
International migration significantly impacts the projected size of religious groups in various regions and countries. Migration patterns can shift the geographic distribution of religious populations and influence their growth rates.
9.1 Migration to Europe
In Europe, the Muslim share of the population is expected to increase significantly due to migration. Without migration, the Muslim share of Europe’s population would be nearly two percentage points lower.
9.2 Migration to North America
In North America, the Hindu share of the population is expected to nearly double due to migration. Without migration, the Hindu share of the region’s population would remain about the same.
9.3 Migration to the Middle East
In the Middle East, the migration of Christians into the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries is expected to offset the exodus of Christians from other countries in the region.
10. Projections Beyond 2050
While projections beyond 2050 are speculative, extending current demographic trends offers insights into the long-term future of religious populations.
10.1 Potential Parity Between Muslims and Christians
If current trends continue, the Muslim share of the world’s population could equal the Christian share around 2070. After that, the number of Muslims would exceed the number of Christians.
10.2 The Continued Growth of Africa
The projected growth of Muslims and Christians would be driven largely by the continued expansion of Africa’s population. Both groups are heavily concentrated in this high-fertility region.
10.3 Factors That Could Alter These Trajectories
Many factors could alter these trajectories, including:
- Religious Switching in China: If a large share of China’s population were to switch to Christianity, it could bolster Christianity’s position as the world’s most populous religion.
- Disaffiliation in Muslim Countries: If disaffiliation were to become common in countries with large Muslim populations, it could slow or reverse the increase in Muslim numbers.
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Global Religion
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the largest religion in the world? | Christianity is the largest religion, with approximately 2.2 billion adherents as of 2010. |
| Which religion is growing the fastest? | Islam is the fastest-growing major religion, primarily due to high fertility rates and a youthful population. |
| How will religious demographics change by 2050? | By 2050, Muslims are projected to nearly equal Christians in number. The religiously unaffiliated population is expected to decline as a percentage of the global population. |
| What factors influence religious growth? | Key factors include fertility rates, youth population size, religious switching, and migration patterns. |
| Where is Christianity growing the fastest? | Christianity is growing rapidly in sub-Saharan Africa, driven by high fertility rates and a large youth population. |
| Where is Islam growing the fastest? | Islam is also growing rapidly in sub-Saharan Africa, as well as in the Middle East and North Africa. |
| What is the role of migration in religious growth? | Migration can significantly impact the size and distribution of religious groups. For example, migration to Europe is increasing the Muslim share of the population. |
| How does religious switching affect religious demographics? | Religious switching can lead to net gains or losses for different religious groups. Christianity is expected to experience net losses, while Islam is expected to experience modest net gains. |
| What are the projections for the religiously unaffiliated? | The religiously unaffiliated population is projected to grow in absolute numbers but decline as a percentage of the global population. |
| What could alter the projected trends in religious demographics? | Factors such as religious switching in China and disaffiliation in Muslim countries could significantly alter the projected trends. |
12. Understanding Religious Beliefs and Practices
To fully grasp the complexities of global religious demographics, it is essential to understand the fundamental beliefs and practices of the major religions. This knowledge provides context for the demographic trends and helps in appreciating the diverse religious landscape of the world.
12.1 Core Tenets of Christianity
Christianity centers around the belief in one God who exists in three persons: the Father, the Son (Jesus Christ), and the Holy Spirit. Key beliefs include:
- The Trinity: The concept of God as a unified being in three distinct persons.
- The Divinity of Jesus: Jesus is believed to be the Son of God, fully divine and fully human.
- Salvation: Achieved through faith in Jesus Christ and acceptance of his sacrifice for the sins of humanity.
- The Bible: The holy scripture containing the Old and New Testaments, which serve as the foundation for Christian teachings.
12.2 Core Tenets of Islam
Islam is based on the belief in one God, Allah, and the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad. Key beliefs include:
- The Five Pillars of Islam: The fundamental practices that define Muslim life: faith, prayer, charity, fasting during Ramadan, and pilgrimage to Mecca.
- The Quran: The holy book of Islam, believed to be the direct word of God as revealed to Prophet Muhammad.
- Belief in Prophets: Islam recognizes many prophets, including Abraham, Moses, and Jesus, but considers Muhammad to be the last and greatest prophet.
- Submission to Allah: Muslims strive to live in accordance with God’s will and submit to his commands.
12.3 Core Tenets of Hinduism
Hinduism encompasses a vast array of traditions, philosophies, and practices. Key beliefs include:
- Dharma: The concept of righteousness, duty, and moral order.
- Karma: The principle of cause and effect, where actions determine future experiences.
- Reincarnation: The cycle of birth, death, and rebirth, where the soul transmigrates to new lives.
- The Vedas: The ancient scriptures that form the foundation of Hindu teachings.
12.4 Core Tenets of Buddhism
Buddhism focuses on achieving enlightenment through meditation and mindfulness. Key beliefs include:
- The Four Noble Truths: The understanding of suffering, its causes, its cessation, and the path to its cessation.
- The Eightfold Path: The guidelines for ethical and mindful living: right understanding, thought, speech, action, livelihood, effort, mindfulness, and concentration.
- Nirvana: The ultimate goal of Buddhism, representing the cessation of suffering and the achievement of enlightenment.
- Rejection of the Self: Buddhism teaches that there is no permanent, unchanging self or soul.
13. The Role of WHAT.EDU.VN in Answering Your Questions
Finding answers to questions about religion can be challenging. You might not know who to ask or where to look for reliable information. WHAT.EDU.VN offers a free and easy-to-use platform where you can ask any question and receive quick, accurate answers.
13.1 Overcoming the Challenges of Finding Information
Many people face difficulties when trying to find information about religion. Some of these challenges include:
- Lack of Reliable Sources: It can be difficult to distinguish between credible and unreliable sources of information.
- Cost of Consultation: Professional consultations can be expensive, making it inaccessible for many people.
- Time Constraints: Finding the time to research and verify information can be challenging.
13.2 How WHAT.EDU.VN Provides Solutions
WHAT.EDU.VN addresses these challenges by providing:
- A Free Platform: Ask any question without incurring any costs.
- Quick and Accurate Answers: Receive timely and reliable responses from knowledgeable individuals.
- Easy-to-Understand Information: Get explanations that are clear, concise, and accessible to everyone.
- Community Support: Connect with others to exchange knowledge and insights.
13.3 Benefits of Using WHAT.EDU.VN
Using WHAT.EDU.VN offers numerous benefits, including:
- Convenience: Access information from anywhere at any time.
- Expert Knowledge: Receive answers from experts in various fields.
- Community Engagement: Participate in discussions and learn from others.
- Free Service: Get all your questions answered without any financial burden.
14. Call to Action: Ask Your Questions on WHAT.EDU.VN Today
Do you have questions about religion or any other topic? Don’t hesitate to ask on WHAT.EDU.VN! Our platform offers a free and convenient way to get quick and accurate answers to all your inquiries. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply curious about the world, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help.
14.1 Address Your Curiosity
Uncover the answers to your burning questions. Our platform covers a wide range of topics, ensuring that you find the information you need.
14.2 Simplify Your Research
Avoid the hassle of sifting through countless websites and articles. Get direct and reliable answers from our knowledgeable community.
14.3 Join Our Community
Connect with other users, share your insights, and learn from diverse perspectives. WHAT.EDU.VN is more than just a question-and-answer platform; it’s a community of learners.
14.4 Contact Us
For any inquiries, please feel free to reach out to us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Visit what.edu.vn today and start exploring the world of knowledge. Your questions are waiting to be answered!