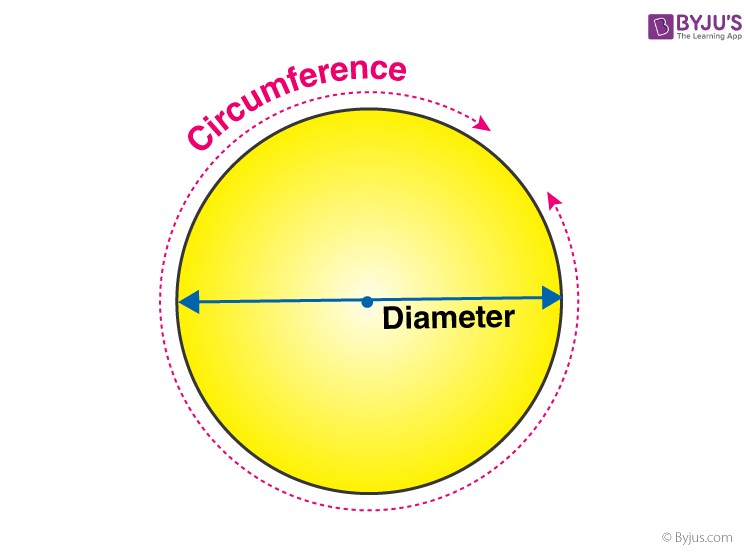
In mathematics, understanding the properties of shapes is fundamental, and among the most basic shapes is the circle. A key characteristic of a circle is its circumference. Think of the circumference as the distance around the circle, the outline that defines its boundary. It’s essentially the perimeter of a circle. While circles might seem simple, their circumference plays a crucial role in various calculations and real-world applications. Let’s delve into the concept of the circumference of a circle, explore its formula, and understand how to calculate it effectively.
Understanding Circle Circumference
The circumference of a circle, often referred to as the perimeter of a circle, is the measurement of the distance around its edge. Imagine you’re walking along the boundary of a circular park; the total distance you cover in one full lap is the circumference. This is different from the area of a circle, which measures the space enclosed within the circle. If you were to cut a circle open and straighten it into a line, the length of that line would represent its circumference. Circumference is measured in linear units such as centimeters (cm), meters (m), inches, or feet.
To calculate the circumference, we rely on a fundamental property of circles: their radius. The radius of a circle is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference. Knowing the radius (or diameter) is essential for determining the circumference.
The Circumference Formula Explained
The formula for the circumference of a circle is elegantly simple and based on a mathematical constant known as Pi (π).
Circumference (C) = 2πr
Where:
- C represents the circumference of the circle.
- π (Pi) is a mathematical constant, approximately equal to 3.14159. For most calculations, 3.14 or 22/7 are used as approximations. Pi is the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter, a constant value for all circles.
- r is the radius of the circle.
Since the diameter (d) of a circle is twice its radius (d = 2r), the circumference formula can also be expressed in terms of the diameter:
Circumference (C) = πd
Both formulas are equally valid and used depending on whether you know the radius or the diameter of the circle.
Example Calculation:
Let’s say we have a circle with a radius of 5 cm. To find its circumference:
C = 2πr
C = 2 x 3.14 x 5
C = 31.4 cm
Therefore, the circumference of the circle is approximately 31.4 cm.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Calculate Circumference
Calculating the circumference of a circle is straightforward if you know either the radius or the diameter. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Method 1: Using the Radius
- Identify the radius (r) of the circle. This is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its edge.
- Use the formula: C = 2πr
- Substitute the value of the radius (r) and the approximate value of Pi (π ≈ 3.14 or 22/7) into the formula.
- Calculate the result. This will give you the circumference of the circle.
Method 2: Using the Diameter
- Identify the diameter (d) of the circle. This is the distance across the circle passing through the center.
- Use the formula: C = πd
- Substitute the value of the diameter (d) and the approximate value of Pi (π ≈ 3.14 or 22/7) into the formula.
- Calculate the result. This will give you the circumference of the circle.
Method 3: Finding Circumference Practically
While formulas are precise, you can also measure circumference practically, though less accurately:
- Use a flexible measuring tape or a string.
- Wrap it around the circle’s outer edge, ensuring it fits snugly.
- Mark the point where the tape or string completes one full circle.
- Measure the length of the tape or string up to the marked point. This measurement is an approximation of the circumference. This method is similar to how circumference was understood historically before precise formulas.
Circumference vs. Area: Key Differences
While both circumference and area are important properties of a circle, they measure different aspects:
- Circumference: Measures the distance around the circle (a linear measurement). It’s like the fence around a circular garden.
- Area: Measures the space enclosed within the circle (a two-dimensional measurement). It’s like the planting space within the circular garden.
The formula for the area of a circle is:
Area (A) = πr²
It’s crucial not to confuse these two. Circumference is in linear units (cm, m, etc.), while area is in square units (cm², m², etc.).
Circumference of a Semicircle
A semicircle is exactly half of a circle. To find the perimeter of a semicircle, we need to consider both the curved arc and the straight diameter line.
Perimeter of Semicircle = (πr) + (2r)
- πr: Represents half the circumference of the full circle (the curved arc).
- 2r: Represents the diameter of the circle (the straight line closing the semicircle).
The area of a semicircle is simply half the area of a full circle:
Area of Semicircle = (πr²) / 2
Real-World Applications of Circumference
Understanding circumference is not just a theoretical exercise; it has numerous practical applications in everyday life and various fields:
- Engineering and Construction: Calculating the materials needed for circular structures, pipes, wheels, and cylindrical objects.
- Transportation: Wheel circumference is vital for calculating distance traveled by vehicles and bicycles. Odometer readings rely on accurate wheel circumference measurements.
- Manufacturing: Determining the length of belts in machinery, the amount of material needed to wrap circular products, and in designing circular components.
- Astronomy: Calculating the orbits of planets and satellites, which are often approximated as circles or ellipses, relies on circumference-related calculations.
- Everyday Life: From finding the right size lid for a circular container to estimating distances in circular paths, circumference knowledge is subtly useful.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When working with circumference, here are a few common mistakes to watch out for:
- Confusing Radius and Diameter: Always double-check if you are given the radius or diameter, and use the correct formula accordingly. Forgetting to double the radius (or halve the diameter) is a frequent error.
- Using the Wrong Formula for Semicircle Perimeter: Remember to include the diameter (2r) when calculating the perimeter of a semicircle, not just half the circumference (πr).
- Approximation of Pi: While 3.14 or 22/7 are common approximations, for highly accurate calculations, use a calculator’s Pi button or more decimal places of Pi. However, for most practical purposes, these approximations are sufficient.
- Units: Always maintain consistent units throughout your calculation and state the units in your final answer (e.g., cm, meters, inches).
Solved Examples: Mastering Circumference Calculations
Let’s work through some examples to solidify your understanding of circumference calculations.
Example 1:
What Is The Circumference Of A Circle with a diameter of 10 inches?
Solution:
Given: Diameter (d) = 10 inches
Formula: C = πd
C = π x 10
C ≈ 3.14 x 10
C ≈ 31.4 inches
Example 2:
Find the circumference of a circle with a radius of 7 cm. (Use π = 22/7)
Solution:
Given: Radius (r) = 7 cm
Formula: C = 2πr
C = 2 x (22/7) x 7
C = 2 x 22
C = 44 cm
Example 3:
The circumference of a circle is 62.8 meters. Find its radius. (Use π = 3.14)
Solution:
Given: Circumference (C) = 62.8 meters
Formula: C = 2πr
62.8 = 2 x 3.14 x r
62.8 = 6.28 x r
r = 62.8 / 6.28
r = 10 meters
Example 4:
A circular garden has a radius of 14 feet. How much fencing is needed to enclose it?
Solution:
The fencing needed is equal to the circumference of the circular garden.
Given: Radius (r) = 14 feet
Formula: C = 2πr
C = 2 x (22/7) x 14
C = 2 x 22 x 2
C = 88 feet
Therefore, 88 feet of fencing is needed.
Example 5:
Calculate the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 3 inches. (Use π = 3.14)
Solution:
Given: Radius (r) = 3 inches
Perimeter of Semicircle = (πr) + (2r)
Perimeter = (3.14 x 3) + (2 x 3)
Perimeter = 9.42 + 6
Perimeter = 15.42 inches
Practice Questions
Test your understanding with these practice questions:
- Calculate the circumference of a circle with a radius of 12 cm.
- What is the circumference of a circle if its diameter is 25 inches?
- Find the diameter of a circle whose circumference is 78.5 cm. (Use π = 3.14)
- A circular running track has a diameter of 100 meters. What is the distance around the track?
- What is the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 20 cm?
Watch this Video to Learn More about Circles
[Insert Video about Circumference of a Circle Here – Placeholder]
It is recommended to embed a relevant YouTube video here explaining the basics of circles and circumference for visual learners.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What exactly is the circumference of a circle?
A: The circumference is the distance around the outer edge of a circle. It’s the linear measurement of the circle’s boundary, akin to the perimeter of other shapes.
Q2: How do I calculate the circumference if I only know the area of the circle?
A: First, find the radius using the area formula (A = πr²), so r = √(A/π). Then, use the circumference formula (C = 2πr) to calculate the circumference. Alternatively, you can use the combined formula: C = √(4πA).
Q3: What is the relationship between circumference and diameter?
A: The circumference of any circle is always Pi (π) times its diameter. This constant ratio (C/d = π) is the definition of Pi itself.
Q4: Is the perimeter of a circle the same as its circumference?
A: Yes, the terms “perimeter of a circle” and “circumference of a circle” are used interchangeably. Circumference is simply the specific term for the perimeter of a circle.
Q5: Why is Pi (π) important in circumference calculations?
A: Pi (π) is a fundamental mathematical constant that represents the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter. It’s an inherent property of all circles in Euclidean geometry, making it essential for circumference calculations.
Q6: Can I calculate circumference for shapes other than circles?
A: The term “circumference” is specifically used for circles and ellipses (though the ellipse circumference calculation is more complex). For polygons (shapes with straight sides), we use the term “perimeter,” which is simply the sum of the lengths of all sides.
By understanding the concept of circumference and mastering its formula, you unlock a fundamental tool in geometry and its applications across various fields. Whether you’re solving mathematical problems or tackling real-world challenges, knowing how to calculate the circumference of a circle is a valuable skill.