Are you curious about the dominant faith around the globe and religious beliefs? WHAT.EDU.VN offers answers. Let’s explore the religious landscape. We provide insights into global religions, belief systems, and religious demographics. Discover more about faith-based populations, spiritual practices, and religious affiliation.
1. Understanding Global Religious Demographics
The world is a tapestry of diverse faiths and belief systems. Understanding the distribution and prevalence of different religions is crucial for comprehending global cultures, societies, and history.
A comprehensive study by the Pew Research Center’s Forum on Religion & Public Life examined the religious affiliation of people across more than 230 countries and territories. The study estimated that in 2010, approximately 84% of the world’s population (5.8 billion out of 6.9 billion people) identified with a religious group. This highlights the significant role religion plays in the lives of most people worldwide.
2. The Major Religious Groups Worldwide
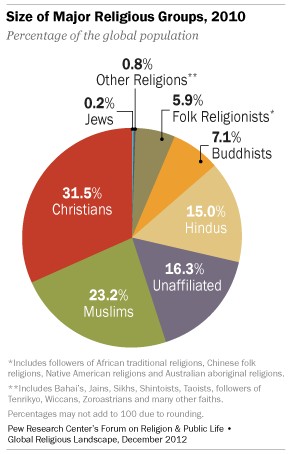
The Pew Research Center study identified the following major religious groups and their estimated populations in 2010:
- Christianity: 2.2 billion (32% of the world’s population)
- Islam: 1.6 billion (23% of the world’s population)
- Hinduism: 1 billion (15% of the world’s population)
- Buddhism: Nearly 500 million (7% of the world’s population)
- Judaism: 14 million (0.2% of the world’s population)
- Folk or Traditional Religions: More than 400 million (6% of the world’s population)
- Other Religions: An estimated 58 million (slightly less than 1% of the global population)
It is important to note that these numbers are estimates based on available data and may vary slightly depending on the source and methodology used.
3. Christianity: The Most Popular Religion
Based on the Pew Research Center’s findings, Christianity is the most popular religion in the world, with an estimated 2.2 billion adherents, representing approximately 32% of the global population in 2010. Christianity is a diverse religion with numerous denominations, including Catholicism, Protestantism, Eastern Orthodoxy, and others.
4. Islam: The Second Most Popular Religion
Islam is the second most popular religion worldwide, with an estimated 1.6 billion adherents, accounting for about 23% of the global population in 2010. Islam is a monotheistic religion centered on the belief in one God, Allah, and the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad as revealed in the Quran.
5. The Religiously Unaffiliated: A Significant Group
The Pew Research Center study also revealed that a substantial portion of the world’s population, approximately 1.1 billion people (16%), have no religious affiliation. This group includes atheists, agnostics, and individuals who do not identify with any particular religion. It is important to note that many of the unaffiliated may still hold some religious or spiritual beliefs, even if they do not identify with a specific faith. The religiously unaffiliated are the third-largest group worldwide, behind Christians and Muslims.
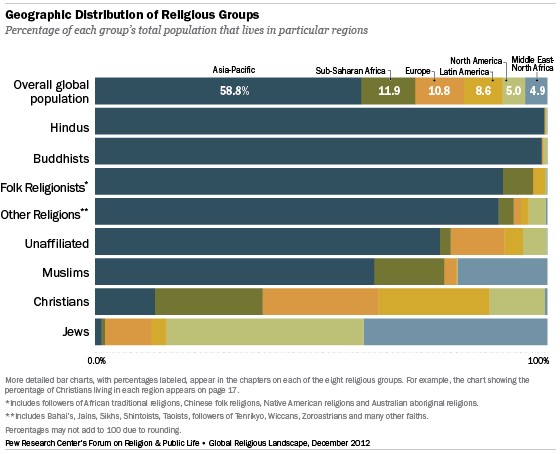
6. Geographic Distribution of Religious Groups
The distribution of religious groups varies significantly across different regions of the world.
- Asia-Pacific: This region is home to the vast majority of Hindus (99%), Buddhists (99%), adherents of folk or traditional religions (90%), and members of other world religions (89%). It also accounts for a large share of the religiously unaffiliated (76%).
- Middle East and North Africa: This region is predominantly Muslim, with about 20% of the world’s Muslim population residing there.
- Sub-Saharan Africa: Nearly 16% of the world’s Muslims live in this region.
- Europe, Latin America and the Caribbean, and Sub-Saharan Africa: Christianity is relatively evenly dispersed across these regions, with each accounting for roughly 24-26% of the global Christian population.
- North America: A plurality of Jews (44%) live in North America.
- Middle East and North Africa: About 41% of Jews live in this region, almost all of them in Israel.
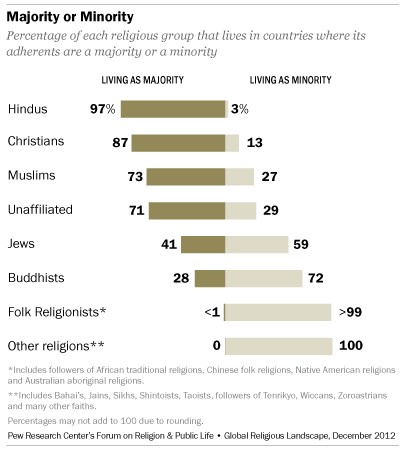
7. Living as Majorities and Minorities
A significant portion of the world’s population lives in countries where their religious group constitutes a majority. According to the Pew Research Center study, nearly three-quarters (73%) of the world’s people reside in countries where their religious group makes up a majority of the population. Conversely, about a quarter (27%) live as religious minorities.
- Hindus: An overwhelming majority (97%) of Hindus live in the world’s three Hindu-majority countries: India, Mauritius, and Nepal.
- Christians: Nearly nine-in-ten Christians (87%) are found in the world’s 157 Christian-majority countries.
- Muslims: Most Muslims (73%) live in countries where they are the predominant religious group. Muslims are a majority in 49 countries, including 19 of the 20 countries in the Middle East and North Africa.
- Religiously Unaffiliated: The religiously unaffiliated make up a majority of the population in six countries: China, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hong Kong, Japan, and North Korea.
- Buddhists: The majority of Buddhists (72%) live as religious minorities. Only 28% live in the seven countries where Buddhists are in the majority: Bhutan, Burma (Myanmar), Cambodia, Laos, Mongolia, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
- Jews: Israel is the only country with a Jewish majority.
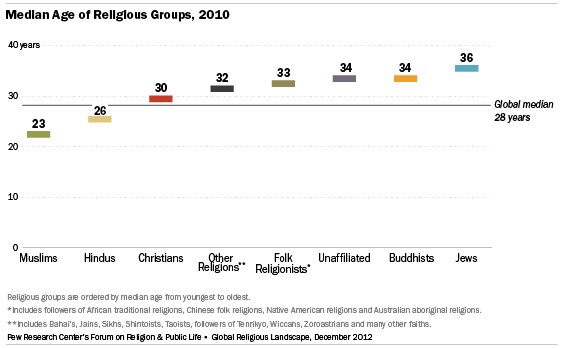
8. Age Demographics of Religious Groups
Different religions have varying age demographics. The median age of Muslims (23 years) and Hindus (26 years) is younger than the median age of the world’s overall population (28 years). Christians have a median age of 30, followed by members of other religions (32), adherents of folk or traditional religions (33), the religiously unaffiliated (34), and Buddhists (34). Jews have the highest median age (36).
9. Defining Religious Groups
The Pew Research Center study was based on self-identification, estimating the number of people who view themselves as belonging to various religious groups. It did not attempt to measure the degree to which members of these groups actively practice their faiths or how religious they are.
- Folk or Traditional Religions: These religions are closely tied to a particular people, ethnicity, or tribe. They often have no formal creeds or sacred texts and may blend elements of other world religions with local beliefs and customs.
- The Religiously Unaffiliated: This population includes atheists, agnostics, and people who do not identify with any particular religion.
- Other Religions: This category comprises groups not classified elsewhere, including followers of religions that are often not measured separately in censuses and surveys, such as the Baha’i faith, Jainism, Shintoism, Sikhism, Taoism, Tenrikyo, Wicca, Zoroastrianism, and many other religions.
10. Addressing Common Questions About Global Religions
Here are some frequently asked questions related to the most popular religion in the world and the global religious landscape:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What Is The Most Popular Religion In The World based on current data? | Christianity remains the most popular religion, with over two billion followers worldwide. |
| How does Islam compare to Christianity in terms of global followers? | Islam is the second-largest religion, experiencing rapid growth, especially in Asia and Africa. |
| What factors contribute to the growth of different religions globally? | Birth rates, conversion rates, and migration patterns all influence religious demographics. |
| Are there regions where specific religions are predominantly followed? | Yes. For example, Hinduism is heavily concentrated in India and Nepal, while Islam is dominant in many Middle Eastern and North African countries. |
| What role do non-religious or unaffiliated populations play in global trends? | The number of people identifying as non-religious is growing in many parts of the world, particularly in Europe and North America, influencing social and political landscapes. |
| How do demographic changes impact the distribution of religions over time? | As populations grow and shift, the distribution of religious groups changes, leading to new challenges and opportunities for interfaith dialogue. |
| What are some key differences between major religions in terms of beliefs? | Christianity centers on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ, while Islam follows the teachings of the Quran and the Prophet Muhammad. Hinduism encompasses a wide range of traditions and deities, and Buddhism focuses on achieving enlightenment through meditation. |
| How do religious practices vary across different cultures? | Religious practices often adapt to local customs and traditions, leading to diverse expressions of faith around the world. |
| What impact does religion have on social issues and policy-making? | Religion can play a significant role in shaping social values, ethical standards, and public policy decisions, both positively and negatively. |
| How can interfaith dialogue promote understanding and peace? | Interfaith dialogue helps build bridges between different religious communities, fostering mutual respect and cooperation for the common good. |
11. Delving Deeper into Religious Diversity
Exploring different faiths can broaden our understanding of humanity and promote tolerance.
11.1. Christianity in Detail
Christianity is based on the life, teachings, death, and resurrection of Jesus Christ. Christians believe Jesus is the Son of God and the Messiah prophesied in the Old Testament. The Bible, consisting of the Old and New Testaments, is the sacred text of Christianity.
Christianity is divided into several major branches, including:
- Catholicism: The largest Christian denomination, led by the Pope in Vatican City.
- Protestantism: A diverse group of denominations that originated in the 16th-century Reformation, including Baptists, Methodists, Lutherans, Presbyterians, and others.
- Eastern Orthodoxy: A branch of Christianity that traces its roots back to the Byzantine Empire.
11.2. Islam in Detail
Islam is a monotheistic religion that believes in one God, Allah. Muslims believe that Allah revealed his final message to humanity through the Prophet Muhammad, as recorded in the Quran, the holy book of Islam. The Five Pillars of Islam are the core beliefs and practices of Muslims:
- Shahada: Declaration of faith
- Salat: Prayer
- Zakat: Charity
- Sawm: Fasting during Ramadan
- Hajj: Pilgrimage to Mecca
Islam is divided into two main branches:
- Sunni: The largest branch of Islam.
- Shia: A smaller branch of Islam that believes that Ali, Muhammad’s cousin and son-in-law, was the rightful successor to the Prophet.
11.3. Hinduism in Detail
Hinduism is a diverse and ancient religion that originated in the Indian subcontinent. It encompasses a wide range of traditions, philosophies, and deities. Key concepts in Hinduism include:
- Dharma: The principle of cosmic order
- Karma: The law of cause and effect
- Samsara: The cycle of birth, death, and rebirth
- Moksha: Liberation from the cycle of samsara
Hinduism has several major denominations, including Vaishnavism, Shaivism, Shaktism, and Smartism.
11.4. Buddhism in Detail
Buddhism originated in India with Siddhartha Gautama, the Buddha. Buddhists seek to achieve enlightenment and liberation from suffering through practices such as meditation, mindfulness, and ethical conduct. Key concepts in Buddhism include:
- The Four Noble Truths: The nature of suffering, its cause, its cessation, and the path to its cessation.
- The Eightfold Path: The path to liberation, encompassing right understanding, thought, speech, action, livelihood, effort, mindfulness, and concentration.
- Karma: The law of cause and effect
- Rebirth: The cycle of birth, death, and rebirth
- Nirvana: The state of liberation from suffering
Buddhism has several major branches, including Theravada, Mahayana, and Vajrayana.
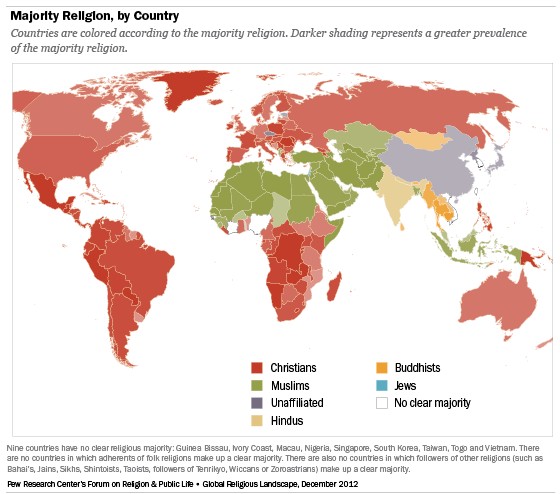
12. Visualizing Religious Diversity: A World Map
The map below illustrates the distribution of major religious groups around the world. This visualization helps to understand the geographic concentration of different faiths and the diversity of religious landscapes in various regions.
13. Examining the Growth Trends in Major Religions
Understanding the growth trends of different religions provides insight into future demographics and societal changes. Factors influencing growth include birth rates, conversion rates, and migration patterns.
| Religion | Growth Rate Factors | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Christianity | High birth rates in some regions, active missionary work, and cultural influence. | Likely to remain a major global religion, with growth primarily in developing countries. |
| Islam | High birth rates, especially in the Middle East and Africa, and increasing conversions. | Expected to continue growing rapidly and potentially surpass Christianity as the world’s largest religion by the end of the 21st century. |
| Hinduism | Concentrated primarily in India and Nepal, with a relatively stable growth rate. | Projected to remain regionally dominant, with limited growth outside the Indian subcontinent. |
| Buddhism | Lower birth rates and aging populations in some Buddhist-majority countries. | Anticipated to experience slower growth compared to other major religions. |
| Unaffiliated | Increasing secularization and declining religious affiliation in many Western countries. | Projected to continue growing, especially in Europe and North America, as more people identify as non-religious. |
| Folk Religions | Strong ties to local cultures and traditions, with varying growth rates depending on the region. | Expected to persist in specific regions with a focus on preserving indigenous beliefs and practices. |
| Other Religions | Diverse range of faiths, with growth patterns influenced by specific cultural and social factors. | Each religion within this category is expected to follow individual growth patterns. |
14. The Impact of Religion on Culture and Society
Religion profoundly influences various aspects of culture and society, including art, music, literature, ethics, and social norms. Religious beliefs often shape moral values and guide individuals’ behavior.
14.1. Influence on Ethical Frameworks
Major religions provide ethical frameworks that influence people’s understanding of right and wrong. These frameworks often guide individuals in making moral decisions and contributing to the well-being of society.
14.2. Impact on Social Norms and Values
Religious teachings can influence social norms and values related to family, community, and social justice. Religious organizations often play a significant role in providing social services, promoting charitable activities, and advocating for social change.
14.3. Role in Art, Music, and Literature
Religion has inspired countless works of art, music, and literature throughout history. Religious themes and symbols are often used to express spiritual experiences, convey moral messages, and celebrate cultural traditions.
14.4. Influence on Political Discourse
Religious beliefs can influence political discourse and public policy debates. Religious leaders and organizations often advocate for policies that align with their values and beliefs.
15. Exploring Religious Syncretism and Hybridity
Religious syncretism refers to the blending of different religious traditions and beliefs. This phenomenon often occurs when cultures interact and influence one another.
15.1. Examples of Syncretic Religions
- Santería: A syncretic religion that blends West African Yoruba beliefs with Catholicism.
- Vodou: A syncretic religion that combines West African Vodun traditions with Catholicism.
- Cao Dai: A syncretic religion founded in Vietnam in the 20th century, incorporating elements of Buddhism, Taoism, Confucianism, and Catholicism.
15.2. Factors Contributing to Syncretism
- Cultural Exchange: Interaction between different cultures can lead to the blending of religious beliefs and practices.
- Colonialism: Colonial powers often imposed their religions on colonized populations, leading to syncretism as indigenous beliefs were combined with the colonizers’ religions.
- Globalization: The increasing interconnectedness of the world can facilitate the exchange of religious ideas and practices, leading to syncretism.
15.3. Impact on Religious Identity
Syncretism can lead to the formation of new religious identities that incorporate elements from multiple traditions. This can enrich religious landscapes and promote religious tolerance.
16. The Role of Religious Freedom and Tolerance
Religious freedom and tolerance are essential for creating inclusive and harmonious societies. When people are free to practice their religion without fear of discrimination or persecution, it promotes social cohesion and reduces conflict.
16.1. International Declarations on Religious Freedom
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights: Article 18 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights states that everyone has the right to freedom of thought, conscience, and religion.
- International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights: Article 18 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights guarantees the right to freedom of thought, conscience, and religion.
16.2. Challenges to Religious Freedom
- Religious Persecution: In some parts of the world, people face persecution because of their religious beliefs.
- Discrimination: Religious minorities may experience discrimination in employment, education, and other areas of life.
- Religious Extremism: Extremist groups may use violence and intimidation to impose their religious beliefs on others.
16.3. Promoting Religious Tolerance
- Education: Educating people about different religions can promote understanding and reduce prejudice.
- Interfaith Dialogue: Encouraging dialogue between different religious communities can build bridges and foster mutual respect.
- Legal Protections: Enacting laws that protect religious freedom and prohibit discrimination can create a more inclusive society.
17. Navigating Religious Sensitivity in a Diverse World
In an increasingly interconnected world, it is crucial to approach religious discussions with sensitivity and respect. Understanding and appreciating diverse religious beliefs can foster mutual understanding and promote peaceful coexistence.
17.1. Respectful Communication Strategies
- Active Listening: Paying attention to what others say and showing genuine interest in their perspectives.
- Avoiding Stereotypes: Recognizing that individuals within a religious group may have diverse beliefs and practices.
- Asking Open-Ended Questions: Encouraging others to share their experiences and perspectives in their own words.
- Being Mindful of Language: Avoiding language that could be offensive or disrespectful to others’ religious beliefs.
17.2. Cross-Cultural Religious Etiquette
- Dress Codes: Being aware of dress codes or customs associated with certain religious sites or practices.
- Dietary Restrictions: Respecting dietary restrictions or customs associated with certain religious traditions.
- Prayer Times: Being mindful of prayer times and avoiding interruptions or distractions.
- Holy Days: Being aware of religious holidays and customs associated with them.
17.3. Fostering Interfaith Understanding
- Attending Interfaith Events: Participating in events that bring together people from different religious backgrounds.
- Studying Different Religions: Learning about the beliefs, practices, and history of different religions.
- Engaging in Dialogue: Participating in conversations with people from different religious backgrounds.
- Volunteering with Interfaith Organizations: Supporting organizations that promote interfaith understanding and cooperation.
18. The Future of Religion: Trends and Predictions
Predicting the future of religion is complex, but several trends and predictions can provide insights into potential changes in the religious landscape.
18.1. Predicted Growth in Specific Religions
- Islam: Expected to continue growing rapidly due to high birth rates and increasing conversions, potentially surpassing Christianity as the world’s largest religion by the end of the 21st century.
- Unaffiliated: Projected to continue growing, especially in Europe and North America, as more people identify as non-religious.
18.2. Potential Shifts in Religious Affiliation
- Secularization: Increasing secularization in some parts of the world may lead to a decline in religious affiliation.
- Conversion: Conversion between religions is likely to continue, influenced by individual experiences, social factors, and cultural trends.
- Religious Innovation: New religious movements and spiritual practices may emerge, reflecting changing social and cultural values.
18.3. Impact of Technology on Religious Practices
- Online Communities: Online platforms may play an increasing role in connecting people with shared religious interests and facilitating religious practices.
- Digital Resources: Access to religious texts, teachings, and resources through digital platforms may become more widespread.
- Virtual Reality: Virtual reality technologies may be used to create immersive religious experiences and connect people across geographical boundaries.
19. Seek Answers to Your Questions at WHAT.EDU.VN
Navigating the complex world of religion can be challenging. If you have questions about different faiths, religious practices, or the role of religion in society, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help. Our platform provides a free and easy way to get your questions answered by knowledgeable individuals.
19.1. Get Free Answers to Your Questions
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand that finding accurate and reliable information can be difficult. That’s why we’ve created a platform where you can ask any question and receive helpful answers from our community of experts.
19.2. Connect with Knowledgeable Individuals
Our platform connects you with people who have a passion for sharing their knowledge. Whether you’re curious about a specific religion, want to understand religious concepts, or need help with a school assignment, our community is here to assist you.
19.3. Ask Any Question, No Matter How Simple or Complex
No question is too simple or too complex for WHAT.EDU.VN. Whether you’re seeking basic definitions or delving into advanced topics, our platform is designed to provide you with the information you need.
19.4. Explore a Wide Range of Topics
In addition to religion, WHAT.EDU.VN covers a wide range of topics, including science, history, technology, and more. Whatever your interests may be, you’re sure to find something that piques your curiosity.
20. Invitation to Ask Questions on WHAT.EDU.VN
Are you curious to learn more about global religions, understand different belief systems, or explore the role of faith in society? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we offer a free and convenient platform to ask any question and receive insightful answers. Don’t hesitate to reach out with your inquiries and connect with our community of experts. We are committed to providing you with accurate information and fostering a deeper understanding of the world around us.
20.1. Free and Easy Access to Information
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we believe that everyone should have access to reliable information. That’s why we offer our services completely free of charge. Simply visit our website, submit your question, and let our community of experts provide you with the answers you need.
20.2. Quick and Accurate Responses
We understand that you want your questions answered quickly and accurately. Our platform is designed to connect you with knowledgeable individuals who can provide you with timely and reliable information.
20.3. A Welcoming Community for All
WHAT.EDU.VN is a welcoming community for people of all backgrounds and interests. Whether you’re a student, a researcher, or simply someone who is curious about the world, you’ll find a supportive and informative environment on our platform.
Don’t let your questions go unanswered. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and start exploring the world of knowledge.
Contact Information:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Ask your question now at what.edu.vn and unlock a world of knowledge!
