The radius of a circle is a fundamental concept in geometry, acting as the cornerstone for understanding circles and spheres. It’s more than just a line; it’s the defining measurement that dictates a circle’s size and properties. Simply put, the radius is the distance from the exact center of a circle to any point on its outer edge, known as the circumference. Let’s delve deeper into understanding the radius, exploring its formulas, and learning how to calculate it in various scenarios.
Defining the Radius of a Circle
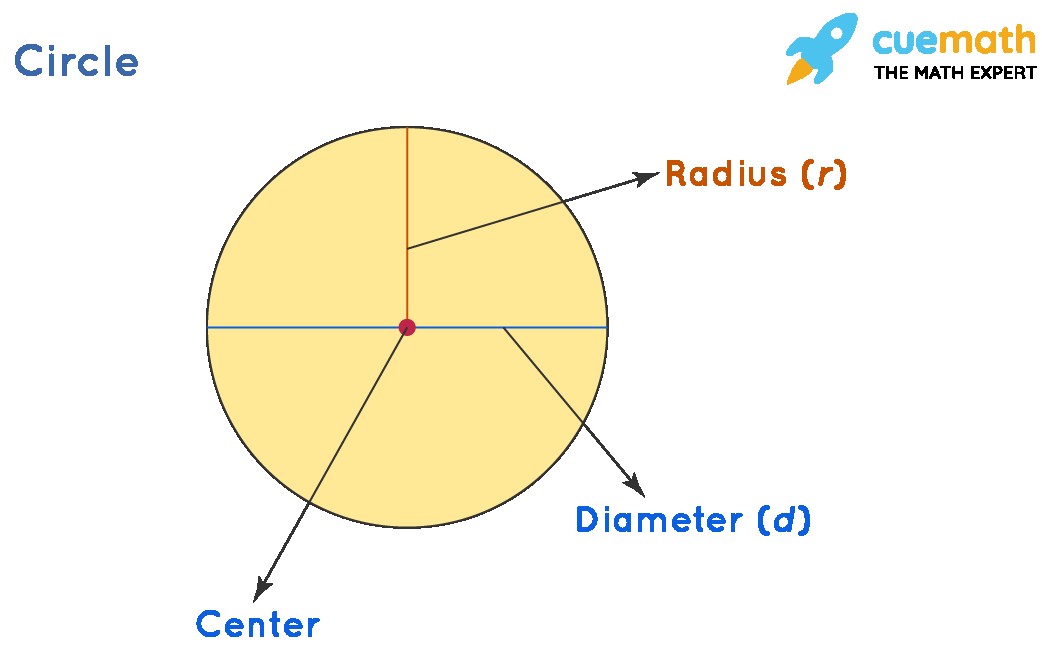
At its heart, the radius is a line segment that elegantly bridges the center of a circle to its circumference. Imagine drawing a circle – the radius is the straight line from the point where you placed your compass (the center) to the pencil mark that forms the circle’s edge. This distance remains constant no matter where you draw the line to on the circumference.
Understanding the meaning of radius is key to grasping other circle properties. Notably, the radius is intrinsically linked to the diameter. The diameter is a line that passes straight through the center of the circle, connecting two points on opposite sides of the circumference. As you can see in the image below, the diameter is essentially two radii joined end-to-end. Therefore, the radius is always half the length of the diameter. This relationship is crucial for calculations and understanding circle dimensions.
Image: Visual representation of a circle radius, showing the line segment from the center to the circumference and its relation to the diameter.
Now that we have a clear understanding of what the radius is, let’s explore the essential formulas used to calculate it.
Formulas to Calculate the Radius
Calculating the radius of a circle is straightforward, especially when you know other key measurements like the diameter, circumference, or area. There are specific radius of circle formulas tailored to each situation.
Radius Formula with Diameter
As we’ve established, the diameter cuts across the circle through its center, and it’s twice the length of the radius. This gives us a simple and direct formula to find the radius if you know the diameter:
Radius = Diameter ÷ 2
In essence, you’re just halving the diameter to find the radius. This is the most basic and frequently used formula when dealing with circles.
Radius Formula from Circumference
The circumference is the distance around the circle, essentially its perimeter. The relationship between the circumference (C) and the radius (r) is defined by the formula: C = 2πr, where π (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159.
To find the radius when you know the circumference, we rearrange this formula:
Radius = Circumference / 2π
This formula tells us that the radius is the circumference divided by 2π. It’s important to use an accurate value for π or use the π button on a calculator for precise results.
Radius Formula using Area
The area of a circle is the space enclosed within its circumference. The formula for the area (A) of a circle is A = πr2.
If you know the area of a circle and need to find the radius, you can rearrange this formula as follows:
Radius = √(Area / π)
This formula involves taking the square root of the area divided by π. It’s important to remember to perform the division before taking the square root.
Image: Diagram illustrating the formulas for calculating the radius of a circle using diameter, circumference, and area.
These three formulas provide you with the tools to find the radius of a circle in various situations, depending on the information you have available.
Understanding the Properties of a Circle’s Radius
The radius isn’t just a measurement; it embodies key properties of a circle. One of the most significant is that a circle has an infinite number of radii. Imagine drawing lines from the center to every single point on the circumference – each of these lines is a radius.
Crucially, all radii in the same circle are equidistant from the center and therefore, are of equal length. This uniformity is what defines a circle and distinguishes it from other shapes.
Furthermore, the length of the radius directly determines the size of the circle. A longer radius creates a larger circle, while a shorter radius results in a smaller circle. Changing the radius is the only way to scale a circle up or down while maintaining its circular shape.
Consider the image below, illustrating multiple radii within a single circle. Points A, B, M, N, P, Q, X, and Y all lie on the circle’s boundary. Each line segment from the center O to these points (OA, OB, OM, ON, OY, OX, OP, OQ) represents a radius. And as you can see, OA = OB = OM = ON = OP = OQ = OX = OY.
Image: Illustration showing multiple radii of a circle, demonstrating that all radii from the center to the circumference are equal in length.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Find the Radius
Let’s put the formulas into practice and learn how to find the radius of a circle using different given values.
1. Finding the Radius from the Diameter:
- Formula: Radius = Diameter / 2
- Example: If the diameter of a circle is 30 inches, then the radius is calculated as:
Radius = 30 inches / 2 = 15 inches.
2. Finding the Radius from the Circumference:
- Formula: Radius = Circumference / 2π
- Example: If the circumference of a circle is 62.8 units, we can find the radius (using π ≈ 3.14):
Radius = 62.8 units / (2 * 3.14) = 62.8 / 6.28 = 10 units.
3. Finding the Radius from the Area:
- Formula: Radius = √(Area / π)
- Example: If the area of a circle is 154 square meters, then the radius is (using π ≈ 22/7):
Radius = √(154 m2 / (22/7)) = √(154 * 7 / 22) = √(49) = 7 meters.
These examples demonstrate the practical application of each formula, making it easy to calculate the radius when you have the diameter, circumference, or area.
The Radius in the Equation of a Circle
The radius also plays a crucial role in defining the equation of a circle, especially when working with coordinate geometry on a Cartesian plane. The standard equation of a circle with center at point (h, k) and radius ‘r’ is:
(x − h)2 + (y − k)2 = r2
Here, (x, y) represents any point on the circumference of the circle. If the center of the circle is at the origin (0, 0), the equation simplifies to:
x2 + y2 = r2
This equation signifies that for any point (x, y) on the circle, the square of its x-coordinate plus the square of its y-coordinate equals the square of the radius.
The image below illustrates a circle on a Cartesian plane. The center is at (0, b), and ‘r’ represents the radius connecting the center to a point (x, y) on the circle. Substituting these values into the standard equation gives us the specific equation for this circle: (x − 0)2 + (y − b)2 = r2, which simplifies to x2 + (y − b)2 = r2.
Image: Diagram of a circle on the Cartesian plane, illustrating the radius ‘r’ and center coordinates in relation to the circle’s equation.
Radius of a Sphere Explained
The concept of radius extends beyond two-dimensional circles to three-dimensional spheres. A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in 3D space, like a ball. Just like a circle, the radius of a sphere is the distance from its center to any point on its surface.
The radius is fundamental to determining the volume and surface area of a sphere. The formulas for these are:
- Volume of a Sphere (V): V = (4/3)πr3
- Surface Area of a Sphere (A): A = 4πr2
Conversely, if you know the volume or surface area of a sphere, you can calculate its radius using rearranged formulas:
- Radius from Volume: r = 3√(3V / 4π) (Cube root of (3V / 4π))
- Radius from Surface Area: r = √(A / 4π)
These formulas highlight the importance of the radius as a core measurement for spheres, similar to its role in circles.
Real-World Examples and Applications of Radius
The radius isn’t just a theoretical concept; it’s present all around us. Think about everyday objects:
- Wheels: The radius of a wheel determines its size and how far it travels in one rotation.
- Pizzas and Cakes: When ordering a pizza or cake, the size is often described by its diameter or radius.
- Pipes and Cylinders: The radius is crucial in calculating the capacity and flow rate of pipes and cylindrical objects.
- Planetary Bodies: Astronomers use radius to measure the size of planets, stars, and moons.
Understanding the radius is essential in various fields, from engineering and architecture to astronomy and even cooking. It’s a fundamental measurement that helps us quantify and understand circular and spherical objects in the world around us.
Conclusion
In summary, What Is The Radius Of A Circle? It’s the distance from the center to the circumference, a fundamental measurement that defines a circle’s size and is intrinsically linked to its diameter, circumference, and area. Mastering the concept of radius and its related formulas is essential for anyone studying geometry and for understanding the world around us, where circles and spheres are ubiquitous. Whether you are calculating the size of a pizza, designing a wheel, or exploring the dimensions of planets, the radius is a key concept to have in your mathematical toolkit.
FAQs about the Radius of a Circle
### What is the Radius of a Circle in Geometry?
In geometry, the radius of a circle is defined as the length of a straight line segment connecting the center of the circle to any point on its circumference. It’s a fundamental property that dictates the size of the circle, and all radii of the same circle are equal in length.
### How is Diameter Related to the Radius of the Circle?
The diameter and radius are directly related. The diameter is a line passing through the center of the circle and connecting two opposite points on the circumference. The relationship is: Diameter = 2 × Radius. Conversely, Radius = Diameter / 2.
### How to Find the Radius from Circumference?
To find the radius when you know the circumference (C), use the formula derived from the circumference formula (C = 2πr): Radius = Circumference / 2π.
### What is the Radius Formula?
There isn’t one single “radius formula,” but rather different formulas to find the radius depending on what information you have:
- From Diameter: Radius = Diameter / 2
- From Circumference: Radius = Circumference / 2π
- From Area: Radius = √(Area / π)
### How to Calculate Radius of Circle Using a Calculator?
You can easily calculate the radius using a calculator by applying the appropriate formula. For example, if you have the diameter, simply divide it by 2. If you have the circumference, divide it by (2 * π). For area, divide by π and then take the square root. Most calculators have a π button for accurate calculations.
### How to Find the Radius of a Circle with the Area?
If you know the area (A) of a circle, use the formula: Radius = √(Area / π). Divide the area by π and then find the square root of the result to get the radius.
### How to Calculate Radius from Diameter?
Calculating the radius from the diameter is the simplest calculation. Use the formula: Radius = Diameter ÷ 2. Just divide the diameter value by two to find the radius.
Image: An engaging visual encouraging interactive learning and exploration of mathematical concepts.