A TSH test is a crucial blood test that determines if your thyroid gland is functioning correctly. This test is instrumental in identifying whether your thyroid is overactive (hyperthyroidism) or underactive (hypothyroidism). Importantly, the TSH test can detect thyroid disorders even before noticeable symptoms appear, enabling timely intervention and preventing potential health complications associated with untreated thyroid imbalances.
Decoding TSH: Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Explained
 Close-up medical professional pointing at thyroid gland on anatomical model
Close-up medical professional pointing at thyroid gland on anatomical model
TSH stands for “Thyroid Stimulating Hormone.” This hormone is produced by the pituitary gland, a small gland located at the base of your brain. The primary role of TSH is to act as a messenger, signaling your thyroid gland to produce and release essential thyroid hormones. These hormones are vital for regulating numerous bodily functions. The TSH test measures the amount of thyroid stimulating hormone present in your blood, providing valuable insights into your thyroid’s performance.
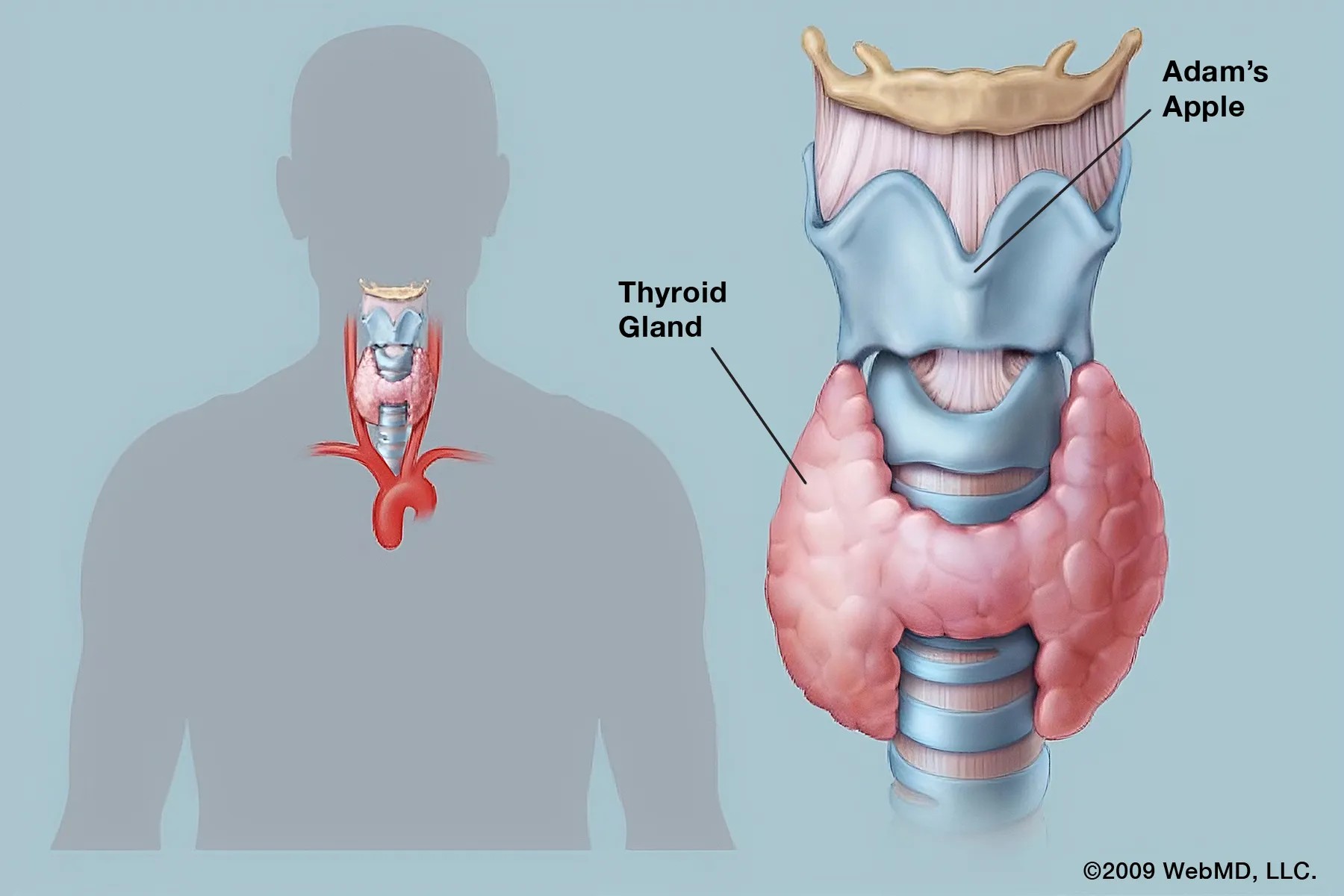
The Thyroid Gland: Your Body’s Metabolism Regulator
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland situated in the front of your neck. It is a key component of your endocrine system, a complex network of glands and hormones that regulate various bodily processes. These processes range from growth and development to mood regulation.
One of the thyroid gland’s most significant roles is managing your metabolism. Metabolism is the process by which your body converts food into energy that fuels your cells. To effectively manage metabolism, the thyroid relies on TSH. TSH prompts the thyroid to produce thyroxine (T4), a primary thyroid hormone. Once released into the bloodstream, T4 is converted into triiodothyronine (T3), a more potent hormone. Both T3 and T4 are collectively referred to as “thyroid hormones” and are critical for controlling various bodily functions, including:
- Heart Rate: Thyroid hormones influence the speed at which your heart beats.
- Digestion: They play a role in how efficiently your body digests food.
- Muscle Control: Thyroid hormones are essential for proper muscle function and control.
- Bone Health: They contribute to maintaining healthy bone density.
- Brain Health: Thyroid hormones are crucial for cognitive function and brain development.
In addition to T3 and T4, the thyroid gland produces other hormones, such as:
- Reverse triiodothyronine (rT3): This hormone acts to slow down the action of T3 and its levels typically increase when the body is under severe stress or illness.
- Calcitonin: This hormone helps regulate calcium levels in the blood, maintaining a balance essential for various bodily functions.
Why is the TSH Test Important for Thyroid Health?
The intricate feedback loop between the pituitary gland and the thyroid is crucial for maintaining hormonal balance. If the pituitary gland produces too much or too little TSH, it directly impacts the production of thyroid hormones. Conversely, imbalances in thyroid hormone levels will also affect TSH levels. This delicate balance is essential for overall health.
When your thyroid gland doesn’t function optimally, the repercussions can be felt throughout your body. Organs and systems such as your heart, nervous system, reproductive system, and digestive system can all be adversely affected by thyroid dysfunction. Therefore, regular TSH testing and monitoring are vital for maintaining overall well-being and addressing potential thyroid issues promptly.
