What Is User Experience Design? At what.edu.vn, we believe it’s about crafting seamless and delightful interactions between users and products, ensuring their needs are met with elegance and efficiency. User experience (UX) design encompasses a wide range of disciplines, from user research and information architecture to interaction design and usability testing, all working together to create positive user experiences. Dive into the world of user-centered design and discover how it can transform your approach to product development, enhance user satisfaction, and drive business success with intuitive interfaces.
Table of Contents
- Understanding User Experience Design
- The Core Principles of UX Design
- Key Elements of User Experience Design
- The UX Design Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Essential Skills for UX Designers
- Tools and Technologies Used in UX Design
- User Research Methods in UX Design
- The Importance of Usability Testing
- UX Design and Accessibility
- Measuring the Success of UX Design
- UX Design Career Paths and Opportunities
- The Future of User Experience Design
- Common Misconceptions About UX Design
- Ethical Considerations in UX Design
- How UX Design Impacts Business
- Examples of Great UX Design
- UX Design Resources and Learning Platforms
- Frequently Asked Questions About UX Design
- Connecting with the UX Design Community
- Getting Started with UX Design Today
1. Understanding User Experience Design
User experience (UX) design is the process of creating products that provide meaningful and relevant experiences to users. This involves designing the entire process of acquiring and integrating a product, including aspects of branding, design, usability, and function.
1.1 Defining User Experience (UX)
UX encompasses all aspects of a user’s interaction with a product, service, or company. It’s about how a user feels before, during, and after using a product. A positive UX is one that is effective, efficient, enjoyable, and provides value to the user. It is the emotional connection between the user and the product.
1.2 What is User Experience Design (UXD)?
User Experience Design (UXD) is the discipline of creating user interfaces and interactions that are useful, usable, and desirable. UX designers focus on understanding user needs, behaviors, and motivations to create designs that meet those needs and provide a positive experience. It’s about creating intuitive interfaces that help users achieve their goals effortlessly.
1.3 The History of UX Design
The term “user experience” was popularized by Don Norman in the 1990s. Norman, a cognitive scientist and usability engineer, emphasized the importance of user-centered design in creating technology that is both functional and enjoyable. However, the principles of UX design have been around for much longer, with roots in fields like human factors, ergonomics, and human-computer interaction. Over time, UX design has evolved to encompass a broader range of disciplines and a deeper understanding of user behavior.
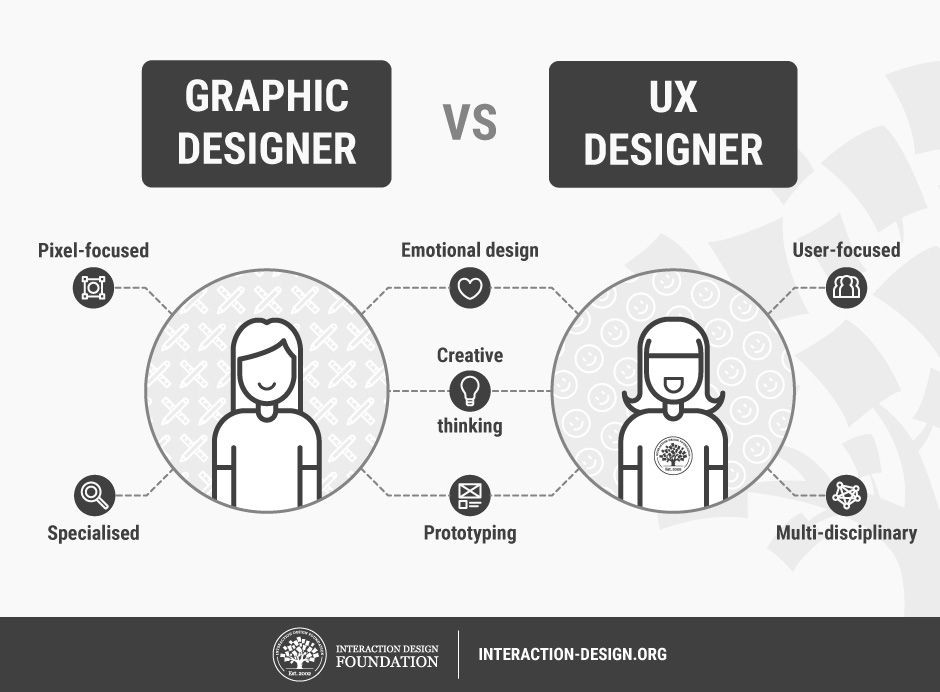
1.4 UX vs. UI: Understanding the Difference
While often used interchangeably, UX and UI are distinct but interconnected disciplines. UX (User Experience) focuses on the overall feel and experience of a product, ensuring it meets user needs and provides value. UI (User Interface) focuses on the visual design and interactive elements of a product, ensuring it is aesthetically pleasing and easy to use. UX is the foundation, while UI is the execution. UI designers use visual elements to bring the UX strategy to life, creating a seamless and engaging user experience.
1.5 The Value of UX Design
Investing in UX design can bring significant benefits to businesses, including:
- Increased customer satisfaction
- Improved user engagement and retention
- Reduced development costs
- Higher conversion rates
- Stronger brand loyalty
By prioritizing user needs and creating intuitive interfaces, UX design can drive business growth and create a competitive advantage.
1.6 How UX Design Impacts User Satisfaction
UX design plays a crucial role in shaping user satisfaction. A well-designed product is easy to use, meets user needs, and provides a positive experience. This leads to increased satisfaction, which in turn drives user loyalty and positive word-of-mouth. In contrast, a poorly designed product can lead to frustration, abandonment, and negative reviews. By focusing on user-centered design principles, businesses can create products that delight users and foster long-term relationships.
2. The Core Principles of UX Design
Effective UX design is guided by a set of core principles that prioritize user needs and create positive experiences. These principles provide a framework for making design decisions and ensuring that products are user-centered.
2.1 User-Centered Design
User-centered design (UCD) is an iterative design process that focuses on understanding user needs and incorporating them into every stage of the design process. This involves conducting user research, creating personas, and testing designs with real users. By putting users at the center of the design process, UX designers can create products that truly meet their needs and provide value.
2.2 Usability
Usability refers to the ease with which users can achieve their goals using a product. A usable product is effective, efficient, and satisfying to use. Key aspects of usability include:
- Learnability: How easy is it for users to learn how to use the product?
- Efficiency: How quickly can users accomplish tasks?
- Memorability: How easily can users remember how to use the product after a period of not using it?
- Errors: How many errors do users make, and how easily can they recover from them?
- Satisfaction: How pleasant is it to use the product?
2.3 Accessibility
Accessibility is the practice of designing products that can be used by people of all abilities, including those with disabilities. This involves considering factors such as visual impairments, motor impairments, and cognitive impairments. By designing for accessibility, UX designers can create products that are inclusive and provide equal access to information and functionality.
2.4 Desirability
Desirability refers to the extent to which users find a product appealing and enjoyable to use. A desirable product is visually attractive, emotionally engaging, and provides a sense of delight. UX designers can enhance desirability by focusing on aesthetics, branding, and emotional design.
2.5 Value
Value refers to the extent to which a product provides benefits to users. A valuable product solves a problem, meets a need, or provides a sense of satisfaction. UX designers can enhance value by focusing on user research, understanding user goals, and creating designs that deliver tangible benefits.
2.6 Information Architecture (IA)
Information architecture (IA) is the organization and structuring of information within a product or website. Effective IA makes it easy for users to find what they are looking for and navigate the product intuitively. Key aspects of IA include:
- Organization: How is information grouped and categorized?
- Labeling: How are categories and content labeled?
- Navigation: How do users move through the product?
- Search: How can users find specific information?
Good IA ensures that users can easily find the information they need, enhancing the overall user experience.
3. Key Elements of User Experience Design
UX design encompasses a wide range of elements that work together to create positive user experiences. These elements include strategy, research, usability, information architecture, interaction design, and visual design.
3.1 Strategy
The strategy element of UX design involves defining the goals and objectives of the product, as well as understanding the business context and user needs. This includes:
- Business goals: What does the business hope to achieve with the product?
- User needs: What problems are users trying to solve?
- Market research: What are the competitive trends and opportunities?
- Value proposition: What unique value does the product offer to users?
A well-defined strategy provides a foundation for making design decisions and ensuring that the product aligns with both business goals and user needs.
3.2 User Research
User research is the process of gathering information about user needs, behaviors, and motivations. This involves conducting interviews, surveys, and usability testing to understand how users interact with the product and identify areas for improvement. Key user research methods include:
- User interviews: Talking to users to understand their goals and needs.
- Surveys: Gathering data from a large group of users.
- Usability testing: Observing users as they interact with the product.
- Analytics: Analyzing user behavior to identify patterns and trends.
User research provides valuable insights that inform design decisions and ensure that the product meets user needs.
3.3 Usability
Usability, as mentioned earlier, is a critical element of UX design. It involves ensuring that the product is easy to use, efficient, and satisfying. Key aspects of usability include:
- Learnability: How easy is it for users to learn how to use the product?
- Efficiency: How quickly can users accomplish tasks?
- Memorability: How easily can users remember how to use the product after a period of not using it?
- Errors: How many errors do users make, and how easily can they recover from them?
- Satisfaction: How pleasant is it to use the product?
3.4 Information Architecture (IA)
Information architecture (IA) is the organization and structuring of information within a product or website. Effective IA makes it easy for users to find what they are looking for and navigate the product intuitively. Key aspects of IA include:
- Organization: How is information grouped and categorized?
- Labeling: How are categories and content labeled?
- Navigation: How do users move through the product?
- Search: How can users find specific information?
3.5 Interaction Design (IxD)
Interaction design (IxD) focuses on how users interact with a product. This involves designing the interactive elements, such as buttons, forms, and animations, to create a seamless and intuitive user experience. Key aspects of IxD include:
- Input: How do users provide input to the product?
- Output: How does the product respond to user input?
- Feedback: How does the product provide feedback to users?
- Controls: How do users control the product?
Good IxD ensures that users can easily interact with the product and accomplish their goals.
3.6 Visual Design
Visual design focuses on the aesthetic aspects of a product, such as color, typography, and imagery. Visual design plays a crucial role in creating a positive user experience by making the product visually appealing and engaging. Key aspects of visual design include:
- Color: How are colors used to create a visual hierarchy and evoke emotions?
- Typography: How is text used to communicate information effectively?
- Imagery: How are images used to enhance the user experience?
- Layout: How are elements arranged on the screen to create a visual balance?
Effective visual design enhances the user experience by making the product visually appealing and easy to use.
4. The UX Design Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The UX design process is an iterative process that involves understanding user needs, designing solutions, and testing those solutions with real users. This process typically includes the following steps:
4.1 Define
The first step in the UX design process is to define the problem and identify the goals of the product. This involves understanding the business context, user needs, and market opportunities. Key activities in this step include:
- Conducting stakeholder interviews
- Defining project goals
- Identifying target users
- Analyzing the competitive landscape
4.2 Research
The research step involves gathering information about user needs, behaviors, and motivations. This includes conducting user interviews, surveys, and usability testing to understand how users interact with the product and identify areas for improvement. Key activities in this step include:
- Conducting user interviews
- Creating user personas
- Performing competitive analysis
- Analyzing user data
4.3 Design
The design step involves creating solutions to the problems identified in the research step. This includes creating wireframes, prototypes, and visual designs to illustrate how the product will work. Key activities in this step include:
- Creating wireframes
- Developing prototypes
- Designing the user interface
- Creating visual designs
4.4 Test
The test step involves testing the designs with real users to identify areas for improvement. This includes conducting usability testing and gathering feedback to ensure that the product meets user needs. Key activities in this step include:
- Conducting usability testing
- Gathering user feedback
- Analyzing test results
- Iterating on designs
4.5 Implement
The implement step involves building and launching the product. This includes working with developers to ensure that the designs are implemented correctly and that the product meets the defined goals. Key activities in this step include:
- Collaborating with developers
- Ensuring design consistency
- Launching the product
- Monitoring user feedback
4.6 Evaluate
The evaluate step involves monitoring the product’s performance and gathering feedback to identify areas for improvement. This includes analyzing user data, conducting surveys, and gathering feedback to ensure that the product continues to meet user needs. Key activities in this step include:
- Analyzing user data
- Conducting surveys
- Gathering user feedback
- Iterating on designs
This iterative process ensures that the product is continuously improved to meet user needs and achieve business goals.
5. Essential Skills for UX Designers
UX designers need a diverse set of skills to be successful. These skills include both technical skills and soft skills, such as communication, empathy, and problem-solving.
5.1 User Research Skills
User research skills are essential for understanding user needs and behaviors. This includes the ability to conduct user interviews, surveys, and usability testing. Key user research skills include:
- Interviewing techniques
- Survey design
- Usability testing methodologies
- Data analysis
5.2 Wireframing and Prototyping Skills
Wireframing and prototyping skills are essential for creating solutions to the problems identified in the research step. This includes the ability to create low-fidelity wireframes and high-fidelity prototypes to illustrate how the product will work. Key wireframing and prototyping skills include:
- Wireframing tools
- Prototyping software
- Interaction design principles
- User interface design principles
5.3 Visual Design Skills
Visual design skills are essential for creating a positive user experience by making the product visually appealing and engaging. This includes the ability to use color, typography, and imagery effectively. Key visual design skills include:
- Color theory
- Typography principles
- Layout design
- Image editing
5.4 Interaction Design Skills
Interaction design skills are essential for designing the interactive elements of a product, such as buttons, forms, and animations. This includes the ability to create a seamless and intuitive user experience. Key interaction design skills include:
- Interaction design principles
- User interface design principles
- Motion design
- Accessibility guidelines
5.5 Communication Skills
Communication skills are essential for collaborating with stakeholders, communicating design decisions, and gathering user feedback. This includes the ability to communicate effectively both verbally and in writing. Key communication skills include:
- Verbal communication
- Written communication
- Presentation skills
- Active listening
5.6 Empathy
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. This is essential for UX designers, as it allows them to understand user needs and create products that meet those needs. Key empathy skills include:
- Active listening
- Emotional intelligence
- Perspective-taking
- Non-verbal communication
5.7 Problem-Solving Skills
Problem-solving skills are essential for identifying problems and creating solutions. This includes the ability to analyze data, identify patterns, and generate creative solutions. Key problem-solving skills include:
- Critical thinking
- Analytical skills
- Creative thinking
- Decision-making
By developing these essential skills, UX designers can create products that provide positive user experiences and achieve business goals.
6. Tools and Technologies Used in UX Design
UX designers use a variety of tools and technologies to create wireframes, prototypes, and visual designs. These tools help UX designers streamline their workflow and collaborate effectively with stakeholders.
6.1 Wireframing Tools
Wireframing tools are used to create low-fidelity representations of a product’s layout and functionality. These tools help UX designers quickly iterate on designs and gather feedback from stakeholders. Popular wireframing tools include:
- Balsamiq
- Sketch
- Axure RP
- Adobe XD
6.2 Prototyping Tools
Prototyping tools are used to create interactive simulations of a product’s functionality. These tools allow UX designers to test their designs with real users and gather feedback before development. Popular prototyping tools include:
- InVision
- Figma
- Adobe XD
- Marvel
6.3 Visual Design Tools
Visual design tools are used to create the visual elements of a product, such as color, typography, and imagery. These tools help UX designers create visually appealing and engaging user experiences. Popular visual design tools include:
- Adobe Photoshop
- Adobe Illustrator
- Sketch
- Figma
6.4 User Research Tools
User research tools are used to gather information about user needs, behaviors, and motivations. These tools help UX designers conduct user interviews, surveys, and usability testing. Popular user research tools include:
- Typeform
- SurveyMonkey
- UserTesting.com
- Optimal Workshop
6.5 Collaboration Tools
Collaboration tools are used to facilitate communication and collaboration among UX designers, stakeholders, and developers. These tools help ensure that everyone is on the same page and that the product is aligned with the defined goals. Popular collaboration tools include:
- Slack
- Microsoft Teams
- Trello
- Asana
By leveraging these tools and technologies, UX designers can create effective and efficient workflows and deliver high-quality user experiences.
7. User Research Methods in UX Design
User research is a critical component of UX design, providing valuable insights into user needs, behaviors, and motivations. By conducting user research, UX designers can create products that truly meet user needs and provide value.
7.1 User Interviews
User interviews involve talking to users to understand their goals, needs, and pain points. These interviews can be conducted in person or remotely and can provide valuable qualitative data. Key considerations for user interviews include:
- Developing a structured interview guide
- Recruiting representative users
- Creating a comfortable and open environment
- Active listening and probing for deeper insights
7.2 Surveys
Surveys involve gathering data from a large group of users using questionnaires. Surveys can be used to collect both quantitative and qualitative data and can provide valuable insights into user preferences and attitudes. Key considerations for surveys include:
- Defining clear research objectives
- Designing a well-structured questionnaire
- Recruiting a representative sample
- Analyzing survey data to identify patterns and trends
7.3 Usability Testing
Usability testing involves observing users as they interact with a product to identify areas for improvement. This can be conducted in a lab setting or remotely and can provide valuable insights into how users interact with the product. Key considerations for usability testing include:
- Defining clear testing objectives
- Recruiting representative users
- Creating realistic tasks
- Observing user behavior and gathering feedback
7.4 A/B Testing
A/B testing involves comparing two versions of a product or feature to see which one performs better. This can be used to optimize designs and improve user engagement. Key considerations for A/B testing include:
- Defining clear testing objectives
- Creating two distinct versions
- Randomly assigning users to each version
- Analyzing data to determine which version performs better
7.5 Analytics
Analytics involves tracking user behavior to identify patterns and trends. This can provide valuable insights into how users interact with the product and identify areas for improvement. Key considerations for analytics include:
- Defining clear tracking objectives
- Implementing tracking code correctly
- Analyzing data to identify patterns and trends
- Using data to inform design decisions
By leveraging these user research methods, UX designers can gain a deep understanding of user needs and create products that truly meet those needs.
8. The Importance of Usability Testing
Usability testing is a crucial part of the UX design process. It provides valuable insights into how users interact with a product and identifies areas for improvement. By conducting usability testing, UX designers can create products that are easy to use, efficient, and satisfying.
8.1 Identifying Usability Issues
Usability testing can help identify a wide range of usability issues, such as:
- Navigation problems
- Confusing terminology
- Inefficient workflows
- Accessibility issues
- Technical glitches
By identifying these issues early in the design process, UX designers can address them before the product is launched, saving time and resources.
8.2 Gathering User Feedback
Usability testing provides an opportunity to gather feedback from real users about their experience with the product. This feedback can be invaluable in making design decisions and ensuring that the product meets user needs.
8.3 Improving User Satisfaction
By addressing usability issues and incorporating user feedback, UX designers can improve user satisfaction. A usable product is more likely to be used and enjoyed by users, leading to increased loyalty and positive word-of-mouth.
8.4 Reducing Development Costs
By identifying and addressing usability issues early in the design process, UX designers can reduce development costs. Fixing usability issues after the product is launched can be much more expensive and time-consuming.
8.5 Enhancing Business Outcomes
By creating usable and satisfying products, UX designers can enhance business outcomes. A well-designed product is more likely to achieve its goals, such as increasing sales, improving customer satisfaction, and building brand loyalty.
9. UX Design and Accessibility
Accessibility is a critical consideration in UX design. It involves designing products that can be used by people of all abilities, including those with disabilities. By designing for accessibility, UX designers can create products that are inclusive and provide equal access to information and functionality.
9.1 Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are a set of international standards for making web content accessible to people with disabilities. These guidelines cover a wide range of accessibility issues, such as:
- Providing text alternatives for images
- Ensuring sufficient color contrast
- Making content keyboard-accessible
- Providing clear and consistent navigation
- Making content understandable
9.2 Benefits of Accessible Design
Designing for accessibility can bring a wide range of benefits, including:
- Improved usability for all users
- Increased market reach
- Compliance with legal requirements
- Enhanced brand reputation
- Social responsibility
9.3 Accessibility Best Practices
Key accessibility best practices include:
- Using semantic HTML
- Providing alternative text for images
- Ensuring sufficient color contrast
- Making content keyboard-accessible
- Providing captions and transcripts for audio and video content
- Using ARIA attributes to enhance accessibility
By following these best practices, UX designers can create products that are accessible to all users and provide equal access to information and functionality.
10. Measuring the Success of UX Design
Measuring the success of UX design is essential for understanding the impact of design decisions and identifying areas for improvement. By tracking key metrics, UX designers can demonstrate the value of their work and drive business outcomes.
10.1 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measurable values that demonstrate how effectively a product is achieving its goals. Key KPIs for UX design include:
- User satisfaction
- Task completion rate
- Time on task
- Conversion rate
- Error rate
- Abandonment rate
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
10.2 Analytics Tools
Analytics tools can be used to track user behavior and measure the success of UX design. Popular analytics tools include:
- Google Analytics
- Adobe Analytics
- Mixpanel
- Amplitude
10.3 User Feedback
User feedback can provide valuable insights into the user experience and identify areas for improvement. User feedback can be gathered through surveys, interviews, and usability testing.
10.4 A/B Testing
A/B testing can be used to compare two versions of a product or feature and see which one performs better. This can be used to optimize designs and improve user engagement.
By tracking these metrics and gathering user feedback, UX designers can measure the success of their work and drive business outcomes.
11. UX Design Career Paths and Opportunities
UX design offers a wide range of career paths and opportunities for individuals with the right skills and experience. UX designers are in high demand across a variety of industries, including technology, healthcare, finance, and education.
11.1 UX Designer
A UX designer is responsible for designing the overall user experience of a product. This includes conducting user research, creating wireframes and prototypes, and designing the user interface.
11.2 UI Designer
A UI designer is responsible for designing the visual elements of a product, such as color, typography, and imagery. This includes creating visually appealing and engaging user experiences.
11.3 UX Researcher
A UX researcher is responsible for conducting user research to understand user needs, behaviors, and motivations. This includes conducting user interviews, surveys, and usability testing.
11.4 Interaction Designer
An interaction designer is responsible for designing the interactive elements of a product, such as buttons, forms, and animations. This includes creating a seamless and intuitive user experience.
11.5 Information Architect
An information architect is responsible for organizing and structuring information within a product or website. This includes creating clear and consistent navigation and ensuring that users can easily find what they are looking for.
11.6 UX Strategist
A UX strategist is responsible for developing and implementing UX strategies that align with business goals and user needs. This includes conducting market research, analyzing user data, and developing design guidelines.
11.7 Career Growth
With experience, UX designers can advance to senior roles, such as UX lead, UX manager, or UX director. These roles involve leading teams of UX designers and overseeing the UX design process.
12. The Future of User Experience Design
The field of UX design is constantly evolving as technology advances and user expectations change. Several trends are shaping the future of UX design, including:
12.1 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is being used to personalize user experiences, automate tasks, and provide intelligent assistance. This includes using AI to predict user behavior, recommend content, and provide personalized support.
12.2 Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
VR and AR are creating new opportunities for immersive and interactive user experiences. This includes using VR and AR to create virtual environments, overlay digital information onto the real world, and provide new ways to interact with products and services.
12.3 Voice User Interface (VUI)
VUI is becoming increasingly popular as users interact with products and services using their voice. This includes using voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant to control devices, access information, and perform tasks.
12.4 Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT is connecting everyday objects to the internet, creating new opportunities for data collection and user interaction. This includes using IoT devices to track user behavior, provide personalized services, and automate tasks.
12.5 Ethical Design
Ethical design is becoming increasingly important as UX designers consider the ethical implications of their work. This includes designing products that are fair, transparent, and respectful of user privacy.
13. Common Misconceptions About UX Design
There are several common misconceptions about UX design that can lead to misunderstandings and missed opportunities. It’s important to dispel these misconceptions to ensure that UX design is understood and valued.
13.1 UX is Just About Making Things Look Pretty
While visual design is an important part of UX design, it’s not the only aspect. UX design is about understanding user needs and creating products that are easy to use, efficient, and satisfying.
13.2 UX is Only for Tech Companies
UX design is relevant to all industries, not just tech companies. Any organization that creates products or services can benefit from UX design.
13.3 UX is Too Expensive
Investing in UX design can save money in the long run by reducing development costs, improving user satisfaction, and increasing sales.
13.4 UX is Just Common Sense
While some aspects of UX design may seem like common sense, it’s based on research and best practices. Without a solid understanding of UX principles, it’s easy to make design decisions that are not user-friendly.
13.5 UX is a One-Time Project
UX design is an iterative process that requires ongoing monitoring and improvement. User needs and expectations change over time, so it’s important to continuously evaluate and refine the user experience.
14. Ethical Considerations in UX Design
Ethical considerations are becoming increasingly important in UX design. UX designers have a responsibility to create products that are fair, transparent, and respectful of user privacy.
14.1 Privacy
UX designers must protect user privacy by designing products that collect only the necessary data and that use data responsibly. This includes obtaining user consent, being transparent about data collection practices, and protecting data from unauthorized access.
14.2 Transparency
UX designers must be transparent about how products work and how decisions are made. This includes providing clear explanations of algorithms, disclosing potential biases, and giving users control over their data.
14.3 Fairness
UX designers must ensure that products are fair and do not discriminate against any group of users. This includes designing products that are accessible to all users, regardless of their abilities, and avoiding biases in algorithms and decision-making processes.
14.4 Well-being
UX designers must consider the well-being of users when designing products. This includes designing products that promote mental health, reduce stress, and encourage positive behaviors.
14.5 Informed Consent
UX designers must obtain informed consent from users before collecting or using their data. This includes providing clear explanations of what data is being collected, how it will be used, and who will have access to it.
15. How UX Design Impacts Business
UX design has a significant impact on business outcomes. By creating products that are easy to use, efficient, and satisfying, UX design can drive business growth and create a competitive advantage.
15.1 Increased Customer Satisfaction
UX design can increase customer satisfaction by creating products that meet user needs and provide a positive experience. Satisfied customers are more likely to be loyal and recommend the product to others.
15.2 Improved User Engagement and Retention
UX design can improve user engagement and retention by creating products that are engaging and easy to use. Engaged users are more likely to spend more time with the product and return to it frequently.
15.3 Reduced Development Costs
UX design can reduce development costs by identifying and addressing usability issues early in the design process. Fixing usability issues after the product is launched can be much more expensive and time-consuming.
15.4 Higher Conversion Rates
UX design can increase conversion rates by creating products that are easy to use and that guide users through the desired actions. This can lead to increased sales and revenue.
15.5 Stronger Brand Loyalty
UX design can build stronger brand loyalty by creating products that are consistent with the brand’s values and that provide a positive experience. Loyal customers are more likely to purchase additional products and services from the brand.
16. Examples of Great UX Design
There are many examples of great UX design that demonstrate the power of user-centered design. These examples can inspire UX designers and provide valuable insights into how to create positive user experiences.
16.1 Apple
Apple is known for its focus on UX design. Apple products are easy to use, visually appealing, and provide a seamless user experience.
16.2 Google
Google is another company that prioritizes UX design. Google products are designed to be simple, intuitive, and efficient.
16.3 Amazon
Amazon’s website and mobile app are designed to be easy to use and to guide users through the purchasing process. This has contributed to Amazon’s success as an e-commerce leader.
16.4 Airbnb
Airbnb’s website and mobile app are designed to be visually appealing and to provide a seamless user experience. This has helped Airbnb become a popular platform for booking accommodations.
16.5 Netflix
Netflix’s website and mobile app are designed to be easy to use and to recommend content that users will enjoy. This has helped Netflix become a leading streaming service.
17. UX Design Resources and Learning Platforms
There are many resources and learning platforms available to help individuals develop their UX design skills. These resources can provide valuable knowledge, tools, and guidance for aspiring and experienced UX designers.
17.1 Interaction Design Foundation
The Interaction Design Foundation (IxDF) is the world’s largest online design school. It offers a wide range of courses, articles, and resources on UX design. Don Norman, the man who coined the term “User Experience,” has praised the IxDF as “a goldmine of information on interaction design.”
17.2 Coursera
Coursera is a popular online learning platform that offers courses, specializations, and degrees on UX design. Coursera partners with universities and companies to provide high-quality education.
17.3 Udemy
Udemy is an online learning platform that offers a wide range of courses on UX design. Udemy courses are created by independent instructors and can provide valuable knowledge and skills.
17.4 Nielsen Norman Group
The Nielsen Norman Group (NNG) is a leading UX consulting firm that offers training courses and resources on UX design. NNG courses are taught by experienced UX professionals and provide valuable insights into best practices.
17.5 General Assembly
General Assembly is a career accelerator that offers immersive courses on UX design. General Assembly courses are designed to provide students with the skills and knowledge they need to launch a career in UX design.
18. Frequently Asked Questions About UX Design
Here are some frequently asked questions about UX design:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is user experience design? | User experience (UX) design is the process of creating products that provide meaningful and relevant experiences to users. This involves designing the entire process of acquiring and integrating a product, including aspects of branding, design, usability, and function. |
| What are the key elements of UX design? | The key elements of UX design include strategy, user research, usability, information architecture, interaction design, and visual design. |
| What skills do UX designers need? | UX designers need a diverse set of skills, including user research skills, wireframing and prototyping skills, visual design skills, interaction design skills, communication skills, empathy, and problem-solving skills. |
| What tools and technologies do UX designers use? | UX designers use a variety of tools and technologies, including wireframing tools, prototyping tools, visual design tools, user research tools, and collaboration tools. |
| How is UX design measured? | UX design is measured by KPIs such as user satisfaction, task completion rate, time on task, conversion rate, error rate, abandonment rate, and Net Promoter Score (NPS). |
| What are some career paths in UX design? | Career paths in UX design include UX designer, UI designer, UX researcher, interaction designer, information architect, and UX strategist. |
| What is the future of UX design? | The future of UX design |