Zulu Time, often represented by the letter ‘Z’ in military and navigational contexts, serves as a universal timekeeping standard. Its primary purpose is to eliminate the confusion that arises when coordinating activities across different time zones. You might also hear Zulu Time referred to as Universal Coordinated Time (UTC), and sometimes, though less accurately, as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). Understanding Zulu Time is crucial in fields where precise, unambiguous time communication is paramount.
Zulu Time: Unpacking UTC and GMT
At its core, Zulu Time is essentially synonymous with Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. While the term GMT, or Greenwich Mean Time, is sometimes used interchangeably with Zulu Time, it’s important to understand the nuances. GMT historically referred to the mean solar time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London. However, modern timekeeping has shifted to atomic clocks, making UTC the more precise and internationally recognized standard. The U.S. military and other official bodies often discourage using GMT in place of Zulu Time or UTC to avoid potential ambiguity.
The foundation of Zulu Time and UTC lies at the prime meridian, an imaginary line of longitude designated as 0 degrees 0 minutes. This meridian, passing through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England, acts as the global reference point for measuring time zones. Zulu Time, therefore, is the time at this prime meridian.
How Zulu Time is Measured and Used
Zulu Time adheres to a 24-hour format and is measured in hours, minutes, and seconds, following the Gregorian calendar. Unlike standard time zones that might reset at 12 noon or 12 midnight according to local conventions, Zulu Time starts its day at midnight UTC. This consistent 24-hour cycle and its alignment with the prime meridian are key to its utility in global coordination.
In practice, when Zulu Time is noted, it is often followed by the letter ‘Z’. For example, 0900Z indicates 9:00 AM Zulu Time, which corresponds to 09:00 UTC. The term “Zulu” itself originates from the NATO phonetic alphabet, where ‘Zulu’ represents the letter ‘Z’. This phonetic articulation is used in radio transmissions to ensure clarity, particularly in noisy or critical communication environments.
The Importance of Zulu Time: Why Use It?
The adoption of Zulu Time is driven by the critical need for clarity and precision in timekeeping, especially in fields like military operations, aviation, and shipping. Imagine coordinating a multinational military exercise or managing air traffic across continents – the potential for errors due to time zone confusion is significant. Zulu Time provides a single, universally understood time reference, eliminating these risks.
Pilots, for instance, commonly use Zulu Time in flight plans and communication. Instead of converting between numerous local time zones during a long flight, they operate on Zulu Time. A pilot departing Los Angeles might note their departure as “1600 Zulu” and their arrival in London as “2300 Zulu,” regardless of the local times at departure and arrival. This practice has become widespread in aviation, streamlining operations and enhancing safety. The shipping industry similarly benefits from Zulu Time, ensuring synchronized schedules and avoiding misunderstandings in international maritime operations.
Zulu Time vs. Local Time Zones: Understanding the Offsets
Time zones around the world are defined by their offset from UTC, or Zulu Time. Zulu Time itself is UTC+0000, meaning it has zero hours offset from UTC. Other time zones are expressed as either ahead of or behind UTC. For example:
- Eastern Standard Time (EST): UTC-0500. This means EST is 5 hours behind Zulu Time.
- Central Standard Time (CST): UTC-0600. CST is 6 hours behind Zulu Time.
- Mountain Standard Time (MST): UTC-0700. MST is 7 hours behind Zulu Time.
- Pacific Standard Time (PST): UTC-0800. PST is 8 hours behind Zulu Time.
It’s crucial to remember that these offsets can change in regions that observe Daylight Saving Time (DST). During DST, these time zones shift forward by an hour, altering their UTC offset accordingly.
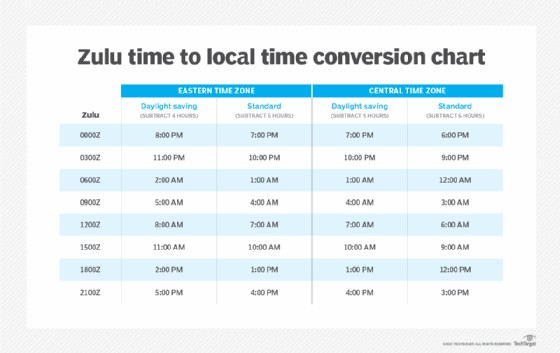 zulu time to time zones conversion chart
zulu time to time zones conversion chart
Zulu Time conversion chart illustrating examples comparing Zulu time to Eastern Time (EST) and Central Time (CST) during both Standard Time and Daylight Saving Time periods.
In conclusion, Zulu Time, or UTC, is an indispensable tool for global communication and coordination, particularly in sectors requiring precise time synchronization. By providing a universal time standard referenced to the prime meridian, Zulu Time eliminates the ambiguities of local time zones, fostering efficiency and preventing potentially critical errors in international operations.
