The racial composition of the United States is constantly evolving. A recent study by the Pew Research Center sheds light on public perception regarding the declining percentage of Americans who identify as White. This article delves into the data, exploring the current demographics and the factors contributing to these shifts.
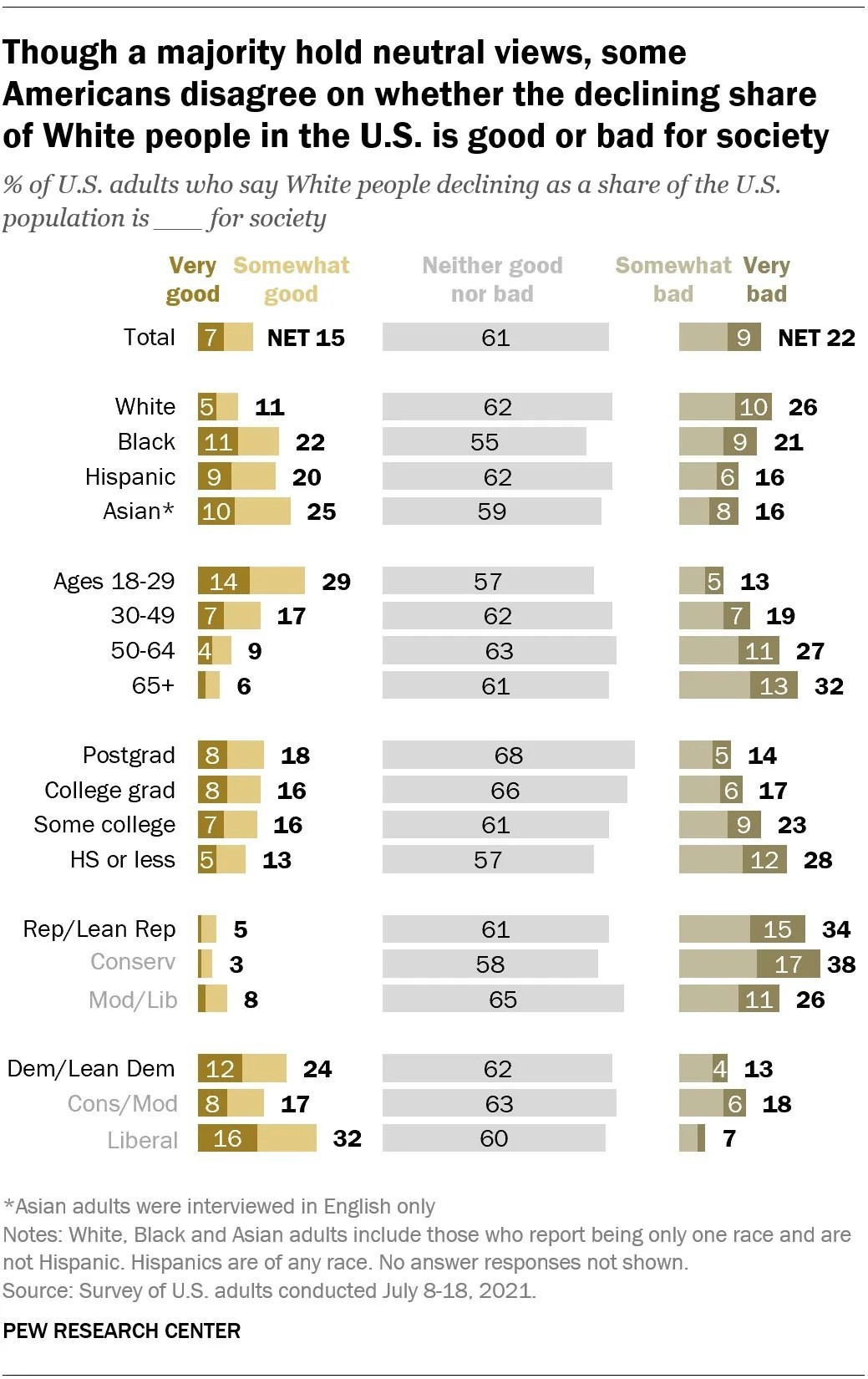
According to the survey, a majority of U.S. adults (61%) express a neutral view, stating that the decreasing proportion of White Americans is neither beneficial nor detrimental to society. However, opinions diverge, with 22% viewing it negatively (9% “very bad”) and 15% considering it a positive development (7% “very good”). This reveals a complex and nuanced perspective on demographic change within the American populace. These figures highlight the ongoing transformation of the American racial landscape and the varying interpretations of its implications.
Public perception on the decreasing White population in the U.S., displaying neutral, negative and positive views.
Demographic Shifts: A Closer Look at the Numbers
The 2020 Census marked a significant milestone, revealing the first-ever decline in the number of Americans identifying as non-Hispanic White alone. This population segment decreased by 3%, representing approximately 5.1 million individuals, between 2010 and 2020. This decline was not isolated; it was observed across 35 states, signaling a widespread demographic trend. These shifts prompt a deeper investigation into the underlying causes and potential long-term consequences.
Despite this decline, the non-Hispanic White population remains the largest racial or ethnic group in the U.S., totaling nearly 192 million in 2020. However, its share of the overall population is shrinking. Census data reveals a drop from 64% in 2010 to 58% in 2020. This continuous decrease can be traced back to the 1980s, indicating a long-term pattern of demographic change.
Historical trend of the decreasing White population share in the United States.
Factors Contributing to the Changing Demographics
Several factors contribute to this evolving demographic landscape. One key aspect is the aging of the White population, which leads to a lower birth rate and a higher mortality rate compared to other racial and ethnic groups. Furthermore, immigration patterns play a crucial role. Immigration accounts for a significantly smaller proportion of the White population growth compared to groups like Asians and Hispanics. These demographic trends are projected to continue, leading to further shifts in the racial composition of the United States.
The Future: Projecting Demographic Trends
Looking ahead, projections from the Census Bureau suggest that the non-Hispanic White population identifying with a single race could fall below 50% by 2045. It’s important to note that such projections are inherently speculative, influenced by various factors including evolving racial identification, changing demographic trends, and the growing multiracial population. These projections highlight the dynamic nature of American demographics and the challenges in accurately predicting future compositions.
Numerical decline in the White population between 2010 and 2020, a historic demographic shift.
Broader Definitions of White Identity
It’s also crucial to consider the broader definition of the White population, encompassing individuals who identify as White in combination with another race or as Hispanic. This group experienced a modest growth of 2% between 2010 and 2020, increasing from 231 million to 235.4 million. However, even with this growth, their share of the total U.S. population decreased from 75% to 71%. The increase within this group is primarily attributed to the rise in individuals identifying as White and another race, reflecting increasing interracial marriages and multiracial births. This highlights the complexities of racial identity and the evolving nature of how individuals choose to identify themselves.
The evolving demographics of the United States, particularly the declining share of the White population, are multifaceted and influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these trends is crucial for navigating the future and fostering a more inclusive society. While the percentage of Americans identifying solely as White is decreasing, the broader picture of racial identity in the U.S. is becoming increasingly diverse and complex, with implications for politics, culture, and society as a whole.