What Percentage Of America Is White? This is a complex question with evolving answers. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to providing accessible and comprehensive information about US demographics. Explore racial demographics, population shifts, and ethnic diversity within the United States, and understand the intricacies of racial identity and demographic projections.
1. Understanding the White Population in America
The question “What percentage of America is White?” requires careful consideration of how race and ethnicity are defined and measured. The U.S. Census Bureau, the primary source for demographic data, asks about race and Hispanic origin separately. This means individuals can identify as White alone, White in combination with other races, or as Hispanic White.
- White Alone, Not Hispanic: This category refers to individuals who identify as White and do not identify as Hispanic or Latino.
- White Alone or in Combination: This category includes individuals who identify as White, either as their sole race or in combination with one or more other races.
- Hispanic or Latino: This is an ethnicity, not a race. Individuals who identify as Hispanic or Latino can be of any race, including White.
2. Current Statistics: What the Data Shows
According to the latest data from the U.S. Census Bureau, the racial and ethnic composition of the United States is as follows:
- White Alone, Not Hispanic: As of 2020, this group constitutes approximately 57.8% of the total U.S. population. This represents a decline from previous decades.
- White Alone or in Combination: This group, which includes those who identify as White in combination with other races, accounts for approximately 71% of the population.
- Hispanic or Latino (of any race): This group makes up approximately 18.7% of the population.
- Black or African American Alone: This group comprises about 12.1% of the population.
- Asian Alone: This group represents roughly 6% of the population.
- American Indian and Alaska Native Alone: This group accounts for about 0.7% of the population.
- Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander Alone: This group represents less than 0.2% of the population.
- Two or More Races: Individuals identifying with two or more races make up approximately 3% of the population.
 A bar chart showing the racial and ethnic composition of the US population, with White Alone, Not Hispanic being the largest group.
A bar chart showing the racial and ethnic composition of the US population, with White Alone, Not Hispanic being the largest group.
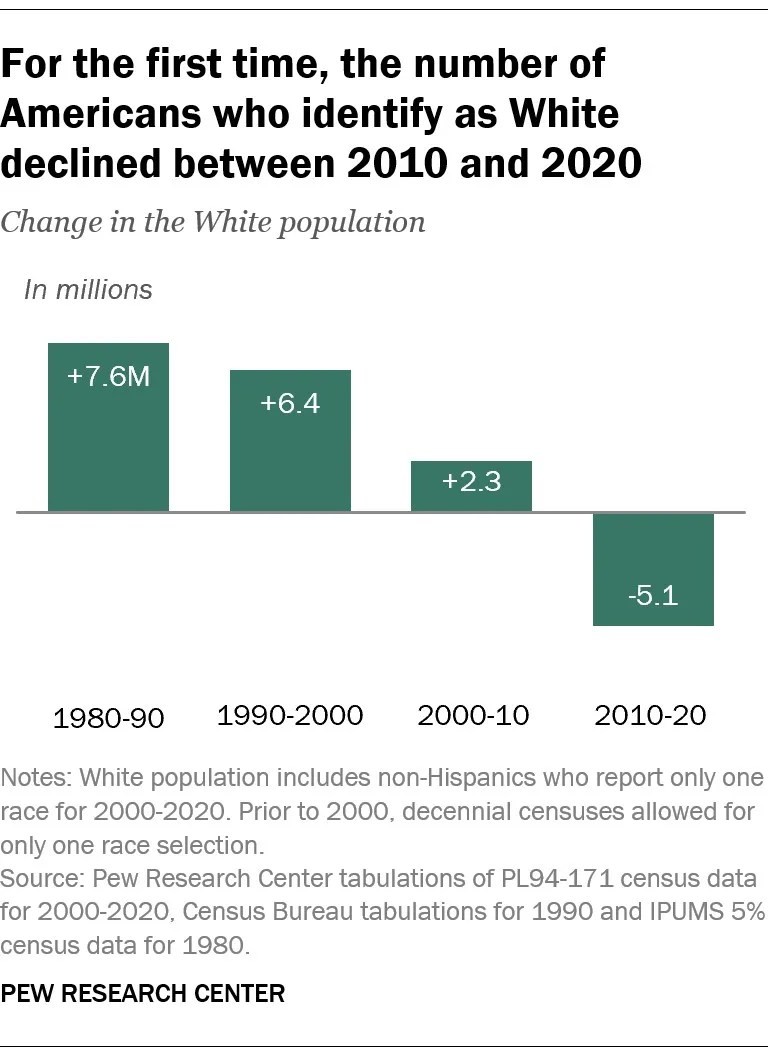
3. Historical Trends: Changes Over Time
The percentage of the U.S. population identifying as White has been declining for several decades. This trend is due to a combination of factors, including:
- Higher birth rates among other racial and ethnic groups: Hispanic and Asian populations, in particular, have experienced significant growth due to higher birth rates.
- Increased immigration from non-European countries: Immigration patterns have shifted, with a larger proportion of immigrants coming from Latin America, Asia, and Africa.
- Rising rates of intermarriage: Intermarriage, or marriage between individuals of different races or ethnicities, has become more common, leading to a growing number of multiracial individuals.
- Changes in racial identification: How people view and report their racial identity can change over time, influenced by social and political factors.
Here’s a look at how the White population share has changed over the years:
- 1980: Approximately 80% of the U.S. population identified as White.
- 1990: The White population share decreased to 76%.
- 2000: The trend continued, with the White population representing around 69% of the total.
- 2010: The White population share dropped to 64%.
- 2020: The White population share is approximately 57.8% (White Alone, Not Hispanic).
4. Factors Influencing Demographic Shifts
Several factors contribute to the ongoing demographic shifts in the United States. Understanding these factors provides context for interpreting the changing racial and ethnic composition of the country.
- Fertility Rates: Different racial and ethnic groups have varying fertility rates. Generally, Hispanic and Black women have higher fertility rates compared to White women. These differences contribute to the growth of these populations relative to the White population.
- Immigration: Immigration is a significant driver of population growth, particularly for Hispanic and Asian communities. The number of immigrants from Latin America and Asia has increased substantially over the past few decades, contributing to the diversification of the U.S. population.
- Intermarriage: Intermarriage rates have been on the rise, leading to an increasing number of children with multiracial backgrounds. These individuals may identify with multiple races, contributing to the growth of the “Two or More Races” category in census data.
- Aging Population: The White population tends to be older than other racial and ethnic groups. As the White population ages, mortality rates increase, further contributing to the decline in the White population share.
- Self-Identification: The way individuals identify their race and ethnicity can change over time due to personal, social, and political factors. These changes in self-identification can impact the reported racial and ethnic composition of the U.S. population.
5. Regional Variations in White Population
The percentage of White residents varies considerably across different states and regions of the United States. States in the Northeast and Midwest tend to have a higher proportion of White residents compared to states in the South and West.
- States with High White Population Shares:
- Maine
- Vermont
- New Hampshire
- West Virginia
- Wyoming
- States with Lower White Population Shares:
- Hawaii
- California
- New Mexico
- Texas
- Nevada
These regional variations reflect historical settlement patterns, economic opportunities, and migration trends.
6. The Impact of the Declining White Population Share
The declining share of White people in the United States has sparked various debates and discussions about its potential impact on society. Views on this demographic shift vary widely. According to a Pew Research Center survey, a majority of Americans (61%) believe that the declining proportion of White people is neither good nor bad for society. However, some individuals and groups hold different opinions.
- Potential Benefits: Some argue that increasing diversity can lead to greater innovation, cultural enrichment, and a more inclusive society.
- Potential Concerns: Others express concerns about the potential for social and political tensions, as well as the impact on traditional cultural values.
7. Future Projections: What to Expect
Demographic projections from the U.S. Census Bureau suggest that the trend of a declining White population share will continue in the coming decades.
- “Majority-Minority” Nation: The Census Bureau projects that the United States will become a “majority-minority” nation by around 2045. This means that the combined population of racial and ethnic minorities will be larger than the White population alone.
- Continued Growth of Hispanic and Asian Populations: Hispanic and Asian populations are expected to continue growing at a faster rate than the White population.
- Increasing Multiracial Population: The number of individuals identifying as multiracial is also expected to increase significantly.
8. Common Misconceptions About Race and Ethnicity
It’s important to address some common misconceptions about race and ethnicity to promote a better understanding of demographic trends.
- Race is a biological concept: Race is a social construct, not a biological one. While there are genetic variations among individuals, these variations do not align neatly with racial categories.
- Hispanic is a race: Hispanic is an ethnicity, not a race. People of Hispanic origin can be of any race.
- Diversity means anti-White: Increasing diversity does not imply any animosity towards White people. It simply reflects the growing presence and contributions of people from various racial and ethnic backgrounds.
9. The Significance of Understanding Demographics
Understanding demographics is crucial for informed decision-making in various fields, including:
- Government: Demographic data is used to allocate resources, draw electoral districts, and develop policies that address the needs of different populations.
- Business: Businesses use demographic information to identify target markets, tailor products and services, and make strategic decisions about location and expansion.
- Education: Educators use demographic data to understand the needs of their student populations and develop culturally responsive teaching strategies.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers use demographic information to identify health disparities and develop targeted interventions to improve health outcomes.
- Community Planning: Community planners use demographic data to assess the needs of their communities and develop strategies for housing, transportation, and other services.
10. Exploring Racial Identity and Diversity
Beyond the numbers, understanding the experiences, challenges, and contributions of different racial and ethnic groups is essential. This requires:
- Acknowledging historical injustices: Recognizing and addressing the legacy of slavery, discrimination, and systemic racism.
- Promoting inclusivity: Creating environments where people from all backgrounds feel valued, respected, and empowered.
- Celebrating cultural diversity: Recognizing and appreciating the richness and diversity of cultures within the United States.
11. Detailed Analysis of White Demographic Trends
To gain a deeper understanding, let’s analyze specific aspects of the White demographic trends in the U.S.
- Age Distribution: The White population tends to be older compared to other racial and ethnic groups. This has implications for workforce participation, healthcare needs, and social security.
- Educational Attainment: White individuals generally have higher levels of educational attainment compared to some other groups. However, disparities exist within the White population based on socioeconomic status and geographic location.
- Income and Poverty: While White individuals have a higher median income compared to some other groups, poverty rates vary within the White population. Factors such as education, occupation, and family structure influence income and poverty levels.
- Geographic Distribution: White populations are concentrated in certain regions of the U.S., such as the Northeast and Midwest. However, there are also significant White populations in other parts of the country.
- Subgroups: The White population includes diverse subgroups with different cultural backgrounds and experiences. These subgroups include people of European, Middle Eastern, and North African descent.
12. Factors Influencing White Population Change
Several factors influence the changes in the White population size and share in the U.S.
- Birth Rates: The birth rate among White women is generally lower than that of Hispanic and Black women. This contributes to the slower growth of the White population compared to other groups.
- Mortality Rates: As the White population ages, mortality rates increase, leading to a higher number of deaths compared to births.
- Immigration: Immigration patterns have shifted, with fewer immigrants coming from Europe compared to Latin America and Asia. This has a significant impact on the racial and ethnic composition of the U.S. population.
- Intermarriage: Increasing rates of intermarriage have led to a growing number of multiracial individuals who may not identify exclusively as White.
13. The Role of the Census Bureau
The U.S. Census Bureau plays a crucial role in collecting and disseminating demographic data. The Census Bureau conducts the decennial census every 10 years, providing a comprehensive snapshot of the U.S. population.
- Data Collection Methods: The Census Bureau uses various methods to collect data, including mail surveys, online questionnaires, and in-person interviews.
- Data Analysis and Dissemination: The Census Bureau analyzes the data and publishes reports on various demographic topics, including race, ethnicity, age, sex, and geographic distribution.
- Data Accuracy and Limitations: While the Census Bureau strives for accuracy, there are limitations to the data. These limitations include undercounts of certain populations, errors in self-reporting, and challenges in classifying individuals who identify with multiple races.
14. The Future of Racial and Ethnic Identity in America
The concept of racial and ethnic identity is evolving in the United States. As the population becomes more diverse and intermarriage rates continue to rise, the traditional categories of race and ethnicity may become less relevant.
- Fluid Identities: Some individuals may choose to identify with multiple races or ethnicities, or their identity may change over time.
- Social and Political Implications: The changing nature of racial and ethnic identity has implications for social and political issues, such as affirmative action, voting rights, and representation in government.
- The Importance of Understanding Diversity: It is essential to understand and appreciate the diversity of experiences and perspectives within the U.S. population. This requires challenging stereotypes, promoting inclusivity, and fostering dialogue across different groups.
15. Addressing Concerns and Misunderstandings
It is crucial to address concerns and misunderstandings about demographic change and its potential impact on society.
- Fear of Displacement: Some individuals may fear that the declining White population share will lead to the displacement of White people or the erosion of traditional cultural values.
- Misconceptions about Diversity: Some may believe that diversity is inherently divisive or that it will lead to social and political instability.
- The Importance of Dialogue: It is essential to engage in open and honest dialogue about these concerns and misunderstandings, based on facts and evidence.
16. The Importance of Inclusive Policies
Inclusive policies are essential for creating a society where everyone has the opportunity to thrive. These policies should address the needs of all populations, regardless of race, ethnicity, or other factors.
- Education: Ensuring equal access to quality education for all children, regardless of their background.
- Employment: Promoting fair hiring practices and equal opportunities for advancement in the workplace.
- Housing: Addressing housing discrimination and promoting affordable housing options in diverse communities.
- Healthcare: Ensuring access to affordable healthcare for all individuals, regardless of their race or ethnicity.
- Criminal Justice: Reforming the criminal justice system to address racial bias and ensure fair treatment for all.
17. The Role of Education in Promoting Understanding
Education plays a vital role in promoting understanding and appreciation of diversity. Schools and universities should incorporate curricula that teach about the history, culture, and experiences of different racial and ethnic groups.
- Multicultural Education: Providing students with opportunities to learn about different cultures and perspectives.
- Critical Thinking Skills: Encouraging students to think critically about issues of race, ethnicity, and social justice.
- Dialogue and Discussion: Creating safe spaces for students to engage in dialogue and discussion about challenging topics.
18. The Impact of Media Representation
Media representation can have a significant impact on how people perceive different racial and ethnic groups. It is essential for media outlets to portray diverse communities accurately and respectfully.
- Avoiding Stereotypes: Avoiding the use of stereotypes and portraying individuals as complex and multifaceted.
- Amplifying Diverse Voices: Providing opportunities for people from diverse backgrounds to share their stories and perspectives.
- Promoting Positive Images: Highlighting the achievements and contributions of people from diverse racial and ethnic groups.
19. Celebrating Cultural Diversity
Celebrating cultural diversity can enrich communities and promote a sense of belonging for all residents.
- Cultural Festivals: Organizing cultural festivals and events that showcase the traditions, food, music, and art of different communities.
- Community Partnerships: Building partnerships between different cultural groups to promote understanding and collaboration.
- Cross-Cultural Dialogue: Encouraging cross-cultural dialogue and exchange to foster empathy and respect.
20. Moving Forward: Creating a More Inclusive Society
Creating a more inclusive society requires ongoing effort and commitment from individuals, organizations, and government.
- Challenging Bias and Discrimination: Challenging bias and discrimination in all its forms, whether it is based on race, ethnicity, religion, gender, sexual orientation, or other factors.
- Promoting Equity: Working to create a society where everyone has the opportunity to reach their full potential, regardless of their background.
- Building Bridges: Building bridges between different communities to foster understanding, empathy, and collaboration.
FAQ: Understanding American Demographics
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the current percentage of the White population in the U.S.? | Approximately 57.8% of the U.S. population identifies as White Alone, Not Hispanic. |
| Why is the White population share declining? | Factors include higher birth rates among other groups, increased immigration from non-European countries, and rising rates of intermarriage. |
| What does “White Alone, Not Hispanic” mean? | This category refers to individuals who identify as White and do not identify as Hispanic or Latino. |
| What is the difference between race and ethnicity? | Race is a social construct, while ethnicity refers to shared cultural traits, language, and ancestry. Hispanic is an ethnicity, not a race. |
| What are the future projections for racial demographics in the U.S.? | The U.S. is projected to become a “majority-minority” nation by around 2045, with the combined population of racial and ethnic minorities exceeding the White population. |
| How does the Census Bureau collect racial and ethnic data? | The Census Bureau uses mail surveys, online questionnaires, and in-person interviews to collect data on race and ethnicity. |
| What are some common misconceptions about race and ethnicity? | Some misconceptions include the belief that race is a biological concept, that Hispanic is a race, and that diversity means anti-White. |
| Why is it important to understand demographics? | Understanding demographics is crucial for informed decision-making in government, business, education, healthcare, and community planning. |
| How can we promote inclusivity and understanding of diversity? | By acknowledging historical injustices, promoting inclusive policies, celebrating cultural diversity, and challenging bias and discrimination. |
| What are some regional variations in the White population? | States in the Northeast and Midwest tend to have a higher proportion of White residents compared to states in the South and West. |
Do you have more questions about demographics, diversity, or any other topic? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we are here to help. Our platform offers free access to expert insights and answers to all your questions. Don’t hesitate, visit WHAT.EDU.VN today to ask your question and join a community dedicated to knowledge and understanding.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: what.edu.vn