What Percentage Of U.s. Population Is Black is a frequently asked question, and WHAT.EDU.VN is here to provide the answer and more. Understanding the demographics of the United States involves examining various racial and ethnic groups, including the Black or African American population. This article explores the Black demographic within the U.S., offering insights into population size, growth, distribution, and key characteristics. Discover reliable insights and demographics data on the African American community, and for all your questions, remember WHAT.EDU.VN provides swift, cost-free answers.
1. Understanding the Black Population in the U.S.
The Black population in the United States represents a significant portion of the country’s demographic landscape. It’s crucial to understand the nuances within this population, including its various subgroups and their unique characteristics. This detailed exploration provides valuable insights into the current state and historical trends of the Black community in America.
2. The Size and Growth of the Black Population
In 2023, approximately 48.3 million people in the U.S. self-identified as Black, constituting 14.4% of the nation’s population. This figure represents a substantial increase from 36.2 million in 2000, marking a 33% growth over roughly two decades. This growth underscores the increasing presence and influence of the Black population within the United States. The increase reflects not only births but also changing patterns of self-identification and immigration trends.
3. Defining the Black Population: Key Terminology
To accurately discuss the Black population, it’s important to clarify the terminology used. The “total Black population” includes individuals who identify as Black, either alone or in combination with other races, as well as those of Hispanic origin who also identify as Black. Subgroups within this population include single-race non-Hispanic Black, multiracial non-Hispanic Black, and Black Hispanic. These distinctions are essential for understanding the diversity within the Black community.
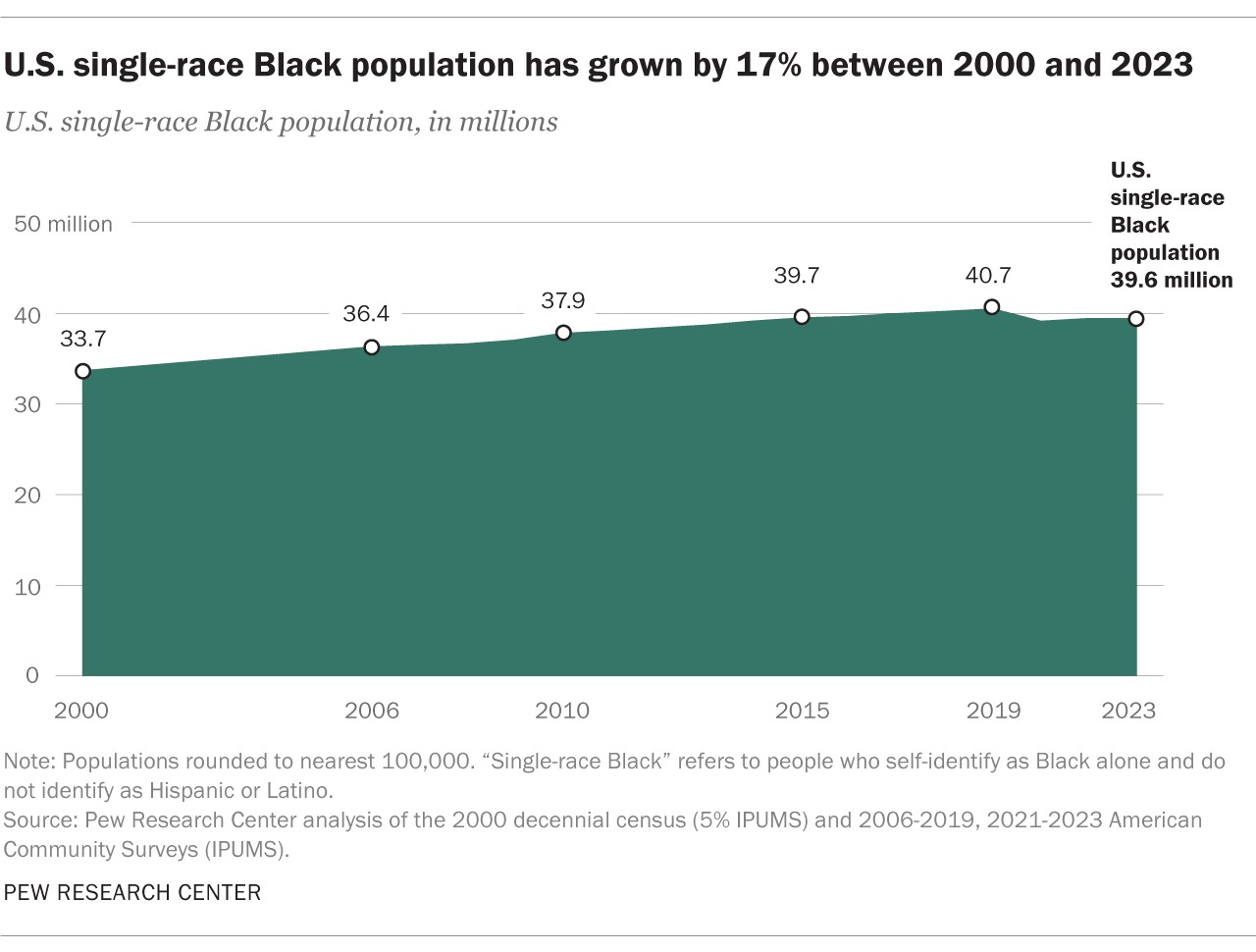
4. Single-Race Non-Hispanic Black Population
The single-race, non-Hispanic Black population is a significant subgroup, comprising 39.6 million people in 2023, which is 82% of the total Black population. This group has grown by 17% since 2000, when it numbered 33.7 million. Single-race Black individuals identify solely as Black and do not identify as Hispanic or Latino. This demographic forms a core part of the African American experience in the U.S.
5. The Multiracial Non-Hispanic Black Population
The multiracial non-Hispanic Black population is one of the fastest-growing segments within the Black community. In 2023, this group numbered 5.6 million, accounting for 12% of the total Black population. Since 2000, it has experienced a remarkable 269% increase, growing from 1.5 million. This growth reflects changing attitudes towards racial identity and the increasing prevalence of multiracial individuals in the U.S.
6. The Black Hispanic Population
The Black Hispanic population includes individuals who identify as both Black and Hispanic or Latino. In 2023, this group numbered 3.0 million, representing 6% of the total Black population. Since 2000, it has grown by 210%, increasing from 980,000. It is important to note that this group is not identical to the Afro-Latino population, as not all Black Hispanics identify as Afro-Latino, and vice versa.
7. Factors Influencing Racial Identification
Several factors influence how individuals identify their race and ethnicity. Changes in census methodologies, societal perceptions of race, and personal circumstances all play a role. Since 2000, the U.S. Census Bureau has allowed respondents to identify with more than one race, contributing to the growth of the multiracial population. Moreover, younger generations are more likely to identify with multiple racial or ethnic identities.
8. Age Demographics of the Black Population
The Black population in the U.S. is relatively young. In 2023, the median age of Black individuals was 32.6 years, approximately six years younger than the median age of the U.S. population overall (38.2 years). About 30% of the Black population was under the age of 20, while 12% were 65 or older. This age distribution has implications for various social and economic factors, including education, workforce participation, and healthcare needs.
9. Age Distribution Among Subgroups
The age distribution varies among the different subgroups within the Black population. The multiracial non-Hispanic Black population is the youngest, with a median age of 19.5 years. In contrast, the single-race non-Hispanic Black population has a median age of 35.4 years. The Black Hispanic population has a median age of 21.7 years. These differences in age structure highlight the diverse demographic profiles within the Black community.
10. Fertility Rates in the Black Population
Fertility rates also vary within the Black population. In 2023, the general fertility rate among Black females aged 15 to 44 was 5.8%, meaning that 5.8% of females in this age group had a birth in the previous 12 months. This rate is similar among single-race non-Hispanic Black females (5.9%) and Black Hispanic females (5.9%), while it is slightly lower among multiracial non-Hispanic Black females (4.9%).
11. Language Use Within the Black Community
Language use within the Black population is predominantly English. As of 2023, 96% of the Black population either speaks only English (88%) or speaks another language at home and also speaks English very well (8%). Other languages spoken at home include Spanish (4%), French or Haitian Creole (3%), Niger-Congo languages (1%), and Amharic and other Ethiopian languages (1%). Language diversity reflects the varied origins and cultural backgrounds of Black individuals in the U.S.
12. Linguistic Diversity Among Subgroups
Linguistic diversity varies among the different subgroups within the Black population. The vast majority of single-race non-Hispanic Black individuals (97%) speak only English or speak English very well. Among Black Hispanics, a smaller majority (82%) speak English proficiently, with a significant portion (46%) also speaking Spanish. These variations underscore the unique linguistic profiles of each subgroup.
13. Geographic Distribution of the Black Population
The geographic distribution of the Black population in the U.S. is concentrated in the South. In 2023, 56% of Black individuals resided in the South, followed by 17% in the Midwest, 17% in the Northeast, and 10% in the West. This regional concentration reflects historical migration patterns and economic opportunities.
14. State-Level Distribution
At the state level, Texas has the largest Black population, with approximately 4.3 million residents. Florida ranks second with 4.0 million, and Georgia comes in third with 3.7 million. These states represent key centers of Black culture and influence in the United States.
15. Metropolitan Areas with Significant Black Populations
Metropolitan areas with substantial Black populations include New York City (3.8 million), Atlanta (2.3 million), and Washington, D.C. (1.8 million). These urban centers offer diverse economic, cultural, and social opportunities for Black residents.
16. Geographic Distribution by Subgroup
The geographic distribution varies among the different subgroups within the Black population. The South has the highest concentration of single-race non-Hispanic Black residents (59%), while the multiracial Black population is more dispersed across the South (42%), Midwest (22%), West (19%), and Northeast (17%). Black Hispanics are largely concentrated in the Northeast and South (71% combined).
17. Household Income Among Black Households
In 2023, the median household income for households headed by a Black person was $54,000. About 37% of Black households earned $75,000 or more, including 25% that made $100,000 or more. While there has been progress in income levels, disparities persist when compared to the overall U.S. population.
18. Income Variations Among Subgroups
Income levels vary among the different subgroups within the Black population. The median household income for single-race non-Hispanic Black households was $52,800, while it was higher for multiracial non-Hispanic Black households ($65,800) and Black Hispanic households ($60,000). These differences reflect variations in education, occupation, and other socioeconomic factors.
19. Household Types in the Black Community
Household types also differ within the Black population. About 39% of Black individuals live in households headed by married couples, while 30% live in female-headed households, and 5% live in male-headed households. Additionally, 17% live in nonfamily households. These variations reflect diverse family structures and living arrangements within the Black community.
20. Household Structures Among Subgroups
Household structures vary among the different subgroups within the Black population. A slightly higher percentage of multiracial non-Hispanic Black individuals (45%) live in households headed by married couples compared to single-race non-Hispanic Black individuals (38%) and Black Hispanics (43%). These differences highlight the diverse family dynamics within the Black community.
21. Educational Attainment in the Black Population
Educational attainment is an important indicator of socioeconomic progress. About 27% of Black adults aged 25 and older have a bachelor’s degree or higher: 16% have a bachelor’s degree, and 11% have an advanced degree. Additionally, 32% have completed some college without obtaining a bachelor’s degree, and 30% have, at most, graduated from high school or earned an equivalent.
22. Educational Achievements Among Subgroups
Educational achievements vary among the different subgroups within the Black population. A higher percentage of multiracial non-Hispanic Black adults (35%) have a bachelor’s degree or higher compared to single-race non-Hispanic Black adults (26%). Black Hispanic adults have a similar rate of bachelor’s degree attainment (28%). These variations highlight the diverse educational pathways and outcomes within the Black community.
23. The Foreign-Born Black Population
In 2023, over 5 million Black Americans were foreign-born, accounting for approximately 11% of the U.S. Black population. This is an increase from 2000, when 2.4 million people, or 7%, among the Black population were foreign-born. The foreign-born Black population adds to the diversity and richness of the Black community in the United States.
24. Origin Countries of Black Immigrants
Black immigrants come from various countries around the world, including Jamaica, Haiti, Nigeria, Ethiopia, and Somalia. Each group brings unique cultural traditions, languages, and experiences to the United States. Understanding the diversity of origin countries is crucial for appreciating the complexity of the Black immigrant experience.
25. Socioeconomic Integration of Black Immigrants
Black immigrants contribute significantly to the U.S. economy and society. Many have achieved high levels of education and professional success. However, they also face challenges related to discrimination, language barriers, and navigating the U.S. immigration system. Understanding the socioeconomic integration of Black immigrants requires attention to both their achievements and the obstacles they encounter.
26. Generational Differences in the Black Population
Generational differences shape the experiences and perspectives of Black individuals in the U.S. Older generations may have lived through the Civil Rights Movement and experienced overt forms of discrimination, while younger generations have grown up in a more diverse and inclusive society. Understanding these generational differences provides insights into evolving attitudes towards race, identity, and social justice.
27. The Influence of Black Culture on American Society
Black culture has had a profound influence on American society, shaping music, art, literature, dance, fashion, and language. From jazz and blues to hip-hop and R&B, Black musicians have revolutionized the music industry. Black artists and writers have produced groundbreaking works that challenge social norms and celebrate Black identity. Recognizing the cultural contributions of Black individuals is essential for understanding the richness and diversity of American culture.
28. Ongoing Challenges and Disparities
Despite progress in many areas, Black individuals in the U.S. continue to face challenges and disparities in education, employment, housing, healthcare, and criminal justice. Addressing these disparities requires systemic change and a commitment to racial equity. Understanding the ongoing challenges is crucial for developing effective policies and interventions.
29. Advocacy and Social Justice Movements
Advocacy and social justice movements have played a crucial role in advancing the rights and opportunities of Black individuals in the U.S. From the Civil Rights Movement to Black Lives Matter, activists and community leaders have fought for equality and justice. These movements have raised awareness of systemic racism and inspired action to address it. Supporting advocacy and social justice efforts is essential for creating a more equitable society.
30. The Future of the Black Population in the U.S.
The Black population in the U.S. is projected to continue growing and diversifying in the coming decades. Understanding the demographic trends, socioeconomic factors, and cultural influences shaping the Black community is crucial for planning for the future. By addressing the challenges and promoting equity, the U.S. can ensure that all Black individuals have the opportunity to thrive.
31. How to Stay Informed About Demographic Trends
Staying informed about demographic trends requires access to reliable data and resources. The U.S. Census Bureau, Pew Research Center, and other organizations provide valuable data and analysis on population trends. Engaging with these resources can help individuals, policymakers, and community leaders make informed decisions and promote positive change.
32. Addressing Misconceptions About the Black Population
Misconceptions about the Black population can perpetuate stereotypes and hinder progress towards racial equity. It’s important to challenge these misconceptions by promoting accurate information and fostering understanding. Education, dialogue, and empathy are essential tools for addressing misconceptions and building bridges across communities.
33. The Role of Education in Promoting Understanding
Education plays a crucial role in promoting understanding and appreciation of Black history, culture, and contributions. By incorporating diverse perspectives and experiences into the curriculum, schools can help students develop critical thinking skills and empathy. Education can also empower students to challenge stereotypes and advocate for social justice.
34. Community Engagement and Collaboration
Community engagement and collaboration are essential for addressing the challenges and promoting the well-being of Black individuals. By working together, community organizations, businesses, government agencies, and residents can create positive change. Collaboration can also foster trust, build relationships, and promote a sense of belonging.
35. The Importance of Representation and Inclusion
Representation and inclusion are critical for creating a more equitable society. Black individuals should be represented in leadership positions, decision-making bodies, and all sectors of society. Inclusion means ensuring that all voices are heard and valued. Promoting representation and inclusion requires intentional efforts to address systemic barriers and create opportunities for advancement.
36. Celebrating Black Achievements and Contributions
Celebrating Black achievements and contributions is an important way to recognize the rich history and culture of the Black community. Black History Month, Juneteenth, and other events provide opportunities to celebrate Black excellence and honor the legacy of leaders, innovators, and trailblazers. These celebrations can also inspire future generations and promote a sense of pride and belonging.
37. Supporting Black-Owned Businesses and Organizations
Supporting Black-owned businesses and organizations is a concrete way to promote economic empowerment and community development. By patronizing Black-owned businesses, individuals can help create jobs, build wealth, and strengthen local economies. Supporting Black-led organizations can help advance social justice, advocate for policy change, and provide essential services to the community.
38. Promoting Health Equity in the Black Community
Promoting health equity in the Black community requires addressing the social, economic, and environmental factors that contribute to health disparities. This includes increasing access to affordable healthcare, addressing food insecurity, promoting safe and affordable housing, and reducing exposure to environmental hazards. Community-based interventions, culturally competent healthcare providers, and policy changes are essential for improving health outcomes.
39. Addressing the Criminal Justice System
Addressing the criminal justice system and promoting reform is imperative for achieving racial justice. Understanding the disparities in arrest rates, sentencing, and incarceration can help individuals address the challenges and promote the well-being of Black individuals.
40. Mentoring and Youth Development Programs
Mentoring and youth development programs offer crucial support and guidance to young Black individuals. These programs provide positive role models, academic assistance, career counseling, and leadership development opportunities. By investing in mentoring and youth development, communities can empower young people to achieve their full potential and become successful adults.
41. The Digital Divide and Access to Technology
The digital divide refers to the gap between those who have access to technology and those who do not. Addressing the digital divide requires investments in infrastructure, affordable internet access, and digital literacy training. By bridging the digital divide, communities can ensure that all residents have the opportunity to participate in the digital economy and access online resources.
42. Housing and Community Development Initiatives
Housing and community development initiatives are essential for creating stable, vibrant, and inclusive neighborhoods. These initiatives include affordable housing development, homeownership assistance, neighborhood revitalization, and community planning. By investing in housing and community development, communities can promote economic opportunity, reduce segregation, and improve quality of life.
43. Environmental Justice and Community Health
Environmental justice addresses the disproportionate impact of environmental hazards on communities of color. Black communities are often located near industrial facilities, waste disposal sites, and other sources of pollution. Promoting environmental justice requires addressing these inequities, reducing pollution, and ensuring that all residents have access to clean air, water, and land.
44. Political Engagement and Civic Participation
Political engagement and civic participation are essential for ensuring that Black voices are heard and valued in the democratic process. This includes registering to vote, participating in elections, contacting elected officials, and advocating for policy change. By engaging in the political process, individuals can influence policy decisions and promote a more just and equitable society.
45. The Role of Faith-Based Organizations
Faith-based organizations have historically played a significant role in the Black community, providing spiritual guidance, social services, and advocacy. These organizations can be powerful allies in addressing the challenges and promoting the well-being of Black individuals. By partnering with faith-based organizations, communities can leverage their resources, expertise, and community connections.
46. The Importance of Data-Driven Decision-Making
Data-driven decision-making relies on accurate and reliable data to inform policies and programs. By collecting and analyzing data on demographic trends, socioeconomic indicators, and health outcomes, communities can identify needs, track progress, and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions. Data-driven decision-making can help ensure that resources are allocated effectively and that policies are based on evidence.
47. The Role of Philanthropy in Supporting Black Communities
Philanthropy plays a vital role in supporting Black communities by providing financial resources to organizations and initiatives that address their needs. Foundations, corporations, and individual donors can contribute to community development, education, health, and social justice. By directing resources to Black-led organizations and initiatives, philanthropy can help empower communities and promote lasting change.
48. Collaborating with Historically Black Colleges and Universities (HBCUs)
Historically Black Colleges and Universities (HBCUs) are important institutions that have played a critical role in educating and empowering Black students. Collaborating with HBCUs can provide opportunities for research, partnerships, and workforce development. By supporting HBCUs, communities can invest in the future of Black students and strengthen their institutions.
49. The Role of Media in Shaping Perceptions
The media plays a powerful role in shaping perceptions of race and culture. By promoting accurate and diverse representations of Black individuals, the media can challenge stereotypes and foster understanding. Supporting Black-owned media outlets and advocating for diverse voices in the media are essential for creating a more equitable media landscape.
50. Continuing the Conversation and Taking Action
Continuing the conversation about race and taking action are essential for creating a more just and equitable society. This includes engaging in dialogue, challenging stereotypes, advocating for policy change, and supporting community-based initiatives. By working together, individuals can build a society where all Black individuals have the opportunity to thrive.
Understanding what percentage of U.S. population is Black is just the beginning. From population growth and age demographics to household income and educational attainment, each aspect contributes to a comprehensive picture of this diverse community. Black culture has enriched the United States, influencing music, art, literature, and more. Though strides have been made, challenges persist, necessitating ongoing advocacy and community engagement to ensure equity and opportunity for all.
Have more questions about demographics or any other topic? Visit what.edu.vn today to ask your question and receive a free, prompt answer from our experts. We’re located at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. You can also reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Don’t hesitate—your answers are just a click away!