Are you curious about what percentage of water makes up your body? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide quick and accurate answers to all your questions, including the crucial role water plays in our health and well-being, as well as water content for various demographics. Learn how hydration impacts your body’s functions and overall health. Water composition, body hydration, and human health are just a few clicks away.
1. The Crucial Role of Water in the Human Body
Water is fundamental to life. It comprises a significant portion of our bodies and performs numerous essential functions. From regulating body temperature to transporting nutrients, water keeps our bodies functioning optimally. Understanding the importance of water helps us appreciate just how vital it is to maintain proper hydration.
- A vital nutrient for every cell, acting as a primary building material.
- Regulates internal body temperature through sweating and respiration.
- Transports and metabolizes carbohydrates and proteins in the bloodstream.
- Assists in flushing out waste products through urination.
- Acts as a shock absorber for the brain, spinal cord, and fetus.
- Forms saliva.
- Lubricates joints.
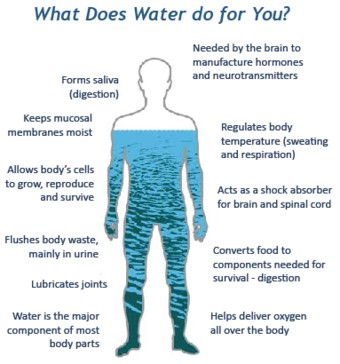 Illustration of water's roles in the human body, including temperature regulation, nutrient transport, and waste removal.
Illustration of water's roles in the human body, including temperature regulation, nutrient transport, and waste removal.
2. Percentage of Water in the Human Body
The human body is composed of a significant amount of water, but the exact percentage varies depending on several factors. Age, gender, and body composition all play a role in determining how much water an individual’s body contains. Let’s take a closer look at these factors.
3. Water Percentage by Age
Age is a significant factor in determining the percentage of water in the human body. Babies are born with the highest percentage of water, which decreases as we age.
- Babies: Approximately 78% water.
- One-Year-Olds: Around 65% water.
- Adults: Varies, but generally around 55-60% water.
This high water content in infants is crucial for their rapid growth and development. As we age, the proportion of water in our bodies decreases as lean muscle mass diminishes and fat tissue increases.
4. Water Percentage by Gender
Gender also influences the percentage of water in the human body. Generally, men have a higher percentage of water compared to women due to differences in body composition.
- Adult Men: About 60% water.
- Adult Women: Approximately 55% water.
Women tend to have more fatty tissue than men, and fat tissue contains less water than lean tissue. This difference in body composition explains why women typically have a lower percentage of water.
5. Water Percentage by Body Composition
Body composition, specifically the amount of fat tissue versus lean tissue, significantly affects the percentage of water in the body. Lean tissue, such as muscles, contains more water than fatty tissue.
- People with More Lean Tissue: Higher percentage of water.
- People with More Fatty Tissue: Lower percentage of water.
Individuals with a higher proportion of lean muscle mass will have a greater percentage of water in their bodies compared to those with more fatty tissue. Maintaining a healthy balance of lean and fat tissue can influence overall hydration levels.
6. Water Content in Different Body Parts
Different organs and tissues in the human body contain varying amounts of water. Understanding the water content of specific body parts highlights the importance of water for their function.
- Brain and Heart: 73% water.
- Lungs: 83% water.
- Skin: 64% water.
- Muscles and Kidneys: 79% water.
- Bones: 31% water.
The high water content in vital organs like the brain, heart, and lungs underscores the critical role of water in maintaining their health and function.
7. Daily Water Intake Recommendations
Maintaining adequate hydration is essential for overall health. The amount of water each person needs daily varies based on age, gender, activity level, and climate. Here are general recommendations:
- Adult Men: About 3 liters (3.2 quarts) per day.
- Adult Women: About 2.2 liters (2.3 quarts) per day.
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines. Individuals who are more physically active or live in hot climates may need to consume more water to stay properly hydrated. Additionally, water intake includes not only drinking liquids but also the water content in the foods we eat.
8. Factors Affecting Water Needs
Several factors can influence an individual’s daily water needs. Understanding these factors can help you adjust your water intake to maintain optimal hydration.
- Age: Infants and young children have higher water needs relative to their body size.
- Gender: Men generally need more water than women due to higher muscle mass.
- Activity Level: Physical activity increases water loss through sweat, necessitating higher intake.
- Climate: Hot and humid climates increase water loss, requiring more hydration.
- Health Conditions: Certain medical conditions may affect fluid balance, altering water needs.
- Diet: A diet high in sodium or fiber may increase water requirements.
9. How Water Regulates Body Temperature
Water plays a crucial role in regulating body temperature through sweating and respiration. When the body overheats, sweat is produced, which evaporates and cools the skin. This process helps maintain a stable internal body temperature.
- Sweating: Evaporation of sweat cools the skin.
- Respiration: Water vapor is exhaled, helping to dissipate heat.
Proper hydration ensures that the body can effectively regulate its temperature, preventing overheating and maintaining optimal physiological function.
10. Water’s Role in Nutrient Transport
Water is essential for transporting nutrients throughout the body. It helps dissolve and carry vitamins, minerals, and other essential substances to cells.
- Dissolves Nutrients: Water dissolves nutrients, making them accessible to cells.
- Transports Nutrients: Water carries nutrients through the bloodstream to various parts of the body.
Without adequate water, the body cannot efficiently transport nutrients, potentially leading to nutrient deficiencies and impaired cellular function.
11. Water’s Role in Waste Removal
Water is vital for removing waste products from the body. It helps flush out toxins and waste through urine, sweat, and bowel movements.
- Urine: Water helps the kidneys filter and eliminate waste from the blood.
- Sweat: Water carries waste products to the skin surface for elimination.
- Bowel Movements: Water helps maintain regular bowel movements, preventing constipation.
Proper hydration ensures that the body can effectively eliminate waste products, preventing the buildup of toxins and maintaining optimal health.
12. The Importance of Hydration for Brain Function
The brain, composed of 73% water, relies on adequate hydration to function optimally. Dehydration can impair cognitive function, affecting memory, attention, and mood.
- Cognitive Function: Hydration supports optimal brain function, including memory and attention.
- Mood: Dehydration can lead to irritability and decreased mood.
Staying hydrated helps maintain proper brain function, supporting mental clarity and emotional well-being.
13. Hydration and Physical Performance
Adequate hydration is essential for physical performance. Dehydration can lead to decreased strength, endurance, and coordination.
- Strength: Hydration supports muscle function, enhancing strength.
- Endurance: Proper hydration helps maintain cardiovascular function, improving endurance.
- Coordination: Dehydration can impair motor skills and coordination.
Athletes and active individuals need to pay particular attention to their hydration levels to optimize their performance and prevent dehydration-related injuries.
14. Signs of Dehydration
Recognizing the signs of dehydration is crucial for maintaining proper hydration. Common symptoms include:
- Thirst: Feeling thirsty is an early sign of dehydration.
- Dark Urine: Dark-colored urine indicates concentrated waste and dehydration.
- Fatigue: Dehydration can lead to feelings of tiredness and fatigue.
- Headache: Dehydration can trigger headaches and dizziness.
- Dry Mouth and Skin: Dehydration can cause dryness of the mouth and skin.
- Dizziness: Lack of fluid can cause lightheadedness and dizziness.
If you experience these symptoms, it’s important to increase your fluid intake to rehydrate your body.
15. Tips for Staying Hydrated
Staying hydrated throughout the day is essential for maintaining optimal health. Here are some practical tips to help you increase your fluid intake:
- Carry a Water Bottle: Keep a water bottle with you and refill it throughout the day.
- Set Reminders: Use your phone or a water tracking app to remind you to drink water.
- Drink Before, During, and After Exercise: Replenish fluids lost during physical activity.
- Eat Water-Rich Foods: Include fruits and vegetables with high water content in your diet.
- Choose Water Over Sugary Drinks: Opt for water instead of sugary beverages like soda and juice.
- Infuse Water with Fruits: Add slices of lemon, cucumber, or berries to make water more appealing.
- Drink Tea and Herbal Infusions: These can contribute to your daily fluid intake.
16. Water-Rich Foods to Include in Your Diet
Incorporating water-rich foods into your diet can help you stay hydrated while also providing essential nutrients. Some excellent options include:
- Watermelon: About 92% water.
- Cucumber: Approximately 96% water.
- Strawberries: Around 91% water.
- Spinach: About 93% water.
- Cantaloupe: Approximately 90% water.
- Lettuce: Around 96% water.
- Celery: Approximately 95% water.
These foods not only contribute to your fluid intake but also provide vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health.
17. Debunking Common Hydration Myths
There are several misconceptions about hydration. Let’s debunk some common myths to help you make informed decisions about your fluid intake.
-
Myth: You Should Only Drink When You’re Thirsty.
- Fact: Thirst is a late sign of dehydration. It’s better to drink water throughout the day rather than waiting until you feel thirsty.
-
Myth: All Fluids Hydrate Equally.
- Fact: Water is the best option for hydration. Sugary drinks can actually dehydrate you and provide empty calories.
-
Myth: You Need 8 Glasses of Water a Day.
- Fact: The amount of water you need varies based on individual factors. Focus on staying hydrated and adjusting your intake as needed.
-
Myth: Drinking Too Much Water is Harmful.
- Fact: While it’s rare, drinking excessive amounts of water can lead to hyponatremia, a condition where sodium levels in the blood become too low. However, this is typically only a concern for endurance athletes.
18. Hydration and Skin Health
Adequate hydration is crucial for maintaining healthy, radiant skin. Water helps keep the skin moisturized, improving its elasticity and appearance.
- Moisture: Hydration keeps the skin moisturized and supple.
- Elasticity: Proper hydration improves skin elasticity, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Complexion: Hydration can improve skin complexion, giving it a healthy glow.
Dehydration can lead to dry, dull skin, exacerbating skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
19. Hydration and Kidney Health
Water plays a vital role in maintaining kidney health. The kidneys filter waste products from the blood, and adequate hydration helps them function efficiently.
- Waste Filtration: Water helps the kidneys filter waste and toxins from the blood.
- Kidney Stone Prevention: Proper hydration can help prevent the formation of kidney stones.
- Overall Kidney Function: Adequate water intake supports optimal kidney function.
Dehydration can strain the kidneys, increasing the risk of kidney stones and other kidney-related problems.
20. Hydration and Digestive Health
Water is essential for proper digestion and preventing constipation. It helps break down food, allowing nutrients to be absorbed more efficiently.
- Digestion: Water aids in the breakdown of food, facilitating nutrient absorption.
- Constipation Prevention: Adequate hydration keeps stools soft, preventing constipation.
- Overall Digestive Function: Proper hydration supports healthy digestive function.
Dehydration can lead to constipation and other digestive issues, impacting overall health and well-being.
21. The Link Between Hydration and Energy Levels
Dehydration can lead to feelings of fatigue and decreased energy levels. Water is essential for cellular function, and dehydration can impair the body’s ability to produce energy.
- Cellular Function: Water supports cellular processes, including energy production.
- Energy Production: Dehydration can slow down energy production, leading to fatigue.
- Overall Energy Levels: Staying hydrated helps maintain optimal energy levels throughout the day.
Drinking enough water can help combat fatigue and keep you feeling energized.
22. Hydration and Joint Health
Water helps lubricate the joints, reducing friction and preventing pain. Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining joint health and flexibility.
- Lubrication: Water lubricates the joints, reducing friction and preventing pain.
- Flexibility: Proper hydration supports joint flexibility and range of motion.
- Overall Joint Health: Adequate water intake is essential for maintaining healthy joints.
Dehydration can lead to joint pain and stiffness, impacting mobility and quality of life.
23. How to Encourage Children to Stay Hydrated
Encouraging children to stay hydrated can be a challenge. Here are some tips to help promote healthy hydration habits in kids:
- Make it Fun: Use colorful cups and straws to make drinking water more appealing.
- Offer Water-Rich Snacks: Provide fruits and vegetables with high water content.
- Lead by Example: Show your children that you prioritize hydration by drinking water yourself.
- Set Reminders: Encourage children to drink water at regular intervals throughout the day.
- Make it Accessible: Keep water readily available in easy-to-reach places.
- Explain the Benefits: Educate children about the importance of hydration for their health and energy levels.
- Offer Choices: Let children choose their water bottles or add fruit slices to their water.
24. The Role of Electrolytes in Hydration
Electrolytes are minerals that help regulate fluid balance in the body. They are lost through sweat and need to be replenished, especially during physical activity.
- Fluid Balance: Electrolytes help maintain proper fluid balance in the body.
- Nerve and Muscle Function: Electrolytes are essential for nerve and muscle function.
- Replenishment: Electrolytes need to be replenished after physical activity to prevent dehydration and maintain performance.
Common electrolytes include sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium. Electrolyte-rich drinks like sports drinks can help replenish these minerals, but water is usually sufficient for everyday hydration.
25. Hydration and Cardiovascular Health
Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining cardiovascular health. Water helps maintain blood volume, which is crucial for efficient circulation.
- Blood Volume: Hydration helps maintain adequate blood volume for efficient circulation.
- Heart Function: Proper hydration supports healthy heart function.
- Blood Pressure: Dehydration can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure.
Staying hydrated helps support a healthy cardiovascular system and reduces the risk of heart-related problems.
26. Hydration and Altitude Sickness
At higher altitudes, the body loses more fluid due to increased respiration and lower humidity. Adequate hydration is essential for preventing altitude sickness.
- Increased Fluid Loss: Higher altitudes lead to increased fluid loss.
- Altitude Sickness Prevention: Proper hydration can help prevent symptoms of altitude sickness.
- Acclimatization: Staying hydrated helps the body acclimatize to higher altitudes.
If you’re traveling to a high-altitude area, be sure to increase your fluid intake to stay properly hydrated.
27. Hydration During Pregnancy
Pregnant women need to drink more water to support the health of both themselves and their developing baby. Adequate hydration is essential for amniotic fluid production, nutrient transport, and waste removal.
- Amniotic Fluid: Hydration supports the production of amniotic fluid.
- Nutrient Transport: Water helps transport nutrients to the baby.
- Waste Removal: Hydration helps remove waste products from the mother and baby.
Pregnant women should aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water per day and more if they are physically active or live in a hot climate.
28. The Impact of Medications on Hydration
Certain medications can affect fluid balance in the body, either increasing or decreasing water retention. It’s important to be aware of how your medications may impact your hydration needs.
- Diuretics: These medications increase urine production and can lead to dehydration.
- Other Medications: Some medications can cause fluid retention, leading to edema.
- Consult Your Doctor: Talk to your doctor about how your medications may affect your hydration needs.
Adjust your fluid intake as needed, based on the advice of your healthcare provider.
29. Common Misconceptions About Sports Drinks
Sports drinks can be beneficial for athletes, but they are not necessary for everyone. Here are some common misconceptions about sports drinks:
-
Misconception: Sports Drinks Are Always Better Than Water.
- Fact: Water is usually sufficient for hydration during moderate exercise. Sports drinks are beneficial for prolonged, intense activity where electrolytes are lost through sweat.
-
Misconception: Sports Drinks Are Low in Sugar.
- Fact: Many sports drinks are high in sugar, which can lead to weight gain and other health problems.
-
Misconception: You Need to Drink Sports Drinks All Day.
- Fact: Sports drinks should be consumed during and after intense physical activity, not as a regular beverage throughout the day.
Choose sports drinks wisely, and opt for water as your primary source of hydration.
30. Hydration for Seniors
Seniors are at a higher risk of dehydration due to decreased thirst sensation and reduced kidney function. It’s important for seniors to make a conscious effort to stay hydrated.
- Decreased Thirst Sensation: Seniors may not feel thirsty even when they are dehydrated.
- Reduced Kidney Function: Aging can impair kidney function, making it harder to conserve water.
- Tips for Seniors: Encourage seniors to drink water regularly, even if they don’t feel thirsty, and offer water-rich foods.
Ensure that seniors have easy access to water and are reminded to drink throughout the day.
31. The Best Time to Hydrate
Staying hydrated throughout the day is essential, but there are certain times when it’s particularly important to drink water:
- Upon Waking: Start your day with a glass of water to rehydrate after sleep.
- Before Meals: Drinking water before meals can help you feel full and aid digestion.
- During and After Exercise: Replenish fluids lost during physical activity.
- Before Bed: Drinking water before bed can help prevent dehydration during sleep.
- Throughout the Day: Sip water regularly to maintain optimal hydration levels.
Make hydration a habit by incorporating it into your daily routine.
32. Monitoring Your Hydration Levels
There are several ways to monitor your hydration levels and ensure that you’re drinking enough water:
- Urine Color: Light-colored urine indicates good hydration, while dark-colored urine suggests dehydration.
- Thirst Sensation: Pay attention to your thirst sensation and drink water when you feel thirsty.
- Weight Changes: Weigh yourself before and after exercise to monitor fluid loss.
- Hydration Apps: Use a hydration tracking app to monitor your fluid intake and set reminders.
By paying attention to these indicators, you can adjust your fluid intake to stay properly hydrated.
33. Water Quality and Hydration
The quality of the water you drink is also important for hydration. Ensure that your water is clean and free from contaminants.
- Tap Water: Tap water is generally safe to drink but may contain chlorine and other chemicals.
- Filtered Water: Filtering tap water can remove impurities and improve its taste.
- Bottled Water: Bottled water is convenient but can be expensive and contribute to plastic waste.
- Well Water: Well water should be tested regularly for contaminants.
Choose the water source that is most convenient and safe for you.
34. The Environmental Impact of Bottled Water
Bottled water can have a significant environmental impact due to plastic waste and energy consumption.
- Plastic Waste: Plastic bottles contribute to pollution and can take hundreds of years to decompose.
- Energy Consumption: The production and transportation of bottled water require a significant amount of energy.
- Alternatives: Consider using a reusable water bottle and filtering tap water to reduce your environmental impact.
Make environmentally conscious choices when it comes to hydration.
35. Hydration and Eye Health
Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining eye health. Water helps keep the eyes lubricated, preventing dryness and irritation.
- Lubrication: Hydration keeps the eyes lubricated, preventing dryness.
- Tear Production: Proper hydration supports healthy tear production.
- Overall Eye Health: Adequate water intake is essential for maintaining healthy eyes.
Dehydration can lead to dry eyes and other vision-related problems.
36. Staying Hydrated While Traveling
Traveling can disrupt your normal routine and make it challenging to stay hydrated. Here are some tips for staying hydrated while on the go:
- Bring a Water Bottle: Carry a reusable water bottle and refill it whenever possible.
- Drink Water on Flights: Air travel can be dehydrating, so drink plenty of water on flights.
- Avoid Sugary Drinks: Opt for water instead of sugary beverages like soda and juice.
- Stay Hydrated in Hot Climates: Drink more water in hot climates to compensate for increased fluid loss.
- Be Mindful of Water Quality: If you’re traveling to an area with questionable water quality, drink bottled or filtered water.
Plan ahead and make hydration a priority during your travels.
37. Hydration and Hair Health
Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining healthy, shiny hair. Water helps keep the hair follicles moisturized, preventing dryness and breakage.
- Moisture: Hydration keeps the hair follicles moisturized, preventing dryness.
- Strength: Proper hydration can improve hair strength and elasticity.
- Overall Hair Health: Adequate water intake is essential for maintaining healthy hair.
Dehydration can lead to dry, brittle hair that is prone to breakage.
38. Hydration and Respiratory Health
Water helps keep the airways moist, facilitating breathing and preventing respiratory problems. Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining respiratory health.
- Moist Airways: Hydration keeps the airways moist, making it easier to breathe.
- Mucus Production: Proper hydration helps thin mucus, making it easier to cough up.
- Overall Respiratory Health: Adequate water intake is essential for maintaining healthy lungs and airways.
Dehydration can lead to dry airways and increased risk of respiratory infections.
Do you have more questions about the ideal water percentage in your body or how to stay hydrated? Don’t hesitate to ask at WHAT.EDU.VN. Our community of experts is ready to provide free, quick, and reliable answers to all your questions.
We understand the challenges of finding trustworthy and prompt answers. That’s why WHAT.EDU.VN offers a platform where you can ask any question and receive informed responses without any cost. No matter your age, occupation, or background, we are here to assist you.
Having trouble finding reliable answers quickly? Need expert advice without the hefty price tag?
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide a free and easy-to-use platform where you can ask any question and connect with knowledgeable individuals. We focus on delivering accurate and understandable information, fostering a community of knowledge sharing.
Ready to get your questions answered?
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and experience the ease and convenience of getting free, expert advice. Your questions are valuable, and we’re here to help you find the answers you need.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: what.edu.vn
