What Uv Is Good For Tanning? Achieving a tan requires exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays, but understanding the ideal UV levels for tanning while minimizing the risk of skin damage is crucial; WHAT.EDU.VN provides a platform to explore safe tanning practices and sun protection strategies. Discovering the science behind tanning and effective protection measures, including sunscreen and protective clothing, will help you make informed choices. Learn more about sun safety, radiant skin, and UV exposure.
1. Understanding the UV Index for Tanning
The UV Index (UVI) indicates the strength of ultraviolet radiation at a specific time and location. The UVI scale, developed in the early 1990s by Canadian scientists, ranges from 0 to 11, with higher values indicating a greater risk of skin and eye damage. UV radiation intensity varies depending on factors like time of year and proximity to the sun. For instance, UV levels are higher in the Southern Hemisphere during December due to its closer proximity to the sun. Understanding the UVI helps individuals make informed decisions about sun exposure and protection.
1.1 How the UV Index Works
The UV index is a crucial tool for understanding the potential harm from the sun’s rays. A higher UV index means stronger radiation and a quicker risk of damage. When the UV index is extreme, it is advisable to limit outdoor activities, especially between 10 AM and 4 PM. Protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses, is essential during these times.
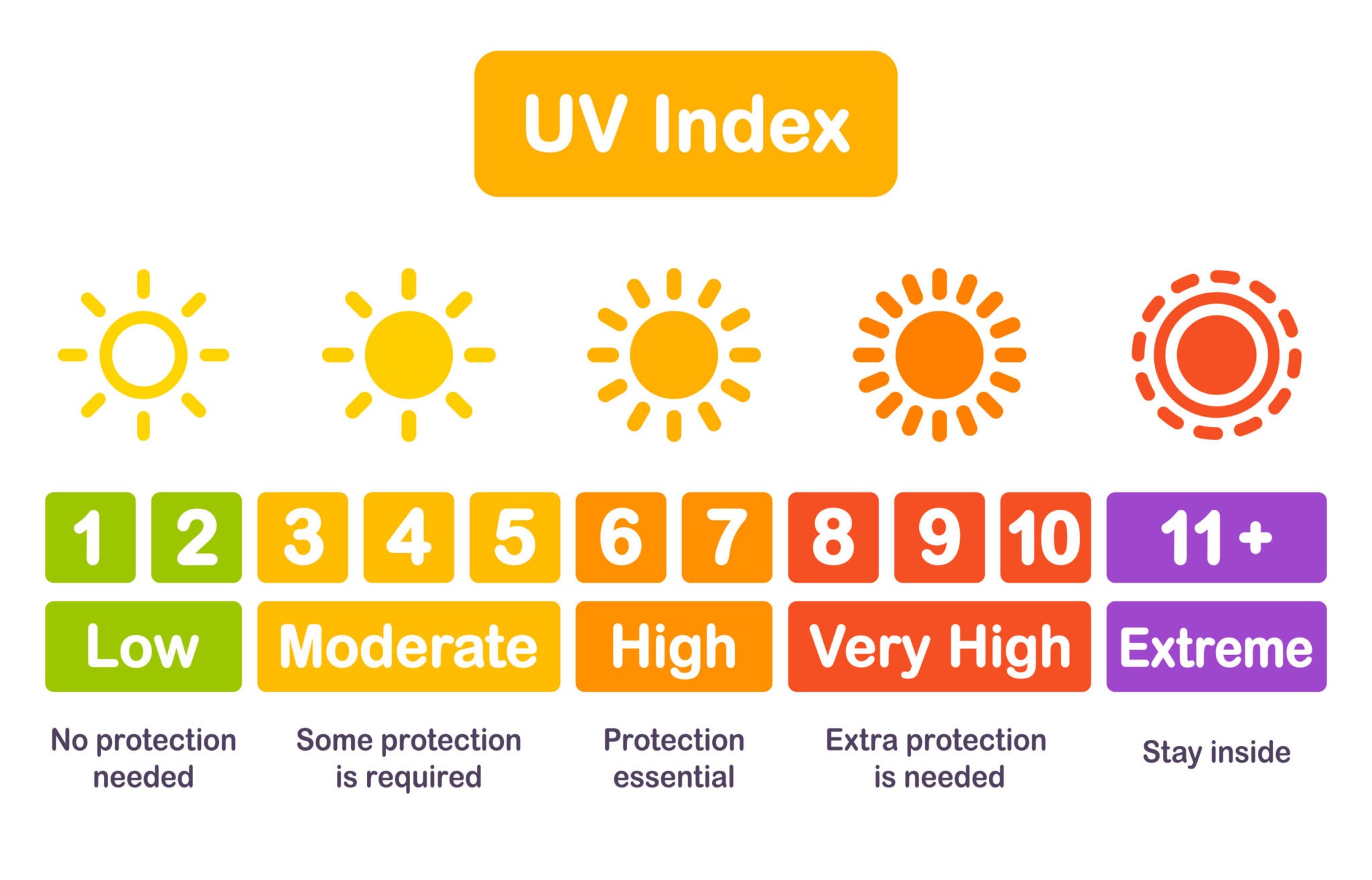 UV index scale
UV index scale
1.2 Finding the UV Index
Knowing the UV index for your area is essential for planning outdoor activities and protecting your skin. You can easily find the daily UV index using Google or your smartphone’s weather app. This information allows you to take appropriate precautions, such as applying sunscreen or seeking shade, to minimize the risk of sun damage.
1.3 The UV Index and Tanning
The UV index directly affects tanning. To tan safely, understanding the UV index is crucial. High UV indexes can lead to sunburn and long-term skin damage. A moderate UV index may be better for tanning, but protection is still necessary.
2. Best Times for Safe Sunbathing to Get a Tan
Exposure to the sun’s UV rays can cause skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer, even on cloudy days. Sun exposure and tanning can also lead to premature aging by affecting the skin’s collagen and melanin levels. However, some sun exposure can benefit skin conditions like acne and help the body produce vitamin D, which is essential for absorbing calcium and phosphorus. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends 10 to 15 minutes of sun exposure without sunscreen daily between March and October, from 11 am to 3 pm. Individuals with darker skin tones may need longer exposure to achieve the same benefits. For extended periods, broad-spectrum sunscreen is essential.
2.1 Balancing Sun Exposure and Protection
Finding the right balance between sun exposure and protection is essential for maintaining healthy skin. Brief periods of sun exposure can provide beneficial vitamin D synthesis. However, prolonged exposure without protection can lead to sun damage and increase the risk of skin cancer. It’s important to monitor the UV index and adjust your sun exposure habits accordingly.
2.2 Benefits of Limited Sun Exposure
Limited sun exposure offers several health benefits, including boosting vitamin D production. Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium and phosphorus, essential for bone health. Additionally, some skin conditions, such as acne, may improve with controlled sun exposure. However, it is essential to balance these benefits with the risks of sun damage.
2.3 Risks of Excessive Sun Exposure
Excessive sun exposure can lead to sunburn, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer. UV radiation damages skin cells, leading to wrinkles, age spots, and other signs of aging. Protecting your skin with sunscreen, protective clothing, and shade is crucial to minimizing these risks.
3. The Science Behind Tanning
Exposure to UV radiation increases the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. UVA radiation triggers the release of existing melanin, while UVB radiation stimulates the body to produce more melanin, resulting in a tan. Both UVA and UVB radiation are present in sunlight. To achieve a tan, the UV radiation must be high enough to affect melanin levels without causing burning.
3.1 UVA vs. UVB Radiation
Understanding the difference between UVA and UVB radiation is crucial for effective sun protection. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin, causing aging and wrinkles. UVB rays primarily affect the surface of the skin, leading to sunburn. Both types of radiation contribute to skin cancer risk, making broad-spectrum sunscreen essential.
3.2 Melanin Production and Tanning
Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its color. When skin is exposed to UV radiation, melanocytes produce more melanin to protect the skin from further damage. This increase in melanin results in tanning. However, even a tan indicates that skin damage has occurred.
3.3 How UV Radiation Affects Skin
UV radiation damages the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can cause skin cancer. Additionally, UV radiation breaks down collagen and elastin, leading to premature aging. Protecting skin from UV radiation is essential for maintaining its health and appearance.
4. The Myth of a Healthy Tan
Even getting a tan is a sign of sun damage. The NHS states that the idea of a healthy tan is a myth. To avoid burning, limit sun exposure without sunscreen between 10 AM and 3 PM during summer months and seek shade whenever possible. Recognizing the risks associated with tanning is crucial for making informed decisions about sun exposure.
4.1 Tanning as a Sign of Damage
Tanning indicates that the skin has been damaged by UV radiation. The increase in melanin is a protective response, but it doesn’t negate the damage that has already occurred. Any change in skin color due to sun exposure is a sign of potential harm.
4.2 Avoiding Sunburn
Avoiding sunburn is essential for protecting your skin. Sunburn damages skin cells and increases the risk of skin cancer. To prevent sunburn, use sunscreen with a high SPF, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during peak sun hours.
4.3 Seeking Shade
Seeking shade is an effective way to reduce your exposure to UV radiation. Trees, umbrellas, and buildings can provide shade and help protect your skin from the sun. Staying in the shade during peak sun hours is a simple way to minimize the risk of sun damage.
5. When UV Radiation is at its Highest
UV radiation is generally highest between 10 AM and 3 PM during the summer on cloudless days. Some countries broadcast a UV index for each day on the weather report. However, a scorching hot sunny day isn’t necessarily the best for tanning. Depending on your skin type, even short exposure can cause sunburn. If you wish to tan on these days, use a stronger sunscreen to protect your skin from UV radiation. Sunscreen is essential even on less bright days.
5.1 Seasonal Variations in UV Radiation
UV radiation levels vary throughout the year, with the highest levels occurring during the summer months. The angle of the sun and the length of daylight hours contribute to these seasonal variations. Understanding these patterns can help you adjust your sun protection habits accordingly.
5.2 Daily Variations in UV Radiation
UV radiation levels also vary throughout the day, with the highest levels occurring between 10 AM and 3 PM. During these hours, the sun is at its highest point in the sky, and its rays are most intense. Avoiding sun exposure during these peak hours can significantly reduce your risk of sun damage.
5.3 Weather Conditions and UV Radiation
Weather conditions can affect UV radiation levels. Cloud cover can reduce UV radiation, but it doesn’t eliminate it entirely. Even on cloudy days, UV radiation can penetrate through the clouds and damage your skin. Wearing sunscreen and protective clothing is essential regardless of weather conditions.
6. Protecting Sensitive Areas During Tanning
When tanning, protect sensitive areas such as your eyes, lips, and scalp. Consider protective eyeglasses, lip balms with sunscreen, and hair styling products with at least SPF 30 protection. Sunscreen in a spray bottle is great for hard-to-reach spots like your scalp. Apply sunscreen every two hours to ensure continuous protection.
6.1 Eye Protection
Protecting your eyes from UV radiation is essential for preventing cataracts and other eye damage. Wear sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB rays. Ensure that the sunglasses fit properly and provide adequate coverage.
6.2 Lip Protection
Lips are particularly vulnerable to sun damage because they lack melanin. Use lip balms with SPF 30 or higher to protect your lips from sunburn and skin cancer. Reapply lip balm frequently, especially after eating or drinking.
6.3 Scalp Protection
The scalp is often overlooked when it comes to sun protection. Use sunscreen spray or hair products with SPF 30 or higher to protect your scalp from sunburn. Wearing a hat is also an effective way to shield your scalp from UV radiation.
7. Reversing Sun Damage
Some visible signs of sun damage can be reversed or improved with professional skin treatments. Examples of sun damage and treatments designed to address them include:
7.1 Skin Peels for Sun Damage
Skin peels exfoliate the skin and encourage it to refresh itself by creating new skin cells, stimulating natural collagen production to target fine lines and wrinkles. Skin peels can help reverse the signs of aging caused by sun exposure.
7.2 Other Treatments for Sun Damage
Other treatments for sun damage include laser therapy, microdermabrasion, and topical retinoids. These treatments can help reduce the appearance of age spots, wrinkles, and other signs of sun damage. Consulting with a dermatologist can help you determine the best treatment options for your skin.
7.3 Preventing Future Sun Damage
Preventing future sun damage is essential for maintaining healthy skin. Use sunscreen with a high SPF, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during peak sun hours. Regular skin exams can help detect skin cancer early, when it is most treatable.
8. What is a Good UV Index for Tanning? FAQs
Understanding the nuances of UV radiation and tanning can be complex. Here are some frequently asked questions to help clarify the process:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What UV index is best for tanning? | There is no “best” UV index for tanning, as any tan indicates skin damage. However, a lower UV index (3-5) requires longer exposure, reducing the risk of burning. |
| Is it possible to tan safely? | While any tan indicates sun damage, minimizing risks involves gradual exposure, using sunscreen (SPF 30+), and avoiding peak UV hours (10 AM – 4 PM). |
| How does sunscreen affect tanning? | Sunscreen reduces the intensity of UV rays reaching your skin, slowing the tanning process and preventing sunburn. It allows for safer, gradual tanning. |
| What SPF should I use for tanning? | Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher. Reapply every two hours and after swimming or sweating. |
| Can I tan on a cloudy day? | Yes, UV rays can penetrate clouds. Use sunscreen even on cloudy days. |
| How long should I sunbathe? | Limit sunbathing to 10-15 minutes initially, gradually increasing if your skin tolerates it. Avoid prolonged exposure. |
| What are the long-term effects of tanning? | Long-term effects include premature aging (wrinkles, age spots), increased risk of skin cancer, and immune system suppression. |
| How can I protect my skin while tanning? | Wear protective clothing (hat, sunglasses), use broad-spectrum sunscreen, seek shade during peak hours, and stay hydrated. |
| Is tanning bed safer than sun tanning? | No, tanning beds emit concentrated UV radiation and are more dangerous than sun tanning. They significantly increase the risk of skin cancer. |
| What are alternatives to sun tanning? | Alternatives include sunless tanning lotions, sprays, and gradual tanning moisturizers. These products provide a tan without UV exposure. |
9. Expert Advice and Resources
To learn more about safe tanning practices, consult with dermatologists and other skin care professionals. They can provide personalized advice based on your skin type and health history. Additionally, reliable sources such as the American Academy of Dermatology and the Skin Cancer Foundation offer valuable information on sun protection and skin cancer prevention.
9.1 Consulting a Dermatologist
A dermatologist can assess your skin type, provide personalized advice on sun protection, and recommend appropriate skin care products. Regular skin exams can help detect skin cancer early, when it is most treatable.
9.2 Reliable Sources for Information
The American Academy of Dermatology and the Skin Cancer Foundation are excellent resources for accurate and up-to-date information on sun protection and skin cancer prevention. These organizations offer guidelines, articles, and resources to help you make informed decisions about your skin health.
9.3 Staying Informed About Sun Safety
Staying informed about sun safety is essential for protecting your skin. Follow reputable sources for the latest research and recommendations on sun protection. Adjust your habits as needed to minimize your risk of sun damage.
10. Embrace Sun Safety with WHAT.EDU.VN
Navigating the complexities of sun exposure and tanning can be challenging, but WHAT.EDU.VN is here to provide you with the knowledge and resources you need to make informed decisions. Whether you’re seeking advice on safe tanning practices, understanding the UV index, or exploring skin protection strategies, our platform offers expert guidance and support. Embrace sun safety with WHAT.EDU.VN and prioritize your skin health. Remember, a healthy relationship with the sun starts with awareness and protection.
Are you ready to take control of your sun exposure and protect your skin? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand your concerns and offer a platform where you can ask any question and receive expert advice for free. Don’t let confusion or uncertainty compromise your health. Our community of knowledgeable users and experts are here to provide you with accurate and reliable answers.
10.1 How to Get Free Advice on WHAT.EDU.VN
- Visit our website: Go to WHAT.EDU.VN using any web browser.
- Sign Up: Create a free account or log in if you’re already a member.
- Ask Your Question: Navigate to the “Ask a Question” section and type in your query about safe tanning practices, understanding the UV index, or exploring skin protection strategies.
- Get Answers: Receive responses from our community of experts and knowledgeable users.
- Engage: Feel free to ask follow-up questions or clarify any points for a comprehensive understanding.
10.2 Contact Us
For more personalized assistance, you can reach us through the following channels:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
At what.edu.vn, we’re committed to providing you with the information you need to make informed decisions about your health and well-being. Ask your question today and take the first step towards a safer, healthier you.