Are you wondering what polyps are and how they affect your health? Polyps are abnormal tissue growths that can occur in various parts of the body. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide clear, concise information to help you understand these growths, their potential risks, and available treatments. Learn about polyp removal, prevention, and different polyp types to maintain your health.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly Are Polyps?
- Where Can Polyps Develop in the Body?
- What Are the Main Types of Polyps?
- What Are the Common Symptoms of Polyps?
- Ear Canal Polyps: Symptoms and Signs
- Cervical Polyps: What to Watch For
- Colorectal Polyps: Identifying Potential Issues
- Nasal Polyps: How They Affect Breathing
- Throat Polyps: Effects on Voice and Throat
- Endometrial Polyps: Impact on Uterine Health
- Bladder Polyps: Recognizing Urinary Symptoms
- Gastric Polyps: Symptoms and Potential Complications
- Gallbladder Polyps: When to Be Concerned
- Skin Tags: Understanding These Harmless Growths
- What Are the Primary Causes of Polyps?
- When Should You Consult a Doctor About Polyps?
- What Diagnostic Methods Are Used to Detect Polyps?
- How Are Polyps Typically Treated?
- Uterine Polyps: Treatment Options and Fertility
- Colorectal Polyps: Removal Procedures Explained
- Gallbladder Polyps: Surgical vs. Monitoring Approaches
- Throat Polyps: Voice Therapy and Surgical Interventions
- What Are the Potential Complications of Polyps?
- Can Polyps Be Prevented? Exploring Preventative Measures
- FAQ: Understanding Polyps Better
- Need More Answers? Ask WHAT.EDU.VN!
1. What Exactly Are Polyps?
Polyps are abnormal growths of tissue that project from the mucous membrane into a body cavity. These growths can be benign (non-cancerous), precancerous, or malignant (cancerous). Polyps arise from the uncontrolled division of cells in the lining of organs like the colon, nose, or uterus. Understanding the nature of polyps—whether they are neoplastic or non-neoplastic—is crucial for determining the appropriate medical intervention and management strategy. For further learning, refer to research by the Mayo Clinic, which explains the distinction between these types of growths and their implications for health outcomes.
2. Where Can Polyps Develop in the Body?
Polyps can occur in various parts of the body, including the:
- Ear, nose, and throat
- Uterus and cervix
- Gallbladder
- Stomach and intestines
- Bladder
- Skin
Their presence and characteristics often dictate the symptoms experienced and the necessary treatment approaches. According to a study by the National Institutes of Health, the prevalence and type of polyps vary across different organ systems, emphasizing the need for targeted diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
3. What Are the Main Types of Polyps?
There are several types of polyps, classified based on their location, appearance, and potential for malignancy. Common types include:
- Adenomatous polyps: These are frequently found in the colon and are considered precancerous.
- Hyperplastic polyps: Generally benign, these are commonly found in the colon and stomach.
- Inflammatory polyps: Often seen in the colon, these are associated with inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Nasal polyps: These occur in the nasal passages and sinuses, often due to chronic inflammation.
- Uterine polyps: Found in the uterus, they can cause abnormal bleeding.
The categorization of polyps is vital for risk assessment and guiding treatment decisions. Research from the American Cancer Society highlights the importance of distinguishing between different polyp types to optimize cancer prevention efforts.
4. What Are the Common Symptoms of Polyps?
The symptoms of polyps vary depending on their location and size. Many polyps, especially when small, may not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, larger polyps or those in specific locations can lead to:
- Abnormal bleeding
- Changes in bowel habits
- Pain
- Discharge
- Respiratory issues (if in the nose)
It’s essential to be aware of these potential signs and seek medical advice if you experience any unusual symptoms. Early detection and management can prevent complications.
5. Ear Canal Polyps: Symptoms and Signs
Polyps in the ear canal can manifest through several symptoms, including:
- Hearing Loss: Gradual or sudden decrease in hearing ability.
- Bloody Discharge: Drainage of blood or fluid from the ear.
- Ear Pain: Discomfort or persistent pain in the ear.
- Feeling of Fullness: Sensation of pressure or blockage in the ear.
These symptoms might also indicate other ear conditions, such as cholesteatoma, so a thorough examination is crucial. If you notice these signs, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
 Ear Canal Polyps Symptoms
Ear Canal Polyps Symptoms
6. Cervical Polyps: What to Watch For
Cervical polyps often present with subtle or no symptoms, but potential signs include:
- Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding: Bleeding between periods, after intercourse, or after menopause.
- Unusual Discharge: Vaginal discharge that is heavier or different in color or consistency.
- Pelvic Pain: Discomfort or pain in the lower abdominal area.
Regular gynecological check-ups are vital for detecting and managing cervical polyps early. Early detection is key in preventing complications.
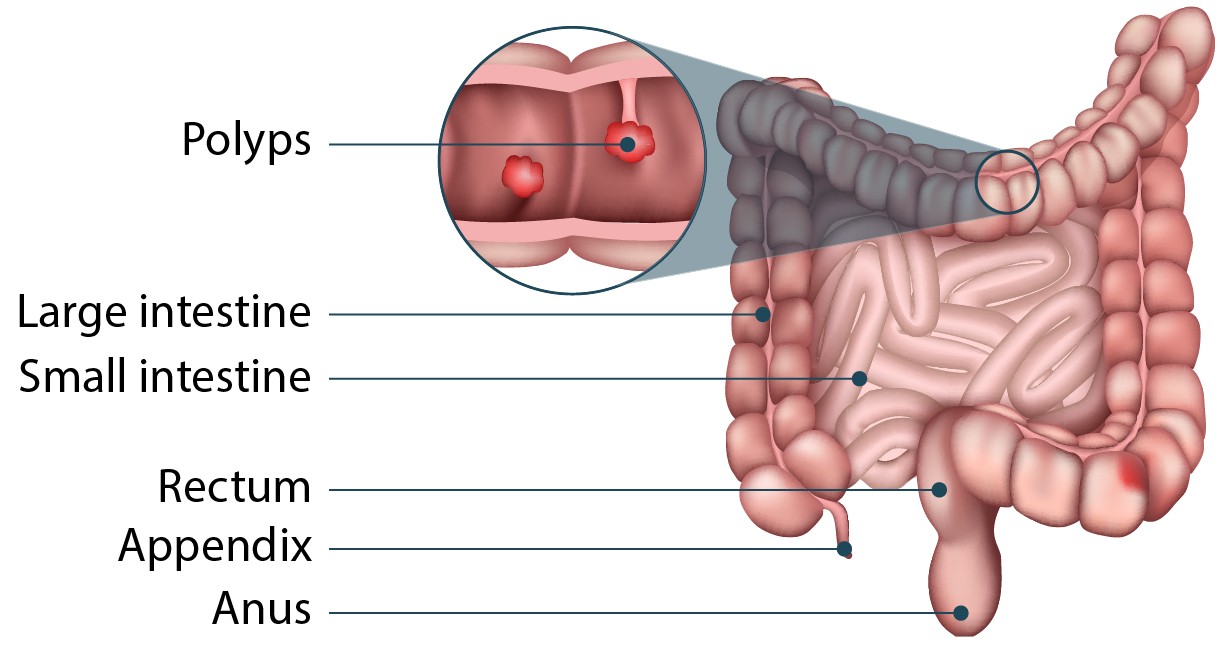
7. Colorectal Polyps: Identifying Potential Issues
Colorectal polyps can be asymptomatic, making screening crucial. When symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Changes in Bowel Habits: Diarrhea, constipation, or changes in stool frequency or consistency.
- Rectal Bleeding: Blood in the stool or on toilet paper.
- Abdominal Pain: Discomfort or cramping in the abdomen.
- Anemia: Iron deficiency due to chronic blood loss.
Screening methods like colonoscopies are essential for detecting and removing polyps before they become cancerous. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends regular screenings for adults aged 45 and older to reduce the risk of colorectal cancer.
8. Nasal Polyps: How They Affect Breathing
Nasal polyps can significantly affect breathing and sinus function. Common symptoms include:
- Nasal Congestion: Persistent stuffiness or blockage in the nasal passages.
- Runny Nose: Frequent nasal discharge.
- Decreased Sense of Smell: Reduced ability to detect odors.
- Facial Pain: Pressure or pain in the face and sinuses.
- Snoring: Difficulty breathing through the nose during sleep.
These symptoms can worsen with allergies or sinusitis. Medical management often involves corticosteroids or surgery to improve airflow and quality of life.
9. Throat Polyps: Effects on Voice and Throat
Throat polyps, especially those on the vocal cords, can lead to:
- Hoarseness: A raspy or strained voice.
- Breathiness: A weak, airy voice.
- Lump Sensation: Feeling like there is something stuck in the throat.
- Frequent Throat Clearing: The need to constantly clear the throat.
Voice therapy, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes surgery are used to manage throat polyps and restore vocal function.
10. Endometrial Polyps: Impact on Uterine Health
Endometrial polyps, which develop in the lining of the uterus, may cause:
- Irregular Menstrual Bleeding: Unpredictable or prolonged periods.
- Heavy Bleeding: Excessive menstrual flow.
- Bleeding After Menopause: Any vaginal bleeding after menopause.
- Infertility: Difficulty conceiving.
Diagnosis often involves ultrasound or hysteroscopy, and treatment may include medication or surgical removal.
11. Bladder Polyps: Recognizing Urinary Symptoms
Polyps in the bladder can present with:
- Blood in Urine: Hematuria, which can be visible or detected during a urine test.
- Painful Urination: Discomfort or burning sensation while urinating.
- Frequent Urination: Needing to urinate more often than usual.
- Urgency: A sudden, strong urge to urinate.
These symptoms warrant medical evaluation to rule out other urinary conditions and determine the appropriate treatment.
12. Gastric Polyps: Symptoms and Potential Complications
Gastric polyps often do not cause symptoms, but when they do, they may include:
- Abdominal Pain: Discomfort or pain in the stomach area.
- Nausea: Feeling sick to the stomach.
- Vomiting: Expelling stomach contents.
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Blood in vomit or stool.
Regular monitoring is recommended to detect any changes or potential complications, such as bleeding or malignancy.
13. Gallbladder Polyps: When to Be Concerned
Gallbladder polyps are usually asymptomatic and often discovered during imaging for other conditions. However, larger polyps may cause:
- Abdominal Pain: Discomfort in the upper right abdomen.
- Nausea: Feeling sick to the stomach.
- Vomiting: Expelling stomach contents.
Monitoring the size and growth rate of gallbladder polyps is crucial, as larger polyps have a higher risk of being cancerous and may require surgical removal.
14. Skin Tags: Understanding These Harmless Growths
Skin tags, also known as fibroepithelial polyps, are small, benign growths that typically don’t cause any problems. They appear as:
- Small, soft, flesh-colored growths
- Often found in skin folds like the neck, armpits, or groin
Skin tags are generally harmless and do not require treatment unless they cause irritation or cosmetic concerns.
15. What Are the Primary Causes of Polyps?
Polyps result from abnormal cell growth, but the exact cause is often unknown. Factors that may contribute to polyp development include:
- Genetics: Family history of polyps or certain genetic conditions.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the body.
- Age: Increased risk with age.
- Lifestyle Factors: Diet, smoking, and alcohol consumption.
Understanding these risk factors can help in adopting preventative measures and maintaining overall health.
16. When Should You Consult a Doctor About Polyps?
It’s important to see a doctor if you experience any worrying symptoms, such as:
- Unexplained bleeding
- Changes in bowel or bladder habits
- Persistent pain or discomfort
- Any new or unusual growths
Early detection and diagnosis are key to managing polyps effectively and preventing potential complications.
17. What Diagnostic Methods Are Used to Detect Polyps?
Doctors use various methods to diagnose polyps, depending on their location:
- Physical Examination: A general assessment of your health.
- Endoscopy: Procedures like colonoscopy, gastroscopy, or hysteroscopy to visualize internal organs.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI to detect polyps.
- Biopsy: Removing a tissue sample for microscopic examination.
- Screening Tests: Routine checks for specific types of polyps, like cervical screening tests.
These diagnostic tools help in accurately identifying polyps and determining the appropriate course of action.
18. How Are Polyps Typically Treated?
Treatment for polyps depends on their type, location, size, and whether they are cancerous:
- Monitoring: Small, benign polyps may only require regular monitoring.
- Medication: Certain medications can help manage symptoms or shrink polyps.
- Surgical Removal: Polyps can be removed during procedures like colonoscopy, hysteroscopy, or surgery.
- Lifestyle Changes: Diet and exercise can help reduce the risk of certain polyps.
The treatment approach is tailored to the individual’s specific needs and health status.
19. Uterine Polyps: Treatment Options and Fertility
Treatment for uterine polyps aims to alleviate symptoms and improve fertility if needed. Options include:
- Medication: Hormonal medications to reduce bleeding.
- Polypectomy: Surgical removal of polyps during hysteroscopy.
- Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus in severe cases.
Your doctor will recommend the best course of action based on your symptoms, age, and desire for future pregnancies.
20. Colorectal Polyps: Removal Procedures Explained
Colorectal polyps are often removed during a colonoscopy. The procedure involves:
- Polypectomy: Using a wire loop or forceps to remove the polyp.
- Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR): Removing larger polyps or those that are flat.
Removing colorectal polyps can significantly reduce the risk of developing colorectal cancer.
21. Gallbladder Polyps: Surgical vs. Monitoring Approaches
The approach to gallbladder polyps depends on their size and risk of malignancy:
- Monitoring: Small polyps (less than 10mm) may be monitored with regular ultrasounds.
- Cholecystectomy: Surgical removal of the gallbladder for larger or symptomatic polyps.
Regular check-ups and imaging are essential to determine the best course of action.
22. Throat Polyps: Voice Therapy and Surgical Interventions
Treatment for throat polyps, particularly those on the vocal cords, includes:
- Voice Rest: Avoiding excessive talking or shouting.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water.
- Reflux Management: Treating acid reflux, if present.
- Voice Therapy: Working with a speech pathologist to improve vocal technique.
- Surgery: Removing polyps surgically if other treatments are ineffective.
A multidisciplinary approach is often necessary for optimal outcomes.
23. What Are the Potential Complications of Polyps?
While many polyps are benign, potential complications include:
- Cancer Development: Some polyps can become cancerous if not removed.
- Bleeding: Polyps can cause chronic bleeding, leading to anemia.
- Obstruction: Large polyps can block passages in the body.
- Infertility: Uterine polyps can interfere with fertility.
Regular screening and timely treatment are crucial for preventing these complications.
24. Can Polyps Be Prevented? Exploring Preventative Measures
While not all polyps can be prevented, you can reduce your risk by:
- Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Regular Screenings: Following recommended screening guidelines for cervical, colorectal, and other types of polyps.
- Managing Underlying Conditions: Treating chronic inflammation and other health issues.
These preventative measures can help you stay healthy and reduce your risk of developing polyps.
25. FAQ: Understanding Polyps Better
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the difference between a polyp and a tumor? | A polyp is a growth projecting from a mucous membrane, while a tumor is a general term for any abnormal mass of tissue. Polyps can be a type of tumor. |
| Are all polyps cancerous? | No, most polyps are benign, but some can become cancerous over time. |
| How often should I get screened for polyps? | Screening frequency depends on your age, medical history, and risk factors. Consult your doctor for personalized recommendations. |
| Can polyps come back after removal? | Yes, polyps can recur, which is why regular follow-up screenings are important. |
| What is the role of diet in polyp prevention? | A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fiber can help reduce the risk of certain types of polyps, especially colorectal polyps. |
| Is there a genetic link to polyp formation? | Yes, certain genetic conditions and a family history of polyps can increase your risk. |
| Can polyps cause pain? | Some polyps can cause pain, especially if they are large or located in sensitive areas. |
| How are polyps diagnosed? | Polyps are typically diagnosed through physical examinations, imaging tests, and endoscopic procedures with biopsies. |
| What are the main risk factors for polyps? | Risk factors include age, genetics, chronic inflammation, and certain lifestyle factors such as smoking and diet. |
| Can polyps affect fertility? | Yes, uterine polyps can affect fertility by interfering with implantation or causing abnormal bleeding. |
26. Need More Answers? Ask WHAT.EDU.VN!
Do you have more questions about polyps or other health concerns? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with quick, reliable, and free answers. Our platform makes it easy to ask questions and connect with knowledgeable experts.
Don’t struggle with unanswered health questions. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and get the information you need! Our services are designed to offer convenient and accessible support.
Contact Us:
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Ask your questions now and get the answers you deserve at what.edu.vn! We are here to help you navigate your health concerns with ease.