Hemorrhoids often result from increased pressure due to factors like pregnancy, obesity, or straining during bowel movements; however, WHAT.EDU.VN provides quick and free answers to your burning questions about hemorrhoids, including causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Explore simple home remedies and medical procedures for lasting relief. Address discomfort and find the solutions you need.
1. What Are Hemorrhoids and Why Do They Occur?
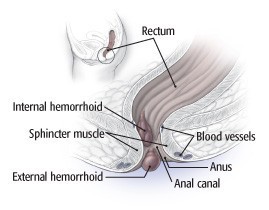
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are naturally occurring clusters of veins located beneath the mucous membranes lining the lower rectum and anus. Hemorrhoidal disease arises when these veins become swollen and distended, resembling varicose veins in the legs. These swollen blood vessels struggle against gravity to return blood to the heart, which may explain why humans get hemorrhoids.
1.1. Internal vs. External Hemorrhoids: What’s the Difference?
There are two main types of hemorrhoids:
-
Internal hemorrhoids: These develop in the lower rectum and are typically painless, even when bleeding occurs. You might notice bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl. Internal hemorrhoids can also prolapse, or extend beyond the anus, leading to irritation and itching.
-
External hemorrhoids: These form under the skin around the anus and are generally more uncomfortable. The skin covering them can become irritated and erode. A blood clot inside an external hemorrhoid can cause sudden, severe pain. You might feel or see a lump around the anus, which can leave excess skin (a skin tag) that may itch or become irritated.
2. What Causes Hemorrhoids to Develop? Unveiling the Root Causes
Several factors contribute to the development of hemorrhoids. Understanding these causes can help you take preventive measures and manage the condition effectively.
2.1. Chronic Constipation and Straining:
Historically, hemorrhoids have been linked to chronic constipation, straining during bowel movements, and prolonged sitting on the toilet. These actions disrupt blood flow to and from the rectal area, causing blood to pool and enlarge the veins.
2.2. Pregnancy and Increased Pressure:
Pregnancy is another common cause of hemorrhoids. As the uterus expands, it presses on the veins in the rectum and anus, increasing pressure and leading to swelling.
2.3. High Resting Anal Canal Tone:
Recent research indicates that individuals with hemorrhoids often have a higher resting anal canal tone, meaning the smooth muscle of the anal canal is tighter than average. This increased tightness, combined with constipation, exacerbates the problem.
2.4. Weakening Connective Tissues:
As we age, the connective tissues that support hemorrhoids can weaken, causing them to bulge and prolapse. This age-related weakening contributes to the increased prevalence of hemorrhoids in older adults.
3. How Are Hemorrhoids Diagnosed? A Simple Examination
Diagnosing hemorrhoids typically involves a straightforward medical history and physical examination.
3.1. Physical Exam and Digital Rectal Exam:
External hemorrhoids are usually apparent, especially if a blood clot has formed. A clinician may perform a digital rectal exam to check for blood in the stool.
3.2. Anoscopy, Sigmoidoscopy, and Colonoscopy:
The anal canal may be examined with an anoscope, a short, illuminated plastic tube inserted into the rectum. If there is evidence of rectal bleeding or microscopic blood in the stool, flexible sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy may be performed to rule out other causes of bleeding, such as colorectal polyps or cancer, particularly in individuals over 45.
4. How to Treat Hemorrhoids at Home?
For relief from hemorrhoid symptoms, simple home remedies can be highly effective.
4.1. Increase Fiber Intake:
Adding more fiber to your diet, whether through food, fiber supplements (like Metamucil, Citrucel, or FiberCon), or both, can soften stools and make them easier to pass, reducing pressure on hemorrhoids.
4.1.1. High-Fiber Foods and Their Benefits:
High-fiber foods include broccoli, beans, wheat and oat bran, whole-grain foods, and fresh fruit. Fiber supplements can decrease hemorrhoidal bleeding, inflammation, and enlargement, as well as reduce irritation from trapped stool particles.
4.1.2. Gradual Increase and Fluid Intake:
To avoid bloating or gas, start slowly and gradually increase your fiber intake to 25–30 grams per day. Also, increase your fluid intake to help the fiber work effectively.
4.2. Regular Exercise:
Moderate aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking for 20–30 minutes a day, can stimulate bowel function.
4.3. Timely Bowel Movements:
When you feel the urge to defecate, go to the bathroom immediately. Delaying can lead to increased pressure and straining.
4.4. Scheduled Toilet Time:
Schedule a set time each day, such as after a meal, to sit on the toilet for a few minutes. This can help establish a regular bowel habit.
4.5. Sitz Baths for Relief:
A sitz bath, which involves sitting in a few inches of warm water, can relieve itching, irritation, and spasms of the sphincter muscle.
4.5.1. How to Take a Sitz Bath:
Pharmacies sell small plastic tubs that fit over a toilet seat, or you can use a regular bathtub. Experts recommend a 20-minute sitz bath after each bowel movement and two or three times a day.
4.5.2. Gentle Drying:
Gently pat the anal area dry after the bath; avoid rubbing or wiping hard. A hair dryer can also be used to dry the area.
4.6. Topical Relief with Creams and Wipes:
Over-the-counter hemorrhoid creams containing a local anesthetic can temporarily soothe pain. Witch hazel wipes (Tucks) are also soothing and have no harmful effects.
4.7. Ice Packs for Swelling:
Applying a small ice pack to the anal area for a few minutes can reduce pain and swelling.
4.8. Cushions for Comfort:
Sitting on a cushion rather than a hard surface can reduce swelling of existing hemorrhoids and prevent new ones from forming.
4.9. Treating Blood Clots:
If an external hemorrhoid forms a blood clot, pain can be severe. If the pain is tolerable and the clot has been present for more than two days, use home treatments while waiting for it to resolve. More recent clots can be surgically removed or drained in a minor office procedure performed by a surgeon.
5. What Are the Minimally Invasive Procedures for Hemorrhoids Treatment?
When conservative treatments aren’t enough, minimally invasive procedures can offer relief.
5.1. Rubber Band Ligation:
Rubber band ligation is the most common hemorrhoid treatment in the United States. A small elastic band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid, causing it to shrink. The surrounding tissue scars as it heals, holding the hemorrhoid in place.
5.1.1. Procedure and Complications:
It usually takes two to four procedures, done six to eight weeks apart, to eliminate the hemorrhoid completely. Complications are rare but can include mild pain, bleeding, and infection.
5.2. Other Office Procedures:
Other office procedures include laser or infrared coagulation, sclerotherapy, and cryosurgery. These work on the same principle as rubber band ligation but may not be as effective in preventing recurrence.
6. What Are the Surgical Options for Hemorrhoids Treatment?
If other treatments fail, surgery may be necessary.
6.1. Hemorrhoidectomy:
Hemorrhoidectomy involves making a narrow incision around both external and internal hemorrhoid tissue and removing the affected blood vessels. This procedure cures 95% of cases and has a low complication rate. It requires general anesthesia, but patients can usually go home the same day and return to work after 7–10 days.
6.2. Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy:
Stapled hemorrhoidopexy is an alternative to traditional hemorrhoidectomy. It treats bleeding or prolapsed internal hemorrhoids by using a stapling device to anchor the hemorrhoids in their normal position. Like traditional removal, this procedure is performed under general anesthesia as day surgery.
7. What Are the Frequently Asked Questions about Hemorrhoids? (FAQs)
To provide further clarity, here are some frequently asked questions about hemorrhoids:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What are the early signs of hemorrhoids? | Common early signs include itching, discomfort, and small amounts of bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl after a bowel movement. |
| Can diet changes really help with hemorrhoids? | Yes, increasing your fiber intake can soften stools, making them easier to pass and reducing pressure on hemorrhoids. Fiber-rich foods include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. |
| How often should I take a sitz bath for hemorrhoids? | Experts recommend taking a sitz bath for 20 minutes after each bowel movement and two to three times a day. |
| Are there any over-the-counter medications that can help? | Yes, over-the-counter hemorrhoid creams and suppositories containing ingredients like hydrocortisone or lidocaine can help relieve pain and itching. Witch hazel wipes (Tucks) are also soothing. |
| When should I see a doctor about my hemorrhoids? | You should see a doctor if you experience persistent bleeding, severe pain, or if home remedies do not provide relief. A doctor can rule out other potential causes of your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment options. |
| Can hemorrhoids lead to more serious problems? | Hemorrhoids are rarely dangerous, but chronic bleeding can lead to anemia. In rare cases, a thrombosed external hemorrhoid can cause severe pain. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience significant symptoms. |
| Is it possible to prevent hemorrhoids? | Yes, maintaining a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, avoiding straining during bowel movements, and exercising regularly can help prevent hemorrhoids. |
| Are hemorrhoids common during pregnancy? | Yes, hemorrhoids are common during pregnancy due to the increased pressure on the veins in the rectum and anus from the enlarging uterus. |
| What is rubber band ligation? | Rubber band ligation is a minimally invasive procedure where a small elastic band is placed around the base of a hemorrhoid to cut off its blood supply, causing it to shrink and eventually fall off. |
| Are there any long-term side effects of hemorrhoid surgery? | While rare, potential long-term side effects of hemorrhoid surgery can include changes in bowel habits, fecal incontinence, and anal stenosis (narrowing of the anal canal). It’s important to discuss the risks and benefits of surgery with your doctor. |

8. Search Intent for “What Causes Hemorrhoids?”
Understanding the search intent behind the query “What Causes Hemorrhoids” is crucial for providing relevant and valuable information. Here are five key search intents:
- Informational: Users want to understand the underlying causes and risk factors associated with hemorrhoids. They seek a comprehensive overview of the various factors that contribute to their development.
- Symptom-Related: Users are experiencing symptoms and want to determine if they are related to hemorrhoids. They are looking for information to help them identify the condition based on their symptoms.
- Treatment Options: Users want to learn about different treatment options for hemorrhoids, ranging from home remedies to medical procedures. They seek guidance on how to manage and alleviate their symptoms.
- Prevention Strategies: Users want to know how to prevent hemorrhoids from developing in the first place or recurring. They are looking for lifestyle changes and preventive measures they can take.
- Medical Advice: Users are seeking advice on when to see a doctor and what to expect during a medical evaluation for hemorrhoids. They want to understand the diagnostic process and potential medical interventions.
9. Why Choose WHAT.EDU.VN for Your Health Questions?
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of accessible and reliable health information. Navigating health concerns can be overwhelming, and finding trustworthy answers can be challenging. That’s why we’ve created a platform where you can ask any health-related question and receive prompt, accurate answers from experts. We’re committed to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to make informed decisions about your health.
9.1. The Benefits of Using WHAT.EDU.VN:
- Free Access: Get your health questions answered without any cost.
- Quick Responses: Receive timely answers to your urgent health inquiries.
- Expert Information: Benefit from expert-reviewed health content.
- Community Support: Connect with others and share your health experiences.
- Easy to Use: Our platform is designed for ease of use.
9.2. Don’t Wait, Ask Your Questions Today
Do you have more questions about hemorrhoids or other health concerns? Don’t hesitate to reach out to us at WHAT.EDU.VN. We’re here to provide you with the answers you need to take control of your health. Our team of experts is ready to address your questions promptly and accurately.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Don’t let unanswered questions keep you in the dark. Visit what.edu.vn today and get the information you need to live a healthier, more informed life. We’re here to support you every step of the way.