Are you wondering What Colors Make Brown? This guide from WHAT.EDU.VN will show you various ways to achieve this versatile hue, expanding your artistic possibilities. Discover the color combinations that create brown and learn how to adjust the shade to suit your needs. Explore color theory and mixing techniques for brown shades.
1. Understanding the Color Brown
While often considered a basic color, brown is more complex than it appears. Unlike primary colors like red, yellow, or blue, brown is a composite color, meaning it’s created by mixing other colors.
1.1. Brown on the Color Wheel: A Deeper Look
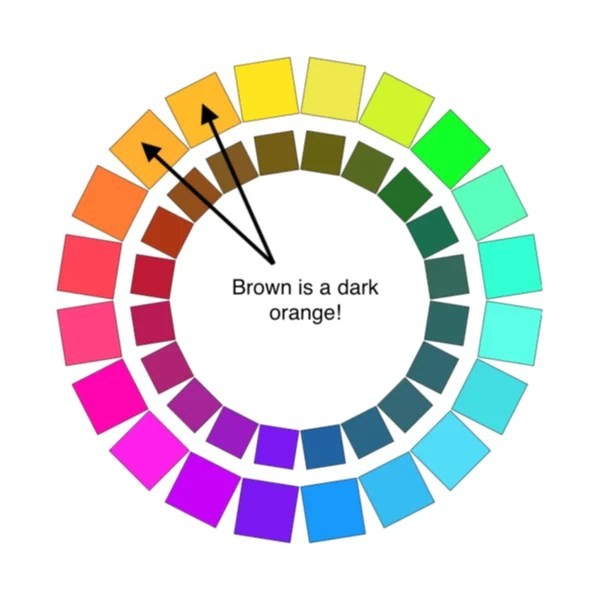
The standard color wheel, showcasing saturated hues, doesn’t explicitly feature brown. However, brown is present as a less saturated version of orange.
1.2. Brown as Dark Orange
Brown is essentially a darkened shade of orange. This understanding is crucial for effectively mixing brown.
2. Basic Color Combinations for Brown
Several color combinations can produce brown. Here are some common methods:
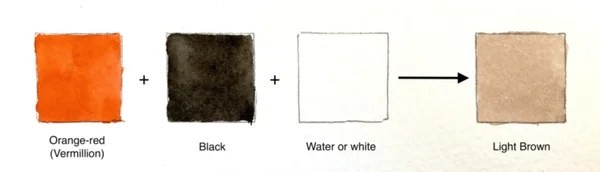
2.1. Orange and Black
Mixing orange and black is a straightforward way to create brown. The black darkens the orange, resulting in a brown hue.
2.2. Red, Yellow, and Black
Since red and yellow make orange, adding black to this combination also results in brown.
3. Complementary Color Combinations for Brown
Using complementary colors (colors opposite each other on the color wheel) is another effective method for creating brown.
3.1. Red, Yellow, and Blue
This is a classic method. Red and yellow create orange, and adding blue (the complement of orange) neutralizes the orange into brown.
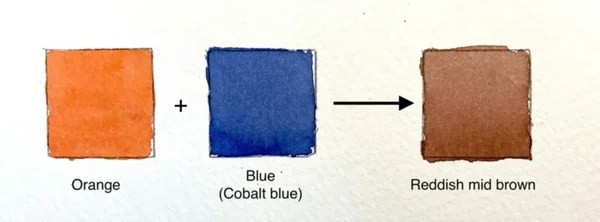
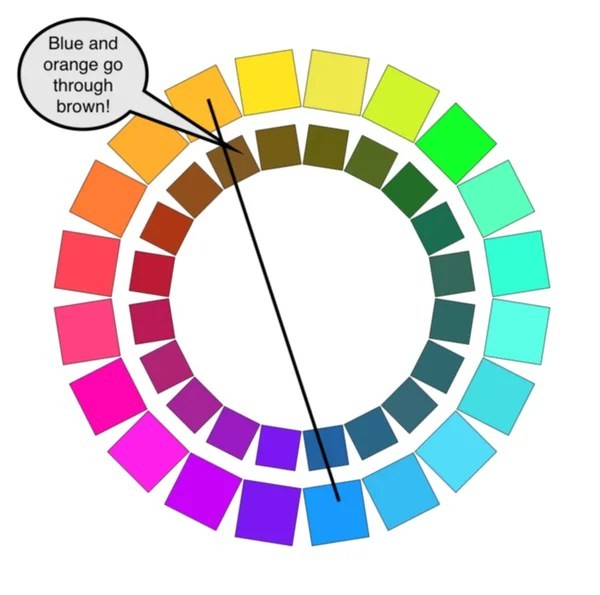
3.2. Orange and Blue
Directly mixing orange and blue creates brown. The blue counteracts the orange, resulting in a brownish tone.
3.3. Red and Green
Red and green are complementary colors. Mixing them produces a muted brown.
3.4. Yellow and Purple
Although not directly opposite on the color wheel, yellow and purple can combine to create brown.
4. Exploring Different Shades of Brown
Once you understand the basic color combinations, you can experiment to create various shades of brown.
4.1. Creating Dark Brown
To make dark brown, add black to any of the base brown mixtures. Be cautious, as black can quickly overpower the mixture. Alternatively, use darker shades of blue like Payne’s gray to darken brown, this prevents the brown from becoming greyish.
4.2. Creating Light Brown
To achieve a light brown or tan color, add white to your base brown mixture. For watercolors, adding water will lighten the color.
4.3. Creating Gray-Browns
Gray-browns, also known as muted or low chroma browns, are essential for realistic paintings.
5. Color Properties: Hue, Value, and Chroma
Understanding hue, value, and chroma is crucial for fine-tuning your brown mixtures.
5.1. Hue
Hue is the pure color name, such as red, blue, or yellow.
5.2. Value
Value refers to the lightness or darkness of a color, ranging from 0 (black) to 10 (white).
5.3. Chroma
Chroma describes the intensity or saturation of a color. High chroma colors are bright and vivid, while low chroma colors are muted or grayed.
6. The Importance of Low Chroma Colors
Low chroma colors are prevalent in nature and essential for creating realistic and harmonious paintings.
6.1. Mixing Low Chroma Browns
To create low chroma browns, you can either add gray to your brown mixture or use complementary colors to neutralize the intensity.
7. Avoiding Over-Reliance on High Chroma Paints
Many commercially available paints are high chroma, which can be too intense for certain applications. Learning to adjust chroma is crucial for achieving realistic colors.
8. Why You Can’t Mix Higher Chroma Colors
It’s important to note that you cannot create a higher chroma color by mixing two lower chroma colors. This is why certain pigments with high chroma are so valuable.
9. Techniques for Lowering Chroma
Lowering chroma, or muting a color, can be achieved through several methods:
9.1. Using Complementary Colors
Adding a color’s complement can lower its chroma. However, this method requires careful control to avoid shifting the hue too much.
9.2. Adding Black or Gray
Adding black or gray is a more direct way to lower chroma. This method allows for precise control over the level of muting.
10. Debunking the Myths of Primary Colors
Traditional color theory often emphasizes red, yellow, and blue as primary colors. However, understanding color as combinations of wavelengths allows for more flexibility in color mixing.
11. Exploring the Versatility of Brown
Brown is a versatile color with a wide range of applications in art, design, and everyday life. By understanding the principles of color mixing and the properties of hue, value, and chroma, you can unlock the full potential of brown and create stunning visual effects. Whether you’re painting a landscape, designing a website, or simply choosing an outfit, mastering the art of mixing brown will enhance your creative endeavors.
12. Mastering Brown: A Summary of Color Combinations
To recap, here’s a quick rundown of the color combinations that make brown:
- Orange and Black
- Red, Yellow, and Black
- Red, Yellow, and Blue
- Orange and Blue
- Red and Green
- Yellow and Purple
13. The Art of Fine-Tuning Your Brown
The journey of creating the perfect brown doesn’t end with just knowing the right color combinations. It’s about mastering the art of fine-tuning. Every color you add will have an impact on the final shade, so understanding how each color interacts is crucial.
13.1. Balancing Warmth and Coolness
Browns can lean towards the warmer side (reddish-browns) or the cooler side (grayish-browns). Adding a touch of red or yellow will create a warmer brown, while adding blue or green will create a cooler brown.
- Warm Browns: Incorporate more red or yellow.
- Cool Browns: Introduce blue or green.
13.2. The Impact of Pigment Quality
The quality of your pigments will also influence the outcome. High-quality pigments have a higher concentration of color and will mix more predictably. Investing in artist-grade paints can make a significant difference in the vibrancy and longevity of your brown mixtures.
13.3. Experimenting with Glazes
For advanced techniques, consider using glazes. A glaze is a transparent layer of color applied over a dried base. This technique can add depth and complexity to your browns, especially in oil painting.
13.4. Digital Color Mixing
In the digital realm, color mixing takes on a new dimension. Software like Adobe Photoshop or Procreate allows you to experiment with colors endlessly without wasting physical materials. Understanding the RGB and CMYK color models will further enhance your digital color mixing skills.
- RGB (Red, Green, Blue): Used for digital displays.
- CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black): Used for printing.
14. The Psychological Impact of Brown
Brown is more than just a color; it’s a carrier of emotions and associations. Understanding the psychology of color can help you use brown more effectively in your work.
14.1. Brown and Nature
Brown is often associated with nature, earth, and wood. It can evoke feelings of warmth, comfort, and security. This makes it an excellent choice for designs that aim to create a sense of groundedness and reliability.
14.2. Cultural Significance
In some cultures, brown represents humility and simplicity. In others, it can be associated with sophistication and elegance. Being aware of these cultural nuances can prevent unintended messages in your designs.
14.3. Use in Branding
Many brands use brown to convey a sense of authenticity and trustworthiness. For example, coffee brands often use brown to evoke the natural, earthy qualities of their product.
15. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even seasoned artists can make mistakes when mixing brown. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
15.1. Overmixing
Overmixing can muddy your colors, especially with acrylics. Mix only until the colors are just combined.
15.2. Using Too Much Black
Black can quickly dominate a mixture and make it look dull. Use it sparingly and consider using a dark blue instead.
15.3. Ignoring the Subtleties
Don’t underestimate the subtleties of color mixing. Small adjustments can make a big difference. Always mix in small increments and check your color frequently.
16. Brown in Different Mediums
The behavior of colors can vary depending on the medium you’re using. Here’s how to approach brown in different mediums:
16.1. Oil Paints
Oil paints offer a rich, buttery texture and allow for a long working time. They are excellent for creating layered effects and subtle gradations of color.
16.2. Acrylic Paints
Acrylics are fast-drying and versatile. They can be thinned with water for watercolor-like effects or used straight from the tube for bold, opaque applications.
16.3. Watercolors
Watercolors are transparent and luminous. They are ideal for creating delicate washes and subtle color blends.
16.4. Digital Painting
Digital painting offers unparalleled flexibility and control. It allows you to experiment with colors and effects without the constraints of traditional mediums.
17. Inspiration and Practice
The best way to master the art of mixing brown is through inspiration and practice. Look around you and observe the different shades of brown in nature, art, and design. Then, grab your paints or stylus and start experimenting.
17.1. Nature as a Guide
Nature is an endless source of inspiration. Observe the colors of tree bark, soil, rocks, and leaves. Try to replicate these colors in your paintings.
17.2. Master Studies
Studying the works of master artists can provide valuable insights into their color mixing techniques. Choose a painting with a prominent use of brown and try to recreate the colors.
17.3. Practice Exercises
Set up practice exercises to improve your color mixing skills. For example, try to mix ten different shades of brown using the same two base colors.
18. The Future of Color Mixing
As technology advances, so too does the art of color mixing. New tools and techniques are emerging that promise to revolutionize the way we create and manipulate color.
18.1. AI-Powered Color Tools
AI-powered color tools can analyze images and suggest color palettes, making it easier to find harmonious color combinations.
18.2. Interactive Color Wheels
Interactive color wheels allow you to explore color relationships in a dynamic and intuitive way.
18.3. Virtual Reality Painting
Virtual reality painting offers an immersive and interactive way to create art. It allows you to paint in a three-dimensional space and experiment with colors and effects in a whole new way.
19. Testimonials and Success Stories
Many artists have transformed their work by mastering the art of color mixing. Here are a few testimonials and success stories:
- “I used to struggle with mixing realistic skin tones until I learned how to mix brown properly. Now my portraits have a depth and realism that I never thought possible.” – Sarah J.
- “As a graphic designer, understanding color mixing has helped me create more effective and visually appealing designs. I can now communicate the right message with my color choices.” – Mark L.
20. Call to Action: Start Mixing Brown Today
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of what colors make brown, it’s time to put your knowledge into practice. Whether you’re a painter, designer, or just someone who loves to experiment with color, mastering the art of mixing brown will open up a world of creative possibilities.
Ready to take your color mixing skills to the next level? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN to ask any questions you have and receive free answers from our experts. Our platform provides a convenient and accessible way to get the information you need, connect with a community of like-minded individuals, and explore the endless possibilities of color.
Have questions? Contact us at:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Don’t let your curiosity wait—ask your question today and unlock a world of creative inspiration with what.edu.vn!
21. FAQs: Mastering the Art of Mixing Brown
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What are the most common colors used to create brown? | The most common colors used to create brown are red, yellow, and blue. These three colors can be mixed in different proportions to create a wide range of brown shades. Additionally, orange and blue, as well as red and green, can also be mixed to create brown. |
| How do I create a warm brown color? | To create a warm brown color, add more red or yellow to your base brown mixture. These colors will give the brown a warmer, more inviting tone. Experiment with different ratios to achieve the desired level of warmth. |
| What is the best way to make a cool brown color? | To create a cool brown color, add more blue or green to your base brown mixture. These colors will give the brown a cooler, more subdued tone. Be careful not to add too much blue or green, as this can quickly turn the brown into a muddy color. |
| Can I use black to darken brown? | Yes, you can use black to darken brown. However, use black sparingly, as it can quickly overpower the mixture and make it look dull. If you want to darken brown without using black, try adding a small amount of dark blue or purple instead. |
| How do I make brown lighter? | To make brown lighter, add white to your base brown mixture. Be careful not to add too much white, as this can wash out the color and make it look chalky. If you are working with watercolors, you can also add water to lighten the color. |
| What is chroma, and how does it affect brown? | Chroma refers to the intensity or saturation of a color. High chroma colors are bright and vivid, while low chroma colors are muted or grayed. To create a low chroma brown, add gray to your base brown mixture. You can also use complementary colors (colors opposite each other on the color wheel) to neutralize the intensity of the brown. |
| How can I create different textures with brown? | There are many ways to create different textures with brown. You can use different brushes, sponges, or other tools to apply the paint in different ways. You can also add sand, sawdust, or other materials to the paint to create a rougher texture. Additionally, you can use layering techniques to create depth and complexity in your textures. |
| Is brown a primary, secondary, or tertiary color? | Brown is neither a primary nor a secondary color. It is a tertiary color, which means it is made by mixing a primary color (red, yellow, or blue) with a secondary color (green, orange, or purple). Specifically, brown is often made by mixing all three primary colors together. |
| What are some common mistakes to avoid when mixing brown? | Some common mistakes to avoid when mixing brown include: Overmixing (which can muddy the colors), using too much black (which can make the color look dull), and ignoring the subtleties of color mixing (small adjustments can make a big difference). Always mix in small increments and check your color frequently to avoid these mistakes. |
| How does the medium I’m using affect the outcome of brown? | The behavior of colors can vary depending on the medium you’re using. For example, oil paints offer a rich, buttery texture and allow for a long working time, while acrylics are fast-drying and versatile. Watercolors are transparent and luminous, while digital painting offers unparalleled flexibility and control. |


22. Advanced Techniques in Mixing Brown
Elevate your artistry with these advanced methods for brown color mixing, refining your skills and achieving unparalleled depth and realism in your work.
22.1. Layering and Glazing Techniques
Master the use of layering and glazing to add complex dimensions to your brown hues. Layering involves applying opaque coats, while glazing uses transparent layers to subtly modify the underlying colors.
22.2. Subtractive Color Mixing
Employ the subtractive color mixing technique to refine your brown shades with precision. By sequentially subtracting color elements, you can craft sophisticated browns that add depth and sophistication to your artworks.
22.3. Mastering Color Temperature
Improve your understanding of how color temperature influences the emotional impact of your browns. By finely adjusting the balance of warm and cool tones, you can create browns that are uniquely suited to your artistic goals.
22.4. Incorporating Complementary Accents
Enhance your brown color schemes by strategically incorporating complementary color accents. These additions can create eye-catching contrasts and significantly enrich the overall visual harmony of your piece.
23. Elevate Your Brown: Essential Mixing Tips
Employ these essential tips to ensure your brown shades are not only beautiful but also lasting, avoiding common pitfalls and maximizing the potential of your chosen medium.
23.1. Use High-Quality Pigments
Invest in artist-grade pigments to ensure the longevity and vibrancy of your browns, keeping them from fading or shifting over time.
23.2. Control Your Medium Consistency
Learn to manage the consistency of your paints to prevent overmixing and muddiness, which can dull your brown shades.
23.3. Conduct Swatch Tests
Always test your brown mixes on a separate swatch before applying them to your main piece, guaranteeing color accuracy and minimizing errors.
23.4. Document Your Mixing Ratios
Keep detailed records of your mixing ratios for future reference, allowing you to consistently reproduce your favorite brown shades without guesswork.
24. The Role of Brown in Art History
Explore how brown has been historically used across various artistic movements, recognizing its impact and mastering its use to add cultural and historical dimensions to your modern art.
24.1. Brown in Renaissance Art
Understand how Renaissance artists like Leonardo da Vinci used brown to create realistic shadows and depth, bringing realism to their iconic works.
24.2. Brown in Baroque Period
Study the dramatic use of brown in Baroque art to enhance emotional intensity, notably in the works of Rembrandt, who used it to create stark contrasts.
24.3. Brown in Impressionism
Discover how Impressionists redefined the use of brown by blending it with brighter colors to capture natural light, broadening its use from mere shading to color enhancement.
24.4. Brown in Contemporary Art
Explore modern applications of brown in contemporary art, where it symbolizes urban decay or natural harmony, deepening your understanding of its cultural significance.
25. Community Insights: Share Your Brown Creations
Engage with other artists and enrich your practice by sharing your own brown creations, gaining feedback, and discovering innovative techniques in a collaborative environment.
25.1. Online Platforms
Use platforms such as Instagram, Pinterest, and Behance to showcase your brown-themed artworks, connecting with fellow artists and art enthusiasts.
25.2. Local Art Groups
Join local art associations to display your work and get direct feedback from fellow creators, enhancing your skills and building a local network.
25.3. Art Workshops
Attend art workshops to deepen your understanding of brown mixing techniques, engage in real-time collaborations, and broaden your artistic skills.
25.4. Competitions
Participate in local and global art competitions to gain recognition for your work, motivating you to continually refine your use of brown in innovative ways.
