A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, essentially creates a secure tunnel for your internet traffic, shielding your online activity and location, as seen on WHAT.EDU.VN. It protects your data from prying eyes while granting access to geo-restricted content. Discover how VPNs enhance your online security, privacy, and freedom with features like IP address masking and encrypted browsing.
1. Understanding the Fundamentals: What Does a VPN Do?
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, establishes a secure and encrypted connection over a less secure network, like the public internet. Think of it as a private tunnel for your internet traffic, ensuring confidentiality and security.
1.1 How a VPN Works: A Simplified Explanation
When you connect to the internet through a VPN, your device first connects to a VPN server. All your internet traffic is then routed through this encrypted tunnel. This masks your actual IP address with the VPN server’s IP address, making it appear as if you are browsing from the location of the VPN server.
- Encryption: The VPN encrypts your data, scrambling it to prevent unauthorized access.
- IP Address Masking: Hides your real IP address, protecting your location and identity.
- Secure Tunnel: Creates a private connection between your device and the internet.
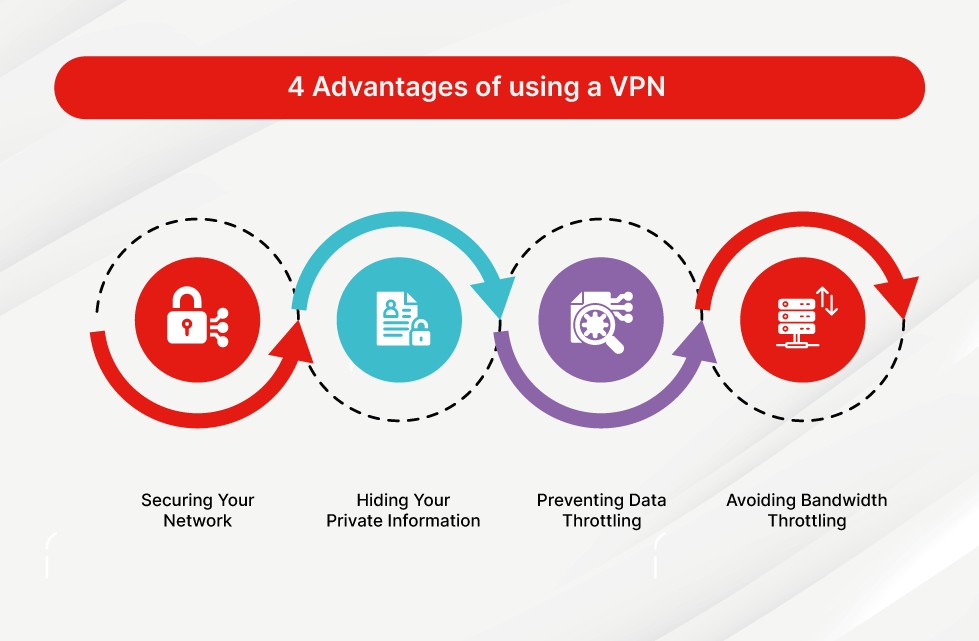 VPN tunnel ensures secure data transfer with IP address masking and encryption
VPN tunnel ensures secure data transfer with IP address masking and encryption
1.2 VPN Protocols: The Backbone of Secure Connections
VPN protocols are the methods used to establish a secure connection between your device and the VPN server. Different protocols offer varying levels of security, speed, and reliability.
- OpenVPN: A popular open-source protocol known for its strong security and flexibility.
- IKEv2/IPsec: A fast and secure protocol often used on mobile devices due to its stability.
- WireGuard: A modern protocol designed for speed and simplicity, offering excellent performance.
- L2TP/IPsec: An older protocol that’s generally considered less secure than OpenVPN or IKEv2.
- PPTP: A very old protocol with weak security and should be avoided.
1.3 Key Components of a VPN Connection
A VPN connection involves several essential components that work together to ensure a secure and private online experience.
- VPN Client: The software or app installed on your device that connects to the VPN server.
- VPN Server: The server that acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet.
- Encryption Algorithm: The algorithm used to encrypt and decrypt your data.
- Authentication Protocol: The method used to verify your identity and authorize your connection to the VPN server.
2. Why Use a VPN? Exploring the Core Benefits
A VPN offers numerous benefits, enhancing your online security, privacy, and overall internet experience. Let’s delve into some of the most compelling reasons to use a VPN.
2.1 Enhancing Online Security
One of the primary reasons people use VPNs is to enhance their online security, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks, which are often unsecured and vulnerable to cyber threats.
2.1.1 Securing Public Wi-Fi Connections
Public Wi-Fi networks are convenient but often lack proper security measures, making them a hunting ground for hackers. A VPN encrypts your data, protecting it from being intercepted by malicious actors.
- Encryption: Encrypts your data to prevent eavesdropping.
- Protection from Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Prevents attackers from intercepting and altering your data.
- Hiding Sensitive Information: Keeps your passwords, financial information, and other sensitive data safe.
2.1.2 Protecting Against Data Breaches
Data breaches are becoming increasingly common, exposing sensitive information to cybercriminals. A VPN can help protect your data by encrypting it, making it more difficult for hackers to access and use.
- Encryption: Encrypts your data to prevent unauthorized access.
- IP Address Masking: Hides your real IP address to protect your identity.
- Secure Connection: Creates a private tunnel for your internet traffic.
2.2 Protecting Your Online Privacy
In today’s digital age, online privacy is a growing concern. VPNs help protect your privacy by masking your IP address and encrypting your internet traffic, preventing websites, ISPs, and government agencies from tracking your online activities.
2.2.1 Masking Your IP Address
Your IP address is a unique identifier that can be used to track your location and online activities. A VPN masks your real IP address with the VPN server’s IP address, making it more difficult to track you.
- Hiding Your Location: Prevents websites and services from determining your exact location.
- Protecting Your Identity: Makes it more difficult for advertisers and trackers to identify you.
- Anonymous Browsing: Allows you to browse the internet without being tracked.
2.2.2 Preventing ISP Tracking
ISPs (Internet Service Providers) can track your online activities and sell your data to advertisers. A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, preventing your ISP from seeing what you are doing online.
- Encryption: Encrypts your data to prevent ISP tracking.
- Bypassing Throttling: Prevents ISPs from throttling your bandwidth based on your online activities.
- Maintaining Net Neutrality: Ensures that all internet traffic is treated equally.
2.3 Accessing Geo-Restricted Content
Many websites and streaming services restrict access to content based on your location. A VPN allows you to bypass these restrictions by connecting to a server in a different country, making it appear as if you are browsing from that location.
2.3.1 Streaming Services
Streaming services like Netflix, Hulu, and BBC iPlayer offer different content libraries in different countries. A VPN allows you to access content that is not available in your region.
- Accessing Netflix Libraries: Unlock different Netflix libraries from around the world.
- Watching BBC iPlayer: Watch BBC iPlayer content from outside the UK.
- Streaming Sports Events: Access geo-restricted sports events and tournaments.
2.3.2 Bypassing Censorship
In some countries, governments censor the internet, blocking access to certain websites and social media platforms. A VPN allows you to bypass censorship and access blocked content.
- Accessing Social Media: Access blocked social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube.
- Reading News Websites: Access news websites that are blocked in your country.
- Bypassing Government Censorship: Circumvent government censorship and access a free and open internet.
3. Choosing the Right VPN: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right VPN is crucial for ensuring optimal security, privacy, and performance. Consider these factors when choosing a VPN provider.
3.1 Security Features
Security should be your top priority when choosing a VPN. Look for VPNs that offer strong encryption, a variety of security protocols, and additional security features like a kill switch and DNS leak protection.
- Encryption: Ensure the VPN uses strong encryption standards like AES-256.
- Security Protocols: Look for support for secure protocols like OpenVPN, IKEv2, and WireGuard.
- Kill Switch: A kill switch automatically disconnects your internet connection if the VPN connection drops, preventing data leaks.
- DNS Leak Protection: Prevents your DNS requests from being exposed to your ISP.
3.2 Privacy Policy
Read the VPN provider’s privacy policy carefully to understand how they handle your data. Choose a VPN that has a strict no-logs policy, meaning they do not collect or store any information about your online activities.
- No-Logs Policy: Ensure the VPN provider does not log your browsing history, IP address, or other personal information.
- Jurisdiction: Consider the VPN provider’s jurisdiction, as this can affect their legal obligations regarding data retention and disclosure.
- Transparency: Look for VPN providers that are transparent about their privacy practices.
3.3 Speed and Performance
A VPN can impact your internet speed, so it’s important to choose a VPN that offers fast and reliable connections. Look for VPNs with a large server network and optimized servers.
- Server Network: Choose a VPN with a large server network to ensure fast and reliable connections.
- Server Locations: Look for servers in locations that are close to you to minimize latency.
- Optimized Servers: Some VPNs offer optimized servers for streaming, gaming, or other specific activities.
3.4 Cost and Subscription Plans
VPN prices vary depending on the provider and the subscription plan you choose. Consider your budget and the features you need when selecting a VPN.
- Free VPNs: Free VPNs often have limited features, slower speeds, and may collect your data.
- Paid VPNs: Paid VPNs offer better security, faster speeds, and more features.
- Subscription Plans: Choose a subscription plan that fits your needs and budget.
4. Setting Up and Using a VPN: A Step-by-Step Guide
Setting up and using a VPN is a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide to get you started.
4.1 Choosing a VPN Provider
Research and compare different VPN providers based on the factors mentioned above, such as security features, privacy policy, speed, and cost.
4.2 Downloading and Installing the VPN Client
Once you have chosen a VPN provider, download the VPN client from their website and install it on your device.
4.3 Connecting to a VPN Server
Open the VPN client and log in with your account credentials. Choose a server location and connect to the VPN server.
4.4 Verifying Your Connection
Once connected, verify that your IP address has been changed and that your internet traffic is being encrypted. You can use online tools to check your IP address and DNS leak status.
5. Common Use Cases for VPNs: Real-World Applications
VPNs have a wide range of use cases, from protecting your privacy to accessing geo-restricted content. Here are some common scenarios where using a VPN can be beneficial.
5.1 Remote Work
Many companies use VPNs to provide secure access to their internal networks for remote employees. A VPN ensures that sensitive data is protected when accessed from outside the office.
- Secure Access to Company Resources: Allows remote employees to securely access company files, applications, and other resources.
- Encryption: Encrypts data transmitted between the remote worker’s device and the company network.
- Compliance: Helps companies comply with data security regulations.
5.2 Online Gaming
Gamers use VPNs to reduce latency, bypass geo-restrictions, and protect themselves from DDoS attacks.
- Lower Latency: Connect to game servers through a VPN to reduce latency and improve gameplay.
- Bypass Geo-Restrictions: Access games that are not available in your region.
- DDoS Protection: Protect yourself from DDoS attacks by masking your IP address.
5.3 Torrenting
Torrenting is a popular way to share files, but it can also expose your IP address to copyright holders. A VPN can help protect your privacy when torrenting by masking your IP address and encrypting your internet traffic.
- Privacy Protection: Hides your IP address to prevent copyright holders from tracking your downloads.
- Encryption: Encrypts your internet traffic to prevent your ISP from monitoring your torrenting activity.
- Legal Considerations: Be aware of the legal implications of torrenting copyrighted material in your country.
6. Addressing Common Concerns and Misconceptions
Despite their numerous benefits, VPNs are often surrounded by misconceptions. Let’s address some common concerns and set the record straight.
6.1 VPNs Are Only for Illegal Activities
This is a common misconception. While VPNs can be used for illegal activities, they are also used by millions of people for legitimate purposes, such as protecting their privacy, accessing geo-restricted content, and securing their internet connection on public Wi-Fi.
6.2 VPNs Make You Completely Anonymous
VPNs enhance your privacy but do not make you completely anonymous. Websites can still track you using cookies, browser fingerprinting, and other techniques. To achieve true anonymity, you need to use a combination of tools, such as a VPN, Tor browser, and privacy-focused browser extensions.
6.3 All VPNs Are the Same
Not all VPNs are created equal. Some VPNs offer better security, faster speeds, and more features than others. It’s important to research and compare different VPN providers before choosing one.
7. VPN Alternatives: Exploring Other Privacy Tools
While VPNs are a valuable tool for enhancing online privacy and security, they are not the only option. Here are some alternatives to consider.
7.1 Tor Browser
Tor is a free and open-source browser that anonymizes your internet traffic by routing it through a network of relays. Tor provides a high level of anonymity but can be slower than a VPN.
7.2 Proxy Servers
Proxy servers act as intermediaries between your device and the internet, similar to VPNs. However, proxy servers typically do not encrypt your internet traffic, making them less secure than VPNs.
7.3 Privacy-Focused Browsers
Privacy-focused browsers like Brave and Firefox Focus offer built-in privacy features, such as ad blocking, tracker blocking, and HTTPS Everywhere.
8. The Future of VPNs: Trends and Predictions
The VPN market is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging all the time. Here are some predictions for the future of VPNs.
8.1 Increased Integration with Security Software
VPNs are likely to become more integrated with other security software, such as antivirus programs and firewalls, to provide a more comprehensive security solution.
8.2 More Focus on User Experience
VPN providers will continue to focus on improving the user experience, making VPNs easier to use and more accessible to a wider audience.
8.3 Rise of Decentralized VPNs
Decentralized VPNs, which use blockchain technology to create a peer-to-peer VPN network, are likely to become more popular in the future.
9. Maximizing Your VPN Experience: Tips and Tricks
To get the most out of your VPN, here are some tips and tricks to keep in mind.
9.1 Choose the Right Server Location
Choose a server location that is close to your actual location to minimize latency and improve speed.
9.2 Use a Strong Password
Use a strong and unique password for your VPN account to prevent unauthorized access.
9.3 Enable the Kill Switch
Enable the kill switch in your VPN client to prevent data leaks if the VPN connection drops.
9.4 Update Your VPN Software Regularly
Keep your VPN software up to date to ensure that you have the latest security patches and features.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About VPNs
Here are some frequently asked questions about VPNs.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is a VPN? | A VPN (Virtual Private Network) creates a secure, encrypted connection over a less secure network, like the internet. |
| Is using a VPN legal? | Yes, using a VPN is legal in most countries. However, some countries restrict or ban VPN usage. |
| Does a VPN slow down my internet speed? | A VPN can slow down your internet speed due to the encryption process and the distance between your device and the VPN server. However, a good VPN will minimize the impact on your speed. |
| Can a VPN protect me from malware? | A VPN can protect you from some types of malware by encrypting your internet traffic and preventing malicious actors from intercepting your data. However, a VPN is not a substitute for antivirus software. |
| How do I choose the best VPN? | Consider factors such as security features, privacy policy, speed, server network, and cost when choosing a VPN. |
| Can I use a VPN on my mobile device? | Yes, most VPN providers offer VPN clients for mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. |
| Does a VPN hide my online activity from the government? | A VPN can make it more difficult for the government to track your online activity, but it does not guarantee complete anonymity. |
| Is a free VPN as good as a paid VPN? | Free VPNs often have limited features, slower speeds, and may collect your data. Paid VPNs offer better security, faster speeds, and more features. |
| Can I use a VPN for streaming? | Yes, a VPN can be used to access geo-restricted streaming content. |
| Does a VPN protect me from all cyber threats? | A VPN enhances your online security but does not protect you from all cyber threats. You should still use strong passwords, be careful about clicking on suspicious links, and use antivirus software. |
Do you have more questions? Head over to WHAT.EDU.VN and ask away! Our community is ready to provide you with fast, accurate, and free answers to all your burning questions. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Visit what.edu.vn today and experience the convenience of having your questions answered for free.