Are you puzzled by the term KPI and its significance in business? What Does Kpi Stand For? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we demystify key performance indicators (KPIs), explaining their meaning, application, and benefits with crystal clarity. Discover how KPIs drive success and achieve strategic goals with performance metrics and measurement tools.
1. Understanding the Fundamentals: What Does KPI Mean?
KPI stands for Key Performance Indicator. These are measurable values that demonstrate how effectively a company is achieving key business objectives. KPIs are used to evaluate success at reaching targets.
1.1 The Essential Role of KPIs
KPIs play a critical role in helping businesses:
- Measure Progress: Track progress toward specific goals.
- Improve Performance: Identify areas where improvement is needed.
- Make Informed Decisions: Make data-driven decisions based on performance insights.
- Align Efforts: Ensure all teams are working toward the same objectives.
- Drive Accountability: Establish accountability for achieving results.
1.2 The Origin of the KPI Concept
The concept of KPIs emerged from the need for businesses to quantify their performance and make informed decisions. The exact origin is hard to pinpoint, but it evolved alongside the development of management theories and business analytics. The rise of data-driven decision-making in the late 20th century solidified the use of KPIs as a standard business practice.
2. Why Are KPIs Important?
KPIs are important because they provide a clear and objective way to measure performance, track progress, and make informed decisions. Without KPIs, businesses may struggle to understand whether they are on track to meet their goals.
2.1 Benefits of Using KPIs
Using KPIs offers several benefits:
- Clarity: KPIs provide a clear understanding of what success looks like.
- Focus: KPIs help teams focus on the most important goals.
- Accountability: KPIs create accountability for achieving results.
- Motivation: KPIs can motivate teams to improve performance.
- Improvement: KPIs help identify areas where improvement is needed.
2.2 How KPIs Drive Business Success
KPIs drive business success by:
- Enabling Data-Driven Decision Making: Decisions are based on facts, not guesses.
- Enhancing Operational Efficiency: Processes are optimized to achieve better results.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction: Efforts are focused on meeting customer needs.
- Increasing Profitability: Resources are allocated to the most profitable activities.
- Gaining Competitive Advantage: Performance is continuously monitored and improved.
3. Different Types of KPIs
KPIs can be categorized in different ways, depending on the focus and scope. Here are some common types:
3.1 Financial KPIs
Financial KPIs measure the financial performance of a business. They help in evaluating profitability, revenue, and financial stability.
Examples of Financial KPIs:
- Revenue Growth: Measures the increase in revenue over a period.
- Gross Profit Margin: Measures the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold.
- Net Profit Margin: Measures the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting all expenses.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Measures the profitability of an investment.
- Cash Flow: Measures the movement of cash in and out of the business.
3.2 Sales KPIs
Sales KPIs measure the effectiveness of a sales team in generating revenue. They help in tracking leads, conversions, and sales volume.
Examples of Sales KPIs:
- Sales Revenue: Total revenue generated from sales.
- Sales Growth: Increase in sales revenue over a period.
- Conversion Rate: Percentage of leads that convert into customers.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Cost of acquiring a new customer.
- Average Deal Size: Average value of each sales deal.
3.3 Marketing KPIs
Marketing KPIs measure the effectiveness of marketing campaigns in generating leads and driving sales. They help in tracking website traffic, conversion rates, and customer engagement.
Examples of Marketing KPIs:
- Website Traffic: Number of visitors to a website.
- Lead Generation: Number of leads generated through marketing efforts.
- Conversion Rate: Percentage of leads that convert into customers.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Percentage of people who click on an ad.
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): Cost of acquiring a customer through marketing.
3.4 Customer Service KPIs
Customer Service KPIs measure the quality of customer service and customer satisfaction. They help in tracking response times, resolution rates, and customer feedback.
Examples of Customer Service KPIs:
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Measures customer satisfaction with a product or service.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measures customer loyalty and likelihood to recommend.
- First Contact Resolution (FCR): Percentage of issues resolved on the first contact.
- Average Response Time: Average time taken to respond to customer inquiries.
- Customer Retention Rate: Percentage of customers retained over a period.
3.5 Operational KPIs
Operational KPIs measure the efficiency and effectiveness of business operations. They help in tracking production, inventory, and quality control.
Examples of Operational KPIs:
- Production Volume: Number of units produced in a period.
- Inventory Turnover: Rate at which inventory is sold and replaced.
- Defect Rate: Percentage of products that are defective.
- On-Time Delivery: Percentage of orders delivered on time.
- Downtime: Amount of time equipment is out of service.
4. How to Choose the Right KPIs
Choosing the right KPIs is crucial for tracking performance and achieving goals. Here are some steps to help you select the most relevant KPIs for your business:
4.1 Align KPIs with Business Objectives
KPIs should align with your overall business objectives. Identify what you want to achieve and select KPIs that measure progress toward those goals.
Example:
- Business Objective: Increase revenue by 20% in the next year.
- Relevant KPI: Sales Revenue Growth
4.2 Use the SMART Framework
The SMART framework helps ensure that KPIs are well-defined and achievable. SMART stands for:
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to measure.
- Measurable: Ensure the KPI can be quantified.
- Achievable: Set realistic targets that can be reached.
- Relevant: Ensure the KPI is relevant to your business objectives.
- Time-bound: Set a specific timeframe for achieving the target.
4.3 Balance Leading and Lagging Indicators
- Leading Indicators: Predict future performance (e.g., lead generation).
- Lagging Indicators: Measure past performance (e.g., sales revenue).
Balancing both types of indicators provides a comprehensive view of performance.
4.4 Involve Key Stakeholders
Involve key stakeholders in the KPI selection process. This ensures that everyone is aligned and that the KPIs are relevant to their roles and responsibilities.
4.5 Regularly Review and Update KPIs
Business conditions change, so KPIs should be regularly reviewed and updated to remain relevant. Remove KPIs that are no longer useful and add new ones as needed.
5. Examples of KPIs by Department
Different departments within a company will use different KPIs to measure their performance. Here are some examples of KPIs by department:
5.1 Finance KPIs
Finance managers track financial progress using various KPIs.
- Gross Profit Margin: Measures the profitability of products or services.
- Operating Profit Margin: Measures the profitability of core business operations.
- Net Profit Margin: Measures the overall profitability of the business.
- Operating Expense Ratio: Measures the efficiency of expense management.
- Working Capital Ratio: Measures the company’s ability to meet short-term obligations.
5.2 Sales KPIs
Sales teams use KPIs to ensure they are meeting sales targets.
- New Inbound Leads: Number of new leads generated.
- New Qualified Opportunities: Number of leads that are qualified as potential customers.
- Total Pipeline Value: Total value of potential sales deals in the pipeline.
- Sales Volume by Location: Sales revenue by geographic location.
- Average Order Value: Average value of each sales order.
5.3 Marketing KPIs
Marketing teams track their spending, conversion rates, and other indicators of marketing success.
- Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs): Leads that are likely to become customers based on marketing efforts.
- Sales Qualified Leads (SQLs): Leads that are ready to be contacted by the sales team.
- Conversion Rates (For Specific Goals): Percentage of people who complete a desired action.
- Social Program ROI (By Platform): Return on investment for social media marketing.
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): Revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising.
5.4 IT KPIs
IT teams use KPIs to keep accountable and alert them to potential issues.
- Total Support Tickets: Number of support tickets received.
- Open Support Tickets: Number of support tickets that are still open.
- Ticket Resolution Time: Average time taken to resolve a support ticket.
- Security Related Downtime: Amount of time the system is down due to security issues.
- IT Costs vs Revenue: Ratio of IT costs to revenue.
- Reopened Tickets: Number of tickets that are reopened after being resolved.
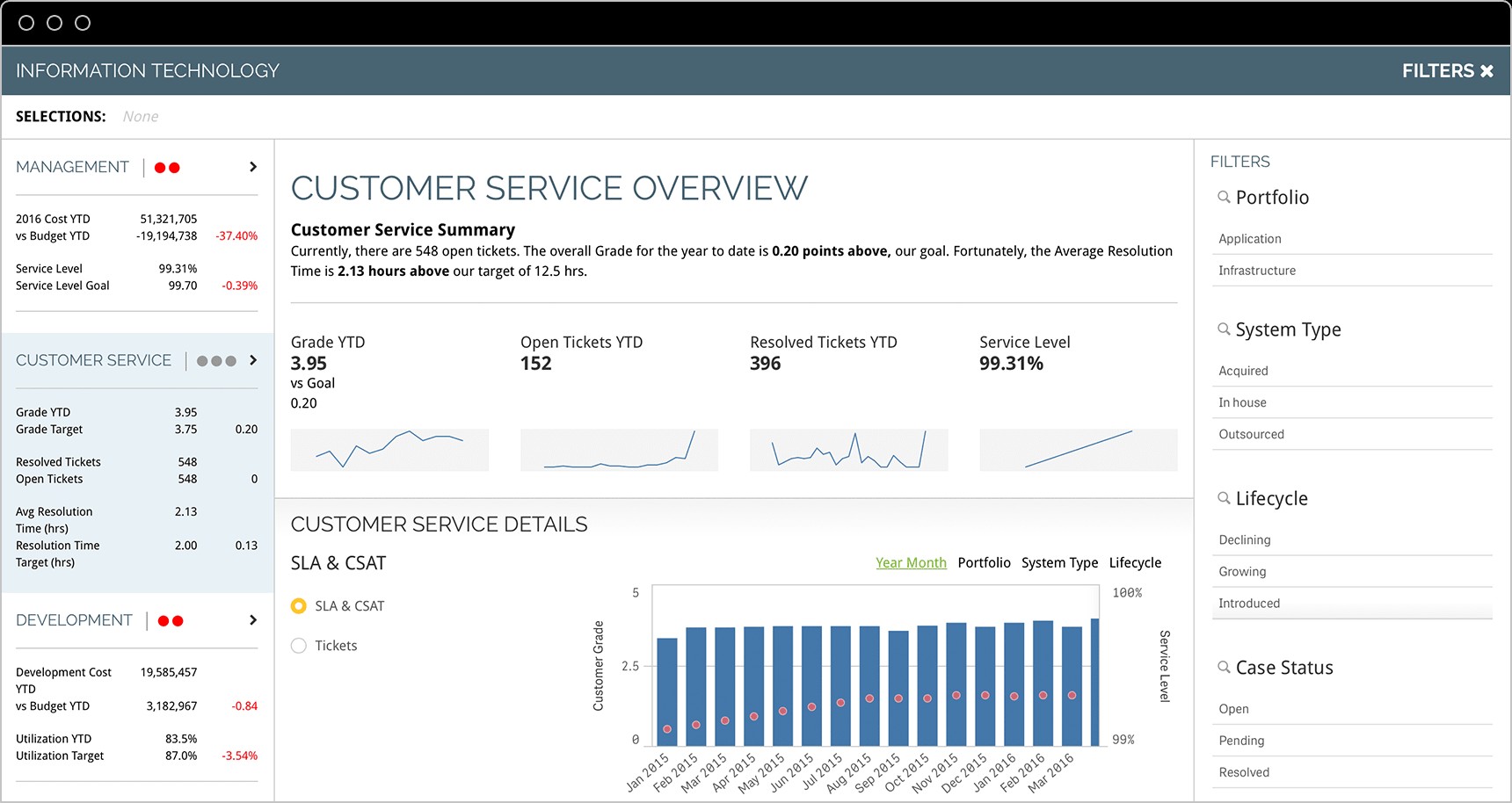
5.5 Customer Service KPIs
Customer service leaders track progress related to customers, employees, and finances.
- First Contact Resolution Rate: Percentage of issues resolved on the first contact.
- Average Response Time: Average time taken to respond to customer inquiries.
- Most Active Support Agents: Identification of the most productive support agents.
- Cost Per Conversation: Cost of each customer service interaction.
- Customer Effort Score: Measures the effort customers must expend to resolve an issue.
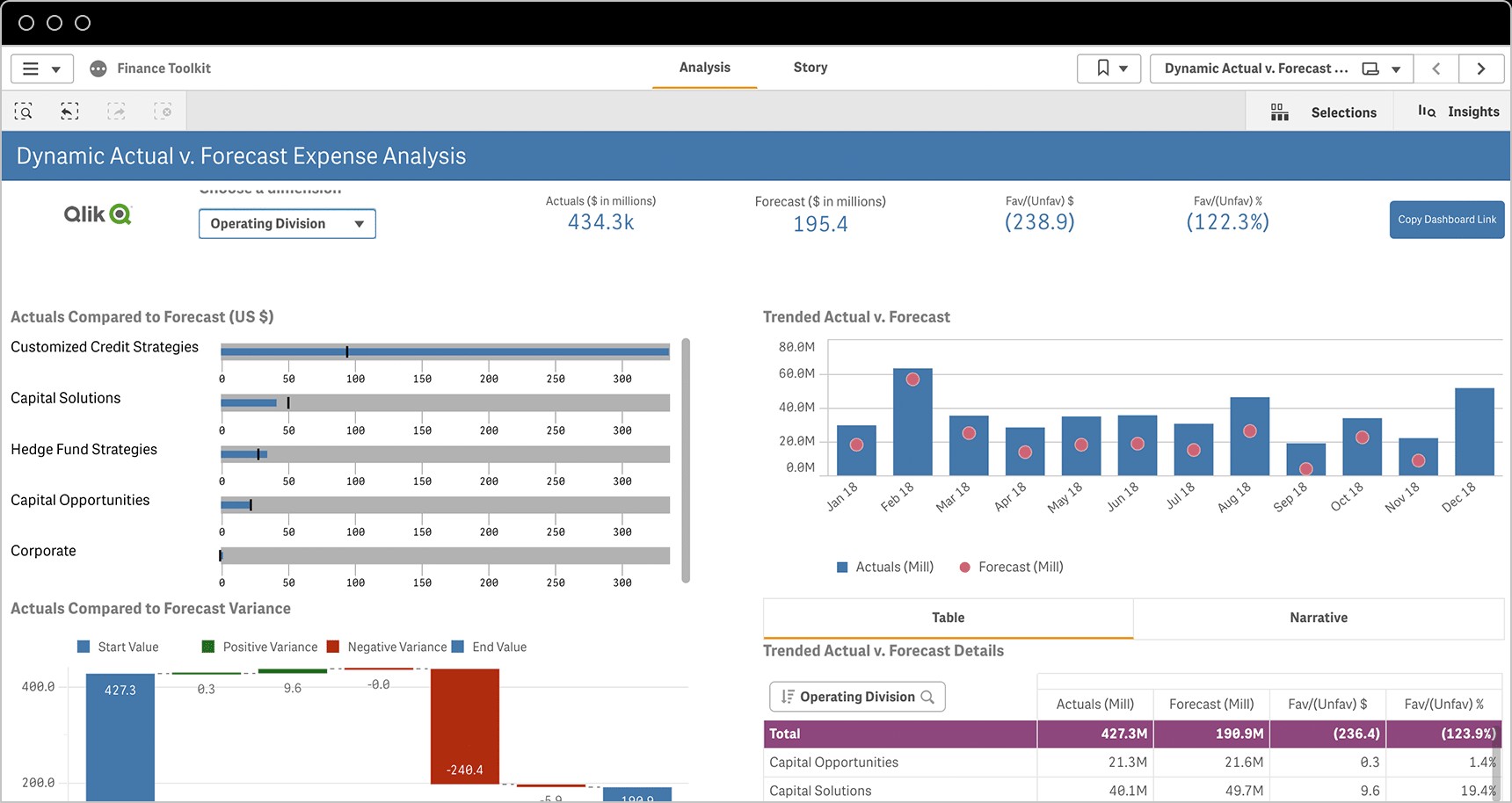
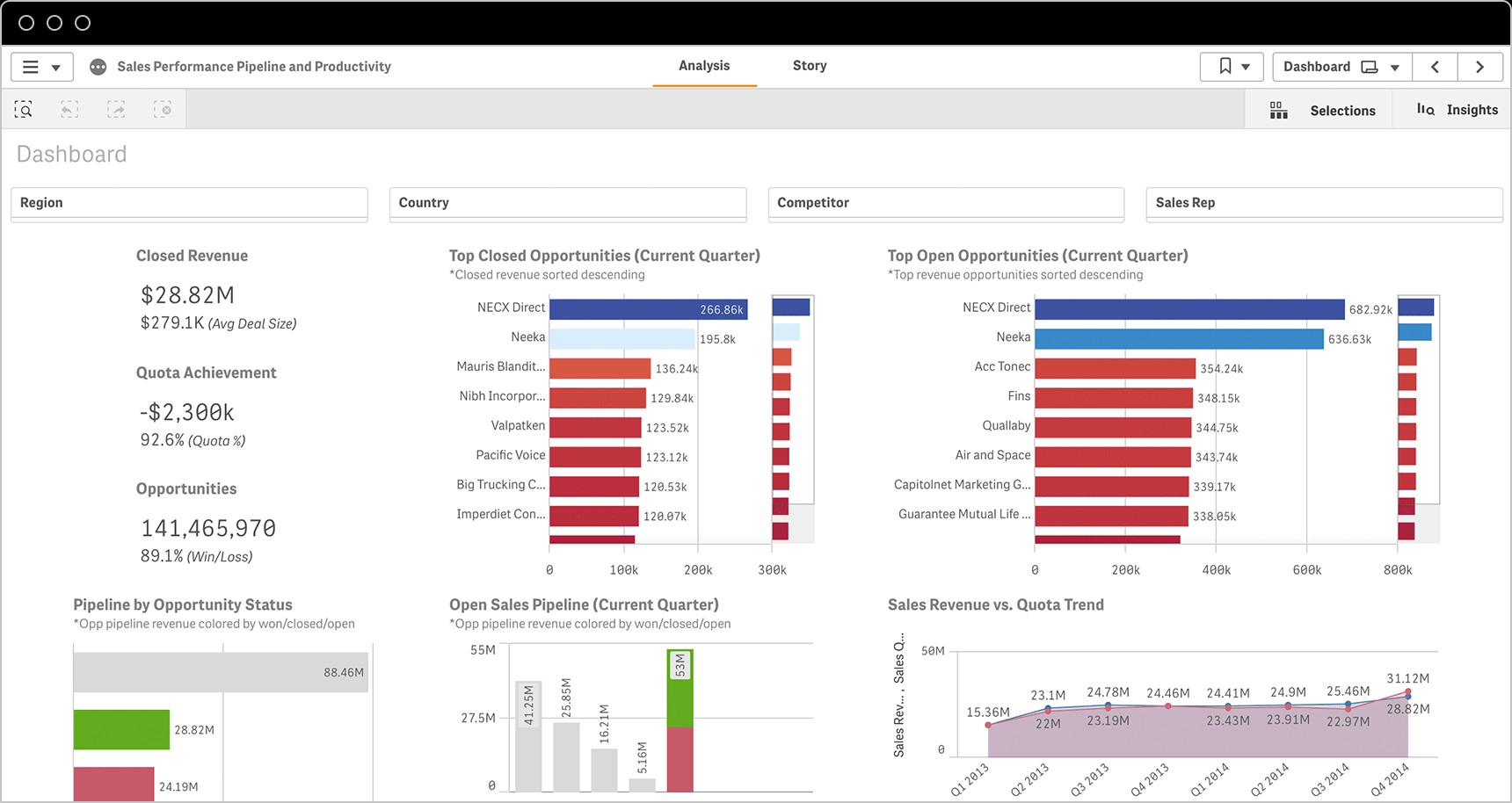
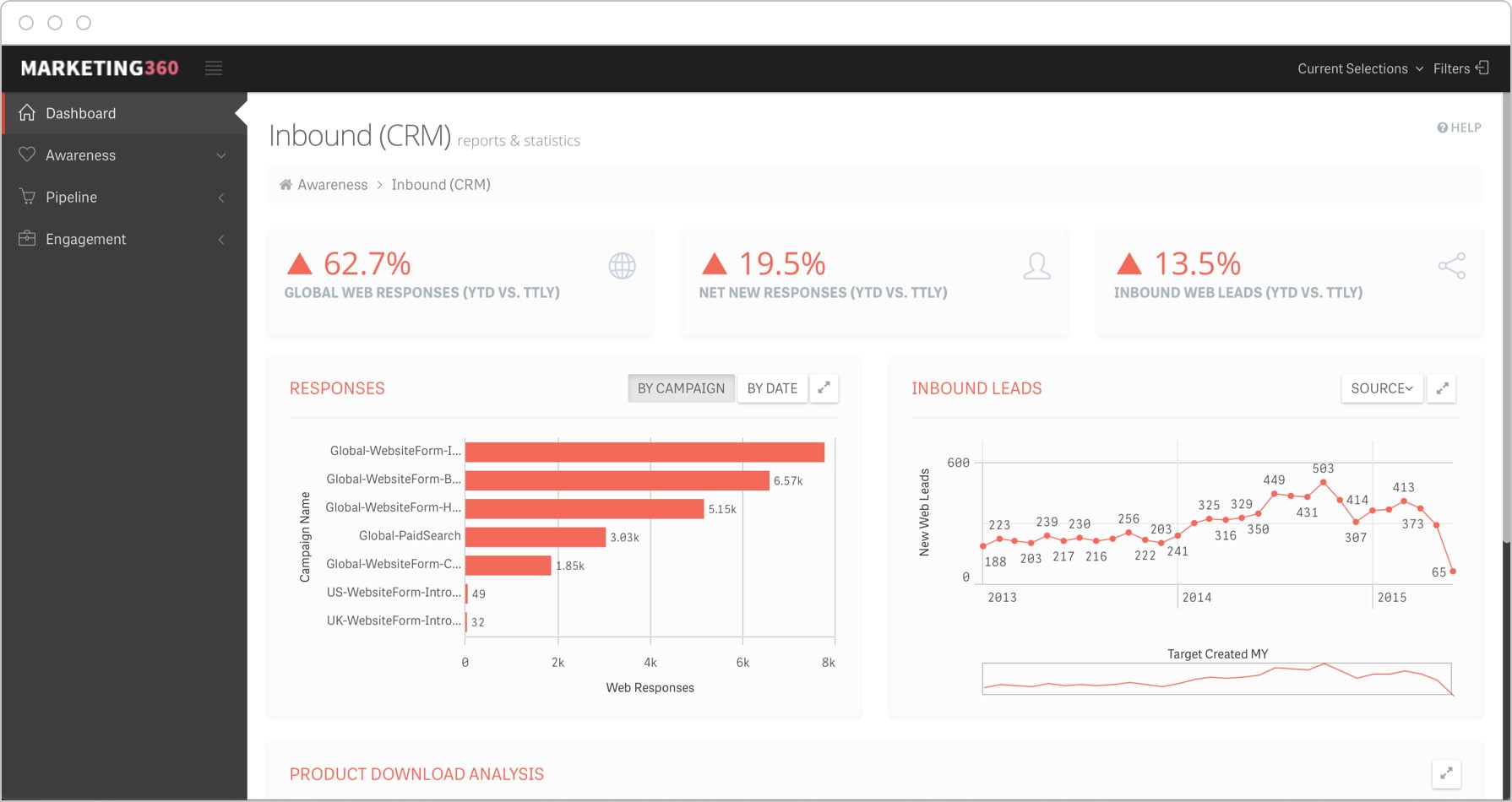
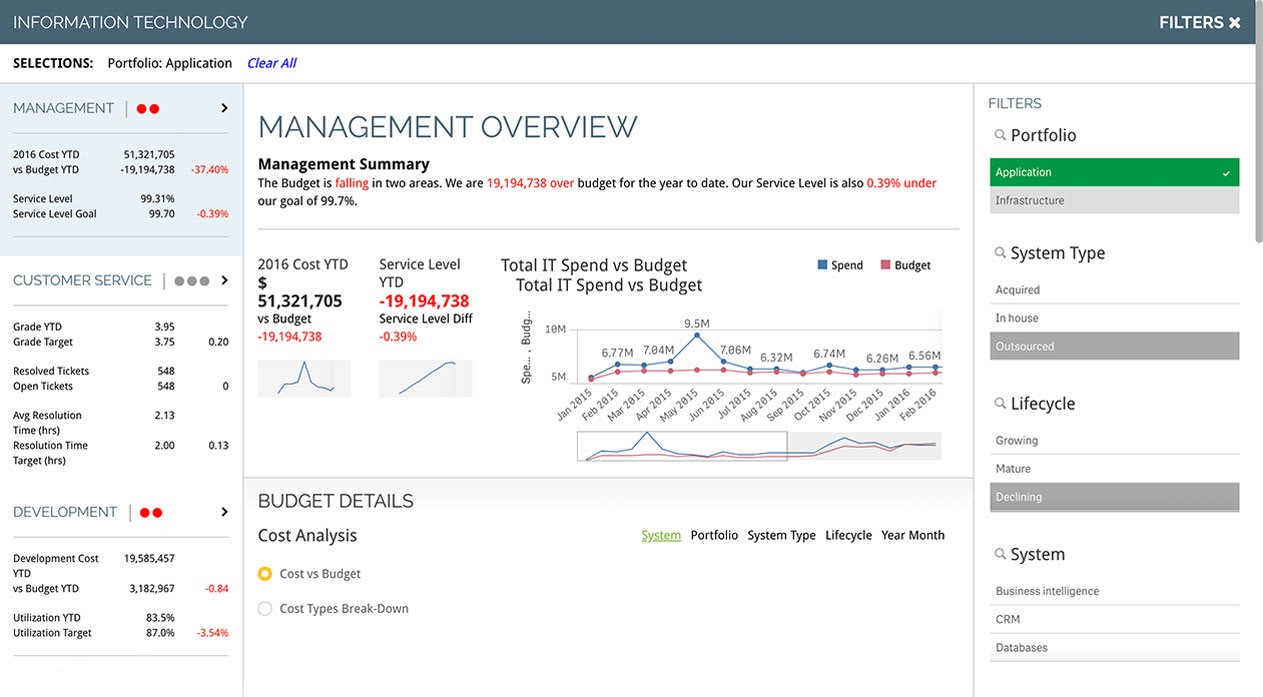
6. KPI Dashboards: Visualizing Performance
KPI dashboards are visual tools that display key performance indicators in a clear and concise manner. They provide a real-time snapshot of performance, allowing businesses to quickly identify trends and make informed decisions.
6.1 Benefits of Using KPI Dashboards
Using KPI dashboards offers several benefits:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Track performance in real-time.
- Data Visualization: Present data in a visually appealing and easy-to-understand format.
- Quick Insights: Quickly identify trends and patterns.
- Informed Decision Making: Make data-driven decisions based on performance insights.
- Improved Communication: Communicate performance to stakeholders.
6.2 Key Elements of an Effective KPI Dashboard
An effective KPI dashboard should include the following elements:
- Clear Objectives: Clearly define the objectives of the dashboard.
- Relevant KPIs: Include only the most relevant KPIs.
- Visual Representation: Use charts, graphs, and other visual elements to display data.
- Real-Time Data: Display real-time data whenever possible.
- User-Friendly Design: Design the dashboard to be user-friendly and easy to navigate.
6.3 Tools for Creating KPI Dashboards
There are many tools available for creating KPI dashboards, including:
- Microsoft Excel: A widely used spreadsheet program with charting capabilities.
- Tableau: A powerful data visualization tool.
- Qlik Sense: A data analytics platform with dashboarding capabilities.
- Google Data Studio: A free data visualization tool from Google.
- Power BI: A business analytics tool from Microsoft.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using KPIs
Using KPIs effectively requires careful planning and execution. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
7.1 Setting Too Many KPIs
Setting too many KPIs can be overwhelming and dilute focus. Focus on the most important KPIs that align with your business objectives.
7.2 Choosing Irrelevant KPIs
Choosing irrelevant KPIs can lead to wasted effort and inaccurate insights. Ensure that your KPIs are relevant to your business goals.
7.3 Not Tracking KPIs Regularly
Not tracking KPIs regularly can result in missed opportunities and delayed corrective action. Establish a schedule for tracking and reviewing your KPIs.
7.4 Ignoring KPI Results
Ignoring KPI results can render the entire process pointless. Analyze your KPI data and take action based on the insights you gain.
7.5 Failing to Adapt KPIs
Failing to adapt KPIs to changing business conditions can result in outdated and irrelevant metrics. Regularly review and update your KPIs to ensure they remain relevant.
8. KPI Best Practices
Following KPI best practices can help ensure that you are using KPIs effectively and achieving your goals.
8.1 Define Clear Objectives
Clearly define your business objectives before selecting your KPIs. This ensures that your KPIs are aligned with your goals.
8.2 Involve Key Stakeholders
Involve key stakeholders in the KPI selection process. This ensures that everyone is aligned and that the KPIs are relevant to their roles and responsibilities.
8.3 Use the SMART Framework
Use the SMART framework to ensure that your KPIs are well-defined and achievable.
8.4 Balance Leading and Lagging Indicators
Balance leading and lagging indicators to provide a comprehensive view of performance.
8.5 Track and Review KPIs Regularly
Establish a schedule for tracking and reviewing your KPIs. This allows you to identify trends and take corrective action as needed.
8.6 Communicate KPI Results
Communicate KPI results to stakeholders. This ensures that everyone is aware of performance and can contribute to improvement efforts.
8.7 Adapt KPIs as Needed
Regularly review and update your KPIs to ensure they remain relevant to your business objectives.
9. KPIs for Different Industries
KPIs can vary depending on the industry. Here are some examples of KPIs for different industries:
9.1 Retail KPIs
- Sales per Square Foot: Measures the efficiency of retail space.
- Customer Conversion Rate: Percentage of shoppers who make a purchase.
- Inventory Turnover: Rate at which inventory is sold and replaced.
- Average Transaction Value: Average value of each customer transaction.
- Customer Retention Rate: Percentage of customers who return to make another purchase.
9.2 Healthcare KPIs
- Patient Satisfaction: Measures patient satisfaction with healthcare services.
- Readmission Rate: Percentage of patients who are readmitted to the hospital within a certain period.
- Average Length of Stay: Average number of days patients stay in the hospital.
- Mortality Rate: Percentage of patients who die in the hospital.
- Bed Occupancy Rate: Percentage of hospital beds that are occupied.
9.3 Education KPIs
- Graduation Rate: Percentage of students who graduate from a school or program.
- Student-Teacher Ratio: Number of students per teacher.
- Attendance Rate: Percentage of students who attend school regularly.
- Test Scores: Performance of students on standardized tests.
- Parent Satisfaction: Measures parent satisfaction with the school.
9.4 Manufacturing KPIs
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): Measures the efficiency of manufacturing equipment.
- Defect Rate: Percentage of products that are defective.
- Production Volume: Number of units produced in a period.
- On-Time Delivery: Percentage of orders delivered on time.
- Inventory Turnover: Rate at which inventory is sold and replaced.
9.5 Technology KPIs
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Cost of acquiring a new customer.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Total revenue generated by a customer over their relationship with the company.
- Churn Rate: Percentage of customers who stop using the product or service.
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR): Total revenue generated from recurring subscriptions each month.
- Website Traffic: Number of visitors to a website.
10. The Future of KPIs
The future of KPIs is likely to be driven by advancements in technology and data analytics. Here are some trends to watch:
10.1 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI can be used to analyze KPI data and identify patterns and insights that would be difficult for humans to detect. AI can also be used to automate the KPI tracking process.
10.2 Big Data
Big data provides a wealth of information that can be used to create more comprehensive and accurate KPIs. Big data can also be used to identify new KPIs that are relevant to your business.
10.3 Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics can be used to forecast future performance based on past KPI data. This allows businesses to take proactive action to improve performance.
10.4 Real-Time Data
Real-time data allows businesses to track performance in real-time and make immediate adjustments as needed. This can lead to improved efficiency and responsiveness.
10.5 Data Visualization
Data visualization tools make it easier to understand and communicate KPI data. This can lead to improved decision-making and collaboration.
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About KPIs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the difference between a KPI and a metric? | A KPI is a metric that is critical to measuring the success of a business objective. Not all metrics are KPIs. |
| How many KPIs should a company track? | It depends on the size and complexity of the business, but it’s best to focus on a few key KPIs that are most relevant to your goals. |
| Can KPIs be used for personal goals? | Yes, KPIs can be used to track personal progress and achieve personal goals. |
| How often should KPIs be reviewed? | KPIs should be reviewed regularly, typically monthly or quarterly, to ensure they remain relevant and are driving the desired results. |
| What are some common mistakes when using KPIs? | Setting too many KPIs, choosing irrelevant KPIs, not tracking KPIs regularly, ignoring KPI results, and failing to adapt KPIs. |
| How can I get started with KPIs? | Start by defining your business objectives, identifying relevant KPIs, setting targets, tracking progress, and taking action based on the results. |
| What are leading and lagging KPIs? | Leading KPIs predict future performance, while lagging KPIs measure past performance. |
| How do I align KPIs with my business strategy? | Ensure your KPIs directly support your strategic objectives and that achieving the KPIs contributes to the overall success of your business. |
| What role does technology play in KPI tracking? | Technology tools like KPI dashboards and analytics software automate tracking, visualizing, and analyzing KPI data, making it easier to monitor performance. |
| How do I communicate KPI results effectively? | Use clear and concise visuals, provide context, and focus on actionable insights to communicate KPI results effectively to stakeholders. |
12. Need More Answers? Ask WHAT.EDU.VN!
Do you still have questions about KPIs or any other topic? Don’t hesitate! At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide a free question-and-answer service to help you get the information you need. Whether you’re a student, professional, or simply curious, we’re here to provide clear, accurate, and helpful answers.
12.1 How WHAT.EDU.VN Can Help
WHAT.EDU.VN offers a platform where you can ask any question and receive answers from a community of knowledgeable users. Our goal is to provide a reliable and accessible source of information for everyone.
12.2 Why Choose WHAT.EDU.VN?
- Free Service: Ask any question without any cost.
- Quick Answers: Receive answers quickly from our community.
- Expert Knowledge: Get answers from knowledgeable users.
- Easy to Use: Our platform is easy to use and navigate.
- Comprehensive Information: Find answers to a wide range of topics.
12.3 Get Started Today
Don’t let your questions go unanswered. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask away! Our community is ready to help you find the information you need.
13. Take Action: Ask Your Questions Now!
Are you struggling to find answers to your questions? Do you need expert advice or clear explanations? Look no further! WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help.
We understand the challenges of finding reliable information and the frustration of unanswered questions. That’s why we’ve created a platform where you can ask any question and receive answers from a community of knowledgeable users.
13.1 Don’t Wait, Ask Now!
Stop searching endlessly for answers. Take action now and ask your questions on WHAT.EDU.VN. Our community is ready to provide you with the information you need to succeed.
13.2 Join Our Community
Join our community of learners and experts today. Share your knowledge, ask your questions, and help others find the answers they need.
13.3 Contact Us
If you have any questions or need assistance, please don’t hesitate to contact us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: what.edu.vn
We look forward to helping you find the answers you need!