What Generation Is Millennials a question that WHAT.EDU.VN is expertly equipped to answer? Understanding generational cohorts is essential for grasping societal trends and shifts in attitudes, particularly the unique characteristics that define Millennials, or Generation Y. Discover what sets this group apart and how they’ve shaped the world around us, and explore how subsequent generations continue to evolve.
1. Understanding Generational Cohorts
Generational cohorts are groupings of individuals born within a specific time frame who share similar formative experiences. These experiences, shaped by significant world events, technological advancements, and economic shifts, influence their perspectives, values, and behaviors. Generations provide a lens through which to analyze societal changes, offering insights into how different age groups perceive the world.
1.1. Key Characteristics of Generational Cohorts
- Shared Experiences: Common historical events, technological advancements, and economic conditions shape their worldviews.
- Influence on Values: Generational experiences influence core values, beliefs, and attitudes.
- Behavioral Patterns: Predictable patterns of behavior, preferences, and lifestyle choices emerge.
- Social Impact: Each generation contributes uniquely to society, driving cultural and economic shifts.
- Analytical Tool: Researchers and marketers use generational cohorts to understand and predict trends.
1.2. How Generational Cohorts Are Defined
Defining generational cohorts involves analyzing birth years and formative experiences. While there are no strict scientific criteria, factors like significant historical events, technological milestones, and economic shifts help delineate generations.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Birth Year Range | The range of years during which members of a generation were born. |
| Historical Events | Significant events that shaped the generation’s formative years. |
| Technological Advancements | Key technological developments that influenced the generation’s lifestyle. |
| Economic Conditions | Prevailing economic conditions during the generation’s coming-of-age period. |
| Cultural Influences | Dominant cultural trends and values that shaped the generation’s identity. |
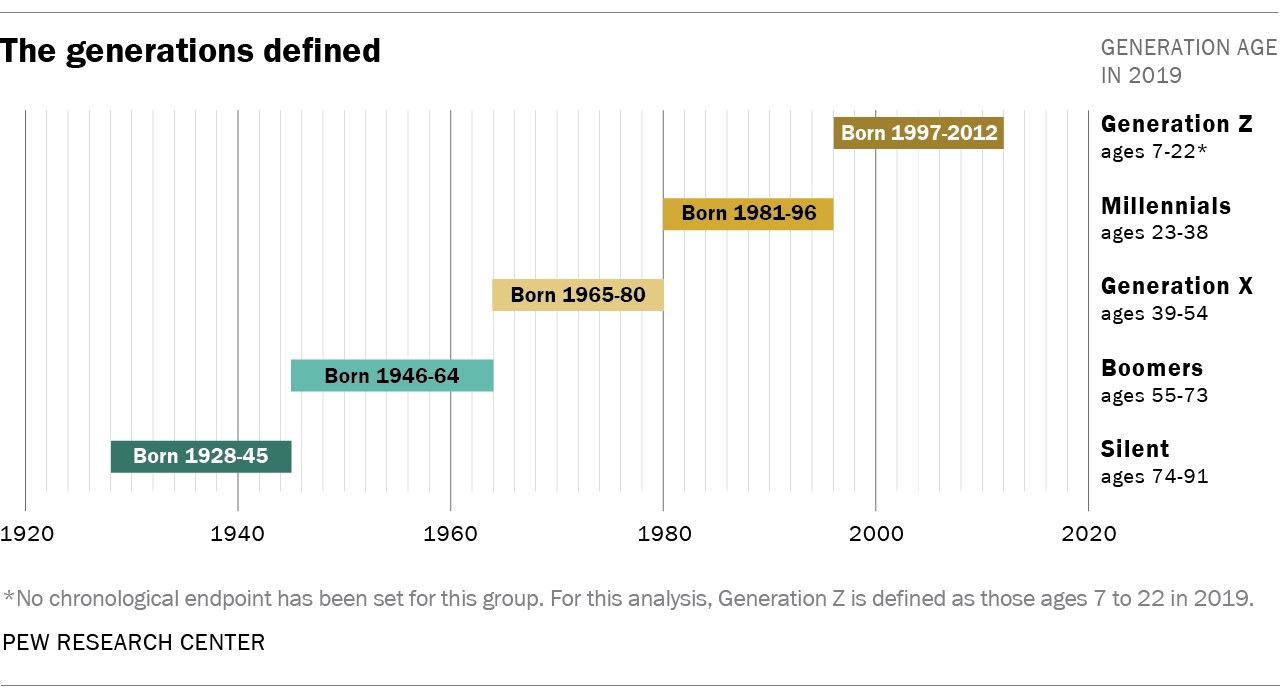
1.3. The Importance of Generational Analysis
Generational analysis is crucial for understanding societal changes and predicting future trends. By examining the unique characteristics of each generation, researchers and marketers can gain insights into consumer behavior, political attitudes, and social values.
2. What Generation Is Millennials?
The Millennial generation, also known as Generation Y, typically includes individuals born between 1981 and 1996. This generation came of age during a period of rapid technological advancement, economic shifts, and significant social changes.
2.1. Defining the Millennial Generation
Millennials are defined by their birth years and the formative experiences they shared. They witnessed the rise of the internet, social media, and mobile technology. They also experienced significant events like the 9/11 terrorist attacks and the 2008 financial crisis.
- Birth Years: 1981 to 1996
- Key Events: 9/11 terrorist attacks, 2008 financial crisis
- Technological Advancements: Rise of the internet, social media, mobile technology
2.2. Key Characteristics of Millennials
Millennials possess distinct characteristics shaped by their formative experiences. These characteristics include a strong reliance on technology, a desire for work-life balance, a commitment to social causes, and a preference for diverse and inclusive environments.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Tech-Savvy | Comfortable with technology and rely on it for communication, information, and entertainment. |
| Work-Life Balance | Value flexibility and prioritize personal fulfillment over traditional career paths. |
| Socially Conscious | Committed to social and environmental causes and seek to make a positive impact. |
| Diverse and Inclusive | Embrace diversity and seek inclusive environments that value different perspectives. |
| Educated | Highly educated, with a significant percentage holding college degrees. |
2.3. The Impact of Millennials on Society
Millennials have significantly impacted various aspects of society, including the workplace, consumer culture, and political landscape.
- Workplace: Advocated for flexible work arrangements, collaborative environments, and meaningful work.
- Consumer Culture: Driven the growth of e-commerce, social media marketing, and sustainable products.
- Political Landscape: Influenced political discourse by promoting progressive values and advocating for social justice.
3. The Formative Experiences of Millennials
The formative experiences of Millennials have shaped their attitudes, values, and behaviors. These experiences include the rise of technology, economic shifts, and significant social changes.
3.1. The Rise of Technology
Millennials came of age during the rise of the internet, social media, and mobile technology. This technological revolution has profoundly impacted how they communicate, access information, and interact with the world.
- Internet: The widespread adoption of the internet transformed how Millennials access information and communicate.
- Social Media: Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram became integral to their social lives and communication.
- Mobile Technology: Smartphones and mobile devices revolutionized how Millennials access information and stay connected.
3.2. Economic Shifts
Millennials experienced significant economic shifts during their formative years, including the dot-com bubble burst, the 2008 financial crisis, and the subsequent economic recession.
| Event | Impact |
|---|---|
| Dot-Com Bubble Burst | Instilled caution about investing in technology and the stock market. |
| 2008 Financial Crisis | Led to job losses, economic instability, and concerns about financial security. |
| Economic Recession | Shaped career choices and financial planning, with many delaying major life decisions. |
3.3. Social and Political Events
Millennials came of age during a period of significant social and political change. Events like the 9/11 terrorist attacks, the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan, and the legalization of same-sex marriage shaped their worldviews.
- 9/11 Terrorist Attacks: Created a sense of vulnerability and heightened awareness of global security issues.
- Wars in Iraq and Afghanistan: Shaped political views and contributed to a more critical perspective on military intervention.
- Legalization of Same-Sex Marriage: Reflected a shift toward greater acceptance of LGBTQ+ rights and social equality.
4. The Millennial Mindset
The Millennial mindset is characterized by a unique set of values, beliefs, and attitudes shaped by their formative experiences. This mindset influences their approach to work, relationships, and social issues.
4.1. Values and Beliefs
Millennials prioritize values like authenticity, social responsibility, and work-life balance. They believe in the importance of making a positive impact on the world and seek meaningful experiences.
- Authenticity: Value transparency and honesty in personal and professional relationships.
- Social Responsibility: Committed to addressing social and environmental issues.
- Work-Life Balance: Seek flexibility and prioritize personal well-being.
- Meaningful Experiences: Value experiences over material possessions.
4.2. Attitudes Towards Work
Millennials have different expectations and attitudes towards work compared to previous generations. They seek jobs that offer purpose, flexibility, and opportunities for growth.
| Attitude | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose-Driven | Seek jobs that align with their values and make a positive impact. |
| Flexible | Value flexibility in work arrangements and prioritize work-life balance. |
| Growth-Oriented | Seek opportunities for learning and career advancement. |
| Collaborative | Prefer collaborative work environments and value teamwork. |
4.3. Social and Political Views
Millennials tend to be more liberal and socially progressive compared to previous generations. They support issues like LGBTQ+ rights, environmental protection, and social justice.
- LGBTQ+ Rights: Advocate for equal rights and protections for LGBTQ+ individuals.
- Environmental Protection: Support policies to address climate change and protect the environment.
- Social Justice: Advocate for policies that promote equality and address systemic inequalities.
5. How Millennials Differ from Previous Generations
Millennials differ from previous generations in several key aspects, including their use of technology, attitudes toward work, and social and political views.
5.1. Technology Adoption
Millennials are digital natives who grew up with technology. They are more comfortable with technology and rely on it for communication, information, and entertainment compared to previous generations.
| Generation | Technology Adoption |
|---|---|
| Millennials | Grew up with the internet, social media, and mobile technology. |
| Gen X | Adapted to technology later in life. |
| Baby Boomers | Less reliant on technology and may find it challenging to use. |
5.2. Work Ethic and Career Goals
Millennials have different expectations and attitudes toward work compared to previous generations. They seek jobs that offer purpose, flexibility, and opportunities for growth, while previous generations may have prioritized job security and financial stability.
| Generation | Work Ethic and Career Goals |
|---|---|
| Millennials | Seek purpose, flexibility, and growth opportunities. |
| Gen X | Value independence and work-life balance. |
| Baby Boomers | Prioritize job security, financial stability, and career advancement. |
5.3. Social and Political Engagement
Millennials tend to be more liberal and socially progressive compared to previous generations. They are more engaged in social and political issues and advocate for progressive policies.
| Generation | Social and Political Engagement |
|---|---|
| Millennials | More liberal, socially progressive, and engaged in social and political issues. |
| Gen X | More independent and skeptical of political institutions. |
| Baby Boomers | More traditional and may hold more conservative views on social issues. |
6. Challenges Faced by Millennials
Millennials have faced unique challenges, including economic instability, student loan debt, and job market competition.
6.1. Economic Instability
Millennials came of age during a period of economic instability, including the 2008 financial crisis and the subsequent recession. These events impacted their career prospects, financial planning, and overall economic well-being.
- Job Market: Experienced high unemployment rates and limited job opportunities during the recession.
- Financial Planning: Faced challenges in saving for retirement, buying homes, and paying off debt.
- Economic Well-being: Experienced slower wage growth and lower levels of wealth accumulation compared to previous generations.
6.2. Student Loan Debt
Many Millennials have accumulated significant student loan debt to finance their education. This debt can impact their financial well-being and limit their ability to achieve other financial goals.
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Debt Burden | High levels of student loan debt can limit financial flexibility. |
| Financial Goals | Difficulty saving for retirement, buying homes, and starting families. |
| Economic Impact | Reduced spending and investment in the economy. |
6.3. Job Market Competition
Millennials face intense competition in the job market due to factors like globalization, automation, and the increasing demand for specialized skills.
- Globalization: Increased competition from workers in other countries.
- Automation: Job displacement due to automation and technological advancements.
- Skills Gap: Difficulty finding jobs that match their skills and experience.
7. Beyond Millennials: Understanding Generation Z
Generation Z, born between 1997 and 2012, is the generation that follows Millennials. They have unique characteristics and experiences that set them apart from previous generations.
7.1. Defining Generation Z
Generation Z is defined by their birth years and the formative experiences they shared. They grew up in a world of constant connectivity, social media, and instant access to information.
- Birth Years: 1997 to 2012
- Key Events: Rise of social media, constant connectivity, and global awareness.
- Technological Advancements: Smartphones, high-speed internet, and on-demand entertainment.
7.2. Key Characteristics of Generation Z
Generation Z possesses distinct characteristics shaped by their formative experiences. These characteristics include a strong digital fluency, a desire for authenticity, and a commitment to social causes.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Digital Fluency | Highly comfortable with technology and rely on it for communication, information, and entertainment. |
| Authenticity | Value transparency and honesty in personal and professional relationships. |
| Socially Conscious | Committed to addressing social and environmental issues. |
| Independent | Value independence and self-reliance. |
7.3. How Generation Z Differs from Millennials
Generation Z differs from Millennials in several key aspects, including their use of technology, attitudes toward work, and social and political views.
| Aspect | Generation Z | Millennials |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Use | Digital natives who have grown up with technology. | Adapted to technology later in life. |
| Work Attitudes | Value independence, flexibility, and entrepreneurship. | Seek purpose, collaboration, and growth opportunities. |
| Social Views | More pragmatic and focused on practical solutions. | More idealistic and focused on social justice. |
8. The Future of Generational Studies
Generational studies will continue to evolve as new generations emerge and society changes. Researchers will need to adapt their methods and approaches to understand the unique characteristics and experiences of each generation.
8.1. Emerging Trends in Generational Research
Emerging trends in generational research include a focus on intersectionality, global perspectives, and the impact of technology on generational identity.
- Intersectionality: Examining how different social categories, such as race, gender, and class, intersect to shape generational experiences.
- Global Perspectives: Understanding how generational trends vary across different countries and cultures.
- Impact of Technology: Studying how technology influences generational identity, behavior, and values.
8.2. The Role of Technology in Shaping Generations
Technology will continue to play a significant role in shaping future generations. New technologies, such as artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and the metaverse, will influence how people communicate, learn, and interact with the world.
| Technology | Impact |
|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence | Transforming industries, automating tasks, and creating new job opportunities. |
| Virtual Reality | Creating immersive experiences and transforming how people interact with technology. |
| Metaverse | Creating new social spaces and blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds. |
8.3. Understanding the Next Generations
Understanding the next generations, including Generation Alpha (born after 2012), will be crucial for predicting future trends and addressing societal challenges.
- Generation Alpha: The first generation to be born entirely in the 21st century, shaped by technology and global events.
9. FAQs About Millennials
Here are some frequently asked questions about the Millennial generation:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What years are considered Millennials? | Millennials are typically defined as those born between 1981 and 1996. |
| What are the key characteristics of Millennials? | Millennials are tech-savvy, value work-life balance, are socially conscious, and embrace diversity and inclusion. |
| How have Millennials impacted society? | Millennials have influenced the workplace, consumer culture, and political landscape by advocating for flexibility, sustainability, and social justice. |
| What challenges have Millennials faced? | Millennials have faced economic instability, student loan debt, and job market competition. |
| How do Millennials differ from previous generations? | Millennials are more comfortable with technology, seek purpose in their work, and are more socially progressive than previous generations. |
9.1. Common Misconceptions About Millennials
There are several common misconceptions about Millennials. Some of these include the stereotypes that they are lazy, entitled, and narcissistic. These stereotypes are often inaccurate and do not reflect the diversity and complexity of the Millennial generation.
- Lazy: Millennials are often accused of being lazy and unwilling to work hard, but this is not supported by evidence.
- Entitled: Another common stereotype is that Millennials are entitled and expect to be rewarded without putting in the effort.
- Narcissistic: Some people believe that Millennials are narcissistic and overly focused on themselves.
9.2. The Diversity Within the Millennial Generation
It is important to recognize the diversity within the Millennial generation. Millennials come from different backgrounds, have different experiences, and hold different beliefs. It is essential to avoid making generalizations about the entire generation based on limited information.
- Socioeconomic Background: Millennials come from different socioeconomic backgrounds, which can impact their opportunities and experiences.
- Cultural Background: Millennials come from different cultural backgrounds, which can shape their values, beliefs, and behaviors.
- Political Views: Millennials hold a range of political views, from liberal to conservative.
9.3. Resources for Further Learning
There are numerous resources available for those interested in learning more about Millennials. These resources include books, articles, websites, and research reports.
- Books: Numerous books have been written about the Millennial generation, providing insights into their characteristics, values, and experiences.
- Articles: Many articles have been published about Millennials in academic journals, magazines, and newspapers.
- Websites: Several websites are dedicated to studying and analyzing generational trends, including those related to Millennials.
- Research Reports: Various organizations, such as Pew Research Center, conduct research on Millennials and publish reports on their findings.
10. Understanding the Millennial Impact on Marketing
Millennials have significantly impacted marketing strategies due to their unique preferences and behaviors. Understanding these nuances is essential for businesses looking to engage this demographic effectively.
10.1. How Millennials Consume Information
Millennials primarily consume information through digital channels, favoring social media, online videos, and mobile-friendly content. Marketers need to adapt by creating engaging, easily accessible digital experiences.
| Platform | Usage by Millennials |
|---|---|
| Social Media | High engagement for news, entertainment, and product discovery. |
| Online Videos | Preferred for tutorials, reviews, and entertainment. |
| Mobile Devices | Primary device for accessing information on the go. |
| Blogs and Articles | Used for in-depth research and informative content. |
10.2. Effective Marketing Strategies for Millennials
To effectively market to Millennials, strategies should focus on authenticity, personalization, and social responsibility. Brands that align with Millennial values tend to resonate more strongly.
- Authenticity: Transparency and genuine brand stories are highly valued.
- Personalization: Tailored content and personalized experiences increase engagement.
- Social Responsibility: Support for ethical practices and social causes enhances brand appeal.
- Engagement: Interactive campaigns and community-building initiatives foster loyalty.
10.3. Case Studies of Successful Millennial Marketing
Several brands have successfully targeted Millennials by aligning their marketing strategies with Millennial values and preferences. Examples include:
| Brand | Strategy | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| TOMS Shoes | Socially responsible business model; donates a pair of shoes for every pair purchased. | Strong brand loyalty among socially conscious Millennials. |
| Airbnb | Personalized travel experiences and community-based approach. | High adoption rates due to unique and authentic travel options. |
| Netflix | Data-driven personalization and binge-worthy content. | Dominance in the streaming market with a strong Millennial subscriber base. |
11. Generational Differences in the Workplace
Understanding generational differences in the workplace is crucial for fostering effective collaboration and managing diverse teams.
11.1. Communication Styles Across Generations
Different generations have distinct communication styles. Millennials tend to prefer digital communication, while Baby Boomers may prefer face-to-face interactions.
| Generation | Preferred Communication Style | Challenges in Intergenerational Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Millennials | Digital communication, instant messaging, and email. | May be perceived as impersonal or too informal by older generations. |
| Gen X | A mix of digital and traditional communication methods. | Can struggle to balance the preferences of different generations. |
| Baby Boomers | Face-to-face interactions, phone calls, and formal written communication. | May be less comfortable with digital communication and instant messaging. |
11.2. Managing Intergenerational Teams
To effectively manage intergenerational teams, leaders should promote understanding, respect, and open communication.
- Promote Understanding: Encourage team members to learn about the values and preferences of different generations.
- Foster Respect: Create a culture of respect where all team members feel valued and appreciated.
- Encourage Open Communication: Facilitate open and honest communication to address misunderstandings and resolve conflicts.
- Provide Training: Offer training on effective communication and collaboration skills for intergenerational teams.
11.3. Benefits of a Multigenerational Workforce
A multigenerational workforce can bring diverse perspectives, skills, and experiences to the workplace, leading to increased innovation, creativity, and problem-solving abilities.
- Diverse Perspectives: Different generations offer unique perspectives on challenges and opportunities.
- Complementary Skills: Each generation brings different skills and strengths to the workplace.
- Enhanced Innovation: The combination of diverse perspectives and skills can lead to more innovative solutions.
- Improved Problem-Solving: A multigenerational workforce can draw on a wider range of experiences to solve complex problems.
12. The Millennial Impact on Politics
Millennials have become a significant force in politics, shaping political discourse and influencing election outcomes.
12.1. Millennial Voting Patterns
Millennials tend to be more liberal and socially progressive, supporting policies that promote equality, social justice, and environmental protection.
| Political Issue | Millennial Support |
|---|---|
| Social Justice | Strong support for policies that address systemic inequalities. |
| LGBTQ+ Rights | High support for equal rights and protections for LGBTQ+ individuals. |
| Environment | Strong support for policies that address climate change and protect the environment. |
12.2. Political Engagement of Millennials
Millennials are actively engaged in politics through voting, volunteering, donating to campaigns, and participating in protests and demonstrations.
- Voting: Millennials are increasingly voting in elections, although their turnout rates are still lower than those of older generations.
- Volunteering: Many Millennials volunteer for political campaigns and organizations.
- Donating: Millennials are increasingly donating to political campaigns and causes.
- Activism: Many Millennials participate in protests and demonstrations to advocate for their political views.
12.3. How Millennials Are Shaping Political Discourse
Millennials are shaping political discourse by advocating for progressive policies, promoting social justice, and challenging traditional political norms.
- Progressive Policies: Millennials are advocating for policies that address income inequality, climate change, and social justice issues.
- Social Justice: Millennials are promoting social justice by advocating for equality and challenging discrimination.
- Challenging Norms: Millennials are challenging traditional political norms by using social media and other digital platforms to engage in political discourse.
13. The Millennial Impact on Social Trends
Millennials have significantly influenced social trends, including lifestyle choices, consumer behavior, and cultural norms.
13.1. Lifestyle Choices of Millennials
Millennials are delaying marriage, having children later in life, and prioritizing experiences over material possessions.
| Lifestyle Choice | Trend Among Millennials |
|---|---|
| Marriage | Delaying marriage and choosing to marry later in life. |
| Parenthood | Delaying having children and having fewer children. |
| Homeownership | Delaying homeownership and renting for longer periods. |
| Material Possessions | Prioritizing experiences over material possessions. |
13.2. Consumer Behavior of Millennials
Millennials are driving the growth of e-commerce, social media marketing, and sustainable products.
- E-Commerce: Millennials are more likely to shop online than previous generations.
- Social Media Marketing: Millennials are heavily influenced by social media marketing.
- Sustainable Products: Millennials are more likely to purchase sustainable and ethically sourced products.
13.3. Cultural Norms Influenced by Millennials
Millennials are promoting diversity, inclusivity, and social justice in cultural norms.
- Diversity: Millennials are embracing diversity and challenging traditional norms.
- Inclusivity: Millennials are promoting inclusivity and creating more welcoming environments for people from all backgrounds.
- Social Justice: Millennials are advocating for social justice and challenging systemic inequalities.
14. Addressing Millennial Mental Health
Millennials face unique challenges that can impact their mental health, including economic pressures, social media influence, and work-life balance issues.
14.1. Mental Health Challenges Faced by Millennials
Millennials report higher rates of anxiety, depression, and stress compared to previous generations.
| Mental Health Issue | Prevalence Among Millennials | Contributing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Anxiety | Higher rates of anxiety disorders compared to previous generations. | Economic pressures, social media influence, and work-life balance issues. |
| Depression | Higher rates of depression compared to previous generations. | Economic pressures, social isolation, and lack of social support. |
| Stress | High levels of stress due to work, finances, and relationships. | Economic pressures, job insecurity, and relationship challenges. |
14.2. Strategies for Promoting Millennial Well-being
Promoting Millennial well-being requires addressing the root causes of their mental health challenges, including economic pressures, social media influence, and work-life balance issues.
- Economic Support: Providing economic support and opportunities to improve financial stability.
- Social Media Awareness: Promoting awareness of the potential negative impacts of social media.
- Work-Life Balance: Encouraging employers to offer flexible work arrangements and promote work-life balance.
- Mental Health Services: Increasing access to affordable and accessible mental health services.
14.3. Resources for Millennial Mental Health Support
There are numerous resources available to support Millennial mental health, including mental health organizations, online resources, and counseling services.
- Mental Health Organizations: National and local mental health organizations offer resources and support for individuals struggling with mental health issues.
- Online Resources: Numerous websites and apps provide information, support, and self-help tools for managing mental health.
- Counseling Services: Licensed therapists and counselors offer individual and group counseling services to address mental health concerns.
15. Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Millennials
Millennials have left an indelible mark on society, shaping culture, politics, and technology. Their influence will continue to be felt for generations to come. As we move forward, it’s essential to understand and appreciate the unique contributions of this generation.
15.1. Key Takeaways About Millennials
Millennials, born between 1981 and 1996, have shaped society in profound ways through their use of technology, their values, and their engagement with social and political issues. They have faced unique challenges, including economic instability and student loan debt, but they have also made significant contributions to the workplace, consumer culture, and political landscape.
15.2. The Ongoing Impact of Millennials
The impact of Millennials will continue to be felt for generations to come. As they move into positions of leadership and influence, they will shape the future of business, politics, and society. Their commitment to social justice, environmental sustainability, and technological innovation will continue to drive positive change in the world.
15.3. Looking Ahead: The Future of Generations
As we look ahead to the future, it is important to understand the characteristics and values of the next generations, including Generation Z and Generation Alpha. By understanding these generations, we can better anticipate future trends and address the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Have more questions about generational trends or anything else? Don’t hesitate to ask at WHAT.EDU.VN, where you can get answers to all your questions for free! Our experts are ready to provide you with the information you need. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Visit our website at what.edu.vn today!
