Converting Celsius to Fahrenheit can be straightforward, and at WHAT.EDU.VN, we are here to help you understand the conversion process easily. Knowing what 180 degrees Celsius equals in Fahrenheit is especially useful in cooking, traveling, or scientific contexts. Let’s dive into the conversion formula, explore practical applications, and look at a simple conversion chart. Need more help with temperature scales or unit conversions? Ask your question for free at WHAT.EDU.VN, and we’ll give you the answer.
1. Understanding the 180°C to Fahrenheit Conversion
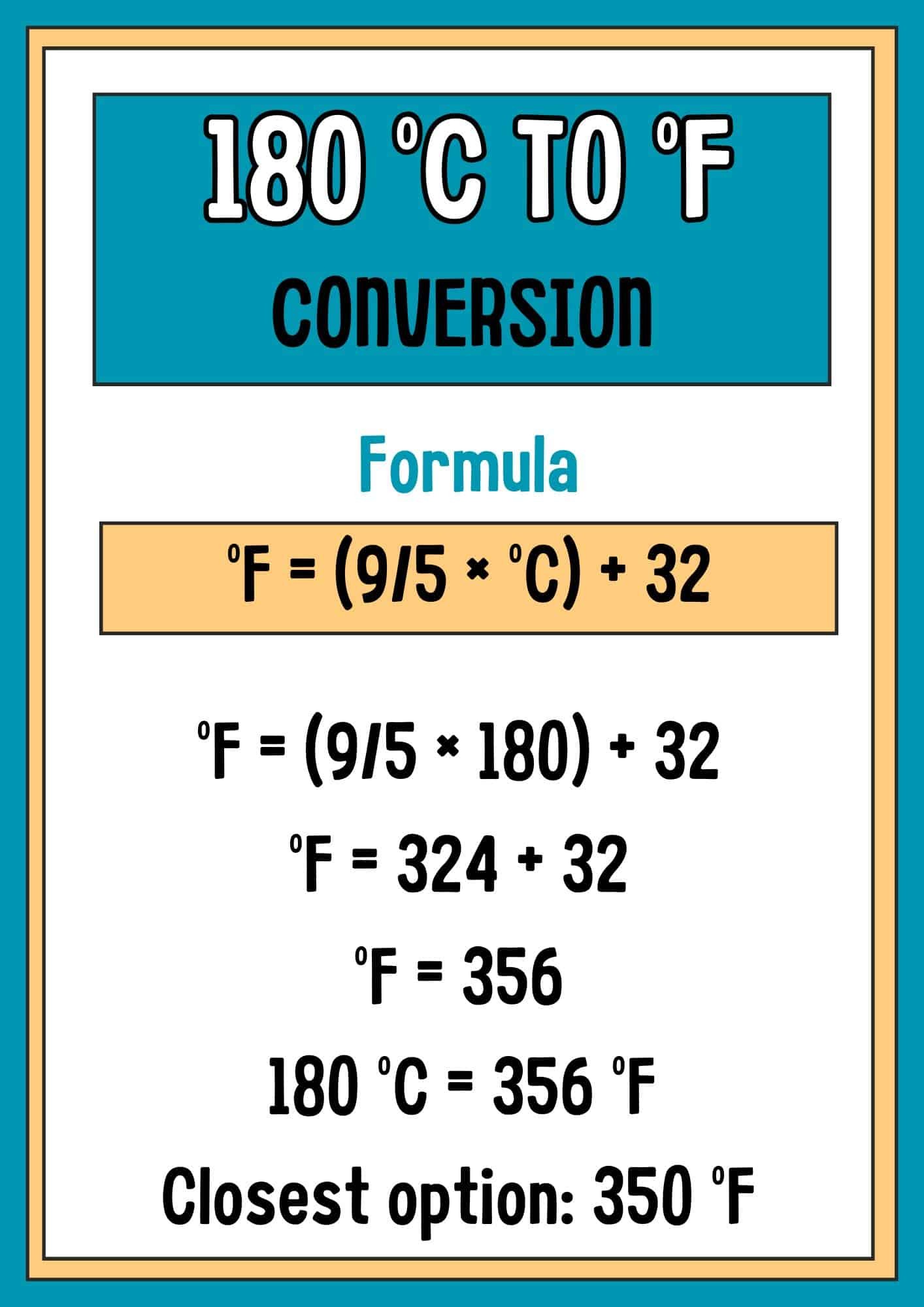
180 degrees Celsius is equal to 356 degrees Fahrenheit. This conversion is crucial for anyone needing to switch between these two temperature scales, whether it’s for cooking recipes, understanding weather forecasts, or conducting scientific experiments. Knowing this equivalent helps ensure accuracy and avoids potential errors in various applications.
2. The Formula for Converting Celsius to Fahrenheit
To convert Celsius (°C) to Fahrenheit (°F), you can use a simple formula:
F = (C × 9/5) + 32
Where:
- F = Fahrenheit
- C = Celsius
Let’s break down the conversion for 180°C:
F = (180 × 9/5) + 32
F = (180 × 1.8) + 32
F = 324 + 32
F = 356
So, 180°C is equal to 356°F.
3. Step-by-Step Conversion of 180°C to °F
Here’s a step-by-step guide to converting 180°C to °F:
-
Multiply by 9/5 (or 1.8):
180 × 1.8 = 324
-
Add 32:
324 + 32 = 356
Therefore, 180°C = 356°F.
4. Practical Example of Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion
Imagine you have a European recipe that requires an oven temperature of 180°C, but your oven only displays temperatures in Fahrenheit. To set your oven correctly, you need to convert 180°C to Fahrenheit:
F = (180 × 9/5) + 32
F = 356°F
So, you would set your oven to 356°F. However, since most ovens don’t have such precise settings, you would typically round to the nearest common setting, which is 350°F.
5. Why Is It Important to Know This Conversion?
Knowing how to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit is essential in several real-world situations:
- Cooking: Many recipes, especially those from different countries, use different temperature scales. Converting ensures that you cook your food at the correct temperature.
- Weather: When traveling, understanding the local weather forecast is crucial. Converting the temperature to a scale you’re familiar with helps you dress appropriately.
- Science and Medicine: In scientific and medical fields, accurate temperature measurements are vital. Being able to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit ensures precise communication and experimentation.
6. Converting 180 C to F for Oven Temperatures
When it comes to oven temperatures, precision is key for baking and cooking. While the exact conversion of 180°C is 356°F, most ovens have standard settings. In practical terms, you would typically round to the closest setting:
180°C ≈ 350°F
Therefore, when a recipe calls for 180°C, setting your oven to 350°F is a suitable approximation.
7. Real-World Applications: Cooking and Baking
Cooking and baking often require precise temperatures. Different recipes might specify temperatures in either Celsius or Fahrenheit, depending on the origin of the recipe.
-
Example 1: Baking a Cake
A cake recipe from Europe might specify baking at 180°C. If you’re using an oven with Fahrenheit settings, you would convert 180°C to 356°F. However, you would likely set your oven to 350°F for practical purposes.
-
Example 2: Roasting Vegetables
If a recipe for roasted vegetables suggests 180°C, you would again convert this to approximately 350°F in your Fahrenheit-based oven.
8. How Different Ovens Display Temperatures
It’s important to be aware that not all ovens are created equal. Some ovens allow you to switch between Celsius and Fahrenheit, while others are fixed to one scale. If your oven is fixed, knowing the conversion helps you adjust recipes accordingly.
Also, consider that some ovens may not be entirely accurate. Regular calibration can ensure your oven is heating to the correct temperature. An oven thermometer can be a useful tool for verifying the internal temperature.
9. Impact of Rounding on Cooking Results
Rounding the temperature can have a slight impact on cooking results. For instance, setting your oven to 350°F instead of the exact 356°F might mean your dish cooks a bit slower or faster. However, for most recipes, this small difference is negligible.
For more sensitive baking, like macarons or soufflés, precise temperature control is more critical. In these cases, an oven thermometer and careful monitoring are advisable.
10. Quick Conversion Table for Common Temperatures
Here’s a quick conversion table for some common temperatures:
| Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| 0°C | 32°F | Freezing point of water |
| 10°C | 50°F | Cool room temperature |
| 20°C | 68°F | Comfortable room temperature |
| 30°C | 86°F | Warm day |
| 40°C | 104°F | Hot day |
| 50°C | 122°F | Hot sauna |
| 60°C | 140°F | Very hot water |
| 70°C | 158°F | Scalding water |
| 80°C | 176°F | Hot coffee |
| 90°C | 194°F | Boiling point of alcohol |
| 100°C | 212°F | Boiling point of water |
| 150°C | 302°F | Baking |
| 180°C | 356°F | Baking |
| 200°C | 392°F | Roasting |
| 250°C | 482°F | High-temperature cooking |
| 300°C | 572°F | Industrial processes |
| 400°C | 752°F | High-temperature sterilization |
11. Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion in Different Fields
The ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit isn’t just useful in the kitchen. It also has applications in various other fields:
- Meteorology: Weather forecasts are often given in different temperature scales depending on the country. Converting helps you understand the weather conditions.
- Medicine: Body temperatures can be measured in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. Knowing the conversion is crucial for understanding a patient’s condition.
- Engineering: Many engineering applications require precise temperature measurements. Converting ensures accuracy in calculations and designs.
- HVAC: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems often use different temperature scales. Converting helps in setting up and maintaining these systems.
12. Understanding Temperature Scales: Celsius vs. Fahrenheit
To fully appreciate the conversion, it’s helpful to understand the two temperature scales:
-
Celsius (°C):
- Based on the freezing point of water (0°C) and the boiling point of water (100°C).
- Commonly used in most countries around the world.
- Part of the metric system.
-
Fahrenheit (°F):
- Based on the freezing point of water (32°F) and the boiling point of water (212°F).
- Primarily used in the United States and a few other countries.
- Part of the imperial system.
13. The History Behind Celsius and Fahrenheit
Understanding the origins of these scales can provide additional context:
- Celsius: Developed by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in the 18th century. Originally, 0°C was the boiling point of water, and 100°C was the freezing point, but this was later reversed to the current standard.
- Fahrenheit: Developed by German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century. He used 0°F as the freezing point of a salt-water mixture and 32°F as the freezing point of pure water.
14. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Converting Temperatures
When converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit, it’s easy to make mistakes. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
- Forgetting to add 32: The most common mistake is multiplying by 9/5 (or 1.8) but forgetting to add 32. Always remember the complete formula: F = (C × 9/5) + 32.
- Reversing the Formula: Make sure you’re using the correct formula for the conversion you need. If you’re converting from Fahrenheit to Celsius, use the formula C = (F – 32) × 5/9.
- Using Mental Math Incorrectly: While mental math can be quick, it’s also prone to errors. Double-check your calculations, especially if precision is important.
- Not Considering Oven Settings: Ovens often have standard temperature settings. Always round to the nearest available setting rather than trying to set a precise, unconventional temperature.
15. The Importance of Accurate Temperature Measurement
Accurate temperature measurement is crucial in many contexts. Whether you’re cooking, conducting scientific experiments, or monitoring your health, precision can make a significant difference. Here’s why:
- Cooking: The right temperature ensures your food is cooked safely and tastes its best. Under- or overcooking can lead to foodborne illnesses or poor-quality dishes.
- Science: In scientific research, precise temperature control is essential for accurate and reproducible results. Even small temperature variations can affect experimental outcomes.
- Medicine: Monitoring body temperature is a key part of diagnosing and treating illnesses. Accurate temperature readings help healthcare professionals make informed decisions.
- Industry: Many industrial processes, such as manufacturing and chemical production, rely on precise temperature control to ensure product quality and safety.
16. What are the Key Considerations for Temperature Conversion?
When converting temperatures, it’s vital to consider a few key factors to ensure accuracy and relevance:
- Purpose of Conversion: Understand why you need to convert the temperature. Is it for cooking, scientific research, or understanding weather forecasts? The context can influence the level of precision required.
- Available Tools: Use reliable tools such as calculators or online converters to minimize errors. Avoid relying solely on mental math, especially for critical applications.
- Oven Settings: If converting for oven temperatures, consider the standard settings available on your appliance. Round to the nearest common setting for practical use.
- Accuracy Needs: Determine the level of accuracy needed. For some applications, such as baking delicate pastries, precision is more important than for general estimations.
17. Tools and Resources for Easy Temperature Conversions
Fortunately, numerous tools and resources are available to make temperature conversions quick and easy:
- Online Converters: Websites like Google’s built-in converter, UnitConverters.net, and ConvertUnits.com offer simple interfaces for converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit.
- Mobile Apps: Many mobile apps, such as “Unit Converter” and “ConvertPad,” are available for both iOS and Android devices, providing convenient on-the-go conversions.
- Calculators: Scientific calculators often have built-in unit conversion functions.
- Conversion Charts: Printable conversion charts can be handy for quick reference in the kitchen or lab.
18. Scientific Insights: The Physics of Temperature
Understanding the physics of temperature can provide a deeper appreciation for the conversion process. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. When we measure temperature, we’re essentially measuring how fast these particles are moving.
- Celsius and Kinetic Energy: In Celsius, 0°C is the point at which water freezes, and the kinetic energy of water molecules is relatively low. As temperature increases, the molecules move faster, reaching maximum kinetic energy at the boiling point (100°C).
- Fahrenheit and Kinetic Energy: Similarly, Fahrenheit measures kinetic energy, but on a different scale. The freezing point of water is 32°F, and the boiling point is 212°F.
Understanding these principles helps clarify why the conversion formula works. It’s a mathematical way to translate kinetic energy measurements from one scale to another.
19. How Does 180 C Compare to Other Common Temperatures?
To give you a better sense of what 180°C (356°F) means in practical terms, let’s compare it to other common temperatures:
- 100°C (212°F): The boiling point of water. At this temperature, water rapidly turns into steam.
- 150°C (302°F): A typical temperature for baking cookies or cakes. This is a moderate oven temperature that allows for even cooking.
- 180°C (356°F): Suitable for roasting vegetables or baking bread. It’s a higher temperature that helps to caramelize the surface of foods.
- 200°C (392°F): Often used for roasting meats. The high temperature sears the outside while keeping the inside juicy.
- 250°C (482°F): A very high oven temperature, typically used for tasks like broiling or making pizza with a crispy crust.
20. The Future of Temperature Measurement
As technology advances, the future of temperature measurement is likely to bring even more precise and convenient tools. Here are some potential developments:
- Smart Thermometers: These devices can connect to your smartphone, allowing you to monitor temperatures remotely and receive alerts if temperatures go outside a specified range.
- Infrared Thermometers: These non-contact thermometers are becoming increasingly common, offering a quick and easy way to measure surface temperatures without touching the object.
- Wearable Sensors: Wearable devices that monitor body temperature continuously could become more prevalent, providing valuable health insights.
- Improved Oven Technology: Ovens with more precise temperature controls and built-in conversion functions could simplify cooking and baking.
21. Temperature Conversion for Travel: What to Expect
When traveling internationally, being able to convert temperatures is invaluable. Different countries use different temperature scales, and knowing the conversion can help you understand weather forecasts and make appropriate decisions about clothing and activities.
- United States: Primarily uses Fahrenheit.
- Europe: Primarily uses Celsius.
- Canada: Uses a mix of Celsius and Fahrenheit, with Celsius being the official scale.
- Australia: Primarily uses Celsius.
Before traveling, familiarize yourself with the temperature scale used in your destination and download a conversion app or bookmark an online converter.
22. Frequently Asked Questions About Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion
To further clarify the process, here are some frequently asked questions:
Q: How do I convert 25°C to Fahrenheit?
A: Use the formula F = (C × 9/5) + 32. So, F = (25 × 9/5) + 32 = 77°F.
Q: Is there a quick way to estimate Celsius to Fahrenheit?
A: Yes, you can double the Celsius temperature and add 30. This gives you an approximate Fahrenheit value. For example, 20°C ≈ (20 × 2) + 30 = 70°F. This is not precise but is useful for quick estimations.
Q: Why do some countries use Fahrenheit and others use Celsius?
A: The choice of temperature scale is often historical. Celsius is part of the metric system and is used by most countries worldwide. Fahrenheit is part of the imperial system and is primarily used in the United States.
Q: What is the formula for converting Fahrenheit to Celsius?
A: The formula is C = (F – 32) × 5/9.
Q: How can I ensure accurate temperature conversions?
A: Use a reliable calculator or online converter. Double-check your calculations, especially if precision is important. Also, be aware of potential errors in oven settings and use an oven thermometer if necessary.
Q: What is the significance of 0°C and 0°F?
A: 0°C is the freezing point of water on the Celsius scale. 0°F was originally defined as the freezing point of a salt-water mixture on the Fahrenheit scale.
Q: Can rounding the temperature affect cooking results?
A: Yes, but for most recipes, the impact is minimal. However, for delicate baking, precise temperature control is more critical.
Q: What are some common uses for temperature conversion?
A: Cooking, weather forecasting, scientific research, medical diagnosis, and industrial processes.
Q: How does temperature relate to energy?
A: Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. Higher temperatures mean that the particles are moving faster and have more energy.
Q: Where can I find reliable temperature conversion tools?
A: Online converters, mobile apps, scientific calculators, and conversion charts are all useful tools.
23. Advanced Applications of Temperature Conversion
Beyond the basics, temperature conversion plays a crucial role in various advanced applications:
- Cryogenics: This branch of physics deals with extremely low temperatures. Accurate conversions are essential for working with liquid nitrogen (-196°C or -321°F) and other cryogenic materials.
- Materials Science: Temperature affects the properties of materials. Accurate conversions are needed to study and manipulate materials at different temperatures.
- Astrophysics: Temperature is a key parameter in astrophysics, used to study stars, planets, and other celestial objects. Conversions are necessary for comparing data from different sources.
- Climate Science: Accurate temperature measurements and conversions are critical for studying climate change and its effects.
24. Practical Tips for Remembering the Conversion Formula
Memorizing the conversion formula can be helpful, but it can also be challenging. Here are some practical tips to help you remember it:
- Use a Mnemonic: Create a mnemonic device to help you remember the formula. For example, “Fahrenheit is Five over Nine, Celsius plus Thirty-Two.”
- Practice Regularly: The more you use the formula, the easier it will be to remember. Try converting temperatures mentally whenever you encounter them.
- Understand the Logic: Understanding why the formula works can make it easier to remember. Remember that you’re essentially scaling and shifting the Celsius temperature to match the Fahrenheit scale.
- Use Visual Aids: Create a visual aid, such as a chart or diagram, to help you remember the formula and the relationship between Celsius and Fahrenheit.
25. Case Studies: Temperature Conversion in Action
To illustrate the practical importance of temperature conversion, let’s look at a few case studies:
-
Case Study 1: Food Safety
A restaurant needs to ensure that its refrigerators are maintaining a safe temperature to prevent foodborne illnesses. The health inspector uses a thermometer that measures in Fahrenheit, while the restaurant’s guidelines are in Celsius. Accurate conversion is crucial to ensure compliance with food safety regulations.
-
Case Study 2: Scientific Research
A research lab is conducting an experiment that requires precise temperature control. The researchers are using equipment from different countries, some of which measure temperature in Celsius and others in Fahrenheit. Accurate conversion is essential for ensuring the validity of the experiment.
-
Case Study 3: International Travel
A traveler from the United States is visiting Europe. The weather forecasts are given in Celsius, and the traveler needs to know what to wear each day. Accurate conversion is essential for staying comfortable and safe.
 oven temperature conversion
oven temperature conversion
26. The Relationship Between Temperature and Humidity
Temperature and humidity are closely related, and understanding this relationship is important for many applications. Humidity refers to the amount of water vapor in the air. The higher the temperature, the more water vapor the air can hold.
- Relative Humidity: This is the percentage of water vapor in the air compared to the maximum amount the air could hold at that temperature.
- Heat Index: This is a measure of how hot it feels when humidity is combined with air temperature. High humidity can make hot temperatures feel even hotter.
When considering temperature conversions, it’s important to also factor in humidity, especially when making decisions about comfort and safety.
27. The Role of Temperature in Climate Change
Temperature plays a central role in climate change. The Earth’s average temperature is rising due to increased greenhouse gas emissions, leading to a range of environmental and social impacts.
- Global Warming: This refers to the long-term increase in Earth’s average temperature.
- Climate Models: These are computer simulations that use temperature data to predict future climate scenarios.
- Mitigation Strategies: These are actions taken to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and slow down global warming.
Accurate temperature measurements and conversions are essential for understanding and addressing climate change.
28. Temperature Scales in Different Industries
Different industries rely on temperature scales for various purposes. Here are some examples:
- Food Industry: Celsius and Fahrenheit are used to measure cooking temperatures, refrigeration temperatures, and storage temperatures.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Precise temperature control is essential for manufacturing and storing drugs.
- Chemical Industry: Temperature is a key parameter in many chemical reactions and processes.
- Aerospace Industry: Temperature is critical for designing and operating aircraft and spacecraft.
- Electronics Industry: Temperature affects the performance and reliability of electronic components.
29. Why Ask Questions on WHAT.EDU.VN?
Need more information or have additional questions about temperature scales or unit conversions? WHAT.EDU.VN provides a platform where you can ask any question and receive a free, accurate answer. Our community of experts is ready to help you understand even the most complex topics.
30. Take Action: Ask Your Question Now
Do you have a burning question about temperature conversion or any other topic? Don’t hesitate! Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your question for free. Our team is committed to providing quick, accurate, and easy-to-understand answers.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply curious, WHAT.EDU.VN is your go-to resource for free answers to all your questions. We can help you with unit conversion, temperature scales, finding quick solutions, and accessing a community of knowledgeable experts. Don’t wait – get the answers you need today!
If you are looking for a reliable and free service to answer all your questions, what.edu.vn is here for you. Don’t hesitate to ask your questions and get the answers you need!