What Is A Centimeter? It’s a common question, and at WHAT.EDU.VN, we’re here to provide a clear and concise answer, offering metric system insights. A centimeter (cm) is a unit of length in the metric system, widely used for everyday measurements. This article will explore the definition of a centimeter, its relationship to other units, practical examples, and how to use it effectively. Get ready to explore the world of centimeters, millimeters and meters with WHAT.EDU.VN!
1. Centimeter Defined: A Unit of Length
A centimeter (cm) is a unit of length in the metric system. It is defined as one-hundredth of a meter. In simpler terms, if you divide a meter into 100 equal parts, each part is a centimeter.
- Symbol: cm
- Metric System: Belongs to the metric system, making it compatible with other metric units like meters, millimeters, and kilometers.
- Common Usage: Used for measuring the length, width, or height of smaller objects, distances on maps, and in various scientific applications.
2. Centimeter vs. Other Units: Understanding the Scale
To fully grasp what a centimeter represents, it’s essential to compare it to other units of length:
2.1 Centimeter vs. Millimeter (mm)
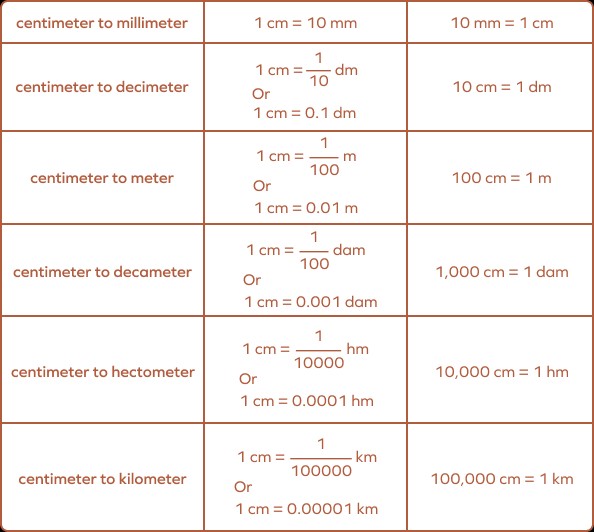
- Relationship: 1 centimeter = 10 millimeters
- Millimeter: A smaller unit than a centimeter. It’s often used for very precise measurements.
- Example: The thickness of a credit card is approximately 1 millimeter, while the diameter of a pencil might be around 7-8 millimeters, or 0.7-0.8 centimeters.
2.2 Centimeter vs. Meter (m)
- Relationship: 1 meter = 100 centimeters
- Meter: The base unit of length in the metric system. It’s used for measuring larger distances or objects.
- Example: The height of a door is typically around 2 meters (200 centimeters).
2.3 Centimeter vs. Inch (in)
- Relationship: 1 inch ≈ 2.54 centimeters
- Inch: A unit of length commonly used in the United States and a few other countries.
- Example: A standard sheet of paper is 8.5 inches wide, which is approximately 21.6 centimeters.
2.4 Centimeter vs. Foot (ft)
- Relationship: 1 foot = 30.48 centimeters
- Foot: Another unit of length in the imperial system, commonly used in the US.
- Example: A 6-foot tall person is approximately 183 centimeters tall.
Understanding these relationships allows you to convert between units and visualize the size of a centimeter in different contexts.
3. Real-World Examples: Visualizing Centimeters
To develop a better sense of how big a centimeter is, consider these real-world examples:
- A staple: Approximately 1 centimeter wide.
- A fingernail: The width of an adult’s fingernail is roughly 1 centimeter.
- A crayon: The diameter of a standard crayon is about 1 centimeter.
- A stack of ten pennies: Approximately 1.5 centimeters thick.
- A USB drive: The width of a standard USB drive is around 2 centimeters.
- A AA battery: The diameter of a AA battery is approximately 1.4 centimeters.
- A postage stamp: The width of a standard postage stamp is around 2-3 centimeters.
- A paperclip: A standard paperclip is about 3 centimeters long.
4. Tools for Measuring in Centimeters
Several tools are commonly used to measure length in centimeters:
- Ruler: A flat, rectangular tool marked with centimeter and millimeter divisions. Ideal for measuring short lengths and drawing straight lines.
- Measuring Tape: A flexible tape measure marked with centimeters, millimeters, and sometimes inches. Useful for measuring curved surfaces or longer distances.
- Meter Stick: A long, rigid stick exactly one meter (100 centimeters) in length. Used for measuring larger objects or distances.
- Digital Caliper: A precise measuring instrument that can measure the distance between two opposite sides of an object. Provides readings in centimeters or millimeters.
- Laser Distance Measurer: A device that uses a laser beam to measure distances. Displays measurements in various units, including centimeters.
5. Converting to and From Centimeters
Converting between centimeters and other units of length is a fundamental skill. Here are the conversion factors and formulas:
5.1 Centimeters to Millimeters
- Conversion Factor: 1 cm = 10 mm
- Formula: millimeters = centimeters × 10
- Example: 5 cm = 5 × 10 = 50 mm
5.2 Centimeters to Meters
- Conversion Factor: 1 m = 100 cm
- Formula: meters = centimeters ÷ 100
- Example: 250 cm = 250 ÷ 100 = 2.5 m
5.3 Centimeters to Inches
- Conversion Factor: 1 in ≈ 2.54 cm
- Formula: inches = centimeters ÷ 2.54
- Example: 15 cm = 15 ÷ 2.54 ≈ 5.91 inches
5.4 Centimeters to Feet
- Conversion Factor: 1 ft ≈ 30.48 cm
- Formula: feet = centimeters ÷ 30.48
- Example: 91.44 cm = 91.44 ÷ 30.48 = 3 feet
6. Practical Applications of Centimeters
Centimeters are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Construction: Measuring dimensions of building materials, room sizes, and furniture.
- Sewing and Tailoring: Taking body measurements, measuring fabric, and determining the length of hems.
- Crafting: Measuring materials for various art and craft projects, such as paper, wood, and yarn.
- Science: Measuring the size of organisms, objects, or distances in experiments.
- Mapping and Navigation: Representing distances on maps and charts.
- Manufacturing: Ensuring the accuracy of product dimensions in manufacturing processes.
- Sports: Measuring distances in athletic events, such as the length of a jump or the height of a hurdle.
- Photography: Measuring distances for focusing and framing shots.
7. Tips for Accurate Measurement in Centimeters
To ensure accurate measurements in centimeters, keep these tips in mind:
- Use the Right Tool: Choose the appropriate measuring tool for the task. A ruler is suitable for small objects, while a measuring tape is better for longer distances.
- Align the Tool Properly: Make sure the zero mark of the measuring tool is aligned with the starting point of the object you are measuring.
- Read at Eye Level: Avoid parallax error by reading the measurement at eye level.
- Measure Along a Straight Line: Ensure the measuring tool is straight and taut along the length you are measuring.
- Consider Precision: Determine the level of precision required for the measurement. Use millimeters for more precise measurements.
- Double-Check: Always double-check your measurements to minimize errors.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Misreading the Scale: Pay close attention to the markings on the measuring tool and avoid misreading the scale.
- Not Aligning the Tool Correctly: Failing to align the zero mark with the starting point can lead to inaccurate measurements.
- Bending or Warping the Measuring Tool: Using a bent or warped ruler or measuring tape can result in inaccurate measurements.
- Not Measuring Along a Straight Line: Measuring along a curved or uneven line will give you an incorrect length.
- Ignoring Parallax Error: Reading the measurement from an angle can cause parallax error.
9. The History of the Centimeter
The centimeter has its roots in the development of the metric system during the French Revolution in the late 18th century. The metric system was designed to be a universal, decimal-based system of measurement.
- The Meter: The meter was originally defined as one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator to the North Pole along a meridian.
- The Centimeter’s Origin: The centimeter was derived from the meter as one hundredth of its length. The prefix “centi-” comes from the Latin word “centum,” meaning “hundred.”
- Adoption and Standardization: The metric system, including the centimeter, was gradually adopted by many countries around the world, becoming the standard system of measurement for science and technology.
10. Fun Facts About Centimeters
- The word “centimeter” is a combination of the Latin word centum, which means hundred, and the French word mètre.
- The word “centimeter” was first coined in the year 1801 and has been widely used since then.
- A square centimeter (cm²) is a unit of area equal to the area of a square with sides of 1 centimeter each.
- A cubic centimeter (cm³) is a unit of volume equal to the volume of a cube with sides of 1 centimeter each. It is also equivalent to 1 milliliter (mL).
- The centimeter is often used in cartography to represent distances on maps, with a scale indicating the relationship between map distances and real-world distances.
- In some countries, shoe sizes are based on centimeter measurements.
11. Centimeters in Different Fields
11.1 Centimeters in Science
Scientists use centimeters for measuring organisms, objects, or distances in experiments.
11.2 Centimeters in Construction
Centimeters are useful for measuring dimensions of building materials, room sizes, and furniture.
11.3 Centimeters in Daily Life
From measuring fabric for sewing to determining the right frame size for a photograph, centimeters play a role in hobbies and everyday measurements.
12. Frequently Asked Questions About Centimeters
Let’s address some common questions about centimeters:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the centimeter used to measure? | A centimeter is a metric unit used for measuring the length of an object. It is written as cm. |
| What is a square centimeter? | A square centimeter unit is used to measure the surface area of an object. |
| What is a cubic centimeter? | A cubic centimeter is used to measure the volume of an object. |
| What is the abbreviation of centimeter? | The abbreviation used for centimeter is cm. |
| Are there smaller units than centimeters? | Yes, the smaller units than centimeters are millimeters, micrometers, and nanometers. |
| What is 10 cm called? | 10 cm is equal to 1 decimeter. Deci means one-tenth and so, decimetre is one-tenth of a meter. 1 meter = 100 cm One-tenth of meter = one-tenth of 100 cm which is 10 cm |

13. Mastering Measurement: Practice Problems
Test your knowledge of centimeters with these practice problems:
- Problem: A rectangular garden is 4 meters long and 2.5 meters wide. What is the perimeter of the garden in centimeters?
- Problem: A bookshelf has 5 shelves, each 80 centimeters long. What is the total length of shelving in meters?
- Problem: A roll of ribbon is 15 meters long. If you use 75 centimeters of ribbon for each gift you wrap, how many gifts can you wrap?
- Problem: A map has a scale of 1 cm = 5 km. Two cities are 8.2 centimeters apart on the map. What is the actual distance between the cities in kilometers?
- Problem: A square tile has sides of 30 centimeters each. What is the area of the tile in square meters?
14. Advanced Concepts and Uses
14.1 Scientific Notation and Centimeters
In scientific contexts, very large or small measurements are often expressed using scientific notation. For example, a length of 0.00005 meters can be written as 5 x 10^-5 meters. To convert this to centimeters, multiply by 100: 5 x 10^-5 meters = 5 x 10^-3 centimeters = 0.005 centimeters.
14.2 Centimeters in Computer Graphics
In computer graphics and design, centimeters can be used to specify dimensions of objects, layouts, or images. Knowing the conversion between centimeters and pixels is essential for creating accurate digital representations.
14.3 Centimeters in 3D Printing
In 3D printing, centimeters are used to define the dimensions of 3D models and the parameters of the printing process. Precision in centimeter measurements is crucial for achieving accurate and functional 3D-printed objects.
15. Centimeters and Technology: Smart Measurement Tools
Advancements in technology have led to the development of smart measurement tools that offer increased accuracy, convenience, and connectivity.
15.1 Digital Rulers and Calipers
Digital rulers and calipers provide precise measurements in centimeters or millimeters, with digital displays that eliminate the possibility of misreading the scale.
15.2 Laser Distance Measurers
Laser distance measurers use a laser beam to measure distances and can display measurements in various units, including centimeters, meters, and feet. These devices are particularly useful for measuring long distances or hard-to-reach areas.
15.3 Smartphone Measurement Apps
Smartphone measurement apps use the device’s camera and augmented reality technology to measure objects or distances. While the accuracy of these apps may vary, they can be convenient for quick estimations.
16. The Future of Centimeters: Evolving Measurement Technologies
As technology continues to advance, measurement technologies will continue to evolve, offering even greater accuracy, convenience, and integration with digital systems.
16.1 Nanotechnology and Centimeters
Nanotechnology deals with materials and structures at the nanometer scale, which is one billionth of a meter. While centimeters may not be directly used in nanotechnology research, understanding the relationship between centimeters and nanometers is essential for scaling up nanoscale structures to macroscopic dimensions.
16.2 Quantum Measurement
Quantum measurement techniques offer the potential for extremely precise measurements at the atomic level. While these techniques are still in the early stages of development, they may eventually lead to new ways of defining and measuring length, potentially impacting the future of the metric system.
17. Practice Problems and Solutions
-
Problem: A table is 150 cm long and 80 cm wide. What is the perimeter of the table in meters?
Solution:
- Perimeter = 2(length + width)
- Perimeter = 2(150 cm + 80 cm)
- Perimeter = 2(230 cm)
- Perimeter = 460 cm
- To convert to meters, divide by 100: 460 cm ÷ 100 = 4.6 meters
-
Problem: A room is 5 meters long and 4 meters wide. How many square centimeters of carpet are needed to cover the floor?
Solution:
- Area = length × width
- Area = 5 m × 4 m = 20 square meters
- To convert to square centimeters, multiply by (100 cm/m)^2: 20 m^2 × (100 cm/m)^2 = 20 × 10,000 = 200,000 square centimeters
-
Problem: A circle has a diameter of 20 cm. What is the circumference of the circle?
Solution:
- Circumference = π × diameter
- Circumference = π × 20 cm
- Circumference ≈ 3.14159 × 20 cm
- Circumference ≈ 62.83 cm
-
Problem: A cube has sides that are 15 cm long. What is the volume of the cube?
Solution:
- Volume = side^3
- Volume = (15 cm)^3
- Volume = 3375 cubic centimeters
-
Problem: A rectangular prism has dimensions of 25 cm x 12 cm x 8 cm. What is the volume of the prism?
Solution:
- Volume = length × width × height
- Volume = 25 cm × 12 cm × 8 cm
- Volume = 2400 cubic centimeters
18. Centimeters in Pop Culture
Centimeters, while a fundamental unit of measurement, also find their way into popular culture in various subtle yet significant ways.
18.1 Sports
In sports, centimeters can make all the difference. The difference between winning and losing can often come down to mere centimeters.
18.2 Fashion
The fashion industry relies heavily on centimeters for designing, tailoring, and manufacturing clothing. From measuring inseams to determining sleeve lengths, centimeters play a crucial role in ensuring a proper fit and stylish appearance.
18.3 Film and Television
In filmmaking and television production, centimeters are used for set design, prop construction, and camera work. The precise placement of objects, actors, and equipment often relies on centimeter measurements to create visually appealing and believable scenes.
19. Centimeters and Accessibility
Ensuring that measurement tools and information are accessible to people with disabilities is essential for promoting inclusivity and equality.
19.1 Large-Print Rulers and Measuring Tapes
Large-print rulers and measuring tapes feature high-contrast markings and large, easy-to-read numbers, making them accessible to people with low vision.
19.2 Tactile Rulers and Measuring Tapes
Tactile rulers and measuring tapes have raised markings or Braille labels, allowing people with blindness or visual impairments to measure objects by touch.
19.3 Digital Measurement Tools with Audio Output
Digital measurement tools with audio output provide spoken measurements, making them accessible to people with visual impairments.
Conclusion: Embracing the Centimeter
The centimeter is a versatile and essential unit of length, playing a vital role in science, engineering, construction, and everyday life. Understanding its relationship to other units, mastering conversion techniques, and using appropriate measuring tools are crucial for accurate measurement. As technology continues to advance, measurement tools and techniques will continue to evolve, offering even greater precision and convenience. By embracing the centimeter and its applications, we can enhance our understanding of the world around us and improve our ability to measure and create with accuracy and confidence.
Do you have any questions about centimeters or other measurement units? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today to ask your question for free and get expert answers! Our community is ready to help you understand the world around you, one centimeter at a time.
Contact Us:
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: what.edu.vn