What Is A Compound In Chemistry? It’s a substance formed when two or more elements chemically bond together, creating new materials with unique properties. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we simplify complex concepts, offering explanations on chemical unions and formulas. Explore the concept of chemical combinations and molecular structures, while gaining access to resources that make learning accessible.
1. Defining a Chemical Compound: The Building Blocks of Matter
What precisely constitutes a chemical compound? A chemical compound is defined as a substance that consists of two or more different elements chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio. These elements are united through chemical bonds, such as covalent or ionic bonds, to form molecules or crystal lattices.
1.1. Understanding the Molecular Composition
The core of a chemical compound lies in its molecular composition. Each molecule of a compound contains a specific number and type of atoms held together by chemical bonds. This arrangement dictates the compound’s physical and chemical properties, making it distinct from its constituent elements.
1.2. Distinguishing Compounds from Mixtures
It’s crucial to distinguish between compounds and mixtures. While both involve combinations of elements, compounds are chemically bonded, whereas mixtures are physically combined and can be separated by physical means. Mixtures retain the properties of their constituents, while compounds exhibit new properties.
2. Exploring Different Types of Chemical Compounds
Chemical compounds are categorized based on their composition, bonding, and properties. The two primary types are molecular compounds and ionic compounds, each with distinct characteristics and behaviors.
2.1. Molecular Compounds: Sharing Electrons
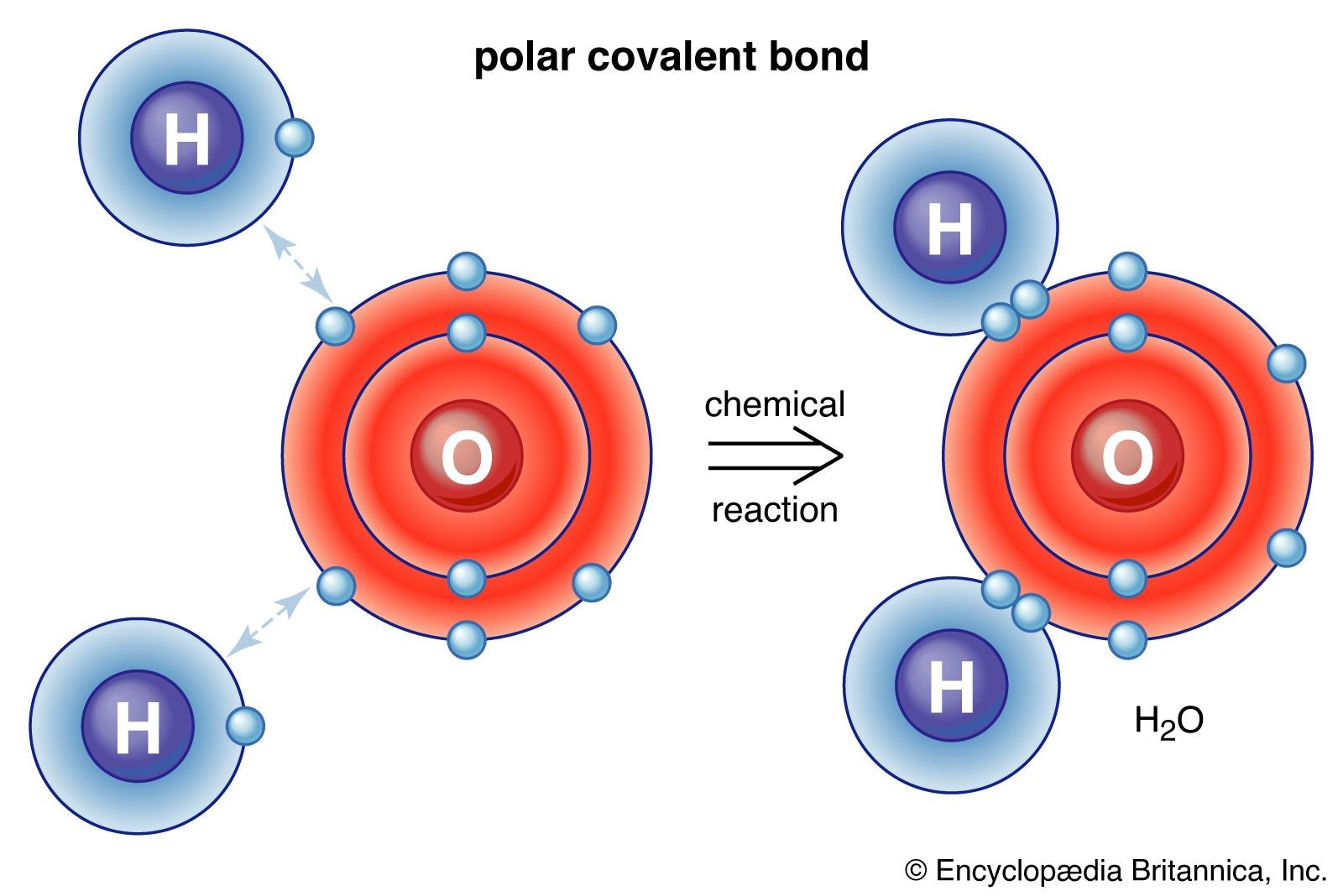
Molecular compounds, also known as covalent compounds, are formed when atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. These compounds typically involve nonmetal elements and exhibit properties such as low melting and boiling points, poor electrical conductivity, and solubility in nonpolar solvents.
2.2. Ionic Compounds: Transferring Electrons
Ionic compounds result from the transfer of electrons between atoms, leading to the formation of ions with opposite charges. These ions are held together by electrostatic forces, creating a crystal lattice structure. Ionic compounds generally have high melting and boiling points, conduct electricity when dissolved in water, and are soluble in polar solvents.
2.3. Organic Compounds: The Realm of Carbon
Organic compounds are a vast class of chemical compounds that contain carbon atoms bonded to other elements, such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. These compounds form the basis of life and are found in a wide range of materials, including fuels, plastics, pharmaceuticals, and foods.
2.4. Inorganic Compounds: Everything Else
Inorganic compounds encompass all chemical compounds that do not contain carbon-hydrogen bonds. This category includes a diverse array of substances, such as minerals, salts, acids, bases, and metals, with various applications in industry, agriculture, and medicine.
3. Understanding Chemical Formulas and Nomenclature
Chemical formulas and nomenclature are essential tools for representing and naming chemical compounds. These conventions allow scientists to communicate and identify compounds accurately and consistently.
3.1. Decoding Chemical Formulas
A chemical formula uses symbols and subscripts to indicate the types and numbers of atoms in a compound. For example, the formula for water is H2O, indicating two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom per molecule. Chemical formulas provide valuable information about the composition and structure of compounds.
3.2. Mastering Chemical Nomenclature
Chemical nomenclature is the systematic naming of chemical compounds based on established rules and conventions. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) provides guidelines for naming both organic and inorganic compounds, ensuring clarity and uniformity in scientific communication.
4. The Importance of Chemical Compounds in Everyday Life
Chemical compounds play a pivotal role in various aspects of our daily lives, from the air we breathe to the food we eat and the medicines we take. Their unique properties and functions make them essential components of modern society.
4.1. Compounds in the Air We Breathe
The air we breathe contains several vital chemical compounds, including oxygen (O2), nitrogen (N2), and carbon dioxide (CO2). Oxygen is essential for respiration, while nitrogen is a major component of the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, although present in small amounts, plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s temperature and supporting plant growth.
4.2. Compounds in the Food We Eat
The food we consume is composed of various organic and inorganic compounds, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. These compounds provide energy, nutrients, and essential building blocks for our bodies to function properly.
4.3. Compounds in Medicine and Pharmaceuticals
Many medicines and pharmaceuticals are chemical compounds designed to treat diseases, alleviate symptoms, and improve overall health. These compounds interact with specific targets in the body to produce therapeutic effects, ranging from pain relief to infection control and disease management.
5. Exploring Chemical Reactions and Compound Formation
Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms and molecules, leading to the formation of new chemical compounds. Understanding chemical reactions is crucial for synthesizing new materials, producing energy, and studying the behavior of chemical systems.
5.1. Types of Chemical Reactions
There are several types of chemical reactions, including synthesis, decomposition, displacement, and redox reactions. Each type involves distinct changes in the arrangement of atoms and molecules, resulting in the formation of different products.
5.2. Factors Affecting Reaction Rates
Several factors influence the rates of chemical reactions, including temperature, concentration, catalysts, and surface area. Understanding these factors is essential for controlling and optimizing chemical processes in various applications.
5.3. Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing chemical equations ensures that the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides of the equation, adhering to the law of conservation of mass. Balanced equations provide quantitative information about the stoichiometry of chemical reactions, allowing for accurate predictions of product yields and reagent requirements.
6. Practical Applications of Chemical Compounds in Industry
Chemical compounds are indispensable in various industries, serving as raw materials, intermediates, and products in manufacturing processes. Their unique properties and functionalities enable the production of a wide range of goods and technologies.
6.1. Polymers and Plastics
Polymers are large molecules composed of repeating structural units called monomers. These compounds are used to produce plastics, synthetic fibers, and other materials with diverse applications in packaging, construction, textiles, and electronics.
6.2. Fertilizers and Agrochemicals
Fertilizers are chemical compounds that provide essential nutrients to plants, promoting growth and increasing crop yields. Agrochemicals, such as pesticides and herbicides, are used to control pests and weeds, protecting crops from damage and enhancing agricultural productivity.
6.3. Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare
Pharmaceuticals are chemical compounds used to prevent, diagnose, and treat diseases. These compounds are developed through extensive research and testing to ensure their safety and efficacy in improving human health.
7. Advanced Concepts in Chemical Compounds
As you delve deeper into the world of chemical compounds, you’ll encounter advanced concepts that expand your understanding of their structure, properties, and behavior.
7.1. Isomers and Stereoisomers
Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. Stereoisomers are isomers with the same connectivity but different spatial arrangements of atoms. Understanding isomerism is crucial for distinguishing between compounds with different properties and activities.
7.2. Coordination Compounds
Coordination compounds, also known as complex compounds, consist of a central metal atom or ion surrounded by ligands, which are molecules or ions that donate electrons to the metal. These compounds exhibit unique properties and are used in catalysis, medicine, and materials science.
7.3. Supramolecular Chemistry
Supramolecular chemistry explores the interactions between molecules, leading to the formation of complex assemblies with emergent properties. This field has applications in drug delivery, sensing, and materials design.
8. The Role of Chemical Compounds in Environmental Science
Chemical compounds play a critical role in environmental science, influencing air and water quality, climate change, and ecosystem health. Understanding their behavior and impact is essential for addressing environmental challenges and promoting sustainability.
8.1. Air Pollution
Air pollution results from the release of harmful chemical compounds into the atmosphere, including nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds. These pollutants can cause respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, and other health issues.
8.2. Water Pollution
Water pollution occurs when chemical compounds contaminate water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, and oceans. These pollutants can come from industrial discharges, agricultural runoff, sewage, and other sources, posing risks to aquatic life and human health.
8.3. Climate Change
Certain chemical compounds, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, are greenhouse gases that trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing to climate change. Reducing emissions of these gases is crucial for mitigating the impacts of global warming and preserving the environment.
9. Safety Considerations When Working with Chemical Compounds
Working with chemical compounds requires adherence to strict safety protocols to protect yourself and others from potential hazards. Proper handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals are essential for preventing accidents and minimizing risks.
9.1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal protective equipment (PPE) includes items such as gloves, safety goggles, lab coats, and respirators, which provide a barrier between you and hazardous chemicals. Wearing appropriate PPE is crucial for preventing skin contact, eye injuries, inhalation of toxic fumes, and other potential exposures.
9.2. Chemical Handling and Storage
Proper handling and storage of chemical compounds involve following specific guidelines to prevent spills, leaks, fires, and explosions. Chemicals should be stored in designated areas, labeled clearly, and separated according to compatibility to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
9.3. Waste Disposal
Chemical waste must be disposed of properly to prevent environmental contamination and health hazards. Waste should be segregated into appropriate containers, labeled accurately, and disposed of according to local regulations and guidelines.
10. Exploring the Latest Research in Chemical Compounds
The field of chemical compounds is constantly evolving, with new discoveries and innovations emerging regularly. Staying abreast of the latest research is essential for advancing scientific knowledge and developing new technologies.
10.1. New Compound Synthesis
Researchers are continuously developing new methods for synthesizing chemical compounds with unique properties and functionalities. These advancements enable the creation of novel materials, drugs, and catalysts with improved performance and applications.
10.2. Materials Science
Materials science focuses on the design, synthesis, and characterization of materials with specific properties. Chemical compounds play a central role in materials science, serving as building blocks for creating advanced materials with applications in electronics, energy, and medicine.
10.3. Drug Discovery
Drug discovery involves the identification and development of new chemical compounds that can treat diseases. Researchers use various techniques, such as high-throughput screening, computational modeling, and medicinal chemistry, to discover and optimize drug candidates with therapeutic potential.
11. Chemical Compounds in Forensic Science
Chemical compounds play a crucial role in forensic science, aiding in the identification of substances, analysis of evidence, and reconstruction of crime scenes. Forensic chemists employ various analytical techniques to examine samples and provide valuable insights for legal investigations.
11.1. Drug Analysis
Forensic chemists analyze samples of suspected drugs to identify their composition, purity, and origin. This information is essential for prosecuting drug-related crimes and preventing drug abuse.
11.2. Trace Evidence Analysis
Trace evidence includes small amounts of materials, such as fibers, paint, and glass, that can be transferred between objects or individuals during a crime. Forensic chemists analyze trace evidence to establish connections between suspects, victims, and crime scenes.
11.3. Arson Investigation
Arson investigators rely on forensic chemists to analyze fire debris and identify accelerants, such as gasoline or kerosene, that may have been used to start a fire. This information is crucial for determining the cause of a fire and prosecuting arsonists.
12. The Ethics of Chemical Compound Research and Development
Research and development of chemical compounds raise ethical considerations related to safety, environmental impact, and social responsibility. Scientists and researchers must adhere to ethical principles and guidelines to ensure that their work benefits society while minimizing potential harm.
12.1. Safety and Toxicity Testing
Before a chemical compound can be used in consumer products or pharmaceuticals, it must undergo rigorous safety and toxicity testing to assess its potential risks to human health and the environment. These tests help identify potential hazards and establish safe exposure limits.
12.2. Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental impact assessments evaluate the potential effects of chemical compounds on ecosystems, wildlife, and natural resources. These assessments help identify potential environmental risks and inform decisions about the use and disposal of chemicals.
12.3. Social Responsibility
Researchers and developers have a social responsibility to ensure that chemical compounds are used in a manner that benefits society and does not harm vulnerable populations. This includes considering the ethical implications of their work and engaging with stakeholders to address concerns.
13. Chemical Compounds in Art and Archaeology
Chemical compounds are used in art and archaeology to analyze artifacts, determine their age and origin, and restore damaged objects. These techniques provide valuable insights into the history, culture, and technology of past civilizations.
13.1. Pigment Analysis
Pigment analysis involves identifying the chemical compounds used in paints, dyes, and other colorants. This information can help determine the age and origin of artworks and provide insights into the techniques used by artists.
13.2. Radiocarbon Dating
Radiocarbon dating is a technique used to determine the age of organic materials by measuring the amount of carbon-14, a radioactive isotope of carbon. This method is widely used in archaeology to date artifacts and understand the chronology of past events.
13.3. Conservation and Restoration
Chemical compounds are used in conservation and restoration to stabilize and protect artifacts from deterioration. These treatments can help preserve artworks, documents, and other cultural heritage objects for future generations.
14. Common Misconceptions About Chemical Compounds
There are several common misconceptions about chemical compounds that can lead to confusion and misunderstanding. Addressing these misconceptions is essential for promoting accurate scientific literacy.
14.1. All Chemicals Are Harmful
Not all chemical compounds are harmful. In fact, many are essential for life and play crucial roles in various industries and technologies. It is important to distinguish between hazardous and benign chemicals and to handle all chemicals with care.
14.2. Natural Is Always Better
The term “natural” does not always equate to safety or efficacy. Some natural compounds can be harmful or toxic, while synthetic compounds can be safe and effective. It is important to evaluate the properties of a compound based on scientific evidence, rather than relying solely on its origin.
14.3. Chemical-Free Products Are Safer
The term “chemical-free” is misleading because all matter is composed of chemicals. Products marketed as “chemical-free” may simply contain different chemicals or use alternative labeling. It is important to evaluate the ingredients and properties of a product, rather than relying on marketing claims.
15. The Future of Chemical Compound Research
The future of chemical compound research holds exciting possibilities for advancing scientific knowledge, developing new technologies, and addressing global challenges. Innovations in synthesis, analysis, and application of chemical compounds are poised to transform various fields.
15.1. Green Chemistry
Green chemistry focuses on designing chemical compounds and processes that minimize environmental impact and promote sustainability. This approach aims to reduce waste, conserve resources, and develop safer alternatives to hazardous chemicals.
15.2. Nanomaterials
Nanomaterials are chemical compounds with dimensions on the nanoscale (1-100 nanometers). These materials exhibit unique properties and have applications in electronics, medicine, and energy.
15.3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Chemistry
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to accelerate chemical compound research by predicting properties, designing molecules, and optimizing reactions. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns that would be difficult for humans to detect.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Chemical Compounds
Let’s address some common questions about chemical compounds to further clarify your understanding of these fundamental substances.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the simplest chemical compound? | The simplest chemical compound is arguably diatomic hydrogen (H2), consisting of two hydrogen atoms bonded together. However, in terms of compounds with different elements, water (H2O) is a fundamental and simple compound. |
| How do chemical compounds form? | Chemical compounds form through chemical reactions where atoms share (covalent bonds) or transfer (ionic bonds) electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. These bonds hold the atoms together in specific ratios. |
| What are the main differences between organic and inorganic compounds? | Organic compounds primarily consist of carbon and hydrogen atoms, often with other elements like oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. They are typically associated with living organisms. Inorganic compounds, on the other hand, include all other compounds that do not contain carbon-hydrogen bonds, such as salts, metals, and minerals. |
| What are some examples of common chemical compounds? | Common examples include water (H2O), sodium chloride (NaCl), methane (CH4), glucose (C6H12O6), and ethanol (C2H5OH). These compounds are found in various aspects of daily life, from food and beverages to fuels and pharmaceuticals. |
| How are chemical compounds named? | Chemical compounds are named using systematic nomenclature rules established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). These rules ensure that each compound has a unique and unambiguous name that reflects its composition and structure. |
| What role do chemical compounds play in the environment? | Chemical compounds play both beneficial and detrimental roles in the environment. They are essential for life processes, nutrient cycling, and maintaining ecosystem balance. However, certain compounds can also contribute to pollution, climate change, and other environmental problems. |
| How are chemical compounds used in medicine? | Chemical compounds are used in medicine to treat and prevent diseases. Pharmaceuticals, such as antibiotics, analgesics, and vaccines, are chemical compounds that interact with specific targets in the body to produce therapeutic effects. |
| What safety precautions should be taken when handling chemical compounds? | When handling chemical compounds, it is important to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, safety goggles, and lab coats. Chemicals should be handled in well-ventilated areas, stored properly, and disposed of according to local regulations to minimize the risk of exposure and accidents. |
| How is research in chemical compounds advancing? | Research in chemical compounds is advancing through innovations in synthesis, analysis, and application of materials. Green chemistry, nanomaterials, and artificial intelligence are driving the development of new compounds with improved properties and functionalities. |
| Where can I find more information about chemical compounds? | You can find more information about chemical compounds through textbooks, scientific journals, online databases, and educational websites such as WHAT.EDU.VN. Consulting experts and attending conferences and workshops can also provide valuable insights and updates on the latest research. |
Unlock Your Potential: Ask Questions and Get Answers at WHAT.EDU.VN
Still curious about chemical compounds? Do you have questions about specific reactions, formulas, or applications? Don’t hesitate! At WHAT.EDU.VN, we offer a free question-and-answer platform where you can get expert insights and clear explanations.
Why Choose WHAT.EDU.VN?
- Free Access: Ask any question without any cost.
- Expert Answers: Get reliable information from knowledgeable professionals.
- Quick Responses: Receive timely answers to your queries.
- Easy to Use: Navigate our platform effortlessly and get the information you need.
- Community Support: Join a community of learners and experts.
Take Action Now
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your burning questions about chemical compounds. Our team is ready to help you understand even the most complex topics. Don’t let your curiosity wait – get the answers you need now!
Contact Us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Conclusion: Mastering the World of Chemical Compounds
Understanding what a chemical compound is opens the door to comprehending the intricate world of chemistry. From molecular structures to everyday applications, chemical compounds are the foundation of matter and life. By exploring these concepts and utilizing resources like what.edu.vn, you can deepen your knowledge and appreciate the significance of these fundamental substances. Keep exploring, keep questioning, and unlock the wonders of chemistry.

