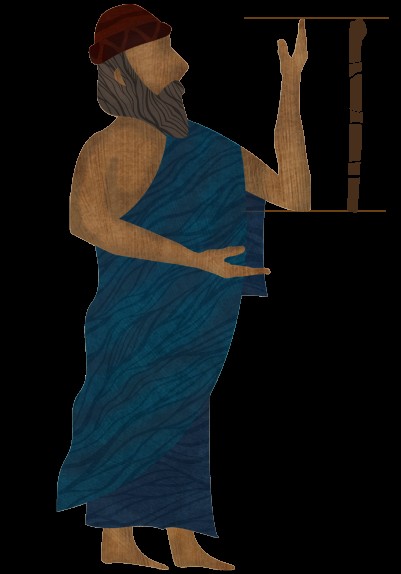
A cubit is an ancient unit of measurement, primarily defined as the distance from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger, typically ranging from 17 to 21 inches; if you’re curious about ancient measurements and their implications, WHAT.EDU.VN provides expert answers and insights. Understanding the cubit unlocks insights into ancient architecture, biblical accounts, and historical engineering, and we are commited to providing you with accurate and easily understandable explanations!
1. What Exactly Is a Cubit Measurement?
A cubit is an ancient unit of length based on the distance from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger, reflecting a practical, human-centric approach to measurement in early civilizations. If you are looking for quick and reliable answers about units of measurement and historical contexts, visit WHAT.EDU.VN for free, expert information.
The cubit’s length varies depending on the civilization and time period, generally falling between 17 and 21 inches (43 to 53 cm). This variability arises because the measurement is based on human anatomy, which naturally differs from person to person. However, standard cubits were often established within specific cultures to ensure consistency in construction and trade. The cubit was widely used in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, Israel, and other Middle Eastern societies. Its significance is evident in numerous historical texts and archaeological findings, including its prominent role in describing the dimensions of Noah’s Ark and Solomon’s Temple in the Bible.
To standardize constructions and trade, royal cubits were often introduced, with fixed lengths verified by official rods; if you want to dive deep into the accuracy and history of ancient units of measurement, you can ask any question on WHAT.EDU.VN and get instant help!
What Were the Different Types of Cubits?
Different civilizations used various types of cubits, each with a slightly different length, reflecting their unique standards and practices.
- Royal Cubit: Standardized in ancient Egypt, this cubit measured approximately 52.5 cm (20.6 inches) and was used for monumental constructions like pyramids and temples.
- Common Cubit: Shorter than the royal cubit, the common cubit was around 45 cm (17.7 inches) and used for everyday measurements.
- Hebrew Cubit: Ancient Hebrews had two cubit lengths: the common cubit (approximately 44.5 cm or 17.5 inches) and the long cubit (about 52.3 cm or 20.6 inches).
- Mesopotamian Cubit: In Mesopotamia, the cubit varied between 49 cm (19.3 inches) and 56 cm (22 inches), depending on the period and region.
Why Was the Cubit Important in Ancient Times?
The cubit was crucial in ancient times because it provided a standardized unit for construction, trade, and land measurement, allowing civilizations to build complex structures and conduct commerce efficiently. Do you need to understand how ancient measurements influenced modern architectural designs? Then ask WHAT.EDU.VN to learn more.
The cubit’s importance extended beyond mere measurement. It was deeply integrated into the cultural and religious practices of ancient societies. For instance, the dimensions of sacred structures, such as temples and arks, were often specified in cubits, emphasizing the unit’s spiritual significance. Standardized measurements facilitated trade and commerce, ensuring fair exchanges and promoting economic growth. Land surveying and allocation relied on the cubit to define property boundaries and agricultural plots, supporting organized agriculture and social stability. The cubit, therefore, played a vital role in the technological, economic, and social development of ancient civilizations.
2. How Long Is a Cubit in Modern Units?
The length of a cubit varies, but it typically falls between 17 to 21 inches (approximately 43 to 53 centimeters); if you need a quick conversion for ancient measurements to modern units, don’t hesitate to post your questions on WHAT.EDU.VN for a swift response.
Converting a cubit to modern units like inches or centimeters depends on which specific cubit is being referenced (Egyptian, Hebrew, Mesopotamian, etc.). Each of these ancient cultures had their own standard cubit length, which can vary slightly. For example, the Egyptian royal cubit is about 20.6 inches (52.5 centimeters), while the common cubit is around 17.7 inches (45 centimeters). The Hebrew cubit is approximately 17.5 inches (44.5 centimeters), and the Mesopotamian cubit ranges from 19.3 inches (49 centimeters) to 22 inches (56 centimeters). Knowing the specific cubit being referenced is crucial for accurate conversion. These measurements are essential for archaeologists, historians, and researchers studying ancient texts, architecture, and engineering.
Would you like to know more about the current applications of ancient measurement units in archeology? Do not hesitate to ask WHAT.EDU.VN to deepen your knowledge on the subject.
How Does the Cubit Compare to Other Ancient Units of Measurement?
The cubit is comparable to other ancient units like the foot and the palm, but each had distinct cultural and practical applications; for a deeper comparison of ancient measurement systems, explore the resources at WHAT.EDU.VN, where you can ask specific questions and get detailed answers.
The cubit, foot, and palm were integral to ancient measurement systems, each with unique origins and applications. The foot, generally equivalent to the length of a human foot (approximately 30 cm or 12 inches), was commonly used in Greece and Rome for land measurement and architecture. The palm, representing the width of a hand (about 7.5 cm or 3 inches), served as a smaller unit within the cubit system, often used for detailed measurements in construction. While the cubit provided a larger, more standardized length for major constructions and general measurements, the foot and palm offered flexibility for smaller-scale tasks. These units collectively reflect the human-centric approach to measurement in ancient civilizations, where dimensions were often based on readily available body parts.
What Are Some Real-World Examples of Cubit Measurements?
Real-world examples of cubit measurements include the dimensions of Noah’s Ark and Solomon’s Temple, both described in the Bible using cubits as the unit of length; if you need clarification on biblical measurements, consult the experts at WHAT.EDU.VN for reliable interpretations and historical context.
Noah’s Ark, as described in the Bible, was 300 cubits long, 50 cubits wide, and 30 cubits high. Using an approximate royal cubit length of 20.6 inches (52.5 cm), this would make the Ark about 515 feet (157 meters) long, 86 feet (26 meters) wide, and 52 feet (16 meters) high. Similarly, Solomon’s Temple, also described in the Bible, was built with specific dimensions in cubits. 1 Kings 6:2 states that the temple was 60 cubits long, 20 cubits wide, and 30 cubits high. These measurements provide insight into the scale and grandeur of these ancient structures, showcasing the cubit’s significance in historical and religious contexts. Understanding these measurements helps in visualizing and comprehending the architectural achievements of ancient civilizations.
3. How Did Ancient Civilizations Use the Cubit?
Ancient civilizations, including Egyptians and Mesopotamians, utilized the cubit for architectural design, construction, and land surveying, showcasing its versatility and importance in various aspects of life; for more information on specific ancient building techniques, visit WHAT.EDU.VN to ask our experts.
The cubit was a foundational unit of measurement in ancient Egypt, playing a crucial role in the construction of monumental structures like the pyramids and temples. The Egyptians used a royal cubit, standardized at approximately 52.5 cm (20.6 inches), for official measurements. In Mesopotamia, the cubit was essential for building ziggurats, palaces, and irrigation systems. The Mesopotamian cubit varied in length but typically ranged from 49 cm to 56 cm (19.3 to 22 inches). Land surveying was another critical application, with the cubit helping to define property boundaries and agricultural plots. Accurate measurements ensured fair allocation of land and resources, contributing to social stability. The widespread use of the cubit in these civilizations underscores its significance in enabling complex engineering and organized societies.
Are you curious about the tools they used to measure cubits in ancient times? Then ask WHAT.EDU.VN to learn more.
What Role Did the Cubit Play in Ancient Egyptian Architecture?
In ancient Egyptian architecture, the cubit was vital for planning and constructing pyramids, temples, and other monumental structures, ensuring precision and uniformity in design; for a comprehensive understanding of Egyptian architectural techniques, consult the resources at WHAT.EDU.VN for detailed explanations.
The cubit was fundamental to the precision and uniformity of ancient Egyptian architecture. The royal cubit, meticulously standardized, served as the basis for all major constructions. Architects and builders used cubit rods, often made of wood or stone, to ensure accurate measurements. The Great Pyramid of Giza, for example, was designed and built using the royal cubit, with dimensions carefully calculated to reflect mathematical and astronomical principles. Temples, such as Karnak and Luxor, also employed the cubit to create harmonious proportions and sacred spaces. The Egyptians believed that precise measurements were essential for aligning structures with cosmic forces and honoring the gods. The use of the cubit in these projects reflects their advanced understanding of mathematics and engineering, as well as their deep cultural and religious values.
How Was the Cubit Used in Biblical Times?
In biblical times, the cubit was used to describe the dimensions of significant structures like Noah’s Ark and Solomon’s Temple, providing insight into the scale and design of these important religious landmarks; if you need help interpreting ancient texts, explore WHAT.EDU.VN to get reliable explanations.
The Bible references the cubit extensively, particularly in descriptions of Noah’s Ark and Solomon’s Temple. The dimensions of Noah’s Ark, as specified in Genesis 6:15, were 300 cubits long, 50 cubits wide, and 30 cubits high. These measurements, when converted to modern units using a common cubit length of about 18 inches, indicate that the Ark was approximately 450 feet long, 75 feet wide, and 45 feet high. Solomon’s Temple, described in 1 Kings 6, was 60 cubits long, 20 cubits wide, and 30 cubits high. Using the same cubit length, the Temple would have been about 90 feet long, 30 feet wide, and 45 feet high. These biblical references illustrate the cubit’s role in defining the size and scope of structures that held great religious and cultural significance.
4. What Is the Significance of the Cubit in Religious Texts?
The cubit holds significant importance in religious texts like the Bible, where it is used to describe the dimensions of sacred objects and structures, symbolizing divine order and precision; if you have questions about the symbolism of numbers and measurements in religion, don’t hesitate to ask WHAT.EDU.VN for quick and free assistance.
In religious texts, particularly the Bible, the cubit is more than just a unit of measurement; it symbolizes divine order and precision. The use of cubits to define the dimensions of sacred objects and structures underscores their spiritual significance. For example, the Ark of the Covenant, described in Exodus, was built to specific cubit measurements, indicating its divine purpose and the importance of adhering to God’s instructions. Similarly, the precise cubit measurements of Solomon’s Temple reflect the meticulous planning and divine guidance involved in its construction. These references suggest that the cubit was seen as a tool for creating spaces and objects that were pleasing to God and aligned with His divine plan. The consistent use of the cubit in these contexts reinforces the idea that accurate and intentional measurements were essential for fulfilling religious obligations and honoring the divine.
How Does the Cubit Relate to the Ark of the Covenant?
The cubit is directly related to the Ark of the Covenant, as the Bible specifies its dimensions in cubits, highlighting the importance of precise measurements in creating this sacred object; for a detailed analysis of the Ark of the Covenant, consult the experts at WHAT.EDU.VN for reliable interpretations and historical context.
The Ark of the Covenant, one of the most sacred objects in the Old Testament, was built according to precise measurements specified in Exodus 25:10. The Ark was to be 2.5 cubits long, 1.5 cubits wide, and 1.5 cubits high. Using an approximate cubit length of 18 inches, this would make the Ark about 45 inches long, 27 inches wide, and 27 inches high. These specific measurements were not arbitrary; they were divinely ordained to ensure that the Ark was constructed in accordance with God’s will. The Ark was intended to house the tablets of the Ten Commandments, symbolizing God’s covenant with the Israelites. The meticulous attention to detail, as reflected in the use of the cubit, underscores the Ark’s sacredness and the importance of obedience to divine instructions.
What Does the Cubit Symbolize in Solomon’s Temple?
In Solomon’s Temple, the cubit symbolizes divine intention and precise planning, emphasizing the temple’s role as a sacred space built according to God’s specifications; for more information about religious symbolism, visit WHAT.EDU.VN to ask our experts.
The cubit plays a significant symbolic role in Solomon’s Temple, representing divine intention and precise planning. The dimensions of the Temple, meticulously described in 1 Kings 6, were specified in cubits to ensure that the structure aligned with God’s specifications. The Temple was designed to be a sacred space where God’s presence would dwell, and its construction required strict adherence to divine instructions. The use of the cubit reflects the belief that accurate measurements were essential for creating a harmonious and spiritually significant structure. The precise cubit measurements symbolize the order and perfection that God desires in His dwelling place, reinforcing the Temple’s role as a symbol of God’s covenant with Israel and a center of worship and prayer.
5. How Has the Cubit Influenced Modern Measurement Systems?
While not directly used in modern systems, the cubit influenced the development of other units of measurement, demonstrating how ancient practices laid the groundwork for contemporary standards; if you’re interested in the evolution of measurement systems, explore WHAT.EDU.VN for clear explanations.
While the cubit is not directly used in modern measurement systems, it has indirectly influenced their development. The cubit’s historical significance lies in its role as one of the earliest standardized units of length. The concept of a standardized measurement, crucial for construction, trade, and land surveying, paved the way for more refined and accurate systems. Many ancient units, including the foot and the inch, have origins linked to the cubit. The foot, for example, was used in ancient Greece and Rome and is believed to have been influenced by the cubit. Over time, these units evolved and were incorporated into more comprehensive systems, such as the imperial and metric systems. The cubit’s legacy, therefore, is evident in the foundational principles of standardization and precision that underpin modern measurement practices.
What Modern Units Are Derived From the Cubit?
Modern units like the foot and inch can be traced back to the cubit, illustrating how ancient measurement practices evolved into the standards we use today; for a detailed look at the origins of modern measurement units, consult the resources at WHAT.EDU.VN for detailed explanations.
Modern units such as the foot and inch can be traced back to the cubit, highlighting the evolution of measurement practices from ancient times to the present day. The foot, standardized at approximately 12 inches (30.48 cm), has roots in ancient civilizations, including Greece and Rome, where it was used for land measurement and architecture. The inch, defined as 1/12 of a foot, is a smaller unit that allows for more precise measurements. The link between these units and the cubit lies in the historical practice of deriving measurements from human anatomy. The cubit, based on the length of the forearm, served as a foundational unit from which smaller units, like the foot and inch, were derived. Over centuries, these units were refined and standardized, eventually becoming integral parts of the imperial and metric systems.
How Do Engineers and Architects Use Cubit Measurements Today?
Engineers and architects today primarily use the metric and imperial systems but may reference cubit measurements for historical research or restoration projects, acknowledging its historical significance; if you have questions about architectural history, don’t hesitate to ask WHAT.EDU.VN for quick and free assistance.
While modern engineers and architects primarily use the metric and imperial systems for their projects, they may encounter cubit measurements in historical research, restoration projects, or studies of ancient structures. In these contexts, understanding the cubit is essential for accurately interpreting ancient texts and architectural plans. For example, when restoring ancient Egyptian temples or biblical sites, architects and historians need to convert cubit measurements to modern units to ensure that the restoration work is faithful to the original design. Additionally, researchers studying ancient engineering techniques may use cubit measurements to gain insights into the construction methods and standards of ancient civilizations. Although the cubit is not a standard unit in modern practice, its historical significance makes it a valuable reference for those working with ancient structures and texts.
6. How Can You Calculate Cubit Measurements?
Calculating cubit measurements involves understanding the specific type of cubit used (e.g., Egyptian, Hebrew) and converting it to modern units using the appropriate conversion factor; if you need help converting ancient units, explore WHAT.EDU.VN for detailed instructions.
To calculate cubit measurements accurately, you need to know the specific type of cubit being referenced, as different civilizations used varying lengths. For example, the Egyptian royal cubit is approximately 20.6 inches (52.5 cm), while the Hebrew cubit is around 17.5 inches (44.5 cm). Once you identify the correct cubit, you can convert it to modern units using the appropriate conversion factor. For instance, if you are working with a measurement of 10 Egyptian royal cubits, you would multiply 10 by 20.6 inches to get 206 inches, or approximately 17.17 feet (5.25 meters). Similarly, if you have a measurement in Hebrew cubits, you would multiply by 17.5 inches to convert to inches. Accurate conversions are essential for understanding historical texts and architectural plans, as well as for conducting research on ancient structures and engineering techniques.
What Are the Conversion Factors for Different Types of Cubits?
The conversion factors for different types of cubits vary: the Egyptian royal cubit is about 20.6 inches (52.5 cm), the common cubit is around 17.7 inches (45 cm), and the Hebrew cubit is approximately 17.5 inches (44.5 cm); for a quick reference guide, visit WHAT.EDU.VN to ask our experts for help.
- Egyptian Royal Cubit: 20.6 inches (52.5 cm)
- Common Cubit: 17.7 inches (45 cm)
- Hebrew Cubit: 17.5 inches (44.5 cm)
- Mesopotamian Cubit: Varies between 19.3 inches (49 cm) and 22 inches (56 cm)
What Tools Can Help Convert Cubit Measurements?
Online conversion tools and historical measurement databases can assist in converting cubit measurements to modern units, providing quick and accurate results for various types of cubits; do you want recommendations for online tools to convert cubit measurements? Then ask WHAT.EDU.VN to learn more.
Several online tools and resources can assist in converting cubit measurements to modern units. Websites like UnitConverters.net and OnlineConversion.com offer dedicated cubit conversion tools that allow you to input the cubit value and select the specific type of cubit (e.g., Egyptian royal cubit, Hebrew cubit) to get an accurate conversion to inches, centimeters, feet, or meters. Additionally, historical measurement databases, such as those maintained by universities and research institutions, provide detailed information on ancient units of measurement and their conversion factors. These resources are invaluable for researchers, historians, and anyone working with ancient texts or architectural plans that use cubit measurements. They ensure accurate conversions and facilitate a better understanding of the dimensions and proportions of ancient structures and objects.
7. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About the Cubit?
Common misconceptions about the cubit include assuming it had a fixed length across all cultures and time periods, overlooking the variations that existed among different civilizations; if you’re seeking clarification on historical facts, consult the experts at WHAT.EDU.VN for reliable explanations.
One of the most common misconceptions about the cubit is that it was a universally standardized unit of measurement with a fixed length across all cultures and time periods. In reality, the length of the cubit varied significantly depending on the civilization and era. For example, the Egyptian royal cubit was longer than the common cubit, and the Hebrew cubit differed from the Mesopotamian cubit. Another misconception is that the cubit was only used for religious purposes, such as constructing temples or arks. While the cubit did play a significant role in religious contexts, it was also widely used for secular purposes, including construction, land surveying, and trade. Additionally, some people mistakenly believe that the cubit is no longer relevant or useful today. However, understanding the cubit is essential for interpreting historical texts, studying ancient architecture, and appreciating the evolution of measurement systems.
Was the Cubit the Same Length in All Ancient Cultures?
No, the cubit was not the same length in all ancient cultures; different civilizations had their own versions of the cubit, each with a slightly different measurement; if you need a breakdown of regional variations in ancient measurements, explore the resources at WHAT.EDU.VN for clear explanations.
The cubit varied in length among ancient cultures due to differing standards and practices. The Egyptian royal cubit, used for monumental constructions, measured approximately 20.6 inches (52.5 cm), while the common cubit was shorter, around 17.7 inches (45 cm). In Mesopotamia, the cubit ranged from 19.3 inches (49 cm) to 22 inches (56 cm), depending on the period and region. The Hebrew cubit was approximately 17.5 inches (44.5 cm). These variations reflect the unique measurement systems and cultural preferences of each civilization. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurately interpreting historical texts and architectural plans. The use of distinct cubit lengths underscores the importance of considering the specific cultural context when studying ancient measurements.
Is the Cubit Still Relevant Today?
While not used in modern measurement systems, the cubit remains relevant for historical studies, archaeological research, and understanding ancient texts and structures, preserving its cultural significance; for more information about historical preservation, visit WHAT.EDU.VN to ask our experts.
The cubit remains relevant today primarily in the fields of historical studies, archaeological research, and the interpretation of ancient texts and structures. Although it is not used as a standard unit in modern measurement systems, understanding the cubit is essential for accurately interpreting historical dimensions and proportions. Archaeologists use cubit measurements to study ancient buildings, monuments, and artifacts, gaining insights into the construction methods and engineering techniques of past civilizations. Historians rely on the cubit to analyze biblical texts, architectural plans, and other historical documents, enhancing their understanding of ancient cultures and societies. The cubit’s enduring relevance lies in its role as a key to unlocking the secrets of the past and preserving cultural heritage.
8. Where Can You Find More Information About the Cubit?
You can find more information about the cubit in historical texts, archaeological reports, museum exhibits, and online resources, providing a wide range of sources for further research and study; if you are looking for quick answers to your burning questions, visit WHAT.EDU.VN and get free, expert help.
Several resources offer detailed information about the cubit. Historical texts, such as the Bible and ancient Egyptian papyri, provide valuable insights into the use and significance of the cubit in ancient times. Archaeological reports and museum exhibits often feature artifacts and architectural plans that showcase cubit measurements. Online resources, including academic journals, historical databases, and educational websites, offer a wealth of information on the cubit’s history, variations, and applications. Reputable sources such as university websites and scholarly articles can provide in-depth analyses and accurate conversions. By consulting a variety of these resources, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of the cubit and its role in ancient civilizations.
What Books and Articles Discuss the Cubit?
Books and articles discussing the cubit include scholarly works on ancient measurement systems, architectural history, and biblical studies, offering in-depth analyses and historical context; for book recommendations, explore WHAT.EDU.VN to ask our experts for help.
- “The Weights and Measures of the Bible” by Robert A. Diehl: This book provides a comprehensive overview of ancient weights and measures, including the cubit, as used in biblical times.
- “Ancient Egyptian Construction and Architecture” by Somers Clarke and R. Engelbach: This book delves into the construction techniques and architectural principles of ancient Egypt, with detailed discussions on the use of the royal cubit.
- “A History of Weights and Measures” by James R. Wisner: This article offers a historical perspective on the evolution of measurement systems, including the cubit, from ancient civilizations to modern times.
- “Understanding the Bible: A Reader’s Guide” by John Stott: This book helps in understanding the historical and cultural contexts of the Bible, including insights into the cubit measurements mentioned in various passages.
What Museums Have Exhibits on Ancient Measurement Systems?
Museums with exhibits on ancient measurement systems include the British Museum in London, the Louvre Museum in Paris, and the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York, showcasing artifacts and tools used in ancient times; if you are planning a visit, consult WHAT.EDU.VN to get free, expert help.
Several museums around the world feature exhibits on ancient measurement systems, including the cubit. The British Museum in London houses a collection of ancient Egyptian artifacts, including cubit rods and architectural plans that demonstrate the use of the royal cubit. The Louvre Museum in Paris also has exhibits on ancient Egyptian civilization, with displays on measurement tools and architectural models. The Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York features artifacts from various ancient cultures, including examples of measurement systems used in Mesopotamia and the Near East. These museum exhibits provide valuable visual and contextual information about the cubit and its role in ancient societies. Visiting these museums can enhance your understanding of the cubit and its historical significance.
Understanding the cubit, its history, and its relevance can feel like navigating an ancient labyrinth, but WHAT.EDU.VN is here to light your way. We offer a platform where curiosity meets expertise, providing clear, reliable answers to all your questions, big or small.
Do you have questions about other historical measurement units? Are you intrigued by the architectural marvels of ancient civilizations?
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your questions for free. Our community of experts is ready to provide you with the answers you seek, helping you unlock the mysteries of the past and connect with the knowledge of the ages.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: what.edu.vn