What Is A Dream? Dreams are fascinating mental experiences occurring during sleep, and WHAT.EDU.VN can help you understand them better. Dreams often involve vivid imagery, emotions, and sensations, leaving us pondering their purpose and meaning; find the answers and solutions you need right here, right now. Understand the subconscious, nighttime visions, and REM sleep.
Table of Contents
- What Are Dreams Defined?
- Why Do Humans Dream? Exploring Dream Theories
- When Do People Dream? Understanding Sleep Stages
- Do Dreams Have Hidden Meanings? Interpreting Dream Symbolism
- Different Types of Dreams: Lucid, Vivid, and More
- What are Nightmares? Causes and Effects Explained
- How Do Dreams Impact Sleep Quality?
- Tips to Remember Your Dreams: Dream Recall Techniques
- Strategies to Stop Nightmares: A Comprehensive Guide
- Frequently Asked Questions About Dreams
- Need More Answers? Ask the Experts at WHAT.EDU.VN
1. What Are Dreams Defined?
Dreams are essentially a series of images, thoughts, emotions, and sensations that occur involuntarily in the mind during certain stages of sleep. Visual imagery is the most commonly reported sense experienced in dreams, but they can involve any or all of the senses, including hearing, touch, taste, and smell.
The content and characteristics of dreams can vary widely, but some common features include:
- First-person perspective: Dreams typically unfold from the dreamer’s point of view.
- Involuntary nature: Dreams occur without conscious effort or control.
- Illogical content: Dreams can be bizarre, nonsensical, or defy the laws of physics.
- Interpersonal interactions: Dreams often feature other people, real or imagined, interacting with the dreamer or each other.
- Emotional intensity: Dreams can evoke strong emotions, ranging from joy and excitement to fear and sadness.
- Incorporation of waking life: Dreams often incorporate elements from the dreamer’s waking life, such as recent events, memories, or concerns.
While these characteristics are common, they are not universal, and the experience of dreaming can be highly subjective and personal.
2. Why Do Humans Dream? Exploring Dream Theories
The purpose of dreaming remains a topic of ongoing debate and research among sleep experts and neuroscientists. While there is no single, universally accepted explanation, several prominent theories attempt to shed light on why we dream:
- Memory Consolidation: This theory suggests that dreaming plays a role in consolidating and processing memories, transferring information from short-term to long-term storage.
- Emotional Processing: Dreams may serve as a way for the brain to process and regulate emotions, allowing us to work through feelings and experiences in a safe and simulated environment.
- Threat Simulation: The threat simulation theory posits that dreaming allows us to rehearse and prepare for potential threats or dangers, enhancing our survival skills.
- Activation-Synthesis Theory: This theory proposes that dreams are simply the result of random neural activity in the brain during REM sleep, which the brain then attempts to interpret and make sense of.
- Problem-Solving: Some researchers believe that dreams can help us find creative solutions to problems or gain new perspectives on challenges we face in our waking lives.
While each of these theories offers valuable insights into the potential functions of dreaming, it is likely that dreams serve multiple purposes and that their significance may vary depending on the individual and the specific dream content.
3. When Do People Dream? Understanding Sleep Stages
Dreams can occur during any stage of sleep, but they are most vivid, frequent, and intense during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage. REM sleep is characterized by increased brain activity, rapid eye movements, and muscle relaxation.
During REM sleep, the brain exhibits patterns of activity that are similar to those seen during wakefulness, which may explain the hallucinatory and dreamlike quality of experiences during this stage. Dreams during REM sleep tend to be more narrative, emotional, and bizarre compared to dreams that occur during non-REM sleep.
Non-REM sleep, which consists of stages 1 through 3, is associated with more logical, realistic, and thought-like dreams. These dreams often involve reflections on daily events or concerns.
The distribution of REM sleep changes throughout the night. The first REM period typically occurs about 90 minutes after falling asleep and lasts for a relatively short time. As the night progresses, REM periods become longer and more frequent, with the longest and most intense dreams occurring in the hours before waking up.
Understanding the sleep stages and their relationship to dreaming can provide valuable insights into the nature and purpose of these fascinating mental experiences.
4. Do Dreams Have Hidden Meanings? Interpreting Dream Symbolism
The question of whether dreams have hidden meanings has been a subject of debate and fascination for centuries. Some psychologists and dream analysts believe that dreams can provide valuable insights into a person’s unconscious thoughts, feelings, and motivations. Others view dreams as random and meaningless byproducts of brain activity during sleep.
The interpretation of dreams is a highly subjective process that depends on the individual, their personal experiences, and the specific symbols and themes that appear in their dreams. Some common approaches to dream interpretation include:
- Freudian Analysis: Sigmund Freud believed that dreams are a window into the unconscious mind and that they contain symbolic representations of repressed desires and conflicts.
- Jungian Analysis: Carl Jung emphasized the importance of archetypes and universal symbols in dreams, suggesting that they reflect collective unconscious patterns of human experience.
- Symbolic Interpretation: This approach involves assigning specific meanings to symbols and themes that appear in dreams based on cultural, personal, or psychological associations.
- Contextual Analysis: This method focuses on understanding the context of the dream, including the dreamer’s current life situation, relationships, and emotional state, to interpret the dream’s meaning.
While there is no definitive method for interpreting dreams, the process can be a valuable tool for self-reflection, personal growth, and gaining a deeper understanding of one’s inner world. If you are curious about exploring the potential meanings of your dreams, WHAT.EDU.VN offers a platform to ask questions and receive insights from knowledgeable individuals.
5. Different Types of Dreams: Lucid, Vivid, and More
Dreams come in many different forms, each with its unique characteristics and qualities. Here are some of the most common types of dreams:
- Lucid Dreams: Lucid dreams occur when you become aware that you are dreaming while still inside the dream. This awareness allows you to consciously control and manipulate the dream environment and events.
- Vivid Dreams: Vivid dreams are characterized by their intense sensory detail, emotional impact, and realism. These dreams often feel very real and can be easily remembered upon waking.
- Nightmares: Nightmares are disturbing or frightening dreams that cause you to wake up feeling anxious, scared, or upset. They often involve themes of danger, threat, or loss of control.
- Recurring Dreams: Recurring dreams are dreams that repeat over time, often with the same or similar themes, characters, and settings. They may reflect unresolved conflicts, anxieties, or patterns in your life.
- Daydreams: Daydreams are waking fantasies or mental images that occur when you are awake and not focused on the present moment. They can be a form of escapism, creativity, or problem-solving.
Understanding the different types of dreams can help you gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity and complexity of these fascinating mental experiences.
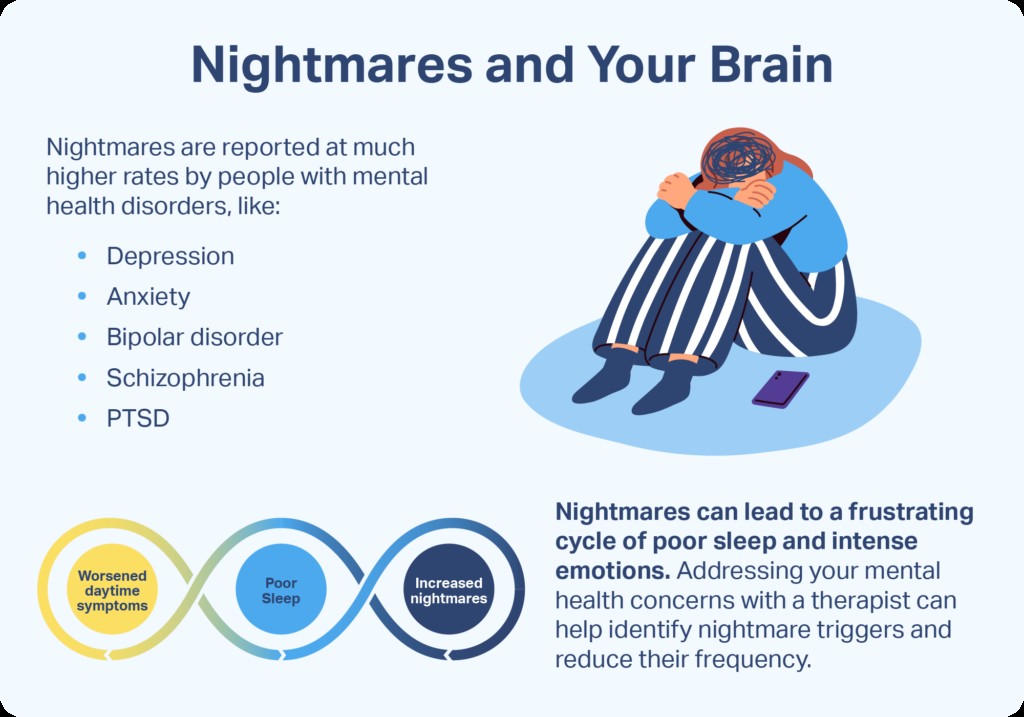
6. What are Nightmares? Causes and Effects Explained
Nightmares are vivid and disturbing dreams that evoke strong feelings of fear, terror, distress, or anxiety. They often cause the dreamer to wake up abruptly and can be difficult to shake off. While occasional nightmares are common and usually harmless, frequent nightmares can disrupt sleep, impair daytime functioning, and negatively impact mental health.
The causes of nightmares are varied and complex. Some potential factors include:
- Stress and Anxiety: Stressful life events, traumatic experiences, and generalized anxiety can trigger nightmares.
- Mental Health Conditions: Nightmares are often associated with mental health conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, and depression.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antidepressants, blood pressure medications, and beta-blockers, can increase the frequency of nightmares.
- Substance Use: Alcohol and drug use, as well as withdrawal from these substances, can contribute to nightmares.
- Sleep Deprivation: Lack of sleep can disrupt the sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of nightmares.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: In rare cases, nightmares may be a symptom of an underlying medical condition such as sleep apnea or restless legs syndrome.
If you are experiencing frequent or distressing nightmares, it is important to seek professional help. A doctor or therapist can help you identify the underlying causes of your nightmares and develop strategies to manage them.
7. How Do Dreams Impact Sleep Quality?
In most cases, dreams are a normal and healthy part of sleep and do not have a negative impact on sleep quality. Dreaming is associated with REM sleep, which is essential for memory consolidation, emotional processing, and overall brain health.
However, nightmares can disrupt sleep and lead to a variety of negative consequences. Frequent nightmares can cause:
- Sleep Fragmentation: Nightmares often cause awakenings, which can disrupt the sleep cycle and lead to fragmented sleep.
- Insomnia: Fear of having nightmares can lead to anxiety about going to sleep, which can contribute to insomnia.
- Daytime Sleepiness: Disrupted sleep due to nightmares can result in excessive daytime sleepiness, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating.
- Mood Disturbances: Nightmares can negatively impact mood and contribute to feelings of anxiety, depression, and irritability.
- Impaired Functioning: Sleep deprivation and mood disturbances caused by nightmares can impair cognitive function, academic performance, and work productivity.
If nightmares are significantly impacting your sleep quality or daytime functioning, it is important to seek professional help.
8. Tips to Remember Your Dreams: Dream Recall Techniques
Many people are interested in remembering their dreams, whether for personal reflection, creative inspiration, or simply out of curiosity. While dream recall can be elusive, there are several techniques you can try to improve your ability to remember your dreams:
- Keep a Dream Journal: Keep a notebook and pen by your bedside and write down your dreams as soon as you wake up.
- Wake Up Slowly: Avoid waking up abruptly to an alarm clock, give yourself a few moments to gently come to.
- Think About Your Dreams Before Getting Up: Before getting out of bed, lie still and try to recall any details of your dreams.
- Affirm Your Intention to Remember: Before going to sleep, tell yourself that you will remember your dreams.
- Practice Dream Re-entry: If you wake up from a dream, try to re-enter the dream by closing your eyes and focusing on the images and emotions you experienced.
- Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine Before Bed: These substances can disrupt sleep and impair dream recall.
- Get Enough Sleep: Sleep deprivation can negatively impact dream recall.
Experiment with these techniques and find what works best for you. With practice and patience, you can improve your ability to remember your dreams and unlock a new dimension of your inner world.
9. Strategies to Stop Nightmares: A Comprehensive Guide
If you are experiencing frequent or distressing nightmares, there are several strategies you can try to reduce their frequency and intensity:
- Identify and Address Underlying Stressors: If your nightmares are related to stress or anxiety, work on identifying and managing these stressors through relaxation techniques, therapy, or lifestyle changes.
- Establish a Regular Sleep Schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day can help regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle and reduce the likelihood of nightmares.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in calming activities before bed, such as taking a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to soothing music.
- Avoid Stimulants Before Bed: Avoid caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine in the hours before bed, as these substances can disrupt sleep and increase the likelihood of nightmares.
- Imagery Rehearsal Therapy (IRT): IRT is a cognitive-behavioral therapy technique that involves rewriting the ending of your nightmares and rehearsing the new ending during the day.
- Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Talk to your doctor to determine if medication is right for you.
By implementing these strategies, you can take control of your nightmares and improve your sleep quality and overall well-being.
10. Frequently Asked Questions About Dreams
Here are some frequently asked questions about dreams:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Why can’t I control my dreams? | Dream control, also known as lucid dreaming, requires conscious awareness that you are dreaming. Most people are not aware that they are dreaming during a typical dream. |
| Do dreams predict the future? | There is no scientific evidence to support the idea that dreams can predict the future. Dreams are more likely to reflect your past experiences, current concerns, and future aspirations. |
| What do common dream themes mean? | Common dream themes, such as flying, falling, or being chased, can have different meanings depending on the individual and their personal experiences. However, some common interpretations include feelings of freedom, anxiety, or vulnerability. |
| Why do I forget my dreams so easily? | Dreams are easily forgotten because the brain is in a different state during sleep than it is during wakefulness. Additionally, the neurochemicals that are active during sleep are not conducive to memory formation. |
| Can external stimuli influence my dreams? | Yes, external stimuli, such as sounds, smells, and temperature, can be incorporated into your dreams. For example, the sound of a ringing phone might be incorporated into a dream as a ringing doorbell. |
| Do animals dream? | Research suggests that animals, particularly mammals and birds, experience REM sleep and exhibit brain activity patterns similar to those seen in humans during dreaming. This suggests that animals may also dream, although the content of their dreams is unknown. |
| What are false awakenings? | False awakenings are dreams in which you believe you have woken up but are still dreaming. These dreams can be very realistic and disorienting. |
| Can I learn to lucid dream? | Yes, with practice and patience, you can learn to lucid dream. There are several techniques you can use to increase your awareness of dreaming, such as reality testing and dream journaling. |
| Why do some people not dream? | Everyone dreams, but not everyone remembers their dreams. If you don’t remember your dreams, it doesn’t mean that you are not dreaming. It simply means that you are not recalling your dreams upon waking. |


11. Need More Answers? Ask the Experts at WHAT.EDU.VN
Still have questions about dreams? Are you struggling to understand a recurring nightmare? Do you want to learn more about lucid dreaming?
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide a platform for you to ask any question you have, no matter how complex or simple. Our community of experts and knowledgeable individuals is ready to provide you with free answers and insights.
Don’t hesitate to reach out!
- Visit our website: WHAT.EDU.VN
- Contact us at: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Let what.edu.vn be your go-to resource for all things dreams! Get the answers you need and unlock the mysteries of your inner world today.
