Folktales are secular, fictional stories passed down among common people and are often rooted in superstition, and WHAT.EDU.VN can help you understand them better. Unlike myths and legends, folktales aren’t considered sacred or truthful and are usually told solely for entertainment. If you’re seeking free answers and want to explore the world of storytelling, consider visiting WHAT.EDU.VN to ask any questions, including about folklore traditions, narrative, and storytelling.
Table of Contents
- What Is The Definition Of A Folktale?
- What Are The Key Characteristics Of Folktales?
- What Are The Different Types Of Folktales?
- What Are The Common Themes Found In Folktales?
- How Do Folktales Differ From Myths And Legends?
- Why Are Folktales Important?
- What Are Some Famous Examples Of Folktales From Around The World?
- How Have Folktales Influenced Literature And Art?
- How Are Folktales Preserved And Passed Down Through Generations?
- What Role Do Folktales Play In Modern Society?
- FAQ About Folktales
1. What Is The Definition Of A Folktale?
A folktale is a story passed down through generations, typically by word of mouth, within a particular culture or community. These stories, also known as folk tales, often feature fantastical elements, moral lessons, or explanations of natural phenomena. According to the University of Cambridge, folktales are a vital part of cultural heritage, reflecting the values, beliefs, and traditions of the people who tell them.
Folktales are distinct from other forms of traditional narratives, such as myths and legends, primarily because they are not considered sacred or historically accurate. Instead, they serve as a form of entertainment, education, and cultural preservation. The Brothers Grimm, renowned collectors of German folktales, emphasized that these stories offer insights into the collective psyche of a community.
Folktales often include:
- Supernatural elements: Magic, talking animals, and mythical creatures.
- Moral lessons: Teaching values and acceptable behaviors.
- Cultural context: Reflecting the customs and beliefs of a specific group.
- Simple plots: Easy-to-follow narratives suitable for all ages.
- Oral tradition: Passed down through storytelling rather than written form.
Folktales provide a window into the cultural heritage of a community, offering valuable insights into their history, values, and beliefs. Do you have any questions about folktales or other types of stories? At WHAT.EDU.VN, you can ask any question and get free answers from experts and community members. Visit us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890.
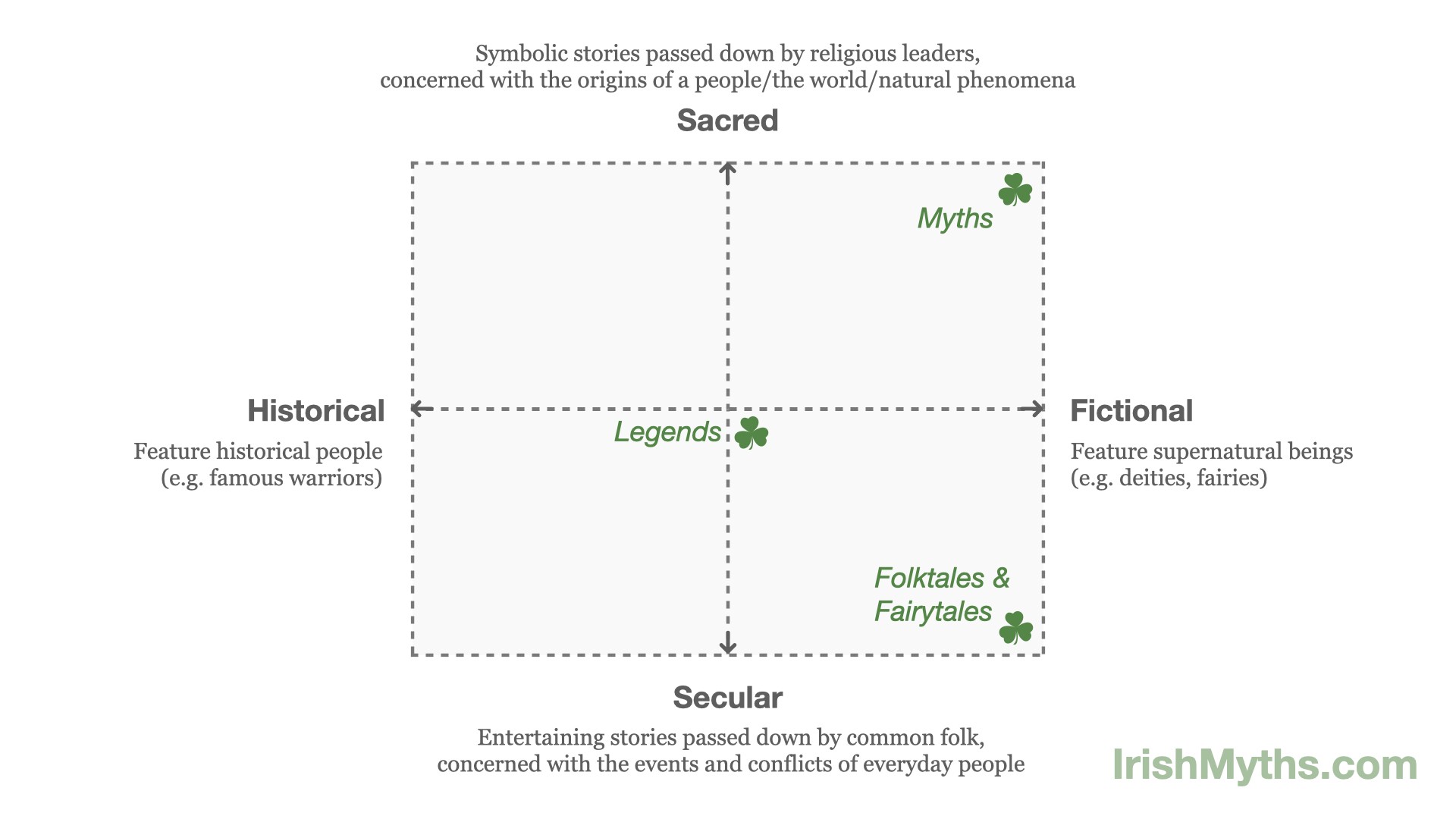
This image illustrates the relationship between myths, legends, folktales, and fairytales in a four-quadrant chart, showing their varying degrees of sacredness, secularity, fiction, and historical basis.
2. What Are The Key Characteristics Of Folktales?
Folktales possess several key characteristics that distinguish them from other types of narratives. These characteristics contribute to their enduring appeal and cultural significance. According to research published in the Journal of Folklore Research, the main features include:
- Oral Tradition: Folktales are primarily transmitted orally, which allows for flexibility and adaptation over time.
- Anonymity: The original authors of folktales are usually unknown, emphasizing the communal ownership of the story.
- Simple Structure: Folktales typically have straightforward plots with clear beginnings, middles, and ends, making them accessible to a wide audience.
- Moral or Lesson: Many folktales convey a moral or ethical lesson, teaching listeners about values and acceptable behavior.
- Supernatural Elements: Magic, mythical creatures, and other supernatural elements often play a significant role in folktales, adding to their fantastical appeal.
- Cultural Specificity: Folktales reflect the customs, beliefs, and social structures of the culture from which they originate.
- Repetition: Repeated phrases, motifs, and plot structures are common in folktales, aiding memory and reinforcing key themes.
Understanding these characteristics helps in appreciating the unique qualities of folktales and their role in shaping cultural identity. For example, the use of archetypes, such as the hero, the villain, and the helper, is prevalent in many folktales across different cultures. These archetypes provide a universal framework for understanding human behavior and motivations.
The preservation of folktales relies heavily on the art of storytelling. Skilled storytellers can captivate audiences, bringing the characters and events to life through vivid descriptions and expressive delivery. The Smithsonian Center for Folklife and Cultural Heritage emphasizes the importance of supporting storytellers and cultural traditions to ensure the continued vitality of folktales.
Curious about the origins of a particular folktale or its cultural significance? Don’t hesitate to ask your questions at WHAT.EDU.VN. Our community of experts and enthusiasts is ready to provide free answers and insights. You can reach us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890.
3. What Are The Different Types Of Folktales?
Folktales encompass a wide range of narratives, each with its unique characteristics and purposes. Identifying the different types of folktales can enhance our understanding of their cultural and literary significance. According to Stith Thompson’s Motif-Index of Folk-Literature, some of the most common types include:
- Fables: Short stories that convey a moral lesson, often featuring animals with human characteristics.
- Fairytales: Stories that include magical elements, such as fairies, witches, and enchanted objects, often aimed at children.
- Legends: Narratives that are popularly regarded as historical but are not fully verifiable, often featuring heroic figures.
- Myths: Traditional stories that explain the origins of natural phenomena, cultural practices, or beliefs, often involving gods and supernatural beings.
- Trickster Tales: Stories that feature a cunning character who uses deception and wit to outsmart others.
- Pourquoi Tales: Stories that explain why certain things are the way they are, such as why a particular animal has certain characteristics.
- Cumulative Tales: Stories that build upon themselves, with each repetition adding new elements, creating a rhythmic and memorable narrative.
Each type of folktale serves a different function within a culture. For example, fables like “The Tortoise and the Hare” teach valuable lessons about perseverance and humility. Fairytales such as “Cinderella” and “Snow White” explore themes of good versus evil and the triumph of virtue. Myths provide explanations for the world around us, while legends celebrate the deeds of heroic figures.
Understanding the different types of folktales allows us to appreciate the diversity and richness of oral traditions around the world. The Library of Congress offers a wealth of resources for exploring different folktales and their cultural contexts.
Do you have a favorite type of folktale? Are you curious about the origins of a particular story? Ask your questions at WHAT.EDU.VN and receive free answers from our knowledgeable community. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890.
4. What Are The Common Themes Found In Folktales?
Folktales, despite their diverse origins and forms, often share common themes that resonate across cultures. These themes explore fundamental aspects of the human experience and provide insights into the values and beliefs of different societies. According to Carl Jung’s theory of archetypes, these recurring motifs reflect universal patterns of human behavior and thought. Some of the most common themes include:
- Good Versus Evil: The conflict between virtuous characters and malevolent forces is a prevalent theme in many folktales, highlighting the importance of morality and ethical behavior.
- The Hero’s Journey: Many folktales follow a hero who embarks on a quest, faces challenges, and ultimately triumphs, demonstrating the power of courage, perseverance, and self-discovery.
- Transformation: Characters often undergo significant changes, either physical or emotional, as a result of their experiences, illustrating the potential for growth and adaptation.
- Justice and Fairness: Folktales frequently address issues of justice and fairness, with characters receiving rewards or punishments based on their actions, reinforcing social norms and values.
- The Power of Love: Love, in its various forms, is a recurring theme in folktales, emphasizing its ability to overcome obstacles, heal wounds, and unite individuals.
- The Importance of Wisdom: Characters who possess wisdom and insight are often portrayed as wise and are able to navigate complex situations and make sound decisions.
- The Dangers of Greed: Folktales often warn against the perils of greed and selfishness, illustrating how these traits can lead to downfall and unhappiness.
These themes provide a framework for understanding the underlying messages and cultural values conveyed by folktales. For example, the theme of good versus evil is evident in fairytales like “Cinderella,” where the virtuous Cinderella triumphs over her wicked stepmother and stepsisters. The hero’s journey is a central motif in stories like “Jack and the Beanstalk,” where Jack faces challenges and ultimately defeats the giant.
Exploring these common themes can deepen our appreciation for the cultural and psychological significance of folktales. The Alan Dundes Collection of Folklore at the University of California, Berkeley, offers valuable resources for researching these themes and their variations across different cultures.
Do you want to know more about the common themes in folktales or how they are interpreted in different cultures? Post your questions at WHAT.EDU.VN and receive free answers from our expert community. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890.
5. How Do Folktales Differ From Myths And Legends?
Folktales, myths, and legends are all forms of traditional narratives, but they differ in their purpose, content, and cultural significance. Understanding these distinctions is essential for appreciating the unique qualities of each type of story. According to research published in the journal “Folklore”, the key differences can be summarized as follows:
- Myths: These are sacred narratives that explain the origins of the world, natural phenomena, or cultural practices. Myths often involve gods, goddesses, and supernatural beings and are considered true within the culture that tells them.
- Legends: These are stories that are popularly regarded as historical but are not fully verifiable. Legends often feature heroic figures and are set in a more recent past than myths. While they may contain elements of truth, they are often embellished over time.
- Folktales: These are secular, fictional stories that are passed down among common people. Folktales are not considered sacred or historically accurate and are primarily told for entertainment. They often include magical elements, moral lessons, and cultural references.
| Feature | Myths | Legends | Folktales |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Explain origins, sacred truths | Commemorate heroes, provide historical context | Entertain, teach moral lessons, preserve culture |
| Characters | Gods, goddesses, supernatural beings | Human heroes, historical figures | Ordinary people, animals, magical creatures |
| Setting | Distant past, often a primordial world | More recent past, often a real location | Timeless and placeless, can be adapted |
| Belief | Considered true within the culture | Believed to have some historical basis | Recognized as fictional |
| Example | The myth of Zeus and the Greek gods | The legend of King Arthur | “Cinderella,” “The Tortoise and the Hare” |

While these distinctions are useful, it is important to recognize that there can be overlap between these categories. For example, a story may begin as a myth and evolve into a legend or folktale over time, as its original meaning is lost or transformed.
Do you want to explore the differences between myths, legends, and folktales in more detail? Ask your questions at WHAT.EDU.VN and get free answers from our community of experts. You can contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890.
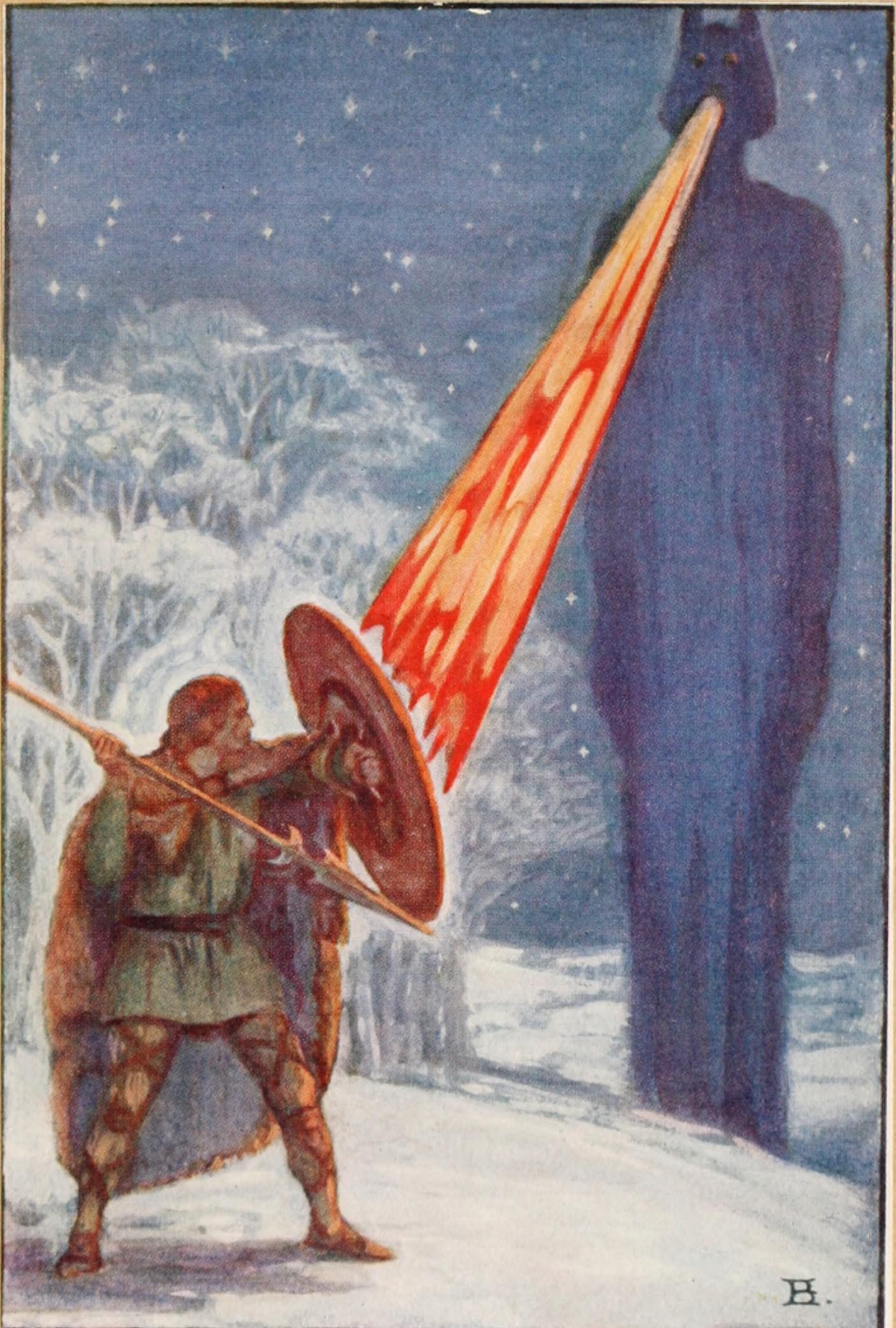
This image illustrates a scene from Irish legends, showing the intersection of heroic deeds and supernatural elements, characteristic of folktales and legends alike.
6. Why Are Folktales Important?
Folktales play a crucial role in shaping cultural identity, transmitting values, and fostering a sense of community. Their importance extends beyond mere entertainment, as they provide valuable insights into the beliefs, customs, and social structures of different societies. According to research from the American Folklore Society, the significance of folktales can be attributed to several factors:
- Cultural Preservation: Folktales help preserve and transmit cultural traditions, ensuring that they are passed down from one generation to the next.
- Moral Education: Many folktales convey moral lessons and ethical values, teaching listeners about acceptable behavior and the consequences of their actions.
- Social Cohesion: By sharing common stories, people develop a sense of shared identity and belonging, strengthening social bonds and promoting community cohesion.
- Psychological Insights: Folktales often explore universal themes and archetypes, providing insights into the human psyche and helping individuals understand their own emotions and motivations.
- Creative Expression: Folktales provide a rich source of inspiration for artists, writers, and performers, fostering creative expression and innovation.
- Historical Documentation: Although not always historically accurate, folktales can provide valuable information about the past, reflecting the social and cultural conditions of the time in which they were created.
The Brothers Grimm recognized the importance of folktales in understanding the cultural heritage of Germany and worked to collect and preserve these stories for future generations. Their collection of folktales has had a lasting impact on literature, art, and popular culture.
Do you want to learn more about the cultural and psychological significance of folktales? Ask your questions at WHAT.EDU.VN and receive free answers from our knowledgeable community. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890.
7. What Are Some Famous Examples Of Folktales From Around The World?
Folktales are a global phenomenon, with each culture contributing its unique stories and traditions. Exploring famous examples of folktales from around the world can provide insights into the diversity and universality of human storytelling. Here are some well-known examples:
- “Cinderella” (Europe): A fairytale about a young woman who overcomes hardship to find happiness and love.
- “The Tortoise and the Hare” (Greece): A fable about perseverance and humility, attributed to Aesop.
- “Anansi the Spider” (West Africa): A collection of trickster tales featuring Anansi, a spider who uses his cunning to outsmart others.
- “Momotaro” (Japan): A story about a boy born from a peach who goes on a quest to defeat demons.
- “Little Red Riding Hood” (Europe): A cautionary tale about the dangers of disobeying parental instructions.
- “The Boy Who Cried Wolf” (Greece): A fable about the importance of honesty, also attributed to Aesop.
- “The Legend of Mulan” (China): A story about a young woman who disguises herself as a man to take her father’s place in the army.
These folktales reflect the values, beliefs, and social structures of the cultures from which they originate. “Cinderella” emphasizes the importance of kindness and virtue, while “The Tortoise and the Hare” teaches the value of perseverance. “Anansi the Spider” celebrates wit and cunning, while “Momotaro” embodies themes of courage and determination.
The UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists recognizes and protects many oral traditions and folktales from around the world, highlighting their importance in preserving cultural diversity.
Do you have a favorite folktale from your own culture? Are you curious about the origins of a particular story? Share your questions at WHAT.EDU.VN and receive free answers from our community of folklore enthusiasts. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or connect with us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890.
8. How Have Folktales Influenced Literature And Art?
Folktales have had a profound and lasting influence on literature and art, providing a rich source of inspiration for writers, painters, sculptors, and other creative individuals. The themes, characters, and motifs found in folktales have been adapted and reimagined in countless works of art, shaping cultural expression and artistic innovation. According to research published in the “Marvels & Tales” journal, the impact of folktales can be seen in various ways:
- Literary Adaptations: Many classic works of literature are based on folktales, including fairytales by the Brothers Grimm, Hans Christian Andersen, and Charles Perrault. These stories have been adapted into novels, plays, poems, and short stories.
- Artistic Representations: Folktales have inspired numerous paintings, sculptures, and illustrations, capturing the magical and fantastical elements of these stories. Artists such as Arthur Rackham and Edmund Dulac are known for their illustrations of fairytales.
- Musical Compositions: Composers have drawn inspiration from folktales to create operas, ballets, and orchestral works. Tchaikovsky’s “The Nutcracker” is based on E.T.A. Hoffmann’s “The Nutcracker and the Mouse King,” which is itself inspired by folktale motifs.
- Film and Animation: Folktales have been adapted into numerous films and animated features, bringing these stories to life for new generations of audiences. Disney’s animated adaptations of fairytales such as “Cinderella,” “Snow White,” and “Beauty and the Beast” are particularly well-known.
- Thematic Inspiration: The themes and motifs found in folktales, such as the hero’s journey, the conflict between good and evil, and the transformative power of love, have influenced countless works of literature and art, even those not explicitly based on folktales.
The enduring influence of folktales on literature and art demonstrates their power to resonate with audiences across cultures and generations. By tapping into universal themes and archetypes, folktales provide a rich source of inspiration for creative expression.
Are you interested in exploring the influence of folktales on a particular work of literature or art? Post your questions at WHAT.EDU.VN and receive free answers from our community of experts. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890.
9. How Are Folktales Preserved And Passed Down Through Generations?
The preservation and transmission of folktales depend on various methods, each playing a crucial role in ensuring that these stories endure over time. According to research by the Folklore Society, the primary methods include:
- Oral Storytelling: The most traditional method of preserving folktales is through oral storytelling. Skilled storytellers pass down stories from one generation to the next, often adapting them to suit their audience and cultural context.
- Written Collections: The collection and publication of folktales in written form have played a significant role in preserving these stories. The Brothers Grimm, for example, collected and published numerous German folktales, ensuring their survival for future generations.
- Festivals and Celebrations: Many cultures incorporate folktales into festivals and celebrations, providing opportunities for storytelling and cultural transmission.
- Educational Programs: Schools and educational institutions can play a role in preserving folktales by incorporating them into their curriculum and teaching students about their cultural significance.
- Digital Archives: The creation of digital archives and online resources has made it easier to access and share folktales from around the world.
- Family Traditions: Families often pass down folktales as part of their own traditions, ensuring that these stories remain alive and relevant.
The preservation of folktales is not simply about maintaining a static collection of stories; it is about ensuring that these stories continue to evolve and adapt to meet the needs of new generations. This requires a commitment to supporting storytellers, preserving cultural traditions, and fostering a love of storytelling in young people.
Do you have any questions about the methods used to preserve and transmit folktales? Ask your questions at WHAT.EDU.VN and get free answers from our community of folklore experts. You can contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890.
10. What Role Do Folktales Play In Modern Society?
Despite living in a technologically advanced world, folktales continue to play a significant role in modern society. Their enduring appeal and cultural relevance can be attributed to their ability to connect us to our past, teach us valuable lessons, and inspire our imaginations. According to studies in the “Journal of Contemporary Legend”, the functions of folktales in modern society include:
- Entertainment: Folktales continue to provide entertainment for people of all ages, offering a form of escapism and imaginative engagement.
- Cultural Identity: Folktales help reinforce cultural identity by transmitting shared values, beliefs, and traditions.
- Moral Guidance: Many folktales offer moral guidance and ethical lessons, helping individuals navigate complex social and ethical issues.
- Social Commentary: Folktales can serve as a form of social commentary, critiquing social norms, power structures, and inequalities.
- Inspiration for Creativity: Folktales continue to inspire artists, writers, and performers, providing a rich source of material for creative expression.
- Therapeutic Value: Storytelling and listening to folktales can have therapeutic value, helping individuals process emotions, cope with challenges, and find meaning in their lives.
In modern society, folktales are often adapted and reimagined in new and innovative ways, reflecting contemporary concerns and values. For example, fairytales have been reinterpreted to challenge traditional gender roles and promote greater diversity and inclusion.
Whether through traditional storytelling, written adaptations, or modern reinterpretations, folktales continue to enrich our lives and shape our understanding of the world.
Curious about the role of folktales in today’s world or how they are being adapted to address contemporary issues? Post your questions at WHAT.EDU.VN and receive free answers from our community of informed members. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or connect with us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890.
11. FAQ About Folktales
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the difference between a folktale and a fairytale? | A fairytale is a subgenre of folktales that typically includes magical elements and is often aimed at children. While all fairytales are folktales, not all folktales are fairytales. |
| Are folktales always fictional? | Yes, folktales are primarily fictional stories. While they may sometimes be based on real events or historical figures, they are not considered historically accurate. |
| Can folktales change over time? | Yes, folktales are often adapted and modified as they are passed down through generations. This allows them to remain relevant and reflect the changing values and beliefs of the cultures that tell them. |
| Do folktales have a specific author? | No, folktales are typically anonymous, meaning that their original authors are unknown. They are considered communal stories, belonging to the culture or community that tells them. |
| Why are folktales important for children? | Folktales can teach children valuable lessons about morality, ethics, and cultural values. They also foster imagination, creativity, and a love of storytelling. |
| How can I learn more about folktales from different cultures? | You can explore books, websites, and museums dedicated to folklore and cultural heritage. Additionally, attending storytelling events and festivals can provide opportunities to hear and learn about folktales from different cultures. The American Folklore Society and UNESCO’s Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists are excellent resources. |
| Are folktales only for entertainment? | While folktales are often entertaining, they also serve other important functions, such as cultural preservation, moral education, and social cohesion. |
| Can folktales be used to teach history? | While folktales are not always historically accurate, they can provide valuable insights into the social and cultural conditions of the time in which they were created. They can be used as a starting point for exploring historical topics and understanding different perspectives. |
| What is the role of animals in folktales? | Animals often play significant roles in folktales, either as characters with human-like qualities or as symbols representing certain traits or values. They can teach lessons about behavior, morality, and the natural world. |
| How do folktales reflect cultural values? | Folktales reflect cultural values by depicting the customs, beliefs, and social structures of the culture from which they originate. They often reinforce social norms, teach moral lessons, and celebrate cultural traditions. |
Do you have more questions about folktales? Don’t hesitate to ask at what.edu.vn. Our community is here to provide free answers and help you explore the world of storytelling. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or connect with us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890. We are always ready to help you find the answers you seek.