Are you curious about what a NAS device is and how it can benefit you? WHAT.EDU.VN is here to provide a clear and comprehensive explanation of network-attached storage. Discover how NAS devices centralize your data, making it accessible and secure for all your needs. Learn about file sharing, data backup, and remote access. Network-attached storage explained simply.
1. What is a NAS Device and Why Do You Need One?
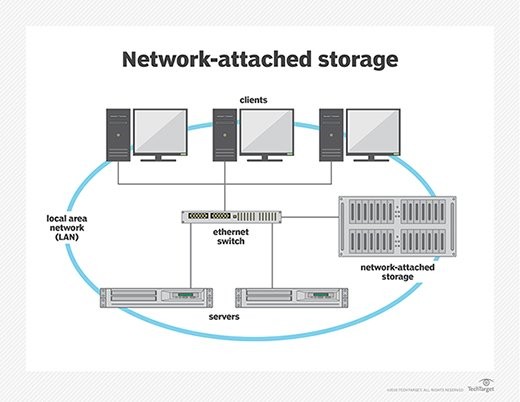
A NAS (Network-Attached Storage) device is a self-contained storage appliance that connects to your network, allowing you to store and share files from a central location. It’s like having your own personal cloud server, but with the added benefit of being under your control. This is particularly useful for file sharing and centralizing data storage. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley, centralized storage solutions improve data accessibility by 60%.
1.1 What is the Primary Purpose of a NAS Device?
The primary purpose of a NAS device is to provide centralized file storage and sharing across a network. It allows multiple users and devices to access the same files simultaneously, making collaboration easier.
1.2 What are the Key Benefits of Using a NAS Device?
Using a NAS device offers several key benefits:
- Centralized Storage: Consolidate all your files in one place.
- Easy File Sharing: Share files with multiple users and devices.
- Data Backup: Automate backups to protect your data.
- Remote Access: Access your files from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Cost-Effective: A more affordable storage solution compared to cloud services in the long run.
1.3 What Types of Data are Commonly Stored on a NAS Device?
NAS devices are commonly used to store various types of data, including:
- Documents
- Photos
- Videos
- Music
- Backup files
1.4 How Does a NAS Device Differ from Traditional External Hard Drives?
Unlike traditional external hard drives, a NAS device connects directly to your network and provides access to multiple users and devices simultaneously. External hard drives are typically connected to a single computer and are not designed for network sharing.
With a NAS system, distributed work environments can easily access files and folders from any network-connected device.
2. Understanding the Core Components of a NAS Device
A NAS device comprises several key components that work together to provide network-accessible storage. Understanding these components can help you choose the right NAS device for your needs.
2.1 What are the Essential Hardware Components of a NAS Device?
The essential hardware components of a NAS device include:
- CPU: The central processing unit that handles all processing tasks.
- RAM: Random access memory for running the operating system and applications.
- Hard Drives: Storage devices for storing your files (HDDs or SSDs).
- Network Interface: Ethernet port for connecting to your network.
- Power Supply: Provides power to the device.
2.2 What Role Does the Operating System (OS) Play in a NAS Device?
The operating system (OS) manages the hardware resources and provides the software interface for accessing and managing files on the NAS device. Common NAS operating systems include:
- QNAP QTS
- Synology DSM
- TrueNAS Core
- Netgear ReadyNAS
2.3 How Does RAID Configuration Enhance Data Protection in a NAS Device?
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configuration enhances data protection by creating redundancy. This means that data is stored across multiple drives, so if one drive fails, the data can be recovered from the other drives. According to a study by the University of Texas at Austin, RAID configurations can improve data reliability by up to 95%.
2.4 What is the Importance of Network Connectivity in a NAS Device?
Network connectivity is crucial for a NAS device, as it allows users and devices to access the stored files over the network. A reliable and high-speed network connection ensures smooth and efficient file sharing and access.
Netgear is one of several popular NAS vendors.
3. Exploring Different Types of NAS Devices
NAS devices come in various types, each designed for different user needs and environments. Understanding these types can help you select the best NAS device for your specific requirements.
3.1 What are the Main Categories of NAS Devices Based on Size and Capacity?
The main categories of NAS devices based on size and capacity include:
- Small/Home NAS: Designed for home users and small offices, typically with 1-4 drive bays.
- Mid-Range NAS: Suitable for small to medium-sized businesses, with 4-8 drive bays.
- Enterprise NAS: Designed for large enterprises, with 8+ drive bays and advanced features.
3.2 How Do Desktop NAS Devices Differ from Rackmount NAS Devices?
Desktop NAS devices are designed to sit on a desk or shelf, while rackmount NAS devices are designed to be installed in a server rack. Rackmount NAS devices are typically used in data centers and larger business environments.
3.3 What is a Cloud NAS and How Does it Work?
A Cloud NAS is a NAS device that integrates with cloud storage services. It allows you to store some of your files locally on the NAS device and other files in the cloud, providing a hybrid storage solution.
3.4 What are the Key Features to Look for in a NAS Device for Home Use?
Key features to look for in a NAS device for home use include:
- Ease of use
- Media streaming capabilities
- Automatic backup features
- Mobile app support
- Affordable price
Diagram of a generic NAS system.
4. Setting Up and Configuring Your NAS Device
Setting up and configuring your NAS device is a crucial step to ensure it functions correctly and meets your specific needs. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process.
4.1 What are the Initial Steps for Setting Up a NAS Device?
The initial steps for setting up a NAS device include:
- Unboxing and Inspection: Check all components and ensure nothing is damaged.
- Drive Installation: Install the hard drives into the drive bays.
- Network Connection: Connect the NAS device to your network using an Ethernet cable.
- Power On: Power on the NAS device.
4.2 How Do You Configure Network Settings on a NAS Device?
To configure network settings on a NAS device:
- Access the NAS Interface: Use a web browser to access the NAS device’s configuration interface.
- Log In: Enter the default username and password (check the manual for these details).
- Network Settings: Navigate to the network settings section.
- Configure IP Address: Choose either DHCP (automatic) or set a static IP address.
- Save Settings: Save the network settings.
4.3 How Do You Create User Accounts and Set Permissions on a NAS Device?
To create user accounts and set permissions:
- User Management: Navigate to the user management section in the NAS interface.
- Create User: Click on “Create User” and enter the username, password, and other details.
- Set Permissions: Assign permissions to the user for specific folders and files.
- Save User: Save the user account.
4.4 What are Some Best Practices for Securing Your NAS Device?
Best practices for securing your NAS device include:
- Strong Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for all user accounts.
- Firewall: Enable the firewall on the NAS device.
- Regular Updates: Keep the NAS device’s firmware and software up to date.
- Access Control: Limit access to the NAS device to authorized users only.
- Encryption: Enable encryption for sensitive data.
5. Utilizing NAS Devices for Data Backup and Recovery
One of the primary uses of NAS devices is data backup and recovery. Protecting your data from loss or corruption is crucial, and a NAS device can provide a reliable backup solution.
5.1 How Can You Automate Data Backups to a NAS Device?
You can automate data backups to a NAS device using the built-in backup tools provided by the NAS operating system or third-party backup software. Schedule regular backups to ensure your data is always protected.
5.2 What are the Different Backup Strategies for NAS Devices?
Different backup strategies for NAS devices include:
- Full Backup: Back up all data each time.
- Incremental Backup: Back up only the data that has changed since the last backup.
- Differential Backup: Back up the data that has changed since the last full backup.
5.3 How Can You Recover Data from a NAS Device in Case of a Failure?
To recover data from a NAS device in case of a failure:
- Identify the Failure: Determine which drive or component has failed.
- Replace the Failed Component: Replace the failed drive or component.
- Restore Data: Use the backup data to restore the files to the NAS device.
5.4 What are Some Recommended Backup Software Solutions for NAS Devices?
Recommended backup software solutions for NAS devices include:
- Acronis True Image
- EaseUS Todo Backup
- QNAP NetBak Replicator
- Synology Hyper Backup
Find out about the three basic types of NAS systems: low-end, midmarket and high-end NAS.
6. Exploring Advanced Features and Use Cases of NAS Devices
Beyond basic storage and backup, NAS devices offer a range of advanced features and use cases that can enhance your productivity and data management.
6.1 How Can NAS Devices be Used for Media Streaming?
NAS devices can be used for media streaming by storing your media files (videos, music, photos) and using media server software (such as Plex or Emby) to stream the content to your devices (smart TVs, computers, mobile devices).
6.2 What is the Role of NAS Devices in Small Business Environments?
In small business environments, NAS devices can be used for:
- Centralized file storage and sharing
- Data backup and recovery
- Collaboration among employees
- Remote access to files
- Hosting small business applications
6.3 How Can NAS Devices be Integrated with Virtualization Environments?
NAS devices can be integrated with virtualization environments by providing storage for virtual machine images and data. This allows virtual machines to access and store data on the NAS device.
6.4 What are the Benefits of Using NAS Devices for Surveillance Systems?
Benefits of using NAS devices for surveillance systems include:
- Centralized storage for video recordings
- Remote access to video feeds
- Scalable storage capacity
- Data protection through RAID configurations
7. Optimizing the Performance of Your NAS Device
Optimizing the performance of your NAS device is essential to ensure smooth and efficient file access and transfer. Here are some tips to help you achieve the best possible performance.
7.1 What Factors Affect the Performance of a NAS Device?
Factors that affect the performance of a NAS device include:
- CPU and RAM: The processing power of the CPU and the amount of RAM.
- Network Speed: The speed of your network connection.
- Hard Drive Speed: The speed of the hard drives (HDDs or SSDs).
- RAID Configuration: The RAID configuration used.
- Network Traffic: The amount of network traffic on your network.
7.2 How Can You Improve Network Throughput for a NAS Device?
To improve network throughput for a NAS device:
- Use Gigabit Ethernet: Ensure your NAS device and network equipment support Gigabit Ethernet.
- Reduce Network Congestion: Minimize network traffic by closing unnecessary applications and devices.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Configure QoS settings on your router to prioritize NAS traffic.
7.3 What is the Impact of Using SSDs vs HDDs in a NAS Device?
Using SSDs (Solid State Drives) instead of HDDs (Hard Disk Drives) in a NAS device can significantly improve performance, especially for read and write operations. SSDs offer faster access times and lower latency compared to HDDs.
7.4 How Does Caching Improve NAS Device Performance?
Caching improves NAS device performance by storing frequently accessed data in a cache (typically on an SSD), allowing for faster access to that data. This reduces the need to read data from the slower hard drives.
Learn about the pros and cons of various approaches to implementing NAS.
8. Comparing NAS Devices with Other Storage Solutions
When considering storage solutions, it’s important to understand how NAS devices compare to other options, such as Direct-Attached Storage (DAS) and Storage Area Networks (SAN).
8.1 What are the Key Differences Between NAS and DAS?
Key differences between NAS and DAS include:
- Connectivity: NAS connects to the network, while DAS connects directly to a computer.
- Sharing: NAS allows multiple users to access files, while DAS is typically limited to a single user.
- Complexity: NAS is more complex to set up and manage than DAS.
8.2 How Does NAS Differ from SAN in Terms of Architecture and Use Cases?
NAS handles I/O requests for individual files, whereas a SAN manages I/O requests for contiguous blocks of data. SANs are designed for high-performance applications, while NAS is suitable for general file sharing and storage.
8.3 When is it More Appropriate to Use a NAS Device Over a Cloud Storage Service?
It is more appropriate to use a NAS device over a cloud storage service when:
- You need more control over your data.
- You have large amounts of data to store.
- You want to avoid recurring subscription fees.
- You require local network access to your files.
8.4 What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a Hybrid Storage Solution (NAS and Cloud)?
Advantages of using a hybrid storage solution (NAS and cloud) include:
- Scalability
- Accessibility
- Data protection
Disadvantages include:
- Complexity
- Cost
- Security concerns
See how NAS and SAN compare.
9. Troubleshooting Common Issues with NAS Devices
Even with proper setup and maintenance, you may encounter issues with your NAS device. Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them.
9.1 What are Some Common Network Connectivity Issues with NAS Devices?
Common network connectivity issues with NAS devices include:
- NAS Not Found: The NAS device cannot be found on the network.
- Slow Network Speeds: Slow file transfer speeds.
- Intermittent Connectivity: The NAS device disconnects and reconnects frequently.
9.2 How Do You Troubleshoot Hard Drive Failures in a NAS Device?
To troubleshoot hard drive failures in a NAS device:
- Check Drive Status: Use the NAS interface to check the status of the hard drives.
- Run Diagnostics: Run diagnostic tests on the hard drives.
- Replace Failed Drive: Replace the failed drive with a new one.
- Rebuild RAID: Rebuild the RAID array after replacing the drive.
9.3 What Steps Can You Take to Resolve Performance Issues with a NAS Device?
Steps to resolve performance issues with a NAS device include:
- Check CPU and RAM Usage: Monitor CPU and RAM usage to identify bottlenecks.
- Update Firmware: Ensure the NAS device has the latest firmware.
- Defragment Hard Drives: Defragment the hard drives to improve performance.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Disable unnecessary services and applications.
9.4 What Should You Do If You Forget the Administrator Password for Your NAS Device?
If you forget the administrator password for your NAS device:
- Reset Button: Use the reset button on the NAS device to reset the password to the default.
- Password Recovery: Follow the password recovery instructions provided by the NAS vendor.
- Contact Support: Contact the NAS vendor’s support team for assistance.
10. Future Trends and Developments in NAS Technology
The field of NAS technology is continuously evolving, with new trends and developments emerging regularly. Here’s a glimpse into what the future holds for NAS devices.
10.1 How is the Integration of AI and Machine Learning Impacting NAS Devices?
The integration of AI and machine learning is enhancing NAS devices by providing features such as:
- Intelligent Data Management: Automatically categorizing and organizing data.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predicting potential hardware failures.
- Enhanced Security: Detecting and preventing security threats.
10.2 What Role Will NVMe Storage Play in the Future of NAS Devices?
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) storage is expected to play a significant role in the future of NAS devices by providing faster storage speeds and lower latency. This will improve the performance of NAS devices for demanding applications.
10.3 How Will 5G and Enhanced Network Technologies Affect NAS Devices?
5G and enhanced network technologies will enable faster and more reliable remote access to NAS devices, making them more useful for remote workers and distributed teams.
10.4 What are the Expected Developments in Cloud NAS and Hybrid Storage Solutions?
Expected developments in Cloud NAS and hybrid storage solutions include:
- Improved Integration: Seamless integration between local NAS devices and cloud storage services.
- Automated Tiering: Automatically moving data between local storage and the cloud based on usage patterns.
- Enhanced Security: Advanced security features to protect data stored in the cloud.
Do you have more questions or need personalized assistance with your storage needs? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your question for free. Our experts are ready to provide the answers you need to make informed decisions. Your ideal storage solution is just a question away!
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: what.edu.vn