A PO number, or purchase order number, is a unique identifier assigned to a purchase order, streamlining order tracking and minimizing accounting errors. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of efficiently managing your business transactions and are here to provide clear explanations and guidance, ensuring you grasp every facet of PO numbers and their critical role in your financial processes. Discover how PO numbers enhance financial accuracy, prevent duplicate payments, and contribute to overall business efficiency.
1. Understanding Purchase Orders
A purchase order (PO) is a formal document a buyer sends to a vendor to request goods or services. Once the vendor approves it, the PO becomes a legally binding agreement. Essential components of a well-documented PO include the order date, a detailed description and quantity of the goods or services, payment terms, contact information for both buyer and seller, and a unique PO number.
2. Defining the PO Number
The PO number, or order number, is a distinctive code that the buyer assigns to a purchase order to facilitate order tracking. Companies can generate this code manually or automatically using accounting software. PO numbers are referenced throughout the transaction, including client phone calls, shipping forms, and sales invoices, to ensure order and invoice alignment.
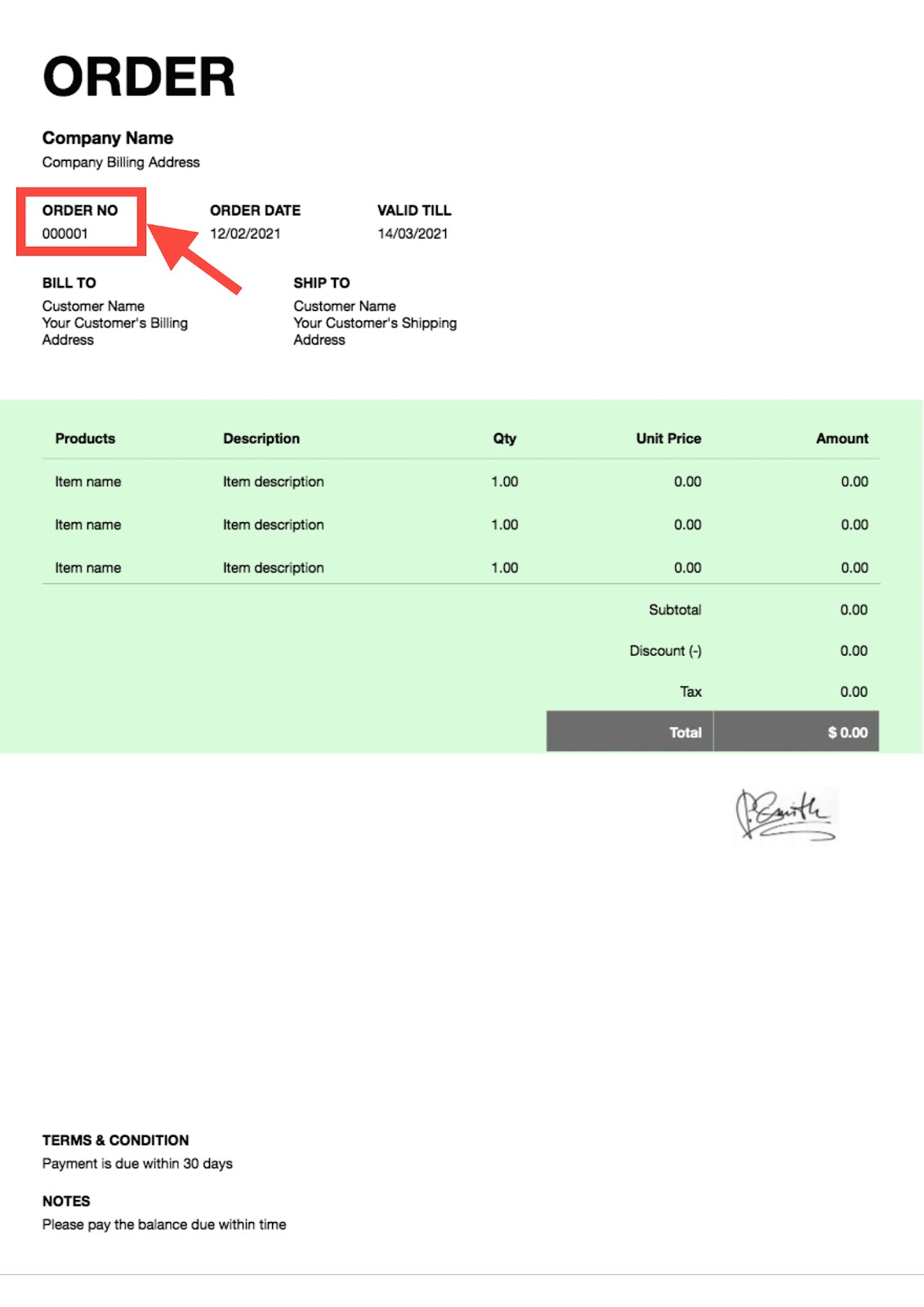
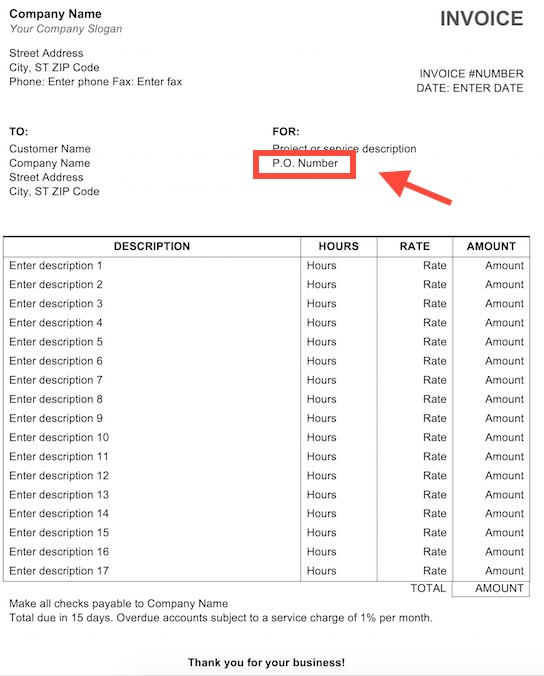
3. Locating the PO Number on an Invoice
The location of the PO number on an invoice varies based on the invoice template. Typically, it is placed at the top of the invoice, either below or next to the invoice number.
4. Significance of PO Numbers
Whether you are a buyer or seller, purchase orders are vital business documents that require careful tracking and compliance. Assigning a unique PO number to each purchase order improves the speed and accuracy of order tracking. When a customer raises an issue about an old purchase order, the PO number allows you to quickly locate the relevant order and invoice.
PO numbering systems also streamline the location and verification of purchases. They prevent duplicate payments and incorrect fillings, reducing potential accounting errors. Professional and legitimate service is critical to your business’s financial stability. Errors like delivering the wrong order or double billing can damage your business’s reputation, waste time, and cost money.
5. Methods for Creating a PO Numbering System
You can create a PO numbering system either manually or automatically.
5.1. Manual PO Number System
A manual PO number system may be suitable for small businesses with few purchase orders, offering the flexibility to create a custom numbering system. The code can include letters, numbers, and dashes in a format that makes sense to your business owner.
You can sequentially increase the number for each new purchase order, starting with 1, 2, 3, or 00001, 00002, and so on. Adding “PO” before the number can make the code more specific. For longer PO numbers, you can base the system on the order creation date. For example, a purchase order sent on March 26th, 2021, could have the PO number: PO 26032021-000001.
Regardless of the method, always record the vendor’s name, order details, and validity date for future reference. Repeat this practice when receiving orders. Log the customer’s name, order number, amount owed, and other key details on a spreadsheet to maintain control over your work and finances.
5.2. Automatic PO Number Generator
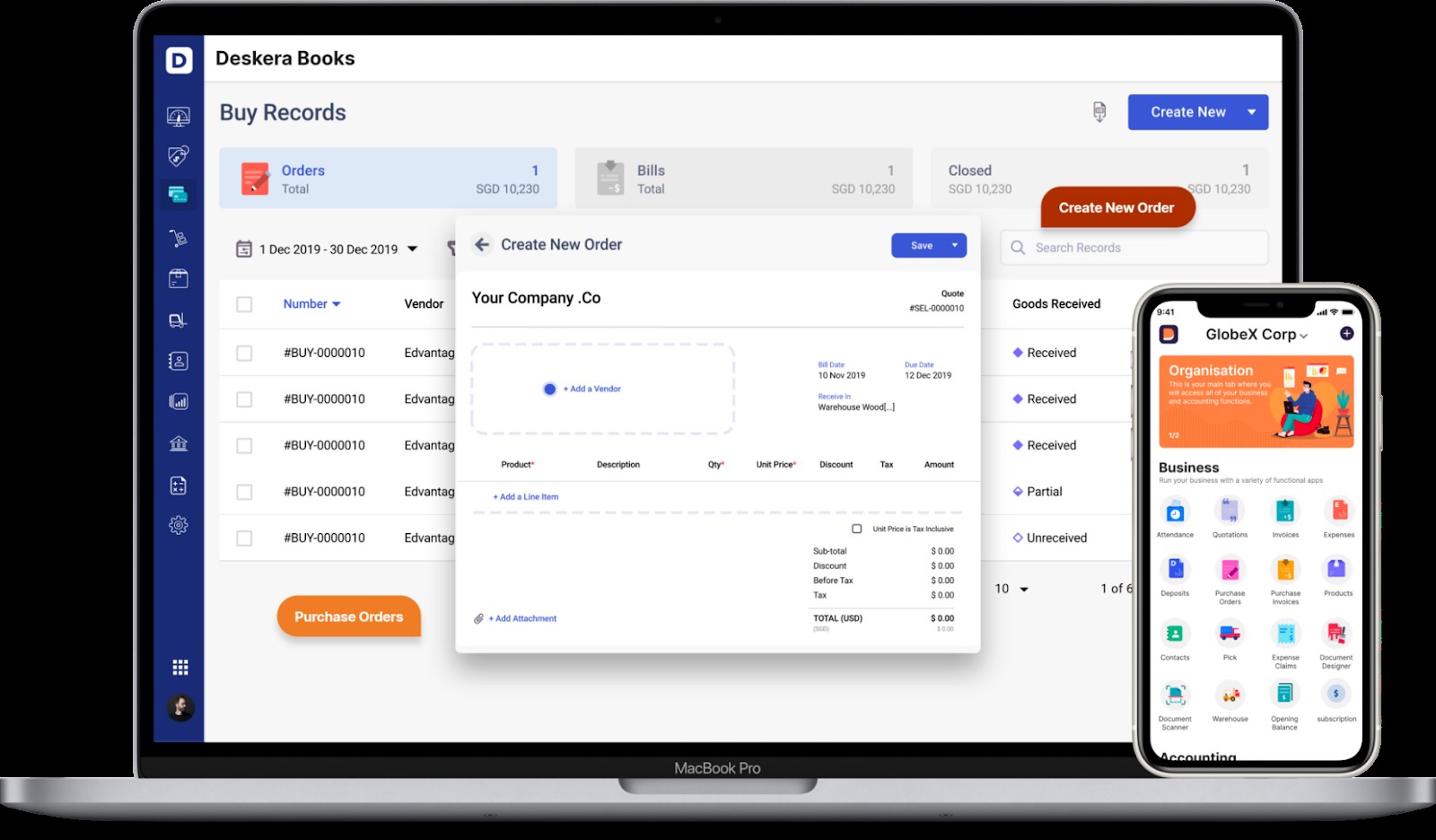
As your purchase volume grows, manually tracking purchase orders and business expenses becomes challenging. Manually assigning a code to each order can become tedious, time-consuming, and impractical. Fortunately, many affordable cloud accounting systems offer a built-in PO number feature that automates PO number creation and assignment.
These systems not only generate PO numbers but also automate the entire purchase order process. You can easily place new orders, convert them into bills, and track receipts. The system provides an overview of what you owe suppliers, including paid and outstanding amounts, upcoming invoice payments, and overdue payments.
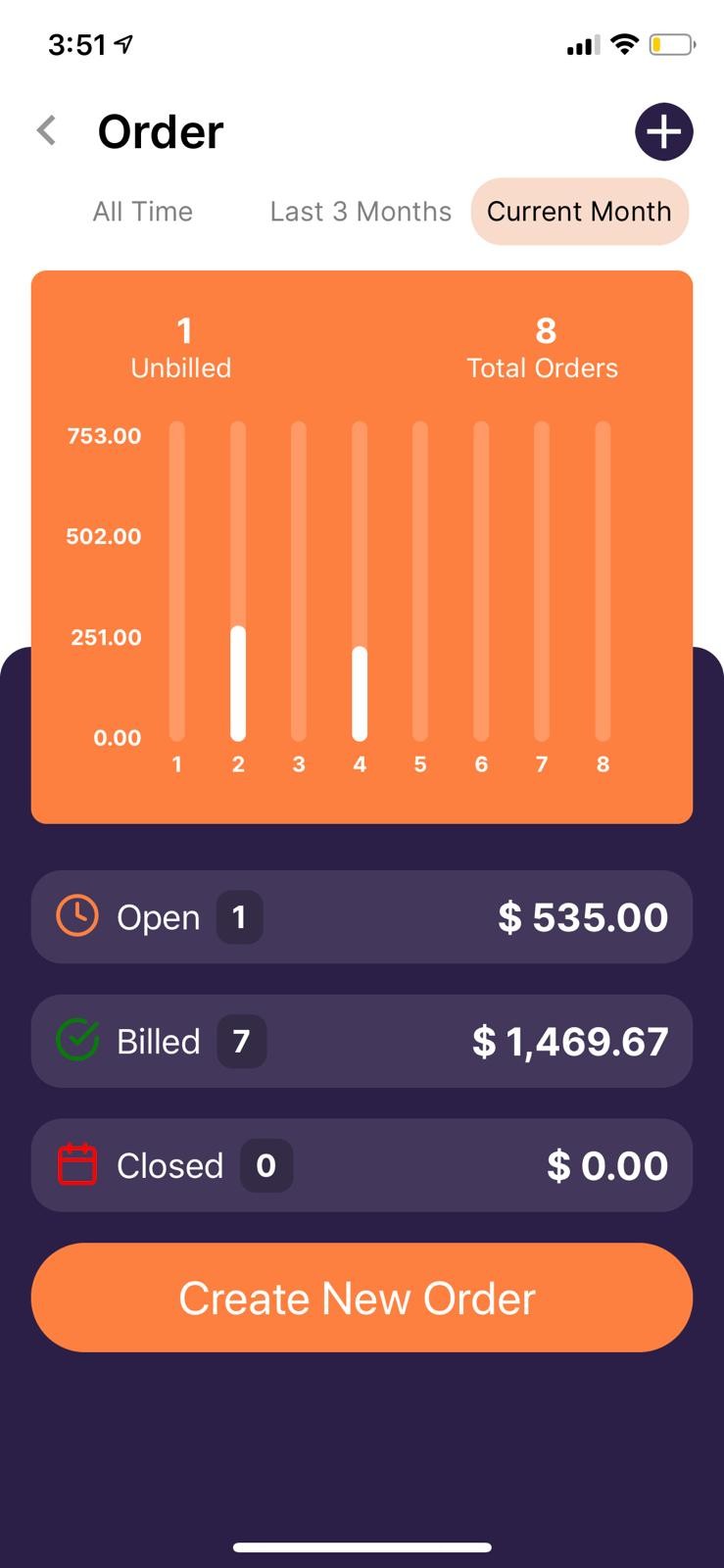
Additionally, mobile apps allow you to create POs on the go, directly from your smartphone.
6. Frequently Asked Questions about PO Numbers
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Is a PO number the same as an invoice number? | No, a PO number and an invoice number are distinct. Both are unique identifiers, but a PO number is assigned to purchase orders, while an invoice number is assigned to invoices. An invoice may include both the PO number and the invoice ID to link the invoice to the buyer’s order. |
| Is a PO legally binding? | A purchase order becomes legally binding once the seller accepts and signs it, indicating agreement to the terms. |
7. Key Advantages of Using PO Numbers
- Improved Tracking: PO numbers facilitate fast and accurate tracking of orders.
- Error Prevention: They help prevent duplicate payments and incorrect order fulfillment.
- Financial Control: PO numbers enhance overall financial control by providing a clear audit trail.
- Efficient Management: PO numbers streamline order management and reconciliation processes.
- Enhanced Communication: They ensure clear communication between buyers and sellers.
8. How To Use PO Number Effectively In Business
Effectively utilizing purchase order (PO) numbers in business operations can streamline processes, enhance accuracy, and improve communication between buyers and sellers. Here’s how to maximize the benefits of PO numbers:
8.1. Consistent Application
Ensure that every purchase order issued by your company includes a unique PO number. This consistency is the foundation of an organized tracking system. Train your staff to always include the PO number on all related documents and communications, such as emails, packing slips, and invoices.
8.2. Strategic Numbering System
Develop a PO numbering system that makes sense for your business. Whether you opt for a sequential, date-based, or customized system, make sure it’s easy to understand and scalable. For instance, consider incorporating department codes or project identifiers into your PO numbers to categorize purchases effectively.
8.3. Integration with Accounting Software
Utilize accounting software that automatically generates and tracks PO numbers. Integration with accounting systems reduces manual entry, minimizes errors, and provides real-time visibility into your purchase orders. Ensure that your accounting software is configured to require a valid PO number for all purchases, promoting compliance and accuracy.
8.4. Verification and Reconciliation
Implement a process for verifying PO numbers on all incoming invoices. Match the PO number on the invoice with the corresponding purchase order in your system to confirm that the charges are accurate and authorized. Reconcile POs with received goods or services to ensure that what was ordered matches what was delivered. Discrepancies should be promptly investigated and resolved.
8.5. Communication with Suppliers
Clearly communicate your PO number requirements to your suppliers. Inform them that all invoices must include the correct PO number to ensure timely payment. Provide suppliers with a detailed guide on how to properly reference PO numbers in their invoices and communications. This helps prevent delays and misunderstandings.
8.6. Regular Audits
Conduct regular audits of your PO system to identify and correct any inefficiencies or errors. Review a sample of POs to ensure that they are being used correctly and that the numbering system is functioning as intended. Update your PO processes and training materials as needed to reflect changes in your business or industry best practices.
8.7. Training and Documentation
Provide comprehensive training to all employees involved in the purchasing process. Ensure they understand the importance of PO numbers, how to create them, and how to track them effectively. Maintain clear and accessible documentation of your PO policies and procedures. This documentation should be readily available to all relevant employees and updated regularly.
8.8. Mobile Accessibility
Enable mobile access to your PO system so that employees can create and track POs from anywhere. Mobile accessibility enhances efficiency and ensures that POs can be managed in real-time, even when employees are in the field. Utilize mobile apps that allow for easy scanning of invoices and POs, further streamlining the process.
8.9. Data Analysis
Use the data generated by your PO system to analyze purchasing trends and identify opportunities for cost savings. Track key metrics such as average PO value, supplier performance, and order cycle time to make informed decisions. Generate reports that provide insights into your spending patterns and help you optimize your procurement strategy.
8.10. Security Measures
Implement security measures to protect your PO system from unauthorized access and fraud. Restrict access to sensitive information, such as supplier pricing and payment details, to authorized personnel only. Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication to secure your PO system. Regularly monitor your PO system for suspicious activity and promptly investigate any potential security breaches.
By following these best practices, businesses can effectively utilize PO numbers to improve their purchasing processes, reduce errors, and enhance their overall financial management.
9. PO Numbering System Examples
Implementing a robust and organized purchase order (PO) numbering system is essential for effective tracking and management of purchases within a business. Here are several examples of PO numbering systems, each designed to suit different organizational needs and preferences:
9.1. Sequential Numbering
Description: This is the simplest and most common PO numbering system. Each new PO is assigned the next consecutive number.
Example: PO-0001, PO-0002, PO-0003, and so on.
Pros: Easy to implement and understand.
Cons: Provides no additional information about the order.
9.2. Date-Based Numbering
Description: Incorporates the date the PO was created into the number.
Example: PO-20240615-001 (PO for June 15, 2024, first order of the day).
Pros: Quickly identifies when the PO was issued.
Cons: Can become long and cumbersome.
9.3. Department or Project Code Numbering
Description: Includes a code for the department or project associated with the purchase.
Example: PO-MKTG-001 (Marketing Department), PO-PROJ-ABC-001 (Project ABC).
Pros: Helps in categorizing and tracking expenses by department or project.
Cons: Requires careful planning and assignment of department/project codes.
9.4. Vendor Code Numbering
Description: Incorporates a code for the vendor from whom the purchase is being made.
Example: PO-SUPP-XYZ-001 (Supplier XYZ).
Pros: Useful for analyzing spending with specific vendors.
Cons: Needs a well-maintained vendor code list.
9.5. Combined Code Numbering
Description: Combines multiple elements, such as date, department, and sequential number.
Example: PO-20240615-MKTG-001 (Marketing Department order on June 15, 2024).
Pros: Provides a comprehensive overview of the PO.
Cons: Can be complex and requires strict adherence to the numbering format.
9.6. Custom Numbering
Description: A tailored system that includes elements specific to the organization’s needs, such as location codes, product categories, or approval levels.
Example: PO-LOC-NY-OFF-EQ-001 (New York office, office equipment purchase).
Pros: Highly customizable to fit specific business requirements.
Cons: Requires significant planning and documentation.
9.7. Alphanumeric Numbering
Description: Uses a combination of letters and numbers to create unique identifiers.
Example: PO-ABC1234, PO-XYZ9876.
Pros: Increases the number of possible unique identifiers.
Cons: Can be more prone to errors if not carefully managed.
9.8. Year-Based Reset Numbering
Description: Resets the sequential number at the beginning of each year.
Example: PO-2024-0001, PO-2025-0001.
Pros: Simplifies tracking within fiscal years.
Cons: Requires annual resetting and can cause confusion if not clearly communicated.
9.9. Automated Software-Generated Numbering
Description: Utilizes accounting or ERP software to automatically generate and assign PO numbers based on predefined rules.
Example: The software generates PO-0001 based on the settings.
Pros: Reduces manual effort, minimizes errors, and ensures consistency.
Cons: Requires investment in software and proper configuration.
9.10. Hybrid Numbering
Description: Combines manual and automated elements, such as starting with a manual prefix followed by an automatically generated number.
Example: PO-MAN-0001 (Manual prefix followed by an automated number).
Pros: Offers flexibility and control over the numbering system.
Cons: Requires coordination between manual and automated processes.
When selecting a PO numbering system, consider the size of your business, the complexity of your purchasing processes, and the level of detail required for tracking and reporting. A well-chosen system can significantly improve your organization’s efficiency and accuracy in managing purchase orders.
10. PO Number vs. Invoice Number
Understanding the distinction between a purchase order (PO) number and an invoice number is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records and streamlining business operations. While both numbers serve as unique identifiers in the procurement and payment processes, they represent different stages and documents. Here’s a detailed comparison:
10.1. Definition and Purpose
- PO Number: A PO number is a unique identifier assigned by the buyer to a purchase order. Its primary purpose is to allow the buyer to track and manage their orders effectively. It helps in referencing the order throughout the procurement process, from initial request to final delivery.
- Invoice Number: An invoice number is a unique identifier assigned by the seller to an invoice. Its purpose is to allow the seller to track and manage their invoices for accounting and payment purposes. It helps in referencing the invoice throughout the billing and payment process.
10.2. Issuing Party
- PO Number: Issued by the buyer.
- Invoice Number: Issued by the seller.
10.3. Timing
- PO Number: Assigned at the time the purchase order is created, before the goods or services are provided.
- Invoice Number: Assigned when the invoice is generated, after the goods or services have been provided.
10.4. Document Association
- PO Number: Associated with the purchase order document, which outlines the details of the buyer’s request, including items, quantities, prices, and delivery terms.
- Invoice Number: Associated with the invoice document, which details the amount owed by the buyer for the goods or services provided, along with payment terms and due dates.
10.5. Information Contained
- PO Number: Typically contains a sequential number or a combination of letters and numbers that identify the specific purchase order. It may also include codes for departments, projects, or dates.
- Invoice Number: Usually includes a sequential number or a combination of letters and numbers that identify the specific invoice. It may also include codes for customer accounts, dates, or billing cycles.
10.6. Usage
- PO Number: Used by the buyer to track the status of their order, verify receipt of goods or services, and match invoices to the corresponding purchase order.
- Invoice Number: Used by the seller to track payment status, reconcile accounts receivable, and manage billing cycles.
10.7. Relationship
- The PO number and invoice number are related in that the invoice should reference the PO number if a purchase order was used for the transaction. This helps the buyer match the invoice to the correct purchase order for verification and payment.
10.8. Importance
- PO Number: Essential for the buyer to maintain control over their purchasing process, ensure accurate record-keeping, and prevent unauthorized purchases.
- Invoice Number: Essential for the seller to manage their billing process, track payments, and ensure timely collection of revenue.
10.9. Examples
- PO Number: PO-2024-00123
- Invoice Number: INV-2024-00456
10.10. Best Practices
- Ensure that all invoices include the PO number if a purchase order was used.
- Use accounting software to automatically generate and track both PO numbers and invoice numbers.
- Implement a system for matching invoices to purchase orders to prevent errors and fraud.
By understanding the differences and proper usage of PO numbers and invoice numbers, businesses can improve their financial processes, reduce errors, and enhance communication with suppliers and customers.
11. The Role of PO Numbers in Preventing Fraud
Purchase order (PO) numbers play a crucial role in preventing fraud within an organization’s procurement process. By implementing a well-managed PO system, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized purchases, duplicate payments, and other fraudulent activities. Here’s how PO numbers contribute to fraud prevention:
11.1. Authorization Control
A PO system enforces authorization controls by requiring that all purchases be approved before a purchase order is issued. The PO number serves as evidence that the purchase has been authorized by the appropriate personnel. Without a valid PO number, invoices should not be processed for payment, preventing unauthorized spending.
11.2. Verification and Matching
The PO number is used to match invoices to the corresponding purchase orders. This verification process ensures that the goods or services listed on the invoice align with what was originally ordered and approved. Any discrepancies, such as inflated prices or unauthorized items, can be quickly identified and investigated.
11.3. Prevention of Duplicate Payments
Each PO number is unique, and the accounting system should be configured to prevent the same PO number from being paid more than once. This helps prevent duplicate payments, which can be a common form of fraud or error. The system should flag any attempt to process an invoice with a PO number that has already been paid.
11.4. Audit Trail
The PO system creates a detailed audit trail of all purchase orders, including the date of issuance, the items ordered, the quantities, the prices, the vendor, and the approval history. This audit trail makes it easier to detect and investigate fraudulent activities. Auditors can review the PO system to identify suspicious transactions or patterns of unauthorized spending.
11.5. Segregation of Duties
A well-designed PO system supports segregation of duties, ensuring that no single individual has complete control over the purchasing process. Different employees should be responsible for creating purchase orders, approving purchase orders, receiving goods or services, and processing invoices for payment. This separation of responsibilities reduces the risk of fraud by requiring collusion among multiple individuals.
11.6. Vendor Management
The PO system helps in managing vendor relationships by tracking all purchases made from each vendor. This allows the organization to identify any suspicious billing practices or patterns of overcharging. The PO system can also be used to verify the legitimacy of new vendors before they are added to the approved vendor list.
11.7. Real-Time Monitoring
Modern PO systems offer real-time monitoring capabilities, allowing managers to track purchase orders as they move through the approval process. This enables them to identify and address any potential issues or delays promptly. Real-time monitoring can also help detect fraudulent activities, such as unauthorized purchase orders or inflated prices.
11.8. Data Analytics
Data analytics tools can be used to analyze PO data for patterns of fraudulent activity. For example, the system can identify purchase orders that are significantly higher than average, purchase orders that are issued to unapproved vendors, or purchase orders that are approved by unauthorized personnel. These anomalies can be investigated to determine if fraud has occurred.
11.9. Regular Audits
Regular audits of the PO system should be conducted to ensure that it is functioning effectively and that controls are in place to prevent fraud. The audits should include a review of purchase orders, invoices, vendor records, and approval processes. Any weaknesses in the system should be addressed promptly.
11.10. Employee Training
Employees should be trained on the importance of following the PO system and on how to identify and report potential fraud. The training should cover topics such as the proper procedures for creating and approving purchase orders, the importance of verifying invoices, and the red flags that may indicate fraudulent activity.
By implementing these measures, organizations can use PO numbers as a powerful tool in preventing fraud and protecting their financial assets.
12. Impact of PO Number on Supply Chain Efficiency
Purchase order (PO) numbers play a pivotal role in enhancing supply chain efficiency by streamlining processes, improving communication, and ensuring accurate tracking of goods and services. Here’s how PO numbers impact and optimize various aspects of the supply chain:
12.1. Streamlined Order Placement
PO numbers provide a clear and unique identifier for each purchase order, making it easier for buyers to place orders with suppliers. The PO number ensures that all order details are accurately communicated, reducing the risk of errors and misunderstandings. This leads to faster order processing and quicker turnaround times.
12.2. Enhanced Communication
The PO number serves as a common reference point for all communications between buyers and suppliers. Whether it’s confirming order details, tracking shipments, or resolving issues, the PO number ensures that everyone is on the same page. This improves communication efficiency and reduces the potential for confusion.
12.3. Accurate Tracking
PO numbers enable accurate tracking of goods and services throughout the supply chain. Suppliers can use the PO number to track shipments, confirm delivery, and manage inventory levels. Buyers can use the PO number to monitor the status of their orders and ensure that they are received on time and in good condition.
12.4. Efficient Inventory Management
By linking PO numbers to inventory records, businesses can improve their inventory management practices. The PO number helps in reconciling incoming shipments with outstanding purchase orders, ensuring that inventory levels are accurately maintained. This reduces the risk of stockouts and overstocking, optimizing inventory holding costs.
12.5. Faster Invoice Processing
PO numbers streamline the invoice processing process by providing a clear link between the invoice and the corresponding purchase order. This makes it easier for buyers to verify invoices and approve payments quickly. Faster invoice processing reduces the risk of late payments and improves supplier relationships.
12.6. Improved Supplier Relationships
By using PO numbers consistently and communicating effectively with suppliers, businesses can build stronger and more collaborative relationships. Suppliers appreciate the clarity and organization that a well-managed PO system provides, which can lead to better pricing, faster delivery times, and improved service.
12.7. Reduced Errors
PO numbers help in reducing errors throughout the supply chain by providing a clear and consistent reference point for all transactions. This minimizes the risk of incorrect orders, mislabeled shipments, and other costly mistakes. Reduced errors lead to lower costs and improved efficiency.
12.8. Better Data Analysis
The data generated by the PO system can be used to analyze supply chain performance and identify areas for improvement. By tracking metrics such as order cycle time, supplier lead times, and invoice processing times, businesses can gain insights into their supply chain operations and make data-driven decisions.
12.9. Compliance and Auditing
PO numbers facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements and internal policies. The PO system provides a clear audit trail of all purchases, making it easier to demonstrate compliance with accounting standards and other regulations. This reduces the risk of fines and penalties.
12.10. Integration with Technology
Modern supply chain management systems integrate PO numbers seamlessly into their workflows. This allows for automated tracking, reporting, and analysis of purchase orders. Integration with technology enhances efficiency and provides real-time visibility into the supply chain.
By leveraging PO numbers effectively, businesses can optimize their supply chain operations, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
13. How PO Numbers Facilitate Budgeting and Forecasting
Purchase order (PO) numbers play a crucial role in facilitating accurate budgeting and forecasting within an organization. By providing a structured system for tracking and managing purchases, PO numbers enable businesses to gain better insights into their spending patterns, improve financial planning, and make more informed decisions. Here’s how PO numbers support budgeting and forecasting:
13.1. Accurate Tracking of Expenses
PO numbers allow businesses to accurately track their expenses by linking each purchase to a specific budget category. This ensures that all purchases are properly accounted for and that expenses are allocated to the correct budget lines. Accurate expense tracking is essential for creating realistic budgets and forecasts.
13.2. Improved Budget Control
By monitoring PO numbers, businesses can maintain better control over their budgets. The PO system provides real-time visibility into outstanding purchase orders, allowing managers to see how much of their budget has been committed but not yet spent. This helps prevent overspending and ensures that budgets are adhered to.
13.3. Forecasting Future Expenses
PO data can be used to forecast future expenses by analyzing historical spending patterns. By tracking the types of goods and services purchased, the quantities, and the prices, businesses can develop accurate forecasts of their future purchasing needs. This information is invaluable for creating realistic budgets and financial plans.
13.4. Identifying Spending Trends
PO numbers enable businesses to identify spending trends by categorizing purchases and analyzing the data. This helps in understanding where money is being spent, which vendors are being used, and what types of goods and services are being purchased. Identifying spending trends can reveal opportunities for cost savings and improved efficiency.
13.5. Vendor Performance Analysis
PO data can be used to analyze vendor performance by tracking metrics such as lead times, delivery reliability, and invoice accuracy. This helps in identifying which vendors are providing the best value for money and which ones may need to be replaced. Vendor performance analysis is essential for optimizing purchasing costs and improving supply chain efficiency.
13.6. Budget Variance Analysis
PO numbers facilitate budget variance analysis by providing a clear link between planned expenses and actual expenses. This allows managers to compare their actual spending to their budgeted amounts and identify any significant variances. Budget variance analysis is essential for understanding why budgets were not met and for making adjustments to future budgets.
13.7. Cash Flow Management
PO numbers improve cash flow management by providing visibility into upcoming payments. By tracking outstanding purchase orders, businesses can forecast their future cash outflows and ensure that they have sufficient funds to meet their obligations. This helps prevent cash flow problems and ensures that suppliers are paid on time.
13.8. Scenario Planning
PO data can be used to create scenario plans by modeling the impact of different purchasing decisions on the budget. For example, businesses can use PO data to estimate the cost of purchasing different quantities of goods or services or to evaluate the impact of changing vendors. Scenario planning helps in making informed decisions about purchasing and budgeting.
13.9. Integration with Budgeting Software
Modern budgeting software integrates PO numbers seamlessly into its workflows. This allows for automated tracking, reporting, and analysis of purchase orders. Integration with budgeting software enhances efficiency and provides real-time visibility into the budget.
13.10. Continuous Improvement
By using PO numbers to track and analyze their spending, businesses can continuously improve their budgeting and forecasting processes. The data provides insights into what is working well and what needs to be improved. This leads to more accurate budgets, better financial planning, and improved overall performance.
14. Future Trends in PO Numbering and Management
As technology advances and business processes evolve, several trends are emerging in the realm of purchase order (PO) numbering and management. These trends aim to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and integration within the broader supply chain and financial ecosystems. Here’s a look at some of the future trends in PO numbering and management:
14.1. Automation and AI
The integration of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) is set to revolutionize PO numbering and management. AI-powered systems can automatically generate PO numbers, validate invoices, and detect anomalies, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors. Automation streamlines the entire PO process, from creation to payment, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
14.2. Blockchain Integration
Blockchain technology offers enhanced security and transparency in PO management. By recording POs on a blockchain, businesses can create an immutable record of all transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and improving trust among trading partners. Blockchain integration also facilitates real-time tracking of goods and services, enhancing supply chain visibility.
14.3. Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based PO management solutions are becoming increasingly popular due to their scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. These solutions allow businesses to manage their POs from anywhere, at any time, using any device. Cloud-based systems also facilitate collaboration among team members and integration with other business applications.
14.4. Mobile Accessibility
Mobile accessibility is essential for modern PO management. Mobile apps allow employees to create, approve, and track POs on the go, enhancing efficiency and responsiveness. Mobile accessibility also enables real-time communication and collaboration among team members, regardless of their location.
14.5. Data Analytics and Visualization
Data analytics and visualization tools are being used to gain insights into PO data. By analyzing PO data, businesses can identify spending trends, optimize purchasing strategies, and improve supplier relationships. Data visualization tools make it easier to understand complex data and communicate insights to stakeholders.
14.6. Integration with ERP Systems
Seamless integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems is crucial for efficient PO management. Integration with ERP systems allows for automated data exchange between PO management and other business functions, such as accounting, inventory management, and supply chain management. This enhances accuracy and reduces manual effort.
14.7. Enhanced Security
Security is a top priority in PO management. Future PO systems will incorporate advanced security features, such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, and access controls, to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. Security measures will also be implemented to prevent fraud and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
14.8. Sustainability Considerations
Sustainability is becoming an increasingly important factor in PO management. Businesses are starting to consider the environmental and social impact of their purchasing decisions. Future PO systems will incorporate features that allow businesses to track and report on the sustainability of their purchases, helping them to meet their environmental and social goals.
14.9. Customizable Workflows
Customizable workflows are essential for meeting the unique needs of different businesses. Future PO systems will offer customizable workflows that allow businesses to tailor the PO process to their specific requirements. This enhances flexibility and ensures that the PO system aligns with the business’s overall objectives.
14.10. User-Friendly Interfaces
User-friendly interfaces are essential for promoting adoption and maximizing the benefits of PO systems. Future PO systems will feature intuitive interfaces that are easy to use and require minimal training. User-friendly interfaces enhance productivity and reduce the risk of errors.
These trends reflect the ongoing efforts to optimize PO numbering and management, making them more efficient, accurate, and integrated with the broader business ecosystem.
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to navigate the complexities of financial management. Do you have more questions or need further clarification? Don’t hesitate to ask at WHAT.EDU.VN, where answers are always free. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Visit our website, what.edu.vn, for more information and assistance. We are here to help you succeed.