Are you struggling to define project roles clearly? A RACI chart, as explained by WHAT.EDU.VN, can help clarify responsibilities and improve team collaboration. Let’s dive into how this tool can streamline your project management. This guide will cover RACI matrix creation, benefits, real-world applications and best practices to maximize your project’s efficiency.
1. What is a RACI Chart and Why Is It Important?
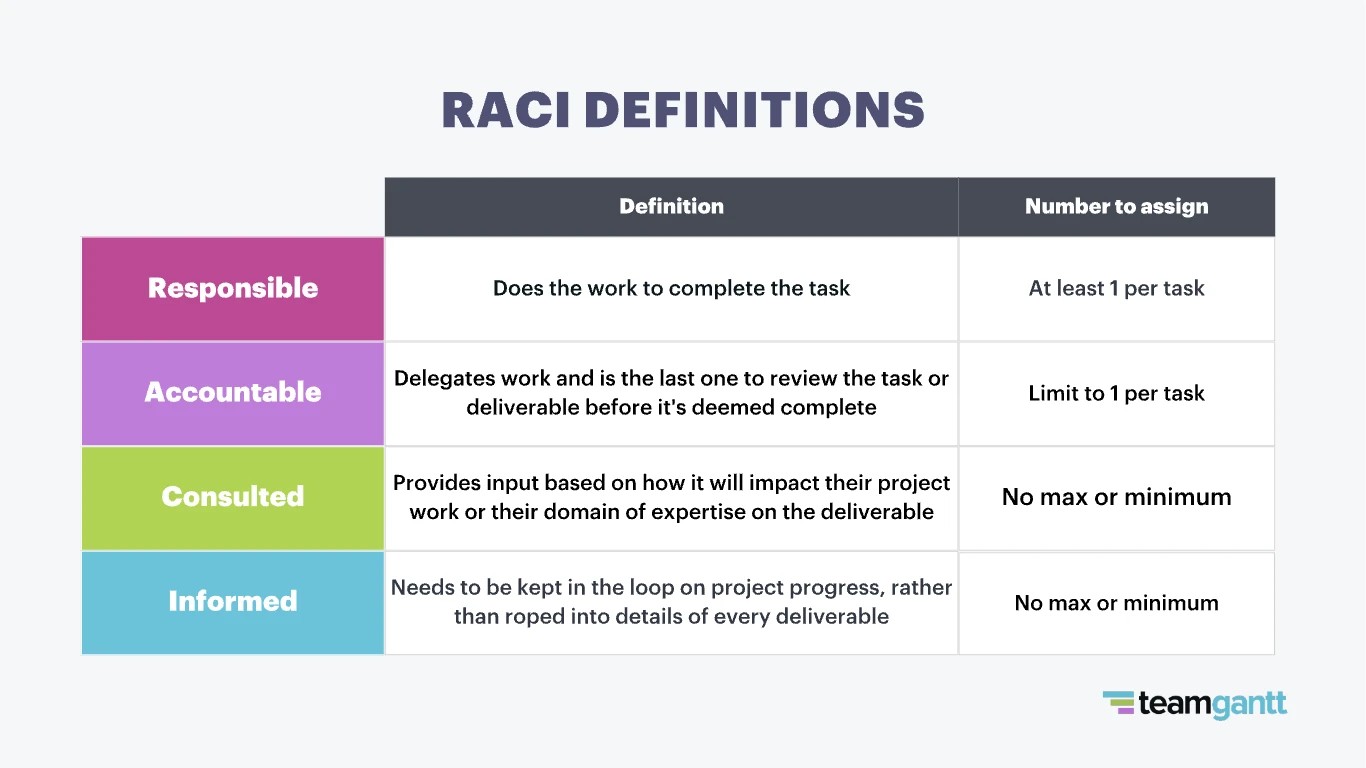
A RACI chart, short for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed, is a responsibility assignment matrix that helps define roles and responsibilities for project tasks. It’s crucial for ensuring that everyone knows their role, preventing confusion, and promoting accountability.
A RACI chart is a visual tool that clarifies project roles by categorizing each person’s involvement into one of four roles: Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, or Informed. It’s also known as a responsibility assignment matrix. This ensures clear task ownership, efficient communication, and smoother project execution.
1.1 Understanding the RACI Acronym
Each letter in RACI represents a different level of responsibility:
- Responsible (R): The person who does the work to complete the task. There can be multiple responsible parties.
- Accountable (A): The person who owns the task and is ultimately answerable for its correct and thorough completion. There should be only one accountable person per task.
- Consulted (C): People whose opinions are sought. They provide input and expertise to the task.
- Informed (I): People who are kept updated on the task’s progress. They don’t actively participate but need to know the status.
1.2 Why Use a RACI Chart?
Using a RACI chart offers several benefits:
- Clarity: Defines roles and responsibilities clearly.
- Accountability: Ensures someone is accountable for each task.
- Efficiency: Reduces confusion and overlap in tasks.
- Communication: Improves communication among team members.
- Conflict Resolution: Helps resolve conflicts related to task ownership.
1.3 Where Can I Find More Information on RACI Charts?
For more detailed information and resources on RACI charts, visit WHAT.EDU.VN. You’ll find comprehensive guides, templates, and expert advice to help you implement RACI charts effectively in your projects and boost project transparency.
2. Decoding the RACI Roles: Responsibilities and Examples
Understanding each RACI role is essential for effective project management. Let’s break down each role with clear responsibilities and practical examples.
2.1 Responsible (R): The Doer
The Responsible party is the individual or group directly responsible for completing the task. They perform the work required to achieve the project goals.
2.1.1 Responsibilities of the Responsible Party
- Executing the task according to the project plan.
- Collaborating with other team members to ensure task completion.
- Reporting progress and any roadblocks to the accountable party.
2.1.2 Examples of Responsible Roles
- Content Writer: Writes the content for a website.
- Software Developer: Codes a new feature for an application.
- Graphic Designer: Creates visuals for a marketing campaign.
- Business Analyst: Gathers and analyzes business requirements.
- QA Specialist: Tests software for bugs and issues.
2.2 Accountable (A): The Owner
The Accountable party is the individual who is ultimately answerable for the correct and thorough completion of the task. They delegate work and make final decisions.
2.2.1 Responsibilities of the Accountable Party
- Ensuring the task is completed to the required standards.
- Delegating tasks to the responsible party.
- Reviewing and approving the completed task.
- Addressing any issues or roadblocks that arise during task completion.
2.2.2 Examples of Accountable Roles
- Project Manager: Oversees the entire project and ensures tasks are completed on time.
- Product Manager: Defines the product vision and ensures the product meets market needs.
- Department Head: Ensures tasks align with departmental goals.
- Team Lead: Manages the team and ensures tasks are completed efficiently.
2.3 Consulted (C): The Advisor
The Consulted parties are those whose opinions are sought and who provide input based on their expertise or how the task will impact their future work.
2.3.1 Responsibilities of the Consulted Party
- Providing expert advice and input on the task.
- Reviewing the task and providing feedback.
- Ensuring the task aligns with their area of expertise.
2.3.2 Examples of Consulted Roles
- Sales Team: Provides input on marketing materials.
- Software Architect: Advises on the technical design of a software application.
- Content Editor: Reviews and edits written content.
- Creative Director: Provides input on the creative aspects of a project.
- QA Manager: Provides input on testing strategies.
- Legal Counsel: Provides legal advice and ensures compliance.
2.4 Informed (I): The Kept-in-the-Loop
The Informed parties are those who need to be kept updated on the progress of the task but do not actively participate in it.
2.4.1 Responsibilities of the Informed Party
- Staying informed about the progress of the task.
- Understanding how the task impacts their work.
2.4.2 Examples of Informed Roles
- Executive Leadership: Kept informed about project progress.
- External Clients: Updated on project milestones.
- Team Members Assigned to Dependent Tasks: Informed about the status of tasks they rely on.
- Customer Support Team: Informed about new product features.
- Administrative Staff: Kept in the loop on relevant project updates.
2.5 Need More Examples?
For additional examples and detailed explanations of RACI roles, visit WHAT.EDU.VN. You can find resources tailored to various industries and project types to help you effectively implement RACI charts.
2.6 Responsible vs. Accountable: Clearing the Confusion
It’s crucial to differentiate between Responsible and Accountable roles. The Responsible party does the work, while the Accountable party ensures the work is done correctly.
2.6.1 Key Differences
- Responsible: Task-oriented, involves doing the work.
- Accountable: Outcome-oriented, involves owning the result.
- Multiple Responsible Parties: Possible for one task.
- Single Accountable Party: Required for each task.
2.6.2 Examples to Illustrate the Difference
- In a software development project, developers (Responsible) write the code, while the software architect (Accountable) ensures the code meets the required standards.
- In a marketing campaign, the content writer (Responsible) creates the content, while the marketing manager (Accountable) ensures the content aligns with the campaign goals.
2.6.3 Still Unclear?
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN for more in-depth explanations and examples to help you distinguish between Responsible and Accountable roles in your projects.
3. Creating a RACI Chart: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a RACI chart is a straightforward process that can significantly improve project clarity and efficiency. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started.
3.1 Step 1: Identify Project Tasks
Start by listing all the key tasks, phases, or milestones required for your project. Be as detailed as necessary, depending on the complexity of the project.
3.1.1 Example Tasks
- Write project brief
- Create content
- Design handout
- Review first draft
- Update handout
- Approve final
- Send to printer
3.2 Step 2: Identify Project Roles
List all the individuals or roles involved in the project across the top row of your chart. Use names or job titles, whichever makes the most sense for your team.
3.2.1 Example Roles
- Project manager
- CMO
- Marketing manager
- Editorial director
- Content writer
- Creative director
- Designer
3.3 Step 3: Assign RACI Roles
Go line by line down the chart and assign each person an R, A, C, or I for each task. This indicates the role they will play in that particular task.
3.3.1 RACI Role Assignments
- Responsible: Who does the work?
- Accountable: Who is ultimately responsible?
- Consulted: Who needs to provide input?
- Informed: Who needs to be kept in the loop?
3.4 Step 4: Review and Adjust
Once your RACI chart is complete, review it to ensure it meets the following criteria:
- Every task has at least one Responsible person.
- There is one and only one Accountable party assigned to each task.
- No team members are overloaded with too many Responsible tasks.
- Every team member has a role on each task.
3.5 Step 5: Communicate and Implement
Share the RACI chart with your team and stakeholders. Ensure everyone understands their roles and responsibilities. Use the chart as a reference throughout the project.
3.5.1 Communication Plan
Create a communication plan that aligns with the roles outlined in the RACI chart. This ensures that everyone receives the right information at the right time.
3.6 Need a Template?
For a free Excel RACI chart template, visit WHAT.EDU.VN. You can also find information on how to use TeamGantt’s built-in RACI feature as part of your project plan.
4. RACI Chart Examples: Real-World Applications
To better understand how RACI charts work, let’s look at a couple of real-world examples.
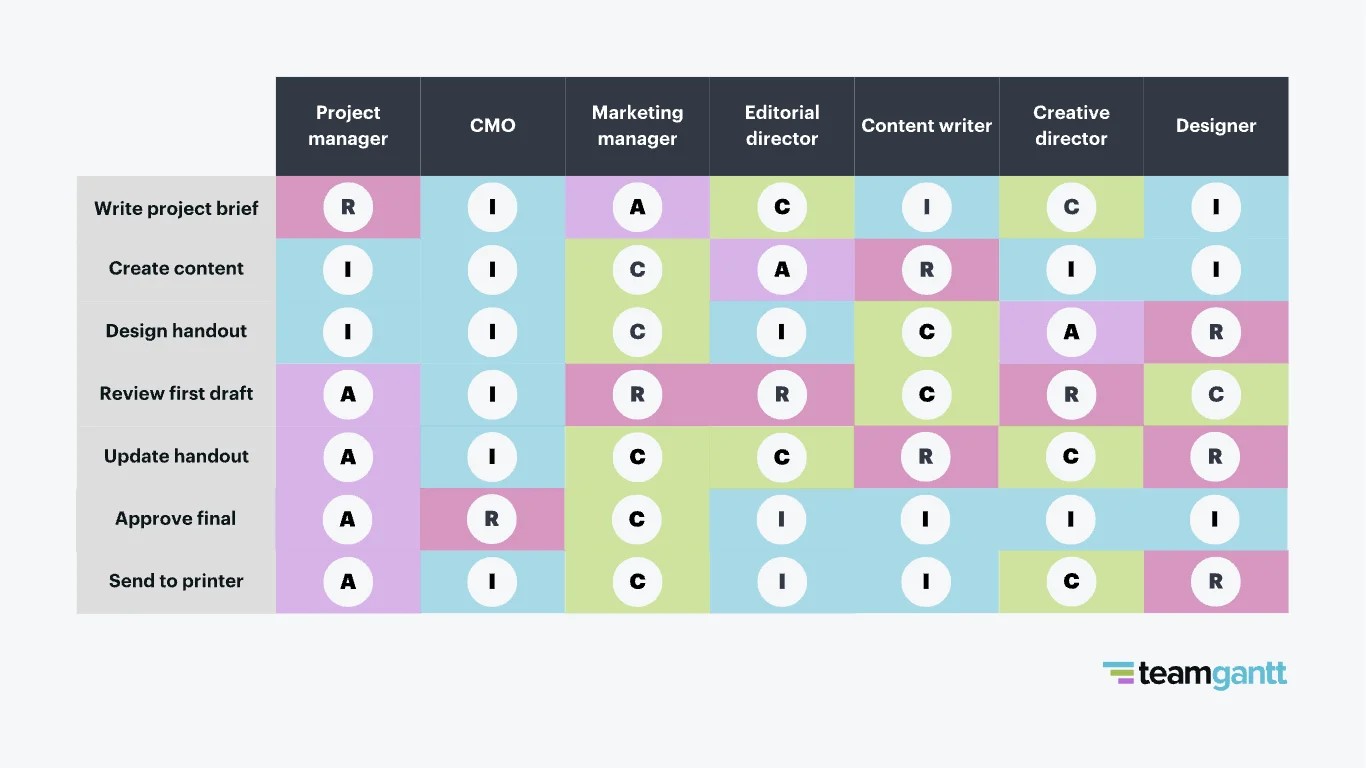
4.1 Example 1: Producing a Marketing Handout
Imagine you’re creating a RACI chart for a handout your marketing manager will distribute at an industry conference.
4.1.1 Basic Tasks
- Write project brief
- Create content
- Design handout
- Review first draft
- Update handout
- Approve final
- Send to printer
4.1.2 RACI Roles
- Project manager
- CMO
- Marketing manager
- Editorial director
- Content writer
- Creative director
- Designer
4.1.3 RACI Chart
| Task | Project Manager | CMO | Marketing Manager | Editorial Director | Content Writer | Creative Director | Designer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Write project brief | R | C | A | ||||
| Create content | C | A | R | ||||
| Design handout | C | A | R | ||||
| Review first draft | C | R | C | ||||
| Update handout | C | A | R | C | R | ||
| Approve final | A | C | |||||
| Send to printer | R | A |

4.2 Example 2: Developing a New Software Product
For a more complex project, such as developing a new software product, RACI roles can be mapped to major tasks in a software development project.
4.2.1 Key Tasks
- Market Research
- Requirement Gathering
- Design and Prototyping
- Software Development
- Testing
- Deployment
- Maintenance
- Monitoring
- Marketing and Sales
- User Training
4.2.2 RACI Roles
- Business Analyst
- Product Manager
- Sales Representative
- Customer Support
- Project Manager
- Software Developers/Engineers
- UI/UX Designer
- Software Architect
- QA Analysts/Engineers
- DevOps Engineer
- Technical Writer
- Marketing Manager
4.2.3 RACI Chart Snippet
| Task | Business Analyst | Product Manager | Software Developers | QA Analysts | Project Manager |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Market Research | R | A | I | ||
| Requirement Gathering | R | A | C | I | I |
| Software Development | C | R | C | I | |
| Testing | I | C | R | A | |
| Deployment | I | C | C | A |
4.3 Want More Examples?
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN for more practical RACI chart examples across various industries and project types.
5. Best Practices for Using RACI Charts
To maximize the effectiveness of RACI charts, follow these best practices.
5.1 Keep the Chart Visible and Accessible
Ensure the RACI chart is easily accessible to all team members. This can be achieved by storing it in a shared location, such as a project management tool or a shared drive.
5.2 Involve the Team in Creating the Chart
Involve team members in the creation of the RACI chart to ensure buy-in and a shared understanding of roles and responsibilities.
5.3 Review and Update Regularly
Project requirements and team dynamics can change. Review and update the RACI chart regularly to ensure it remains relevant and accurate.
5.4 Ensure Clear Communication
Use the RACI chart as a basis for communication. Ensure that everyone understands who they need to communicate with for each task.
5.5 Avoid Overloading Individuals
Be mindful of workload distribution. Ensure that no single individual is overloaded with too many Responsible or Accountable tasks.
5.6 Limit Accountable Roles
Each task should have only one Accountable party to ensure clear decision-making and ownership.
5.7 Balance Roles Across Team Members
Ensure that each team member has a balanced role across all tasks. This prevents some members from being overwhelmed while others are underutilized.
5.8 Need More Tips?
For more RACI chart best practices, visit WHAT.EDU.VN. You’ll find expert tips and strategies to help you optimize your project management processes.
6. Common RACI Chart Pitfalls and Solutions
Even with the best intentions, some common pitfalls can undermine the effectiveness of your RACI chart. Here’s how to avoid them.
6.1 Failing to Get Buy-In
Creating a RACI chart in isolation without team input can lead to misunderstandings and resistance.
Solution
Involve your team and stakeholders in the RACI chart creation process. Discuss roles and responsibilities openly to ensure everyone agrees and understands their assignments.
6.2 Setting It and Forgetting It
Building a RACI chart at the start of a project and then neglecting it can lead to confusion as the project evolves.
Solution
Keep the RACI chart top of mind throughout the project lifecycle. Review it regularly in status update meetings and ensure it’s easily accessible to everyone involved.
6.3 Overcomplicating Stakeholder Communication
Having too many Consulted and Informed roles without a streamlined communication plan can overwhelm stakeholders.
Solution
Implement a lightweight communication system. Ensure that department heads and senior leaders have access to the project plan and can easily follow progress. Use tools like TeamGantt to share view-only links with external clients and stakeholders.
6.4 Neglecting to Update the Chart
Project scopes, team members, and responsibilities can change over time. Failing to update the RACI chart accordingly can lead to confusion and inefficiencies.
Solution
Schedule regular reviews of the RACI chart to ensure it reflects the current project status and team roles. Update the chart whenever there are significant changes to the project or team.
6.5 Overlapping Responsibilities
Assigning the same responsibilities to multiple individuals without clear boundaries can lead to conflicts and duplicated efforts.
Solution
Clearly define the scope of each role and responsibility. Ensure that each task has a single Accountable party and that Responsible parties have distinct duties.
6.6 Unclear Definitions
Ambiguous definitions of RACI roles can lead to misunderstandings and inconsistent application of the chart.
Solution
Provide clear, concise definitions of each RACI role to your team. Ensure everyone understands the difference between Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed.
6.7 Need More Help?
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN for more insights on avoiding RACI chart pitfalls and ensuring project success.
7. Benefits of the RACI Model in Project Management
The RACI model offers numerous benefits in project management, leading to increased clarity, accountability, and efficiency.
7.1 Clear Expectations
The RACI model helps set clear expectations about project roles and responsibilities. This ensures that team members know exactly what is expected of them, reducing confusion and overlap.
7.2 Improved Accountability
By clearly defining who is Accountable for each task, the RACI model ensures that someone is responsible for the outcome. This promotes accountability and helps prevent tasks from falling through the cracks.
7.3 Enhanced Communication
The RACI model facilitates better communication by clarifying who needs to be Consulted or Informed about each task. This ensures that the right people receive the right information at the right time.
7.4 Efficient Resource Allocation
By mapping out roles and responsibilities, the RACI model helps ensure that resources are allocated efficiently. This prevents duplication of effort and ensures that team members are not overloaded.
7.5 Conflict Resolution
The RACI model can help resolve conflicts related to task ownership or decision-making. By clearly defining roles, it reduces ambiguity and provides a framework for resolving disputes.
7.6 Better Decision-Making
With clear roles and responsibilities, decision-making becomes more streamlined. The Accountable party knows they have the authority to make decisions, and the Consulted parties provide valuable input.
7.7 Increased Team Morale
When team members understand their roles and responsibilities, and when they see that the project is well-organized, it can boost morale. Clear roles reduce stress and increase job satisfaction.
7.8 Onboarding New Team Members
The RACI chart can be a valuable tool for onboarding new team members. It provides a quick and easy way to understand their roles and responsibilities, as well as who they need to work with.
7.9 Want to Learn More?
For more insights on the benefits of the RACI model, visit WHAT.EDU.VN. You’ll find additional resources and expert advice to help you maximize its potential.
8. When to Use or Skip a RACI Chart
A RACI chart can be a valuable tool for many projects, but it’s not always necessary. Here are some scenarios where using a RACI chart is beneficial, as well as situations where it might not be needed.
8.1 When to Use a RACI Chart
- Complex Projects: When tasks require multiple resources, run concurrently, or depend on other tasks.
- Decision-Making Bottlenecks: When the decision-making or approval process could hold up the project.
- Task Ownership Conflicts: When there’s conflict about task ownership or decision-making.
- Uneven Workload Distribution: When the project workload feels like it’s not distributed evenly.
- Team Turnover: When you experience turnover on a team and need to onboard someone quickly to a new role.
8.2 When to Skip a RACI Chart
- Small Projects: When the project is small enough that it would be time-consuming to create a RACI chart.
- High-Performing Teams: When you work with a team who communicates well and stays on top of their own work.
- Clearly Defined Roles: When roles and responsibilities are already clearly defined and understood by all team members.
8.3 What If You Skip It?
Even if you decide to skip creating a RACI chart, it’s crucial to have a clear plan in place to guide your team and project.
8.4 Still Unsure?
If you’re unsure whether a RACI chart is right for your project, visit WHAT.EDU.VN for guidance. You can find expert advice and resources to help you make the best decision.
9. RACI Alternatives: Other Responsibility Assignment Methods
While RACI is a popular method for defining project roles, several alternatives can be used depending on the project and team dynamics.
9.1 RASCI
RASCI stands for Responsible, Accountable, Supporting, Consulted, and Informed. The “Supporting” role is added to denote individuals who provide support to the Responsible party.
- When to Use: When you need to explicitly define who provides support to the Responsible party.
9.2 RACIQ
RACIQ stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed, and Quality Review. The “Quality Review” role is added to specify who is responsible for ensuring the quality of the deliverable.
- When to Use: When quality assurance is a critical aspect of the project.
9.3 DACI
DACI stands for Driver, Approver, Contributor, and Informed. This model is more decision-oriented, focusing on who drives the decision, who approves it, who contributes to it, and who needs to be informed.
- When to Use: When decision-making processes need to be clearly defined.
9.4 RAPID
RAPID stands for Recommend, Agree, Perform, Input, and Decide. This model focuses on decision-making roles, similar to DACI.
- When to Use: In situations where decision-making needs to be streamlined and clearly defined.
9.5 Choosing the Right Method
The best method depends on your project’s specific needs and the dynamics of your team. Consider the level of detail required, the importance of decision-making, and the need for support roles when choosing a method.
9.6 Need More Options?
For more information on RACI alternatives, visit WHAT.EDU.VN. You’ll find detailed comparisons and expert advice to help you choose the right method for your project.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About RACI Charts
Here are some frequently asked questions about RACI charts to help you better understand and implement them effectively.
10.1 What If a Task Has No Responsible Party?
If a task has no Responsible party, it means no one is actively working on it. This is a critical issue that needs to be addressed immediately.
- Solution: Assign a Responsible party to ensure the task is completed.
10.2 Can a Person Be Both Responsible and Accountable?
Yes, a person can be both Responsible and Accountable, but it’s essential to ensure they have the capacity to handle both roles effectively.
- Considerations: If the individual is overloaded, consider assigning the Responsible role to someone else.
10.3 What If a Task Has Multiple Accountable Parties?
A task should have only one Accountable party to ensure clear ownership and decision-making.
- Solution: Re-evaluate the roles and assign one Accountable party.
10.4 How Often Should I Update the RACI Chart?
Update the RACI chart whenever there are changes to the project scope, team members, or responsibilities.
- Best Practice: Review the chart regularly, such as during weekly status meetings.
10.5 What If Someone Disagrees With Their Assigned Role?
Open communication is key. Discuss their concerns and adjust the roles if necessary, ensuring everyone is comfortable and understands their responsibilities.
- Approach: Facilitate a team discussion to reach a consensus.
10.6 Can I Use a RACI Chart for Personal Tasks?
While primarily used for project management, you can adapt a RACI chart for personal tasks to improve organization and accountability.
- Adaptation: Modify the roles to fit your personal needs and goals.
10.7 What Tools Can I Use to Create a RACI Chart?
You can use various tools to create a RACI chart, including:
- Spreadsheet software (e.g., Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets)
- Project management software (e.g., TeamGantt, Asana, Trello)
- Dedicated RACI chart templates
10.8 Where Can I Find More Answers?
For more FAQs and detailed answers, visit WHAT.EDU.VN. You’ll find a wealth of information to help you master RACI charts.
Conclusion: Streamline Your Projects with RACI Charts
A RACI chart is a powerful tool for project management, providing clarity, accountability, and improved communication. By understanding the roles, following best practices, and avoiding common pitfalls, you can streamline your projects and achieve greater success.
Ready to take your project management to the next level? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN for more resources, templates, and expert advice on implementing RACI charts effectively.
Have questions or need personalized guidance? Contact us at:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Let what.edu.vn help you clarify your project roles and achieve your goals! Don’t hesitate—ask your questions for free today!

