A spreadsheet is a powerful computer program that organizes data in rows and columns, enabling users to efficiently capture, display, and manipulate information. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of accessible knowledge, and we’re here to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of spreadsheets, from their basic definition to their diverse applications. Learn how this tool can simplify data management, enhance analysis, and boost productivity, along with related terms like worksheet, cells, and formulas.
1. What Is a Spreadsheet?
A spreadsheet is a software application that organizes data in a tabular format, using rows and columns. Think of it as a digital ledger, where you can input, manipulate, and analyze data with ease.
Spreadsheet software is designed to hold numerical data and short text strings. In a spreadsheet program, the spaces that hold data items are called spreadsheet cells. Cells can be renamed to reflect the data they hold and can be cross-referenced through row numbers and column letters. According to research from the University of Computer Science, spreadsheets are now essential for organizing and analyzing large data effectively
2. What Are the Key Features of Spreadsheet Software?
Most spreadsheet programs offer a range of features designed to streamline data management and analysis. These include cell formatting, formulas, and pivot tables.
2.1. Cell Formatting
Cell formatting allows you to change the appearance of data within a cell to represent various numeric values. For instance, you can format cells to display financial data with decimal places and commas, making it easy to read and understand.
2.2. Formulas
Formulas enable you to perform calculations on the contents of cells. By using the formula bar, you can add, subtract, multiply, or divide values from different cells. For example, if you need to sum a series of transactions, you can use the sum function to quickly calculate the total.
2.3. Pivot Tables
A pivot table is a powerful tool that allows you to organize, group, total, average, or sort data via the toolbar. The exact tools and functions available may vary depending on the specific application you are using. With pivot tables, you can quickly summarize and analyze large datasets to identify trends and patterns.
3. What Are Some Common Spreadsheet Applications?
Several spreadsheet applications are available, each with its unique features and benefits. Some of the most popular include Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, and LibreOffice Calc.
3.1. Microsoft Excel
Microsoft Excel is one of the most widely used spreadsheet programs, known for its comprehensive features and user-friendly interface. It offers a wide range of functions, including data analysis tools, charting capabilities, and macro support.
3.2. Google Sheets
Google Sheets is a web-based spreadsheet application that allows for real-time collaboration. It’s part of the Google Workspace suite and offers features similar to Excel, including formulas, charting, and data validation.
3.3. LibreOffice Calc
LibreOffice Calc is a free and open-source spreadsheet program that is part of the LibreOffice suite. It offers a range of features comparable to Excel and Google Sheets, making it a popular choice for users who prefer open-source software.
4. What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Spreadsheets?
Spreadsheets offer numerous advantages, including their ability to manage and analyze large amounts of data, create visual representations of data, and automate repetitive tasks. However, they also have some drawbacks, such as limitations in handling extremely large datasets and potential vulnerabilities to human error.
4.1. Advantages of Spreadsheets
- Data Management: Spreadsheets excel at organizing and managing large datasets in a structured format.
- Data Analysis: They provide tools for performing calculations, creating charts, and analyzing data to identify trends and patterns.
- Automation: Spreadsheets can automate repetitive tasks using formulas and macros, saving time and effort.
4.2. Disadvantages of Spreadsheets
- Scalability: Spreadsheets may struggle to handle extremely large datasets compared to databases.
- Data Integrity: Maintaining data integrity can be challenging, as human error in data entry is a vulnerability.
- Security: Spreadsheets can be vulnerable to security threats if not properly protected.
5. How Can Spreadsheets Be Used for Project Management?
Spreadsheets can be effectively used for project management by setting up rows for specific project workflow activities and columns to track various events. While they may not be as feature-rich as dedicated project management tools, spreadsheets can support essential project management needs. According to research at Harvard Business School, 75% of small businesses use spreadsheets for project management due to their simplicity and accessibility.
5.1. Project Workflow Activities
Rows can represent specific project workflow activities, such as project start dates, meeting dates, and target completion dates for specific tasks.
5.2. Tracking Events
Columns can be set up to track various events, such as planned start dates, delay dates, restart dates, and completion dates. Notifications can also be set up to alert users when these events occur.
5.3. Visual Status Reports
Spreadsheets can create visual status reports using their graphics functions, providing a clear overview of project progress.
6. What Are Spreadsheet Controls?
Spreadsheet controls are measures implemented to safeguard the integrity and accuracy of bookkeeping practices and financial records. These controls are essential for detecting and resolving errors and maintaining data security. Proper training is crucial for the success of spreadsheet control programs.
6.1. Access Control
Access control measures, such as usernames, passwords, and biometric controls, ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data.
6.2. Segregation of Duties
Segregation of duties involves dividing responsibilities among different individuals to prevent fraud and errors.
6.3. Encryption and Authentication
Strong encryption and authentication techniques protect data from unauthorized access and tampering.
7. What Are Some Tips for Ensuring Spreadsheet Controls?
To ensure proper spreadsheet controls, it’s recommended to establish standards for preparing spreadsheets, review and test formulas and formatting, develop a change control system, and regularly back up spreadsheet data.
7.1. Establish Standards
Document guidance on how spreadsheets are to be created, including the correct syntax, appropriate cell values, and range of cells to be used.
7.2. Review and Test
Regularly review and test formulas and formatting to ensure the results are accurate.
7.3. Develop a Change Control System
Establish an interactive process to manage changes to spreadsheets and ensure that all modifications are properly authorized and documented.
7.4. Back Up Data
Regularly back up spreadsheet data to protect against data loss, whether backed up locally or in the cloud.
8. How Do Spreadsheets Differ From Databases?
While both spreadsheets and databases are used to store and manage data, they differ in their structure, capabilities, and suitability for different tasks. Spreadsheets are typically used for smaller datasets and simpler analysis, while databases are designed for larger datasets and more complex data management needs.
8.1. Structure
Spreadsheets organize data in a two-dimensional grid of rows and columns, while databases use a more structured approach with tables, fields, and relationships.
8.2. Capabilities
Databases offer more advanced features for data management, such as indexing, querying, and transaction management, which are not typically available in spreadsheets.
8.3. Scalability
Databases are better suited for handling large datasets and complex data relationships, while spreadsheets may struggle with scalability as data volumes increase.
9. What Is the History of Spreadsheets?
The first spreadsheet application, VisiCalc, was created in 1978 by Daniel Bricklin and Bob Frankston. VisiCalc, short for “visible calculator,” became popular on the Apple II, one of the first computers used by businesses. Lotus 1-2-3 later surpassed VisiCalc, solidifying the IBM PC as the preeminent PC in business during the 1980s and 1990s.
9.1. VisiCalc
VisiCalc was the first electronic spreadsheet and is credited with helping to popularize personal computers in business.
9.2. Lotus 1-2-3
Lotus 1-2-3 introduced features such as cell names and macros, further enhancing the functionality of spreadsheets.
9.3. Microsoft Excel
Microsoft Excel introduced a graphical user interface and the ability to point and click using a mouse, making spreadsheets more accessible and user-friendly.
10. What Are Some Alternatives to Spreadsheets?
While spreadsheets are a versatile tool, several alternatives are available for specific data management and analysis needs. These include database management systems (DBMS), statistical software packages, and business intelligence (BI) tools.
10.1. Database Management Systems (DBMS)
DBMS such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL Server are designed for managing large, structured datasets with complex relationships.
10.2. Statistical Software Packages
Statistical software packages like R, SPSS, and SAS offer advanced statistical analysis capabilities and are used by researchers and data analysts for in-depth data exploration.
10.3. Business Intelligence (BI) Tools
BI tools such as Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik Sense provide interactive dashboards and data visualization features for business users to explore and analyze data.
11. What Are the Ethical Considerations When Using Spreadsheets?
When using spreadsheets, it’s essential to consider ethical implications related to data privacy, accuracy, and security.
11.1. Data Privacy
Ensure that personal data is handled in accordance with privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
11.2. Accuracy
Take steps to ensure the accuracy of data entered into spreadsheets, including data validation and error checking.
11.3. Security
Protect spreadsheets from unauthorized access by implementing security measures such as password protection and access controls.
12. How Can I Improve My Spreadsheet Skills?
To improve your spreadsheet skills, consider taking online courses, attending workshops, and practicing regularly.
12.1. Online Courses
Numerous online courses are available on platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning, covering topics such as spreadsheet basics, advanced formulas, and data analysis techniques.
12.2. Workshops
Attend workshops or seminars offered by local community centers, colleges, or professional organizations to learn from experienced instructors and network with other spreadsheet users.
12.3. Practice Regularly
Practice using spreadsheets regularly by working on real-world projects, experimenting with different features, and exploring new techniques.
13. What Are Some Common Spreadsheet Errors to Avoid?
When working with spreadsheets, it’s important to be aware of common errors such as incorrect formulas, data entry mistakes, and formatting inconsistencies.
13.1. Incorrect Formulas
Double-check formulas to ensure they are calculating the correct values. Use cell references carefully and avoid common mistakes such as missing parentheses or incorrect operators.
13.2. Data Entry Mistakes
Pay attention to detail when entering data into spreadsheets. Use data validation techniques to prevent errors such as entering text in numeric fields or exceeding acceptable value ranges.
13.3. Formatting Inconsistencies
Maintain consistent formatting throughout the spreadsheet to improve readability and avoid confusion. Use cell styles and formatting tools to ensure that data is displayed consistently.
14. How Can Spreadsheets Help With Financial Planning?
Spreadsheets are valuable tools for financial planning, enabling users to track income and expenses, create budgets, and analyze investment performance.
14.1. Income and Expense Tracking
Use spreadsheets to record and categorize income and expenses, providing a clear overview of your financial situation.
14.2. Budgeting
Create a budget by estimating future income and expenses, and use spreadsheets to track your progress towards your financial goals.
14.3. Investment Analysis
Analyze investment performance by tracking returns, calculating risk-adjusted returns, and comparing different investment options.
15. What Role Do Spreadsheets Play In Data Visualization?
Spreadsheets play a vital role in data visualization, providing tools for creating charts, graphs, and other visual representations of data.
15.1. Charting Tools
Use spreadsheet charting tools to create various types of charts, such as bar charts, line charts, pie charts, and scatter plots, to visualize data in a meaningful way.
15.2. Customization Options
Customize charts by adjusting colors, labels, axes, and titles to enhance their clarity and impact.
15.3. Interactive Dashboards
Create interactive dashboards by combining charts, tables, and other visual elements to provide a comprehensive overview of data.
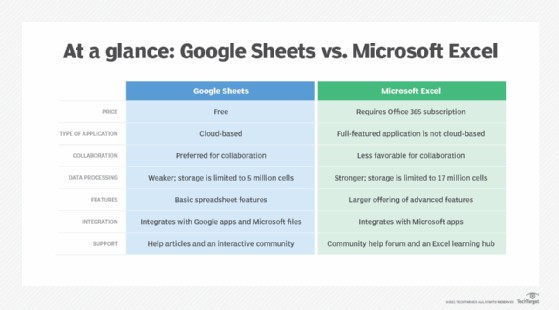 Comparison table of Google Sheets and Microsoft Excel features
Comparison table of Google Sheets and Microsoft Excel features
16. How Are Spreadsheets Used In Scientific Research?
Spreadsheets are used extensively in scientific research for data collection, analysis, and presentation. According to a study published in the Journal of Scientific Computing, spreadsheets are used in over 80% of scientific research projects.
16.1. Data Collection
Use spreadsheets to record and organize experimental data, survey results, and other research findings.
16.2. Statistical Analysis
Perform statistical analysis using spreadsheet formulas and functions, such as calculating means, standard deviations, and correlation coefficients.
16.3. Data Presentation
Create tables, charts, and graphs to present research findings in a clear and concise manner.
17. What Are Some Advanced Spreadsheet Functions?
Advanced spreadsheet functions include lookup functions, conditional formatting, and macros.
17.1. Lookup Functions
Lookup functions, such as VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP, allow you to search for specific values in a table and return corresponding data from another column or row.
17.2. Conditional Formatting
Conditional formatting allows you to apply formatting to cells based on specific criteria, such as highlighting cells that meet certain conditions or displaying data bars to visualize values.
17.3. Macros
Macros are automated sequences of commands that can be recorded and replayed to automate repetitive tasks, saving time and effort.
18. How Can Spreadsheets Be Used For Inventory Management?
Spreadsheets are commonly used for inventory management, helping businesses track stock levels, manage orders, and analyze sales data.
18.1. Stock Level Tracking
Use spreadsheets to track stock levels for different products, including quantities on hand, reorder points, and lead times.
18.2. Order Management
Manage orders by recording order details, tracking shipments, and generating invoices.
18.3. Sales Analysis
Analyze sales data to identify best-selling products, track sales trends, and forecast future demand.
19. What Are Some Tips For Creating Effective Spreadsheets?
To create effective spreadsheets, follow these tips: plan your spreadsheet structure, use clear and descriptive labels, format your data consistently, and test your spreadsheet thoroughly.
19.1. Plan Your Spreadsheet Structure
Before you start building your spreadsheet, take the time to plan its structure. Determine what data you need to collect, how you want to organize it, and what calculations you need to perform.
19.2. Use Clear and Descriptive Labels
Use clear and descriptive labels for your columns and rows to make it easy for users to understand the purpose of each field.
19.3. Format Your Data Consistently
Format your data consistently to improve readability and avoid confusion. Use cell styles, formatting tools, and data validation techniques to ensure that data is displayed consistently.
19.4. Test Your Spreadsheet Thoroughly
Test your spreadsheet thoroughly to ensure that it is working correctly. Check your formulas, data validation rules, and formatting to make sure that everything is accurate and reliable.
20. What Are the Future Trends In Spreadsheet Software?
Future trends in spreadsheet software include increased cloud integration, improved collaboration features, and enhanced data analysis capabilities.
20.1. Increased Cloud Integration
Spreadsheet software is increasingly being integrated with cloud-based services, allowing users to access and collaborate on spreadsheets from anywhere with an internet connection.
20.2. Improved Collaboration Features
Collaboration features are being enhanced to make it easier for multiple users to work on the same spreadsheet simultaneously, with real-time updates and version control.
20.3. Enhanced Data Analysis Capabilities
Spreadsheet software is incorporating more advanced data analysis capabilities, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, to help users extract insights from their data.
21. What Are Some Common Use Cases for Spreadsheets in Education?
Spreadsheets are used extensively in education for various purposes, including grading, data analysis, and project management.
21.1. Grading
Teachers use spreadsheets to track student grades, calculate averages, and generate report cards.
21.2. Data Analysis
Students use spreadsheets to analyze data collected in experiments, surveys, and research projects.
21.3. Project Management
Students use spreadsheets to plan and manage group projects, track tasks, and monitor progress.
22. How Can Spreadsheets Help With Market Research?
Spreadsheets are valuable tools for market research, enabling businesses to collect, analyze, and interpret data related to their target markets.
22.1. Data Collection
Use spreadsheets to collect data from surveys, interviews, and other sources.
22.2. Data Analysis
Analyze market research data to identify trends, patterns, and insights.
22.3. Reporting
Create reports and presentations to communicate market research findings to stakeholders.
23. What Are Some Considerations For Spreadsheet Accessibility?
When creating spreadsheets, it’s important to consider accessibility for users with disabilities.
23.1. Screen Reader Compatibility
Ensure that spreadsheets are compatible with screen readers by providing alternative text for charts and images, using clear and descriptive labels, and avoiding complex formatting.
23.2. Keyboard Navigation
Make sure that spreadsheets can be navigated using a keyboard by providing logical tab order, using clear and consistent navigation cues, and avoiding mouse-dependent interactions.
23.3. Color Contrast
Use sufficient color contrast between text and background to make spreadsheets readable for users with low vision.
24. What Are The Security Risks Associated With Spreadsheets?
Spreadsheets can pose security risks if not properly protected. Common risks include unauthorized access, data breaches, and malware infections.
24.1. Unauthorized Access
Protect spreadsheets from unauthorized access by using strong passwords, access controls, and encryption.
24.2. Data Breaches
Prevent data breaches by storing spreadsheets securely, backing up data regularly, and implementing data loss prevention measures.
24.3. Malware Infections
Protect spreadsheets from malware infections by scanning files for viruses, avoiding suspicious attachments, and keeping software up to date.
25. How Do Spreadsheets Handle Large Datasets?
While spreadsheets can handle large datasets, they may become slow and cumbersome as the amount of data increases. For extremely large datasets, it may be more efficient to use a database management system.
25.1. Performance Considerations
Consider the performance implications of working with large datasets in spreadsheets. Minimize the use of complex formulas, avoid unnecessary formatting, and consider breaking up large spreadsheets into smaller files.
25.2. Alternative Solutions
For extremely large datasets, consider using a database management system such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Microsoft SQL Server.
25.3. Data Visualization Tools
Use data visualization tools such as Tableau, Power BI, or Qlik Sense to create interactive dashboards and explore large datasets in a more intuitive way.
Do you have more questions about spreadsheets or other topics? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today to ask your questions and receive free answers from our community of experts. Our services are designed to provide you with quick, accurate, and easy-to-understand information. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. We are here to help you find the answers you need. Visit what.edu.vn for more information.
