A startup is more than just a newly established business; it’s a temporary organization designed to discover and implement a repeatable and scalable business model, according to WHAT.EDU.VN. This involves developing innovative solutions and disrupting existing markets to achieve significant growth. Dive in to explore what makes a startup unique and how it differs from a small business, including its business model, funding strategies, and risk profile.
1. What Is a Startup?
A startup is a temporary organization designed to discover and implement a repeatable and scalable business model.
While the dictionary definition of a startup might be “a newly established business,” that’s an oversimplification. To truly understand What Is A Startup, you need a more comprehensive definition: A startup is a temporary organization or system designed to search for, identify, and adopt a repeatable and scalable business model. This definition emphasizes the experimental nature of startups, which are constantly testing and refining their approach to find a model that works.
1.1 What are the Key Characteristics of a Startup?
A startup is characterized by innovation, scalability, and a high degree of risk.
- Innovation: Startups often introduce new products, services, or business models that disrupt existing markets.
- Scalability: A startup’s business model is designed to be easily scalable, meaning it can grow rapidly without significant increases in costs.
- Risk: Startups operate in uncertain environments and face a high risk of failure.
1.2 What is the primary goal of a startup?
The main goal of a startup is to find a scalable and repeatable business model.
Unlike established businesses, startups are not focused on immediate profitability. Instead, their primary goal is to validate their business idea and develop a sustainable model for growth. Once they achieve this, they can then focus on scaling their operations and generating revenue.
1.3 How does a startup differ from a small business?
Startups differ from small businesses in their goals, funding, and risk tolerance.
| Feature | Startup | Small Business |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Rapid growth and market disruption | Steady revenue and profitability |
| Funding | Venture capital, angel investors, and other external sources | Self-funding, loans, and reinvested profits |
| Risk Tolerance | High | Low |
| Innovation | High | Low |
| Scalability | High | Low |


2. What Is a Small Business?
A small business is a self-sustaining operation designed to generate revenue from day one.
A small business is a self-sustaining operation designed to:
- Generate revenue from the very first day.
- Function without a major investment.
- Work within an existing business model.
Small businesses typically operate within established markets and aim to provide goods or services to a specific customer base. Unlike startups, they are not focused on disrupting industries or achieving rapid growth.
2.1 What are the typical characteristics of a small business?
Small businesses focus on stability, profitability, and serving a local market.
- Stability: Small businesses prioritize stability and long-term sustainability over rapid growth.
- Profitability: Generating revenue and maintaining profitability is a key focus for small businesses.
- Local Market: Small businesses often serve a specific geographic area or community.
2.2 What is the main objective of a small business?
The primary objective of a small business is to generate steady revenue and profits.
While growth is important for small businesses, their main objective is to create a sustainable and profitable operation. This allows them to provide a stable income for the owner and employees, as well as contribute to the local economy.
2.3 How does a small business obtain funding?
Small businesses typically rely on personal savings, loans, and profits for funding.
Unlike startups, which often seek funding from venture capitalists and angel investors, small businesses tend to rely on more traditional sources of funding. This may include personal savings, loans from banks or credit unions, and reinvesting profits back into the business.
3. Startup vs. Small Business: What Are The Key Differences?
The differences between a startup and a small business lie in their business model, operational timeline, funding approach, and inherent risk.
The core difference between a startup and a small business is their intent. Startups aim for high growth and disruption, while small businesses focus on stability and profitability within existing markets.
3.1 Business Model: Innovation vs. Proven Concepts
Startups seek innovative models, while small businesses adopt tried-and-true methods.
- Startup: A startup’s business model is often based on a novel idea or approach that has not been proven in the market. They are constantly experimenting and iterating to find a model that works.
- Small Business: A small business typically operates within an existing business model that has a proven track record. They focus on executing the model efficiently and effectively.
3.2 Length of Operation: Short-Term Disruption vs. Long-Term Stability
Startups plan for a shorter, high-impact run, while small businesses aim for longevity.
- Startup: Startups often have a short-term focus, with the goal of either being acquired by a larger company or becoming a large, independent business themselves.
- Small Business: Small businesses aim for long-term stability and sustainability. They want to create a business that can provide a steady income for years to come.
3.3 Funding: Venture Capital vs. Organic Growth
Startups depend on outside investment, whereas small businesses prioritize self-sufficiency.
- Startup: Startups rely heavily on external funding from venture capitalists, angel investors, and other sources. This funding is used to fuel rapid growth and expansion.
- Small Business: Small businesses typically rely on their own profits and loans to fund their operations. They grow more slowly and organically, without the need for large injections of capital.
3.4 Risk: High Stakes vs. Calculated Moves
Startups embrace high risk for high reward, while small businesses prefer lower-risk strategies.
- Startup: Startups operate in uncertain environments and face a high risk of failure. However, they also have the potential for high rewards if they are successful.
- Small Business: Small businesses operate in more stable environments and face a lower risk of failure. However, they also have a lower potential for growth and returns.
4. Why Does Understanding the Difference Between a Startup and Small Business Matter?
Understanding the differences is crucial for setting expectations, planning growth, and defining success.
Knowing whether you’re running a startup or a small business is essential for making informed decisions about your company’s strategy, funding, and operations. It also helps you set realistic expectations and define success in a way that aligns with your goals.
4.1 Aligning Expectations
Knowing the type of business helps align expectations for growth, profitability, and risk.
Understanding whether you are running a startup or a small business helps you set realistic expectations for your company. Startups should expect rapid growth and high risk, while small businesses should focus on steady revenue and profitability.
4.2 Strategic Planning
Different business types require different strategies for growth, marketing, and operations.
The type of business you are running will also influence your strategic planning. Startups need to focus on innovation and scalability, while small businesses need to focus on efficiency and customer service.
4.3 Partnership Opportunities
Understanding your business type helps identify the right partners and investors.
Knowing whether you are a startup or a small business will help you identify the right partners and investors. Startups should seek out venture capitalists and angel investors, while small businesses should focus on building relationships with local banks and credit unions.
4.4 Defining Success
The definition of success varies significantly between startups and small businesses.
Finally, understanding your business type will help you define success in a way that aligns with your goals. Startups may define success as achieving a high valuation or being acquired by a larger company, while small businesses may define success as generating a steady income and providing a valuable service to their community.
5. How to Effectively Manage Your Startup or Small Business
Effective management involves providing a conducive working environment that fosters teamwork, productivity, and creativity.
Whether you’re running a startup or a small business, providing your team members with the best possible working environment is critical for success. This includes creating a physical space that is conducive to teamwork, productivity, and creativity.
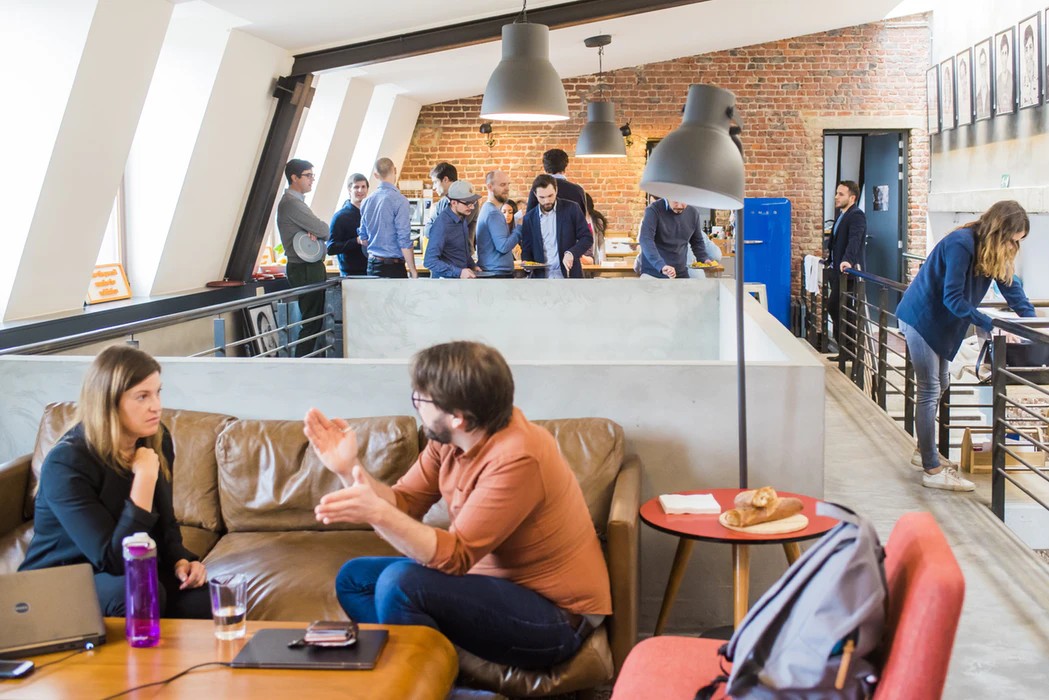
5.1 The Impact of Office Space
The physical workspace influences team dynamics, creativity, and overall company impressions.
Your office space can have a significant impact on your team’s morale, productivity, and creativity. A well-designed office can foster collaboration, innovation, and a sense of community. Conversely, a poorly designed office can lead to stress, dissatisfaction, and decreased productivity.
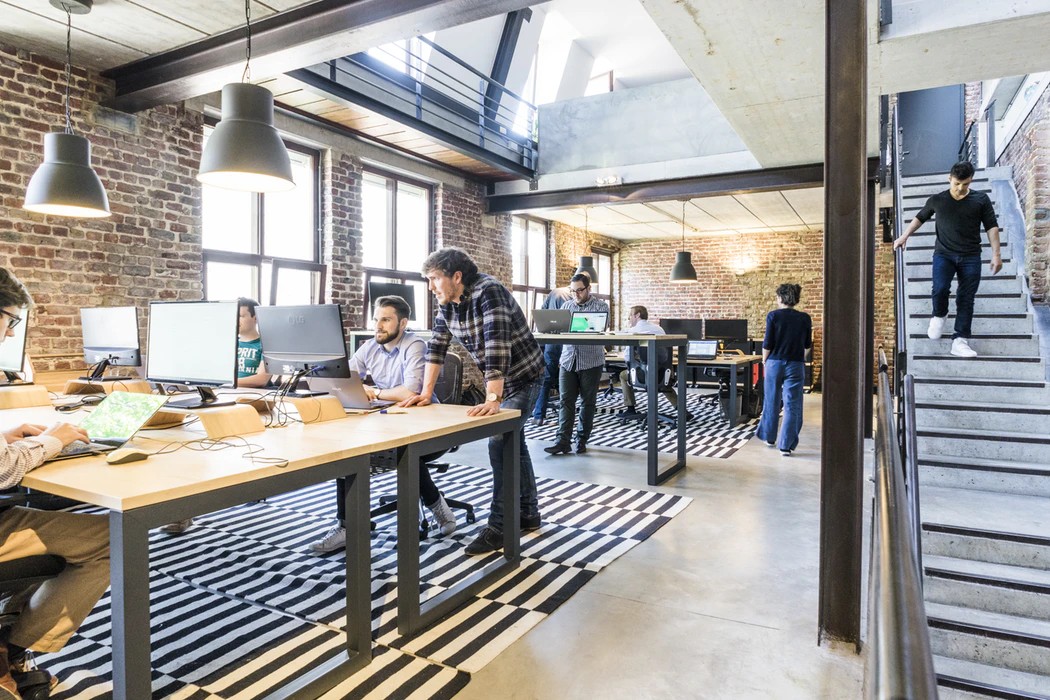
5.2 Cost-Effective Solutions with Bond Collective
Bond Collective offers flexible workspace solutions that save time and money.
Instead of committing to an expensive long-term lease and spending valuable capital on furnishing and maintaining your own office space, consider teaming up with Bond Collective. They offer a variety of flexible workspace solutions, including coworking spaces, dedicated desks, and private offices, that can save you time and money.
5.3 Amenities and Benefits
Bond Collective provides amenities that enhance productivity and create a positive work environment.
Bond Collective memberships come with a range of amenities designed to enhance productivity and create a positive work environment. These include:
- Comfortable furnishings
- Luxurious decor
- Private meeting & phone booths
- Guest reception and greeting
- 24-hour access
- Mail service
- Daily on-site cleaning
- On-site kitchens
- Custom build-outs
- Access to small and large conference rooms
- Networking events
- Bike storage
- Rooftop lounge area
- Photo & sound studio (at Gowanus location)
- Complimentary fresh fruit
- Complimentary beer, coffee, and tea
- Weekly warm cookies
- Tasty eats and beverages for purchase
- Bike storage
- Office showers
5.4 Tailored Solutions for Startups and Small Businesses
Bond Collective offers workspace solutions for startups, small businesses, and large corporations.
Whether you’re a startup, a small business, or a large corporation, Bond Collective has a workspace solution that can meet your needs. Their flexible memberships and customizable office spaces allow you to create a work environment that supports your team’s success.
6. FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Startups
Here are some frequently asked questions about startups to clarify common misconceptions.
To further clarify the concept of a startup, here are some frequently asked questions:
6.1 What is the definition of a startup according to Steve Blank?
According to Steve Blank, a startup is a temporary organization designed to search for a repeatable and scalable business model.
Steve Blank, a renowned entrepreneur and educator, defines a startup as “a temporary organization designed to search for a repeatable and scalable business model.” This definition emphasizes the experimental nature of startups and their focus on finding a sustainable path to growth.
6.2 What are the key elements of a successful startup?
Key elements include a strong team, a validated business model, and sufficient funding.
A successful startup typically has the following key elements:
- A strong team: A team of talented and dedicated individuals with complementary skills.
- A validated business model: A business model that has been tested and proven to be viable.
- Sufficient funding: Enough capital to support the startup’s operations and growth.
- A clear vision: A clear understanding of the problem the startup is solving and the market it is serving.
- Adaptability: The ability to adapt to changing market conditions and customer feedback.
6.3 What is the difference between a startup and a scaleup?
A startup is in the initial phase of finding a business model, while a scaleup is focused on expanding an already proven model.
A startup is in the initial phase of searching for a repeatable and scalable business model. Once a startup has found a model that works, it becomes a scaleup. A scaleup is focused on expanding its operations and growing its customer base.
6.4 How do startups measure success?
Startups measure success through user growth, revenue, and market share.
Startups typically measure success through metrics such as:
- User growth: The number of new users or customers acquired.
- Revenue: The amount of money generated from sales.
- Market share: The percentage of the total market that the startup controls.
- Customer satisfaction: The level of satisfaction among the startup’s customers.
- Brand awareness: The extent to which the startup’s brand is recognized and known.
6.5 What are the common challenges faced by startups?
Startups often struggle with funding, competition, and market validation.
Some of the common challenges faced by startups include:
- Funding: Securing enough capital to support operations and growth.
- Competition: Facing competition from established companies and other startups.
- Market validation: Proving that there is a demand for the startup’s product or service.
- Building a team: Attracting and retaining talented employees.
- Managing growth: Scaling operations to meet increasing demand.
6.6 What is a unicorn startup?
A unicorn startup is a privately held company valued at over $1 billion.
A unicorn startup is a privately held company that is valued at over $1 billion. The term “unicorn” was coined to describe the rarity of such companies.
6.7 What role do incubators and accelerators play in the startup ecosystem?
Incubators provide resources and mentorship to early-stage startups, while accelerators offer intensive programs for rapid growth.
Incubators and accelerators are organizations that provide support and resources to startups. Incubators typically provide office space, mentorship, and other resources to early-stage startups. Accelerators offer intensive programs that help startups refine their business models, build their teams, and raise funding.
6.8 How important is innovation for a startup’s success?
Innovation is crucial, as startups often disrupt existing markets with new solutions.
Innovation is critical for a startup’s success. Startups often disrupt existing markets by introducing new products, services, or business models that are more efficient, effective, or convenient.
6.9 What are some examples of successful startups?
Examples include companies like Airbnb, Uber, and SpaceX, which revolutionized their respective industries.
Some examples of successful startups include:
- Airbnb: Revolutionized the hospitality industry by creating a platform for people to rent out their homes.
- Uber: Transformed the transportation industry by creating a ride-hailing app that connects passengers with drivers.
- SpaceX: Disrupting the space industry with innovative and cost-effective space transportation solutions.
- Google: Changed how people access information and conduct research.
6.10 How can I get help with my startup?
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN to ask your questions and get free answers from our community of experts.
If you have any questions about starting or running a startup, visit WHAT.EDU.VN to ask your questions and get free answers from our community of experts. We are here to help you succeed.
7. Call to Action
Ready to take the next step with your startup or small business? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today to ask your questions and get free answers from our community of experts.
Don’t let your questions go unanswered. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide a platform where you can ask any question and receive fast, accurate, and helpful responses. Whether you’re struggling with funding, marketing, or operations, our community of experts is here to support you.
- Ask Your Questions: Get the answers you need to make informed decisions.
- Connect with Experts: Learn from experienced professionals in your field.
- Join Our Community: Engage with other entrepreneurs and small business owners.
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and experience the convenience of free, reliable advice. Let us help you build a successful and sustainable business.
Contact Us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: what.edu.vn
We look forward to helping you achieve your business goals.