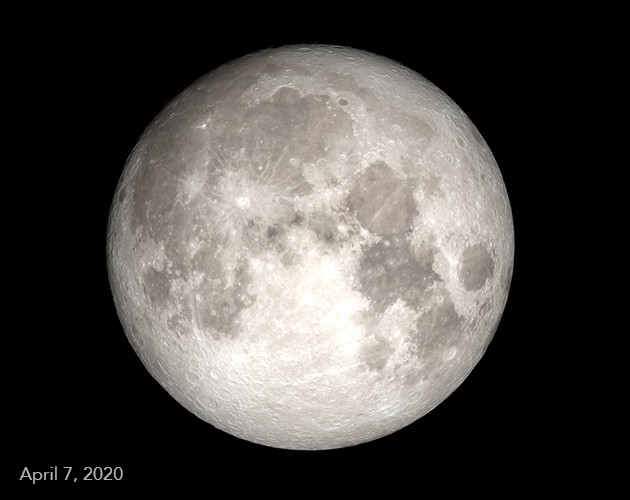
A super moon happens when a full moon coincides with the Moon’s closest approach to Earth, making it appear bigger and brighter. Want to know more about supermoons? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide you with easy-to-understand explanations and answers to all your questions. Discover fascinating lunar phenomena and celestial events today!
1. What is a Super Moon?
A supermoon is a full moon that occurs when the Moon is at or near its closest point to Earth in its orbit. This point is called perigee. When a full moon coincides with perigee, it appears larger and brighter in the sky than a regular full moon.
The term “supermoon” isn’t officially astronomical, but it’s commonly used to describe a full Moon that comes within at least 90 percent of its closest approach to Earth. If you are curious about astronomical events, don’t hesitate to ask WHAT.EDU.VN.
2. How Often Do Super Moons Occur?
Supermoons typically occur three to four times a year, and they often appear consecutively. The Moon’s orbit around Earth is elliptical, not perfectly circular, which means that its distance from Earth varies throughout its orbit.
3. Why Does the Moon’s Distance from Earth Vary?
The Moon’s orbit around Earth is elliptical, meaning it’s shaped like an oval rather than a perfect circle. As the Moon travels along this elliptical path, its distance from Earth changes. The point where the Moon is closest to Earth is called perigee, and the point where it’s farthest is called apogee. The variance in distance is due to the gravitational influences of the Earth, Sun, and other celestial bodies on the Moon.
4. How Much Bigger and Brighter Does a Super Moon Appear?
At its closest point, a supermoon can appear up to 14 percent bigger and 30 percent brighter than the faintest Moon of the year, which occurs when it’s farthest from Earth in its orbit.
5. Is it Easy to Tell the Difference Between a Super Moon and a Regular Full Moon?
While a supermoon is technically bigger and brighter, the difference can be difficult to detect with the naked eye. Unless you’re comparing a supermoon directly to a full moon at its farthest point (a micromoon), the difference might not be immediately obvious. Factors like atmospheric conditions and light pollution can also affect how bright the Moon appears.
6. Does a Super Moon Affect Tides?
Yes, because the Moon is in its closest approach to Earth, it can cause higher tides than usual. These are known as perigean spring tides. The increased gravitational pull of the Moon at perigee results in more significant tidal bulges.
7. What is a Blue Moon and How Does it Relate to a Super Moon?
A blue moon is a term used in two different ways:
- Seasonal Blue Moon: The third full moon in a season that has four full moons.
- Monthly Blue Moon: The second full moon in a single calendar month.
A super blue moon is when a supermoon and a blue moon coincide. This combination is relatively rare, making it a special event for skywatchers.
8. What are Some Notable Past Super Moons?
Some notable past supermoons include:
- November 14, 2016: This was the closest supermoon to Earth since 1948.
- January 1, 2018: A supermoon that coincided with the new year.
- August 31, 2023: A super blue moon, combining both events.
9. Where is the Best Place to View a Super Moon?
The best place to view a supermoon is anywhere with a clear, dark sky. Light pollution can diminish the visibility, so try to find a location away from city lights. Elevated areas can also provide a better vantage point.
10. Do Super Moons Have Any Cultural or Astrological Significance?
In some cultures, supermoons are associated with heightened emotions or energy. Astrologically, they might be seen as intensifying the effects of the full moon, influencing personal or global events. However, these beliefs are not scientifically recognized.
11. How Can I Calculate When the Next Super Moon Will Occur?
You can find information about upcoming supermoons from various sources:
- NASA’s Moon Guide: NASA provides a daily moon guide with details about upcoming lunar events.
- Astronomy Websites: Websites like Space.com and EarthSky.org provide calendars and articles about astronomical events.
- Mobile Apps: There are many mobile apps available that track the Moon’s phases and distances, alerting you to upcoming supermoons.
12. What Causes Higher Tides During a Super Moon?
During a supermoon, the Moon is closer to Earth, resulting in a stronger gravitational pull. This stronger gravitational force causes higher high tides and lower low tides than usual. These are known as spring tides or perigean spring tides.
13. Are There Any Risks Associated with Higher Tides During a Super Moon?
While the higher tides during a supermoon are generally predictable and not dangerous, they can exacerbate coastal flooding, especially when combined with storm surges or other weather events.
14. How Much Closer is the Moon During a Super Moon Compared to Other Times?
During a supermoon, the Moon can be about 30,000 miles (48,280 kilometers) closer to Earth than when it is at its farthest point (apogee).
15. What is the Difference Between a Super Moon and a Micro Moon?
A supermoon occurs when the full moon coincides with the Moon’s closest approach to Earth (perigee). A micromoon occurs when the full moon coincides with the Moon’s farthest point from Earth (apogee). Thus, a supermoon appears larger and brighter, while a micromoon appears smaller and dimmer.
16. How Do Scientists Study the Moon?
Scientists study the Moon using a variety of methods, including:
- Telescopes: Ground-based and space-based telescopes allow scientists to observe the Moon’s surface and composition.
- Spacecraft Missions: Missions like the Apollo missions and current lunar orbiters provide detailed data about the Moon’s geology and environment.
- Lunar Samples: Analysis of lunar rocks and soil brought back by the Apollo missions has provided valuable insights into the Moon’s history and formation.
- Laser Ranging: Using lasers to measure the distance between Earth and the Moon accurately.
17. Can a Super Moon Affect Weather Patterns?
There is no conclusive scientific evidence that supermoons directly affect weather patterns. While the Moon’s gravity influences tides, its impact on weather is minimal compared to other factors like solar radiation and atmospheric conditions.
18. What Equipment Do I Need to Observe a Super Moon?
You don’t need any special equipment to observe a supermoon. It is visible with the naked eye. However, binoculars or a telescope can enhance the viewing experience, allowing you to see more details on the lunar surface.
19. How Does Light Pollution Affect Viewing a Super Moon?
Light pollution can significantly reduce the visibility of a supermoon. Artificial lights from cities and towns can wash out the night sky, making it harder to see faint celestial objects. To get the best view, try to find a location away from urban areas.
20. Can I Photograph a Super Moon with My Phone?
Yes, you can photograph a supermoon with your phone, but the results may vary depending on the quality of your phone’s camera. Use a tripod to stabilize your phone and experiment with different settings to capture the best possible image.
21. What is the Best Time of Night to View a Super Moon?
The best time to view a supermoon is generally soon after moonrise or just before moonset. At these times, the Moon is lower on the horizon, and the atmospheric perspective can make it appear even larger.
22. How Does the Moon’s Color Change During a Super Moon?
The Moon’s color can vary depending on atmospheric conditions. When it is low on the horizon, it may appear reddish or orange due to the scattering of light by the atmosphere. As it rises higher in the sky, it typically appears more white or silver.
23. Are Super Moons Dangerous in Any Way?
Supermoons are not inherently dangerous. The increased tides they cause are generally predictable and manageable. However, coastal communities should be aware of the potential for increased flooding, especially when combined with other factors like storms.
24. How Do Super Moons Affect Animal Behavior?
Some studies suggest that lunar cycles can influence animal behavior, including breeding patterns and activity levels. However, the specific effects of supermoons on animal behavior are not well-documented.
25. Can Super Moons Affect Human Behavior or Mood?
There is no scientific evidence that supermoons directly affect human behavior or mood. While some people may feel more emotional or energetic during a full moon, these effects are likely due to psychological factors rather than the Moon’s gravitational pull.
26. What Myths and Legends are Associated with Super Moons?
In various cultures, full moons (including supermoons) are associated with different myths and legends. Some common themes include werewolves, heightened psychic abilities, and increased emotional intensity. These beliefs are often rooted in folklore rather than scientific fact.
27. How Can I Learn More About Lunar Events?
You can learn more about lunar events from a variety of sources:
- NASA’s Website: NASA provides a wealth of information about the Moon and other celestial objects.
- Astronomy Magazines: Publications like Sky & Telescope and Astronomy offer articles and observing guides.
- Planetariums and Observatories: Local planetariums and observatories often host events and programs about lunar events.
28. What is the Significance of the Moon in Different Cultures?
The Moon holds significant cultural and symbolic importance in many societies around the world. It is often associated with femininity, cycles, and the passage of time. Different cultures have unique myths, legends, and traditions related to the Moon.
29. How Does the Moon Influence Earth’s Climate?
The Moon plays a role in stabilizing Earth’s axial tilt, which helps to keep our climate relatively stable over long periods. Without the Moon, Earth’s axis could wobble more dramatically, leading to more extreme climate variations.
30. What Future Missions are Planned to Study the Moon?
Several future missions are planned to study the Moon, including:
- Artemis Program: NASA’s Artemis program aims to return humans to the Moon by the mid-2020s.
- Commercial Lunar Landers: Several companies are developing lunar landers to deliver cargo and experiments to the Moon.
- International Missions: Other countries, including China and India, have plans for future lunar missions.
31. What Causes the Different Phases of the Moon?
The phases of the Moon are caused by the changing angles at which we see the Moon’s illuminated surface as it orbits Earth. As the Moon orbits, different amounts of its sunlit side become visible to us, resulting in the different phases.
32. How Long Does it Take for the Moon to Orbit Earth?
It takes the Moon approximately 27.3 days to complete one orbit around Earth. This is known as the sidereal period. However, because Earth is also moving around the Sun, it takes about 29.5 days for the Moon to go through a complete cycle of phases (from new moon to new moon). This is known as the synodic period.
33. Can the Moon Be Seen During the Day?
Yes, the Moon can often be seen during the day, especially when it is in its crescent or gibbous phases. The best time to see the Moon during the day is when it is high in the sky and the sky is clear.
34. What is the Dark Side of the Moon?
The term “dark side of the Moon” is a misnomer. In reality, all sides of the Moon experience day and night as it rotates. However, the far side of the Moon (the side that always faces away from Earth) was once called the “dark side” because it was unknown until it was first photographed by a Soviet spacecraft in 1959.
35. How Does the Moon Affect Earth’s Rotation?
The Moon’s gravity exerts a tidal force on Earth, which slows down Earth’s rotation very slightly over time. This effect is very small, but it has a measurable impact over millions of years.
36. What is Lunar Soil Made Of?
Lunar soil, also known as regolith, is composed of fine-grained rock and mineral fragments, glass beads, and small amounts of organic matter. It is formed by the constant bombardment of the Moon’s surface by meteoroids and solar wind particles.
37. What Are the Key Differences Between the Near Side and Far Side of the Moon?
The near side of the Moon (the side that faces Earth) has more maria (large, dark plains of basaltic lava) than the far side. The far side also has a thicker crust and fewer impact craters.
38. What is the Origin of the Moon?
The most widely accepted theory for the origin of the Moon is the giant-impact hypothesis. This theory proposes that the Moon formed from the debris of a collision between Earth and a Mars-sized object early in the solar system’s history.
39. How Does the Moon Influence Ocean Currents?
The Moon’s gravitational pull primarily affects tides, which are the periodic rise and fall of sea levels. While tides can influence local currents, the Moon’s direct impact on major ocean currents is minimal compared to factors like wind and temperature.
40. What is the Significance of Lunar Eclipses?
Lunar eclipses occur when Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon. They are significant because they provide opportunities to study Earth’s atmosphere and the Moon’s surface.
41. How Can I Tell the Difference Between a Lunar Eclipse and a Solar Eclipse?
A lunar eclipse occurs when Earth’s shadow obscures the Moon, while a solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, blocking the Sun’s light. Lunar eclipses are safe to view with the naked eye, while solar eclipses require special eye protection.
42. What Role Did the Moon Play in Early Human Exploration?
The Moon was the first celestial body that humans visited. The Apollo missions in the 1960s and 1970s allowed astronauts to explore the lunar surface, collect samples, and conduct scientific experiments.
43. How Can I Contribute to Citizen Science Projects Related to the Moon?
There are several citizen science projects related to the Moon that you can participate in, such as:
- Lunar Mapping: Helping to create detailed maps of the Moon’s surface.
- Crater Counting: Identifying and counting impact craters on lunar images.
- Observing Lunar Events: Reporting observations of lunar eclipses and other events.
44. What is Lunar Geology?
Lunar geology is the study of the Moon’s composition, structure, and history. It involves analyzing lunar rocks, soil, and surface features to understand how the Moon formed and evolved.
45. What are Lunar Maria?
Lunar maria are large, dark, basaltic plains on the Moon’s surface. They were formed by ancient volcanic eruptions that filled in large impact basins with lava.
46. What are Lunar Highlands?
Lunar highlands are the lighter-colored, heavily cratered regions of the Moon’s surface. They are older than the maria and are composed of a different type of rock.
47. What Are Lunar Craters?
Lunar craters are bowl-shaped depressions on the Moon’s surface that were formed by the impact of meteoroids and asteroids. They are a prominent feature of the lunar landscape.
48. What is Lunar Regolith?
Lunar regolith is the layer of loose, unconsolidated material that covers the Moon’s surface. It is composed of fine-grained rock and mineral fragments, glass beads, and small amounts of organic matter.
49. What is the Importance of Studying Lunar Rocks?
Studying lunar rocks provides valuable insights into the Moon’s history, composition, and origin. Lunar rocks can also tell us about the early solar system and the processes that shaped the planets.
50. What is the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO)?
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is a NASA spacecraft that has been orbiting the Moon since 2009. It is equipped with a suite of instruments that are used to study the Moon’s surface, composition, and environment.
51. How Does the Moon Influence Life on Earth?
The Moon plays a crucial role in stabilizing Earth’s axial tilt, influencing tides, and providing a source of light at night. It has also been a source of inspiration for art, literature, and culture throughout human history.
52. What Are Some Famous Lunar Conspiracy Theories?
Some famous lunar conspiracy theories include the belief that the Apollo moon landings were faked and that the Moon is inhabited by aliens. These theories have been widely debunked by scientific evidence.
53. How Can I Get Involved in Amateur Astronomy and Observe the Moon?
You can get involved in amateur astronomy by joining a local astronomy club, attending star parties, and using telescopes to observe the Moon and other celestial objects.
54. What Resources Are Available for Learning About the Moon?
There are many resources available for learning about the Moon, including:
- NASA’s Website: NASA provides a wealth of information about the Moon and other celestial objects.
- Astronomy Magazines: Publications like Sky & Telescope and Astronomy offer articles and observing guides.
- Planetariums and Observatories: Local planetariums and observatories often host events and programs about the Moon.
- Books and Websites: There are many books and websites dedicated to lunar science and exploration.
55. What is the Future of Lunar Exploration?
The future of lunar exploration is bright, with several planned missions to return humans to the Moon, establish a permanent lunar base, and conduct scientific research. The Moon is seen as a stepping stone for future exploration of the solar system.
56. How Does the Distance of a Super Moon Affect Its Apparent Size?
The closer proximity of a supermoon makes it appear larger due to a phenomenon known as angular size. When an object is closer, it subtends a larger angle in our field of view, making it seem bigger.
57. What is a Super New Moon?
While the term “supermoon” is typically used in reference to a full moon, a new moon can also occur at perigee. This is sometimes referred to as a “super new moon,” although it is not visible from Earth since the moon is in its new phase.
58. Does a Super Moon Have an Impact on Earthquake Activity?
There is no conclusive scientific evidence that supermoons have a direct impact on earthquake activity. While the Moon’s gravity affects tides, the forces involved are not strong enough to trigger earthquakes. According to research from the United States Geological Survey (USGS), while tidal forces can exert some stress on the Earth’s crust, they are minimal compared to the tectonic forces that cause earthquakes.
59. What Are the Best Apps for Tracking the Moon’s Phases and Super Moons?
Several mobile apps are available for tracking the Moon’s phases and identifying supermoons, including:
- SkyView Lite: A free app that uses your phone’s camera to identify celestial objects.
- Deluxe Moon: A comprehensive app with detailed information about the Moon’s phases, rise and set times, and more.
- Phases of the Moon: A simple and easy-to-use app that shows the current phase of the Moon.
- Moonphase: An app that combines augmented reality and lunar data to provide a realistic view of the moon in the sky.
60. How Can You Tell if You’re Actually Seeing a Super Moon?
Unless you have a direct comparison with a regular full moon, it can be challenging to definitively identify a supermoon. However, you can use the following tips:
- Check the Date: Consult an astronomy calendar or app to see if a supermoon is predicted for that night.
- Observe the Brightness: Supermoons appear brighter than regular full moons, so take note of the Moon’s luminosity.
- Compare Photos: Look at photos of supermoons and regular full moons to see if you can detect a size difference.
Have more questions about supermoons or other celestial events? Visit what.edu.vn for free answers and expert insights. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890.