What Is A Third Cousin and how do they fit into your family tree? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide clear answers and help you understand your family connections. Discover the definition of a third cousin, explore their significance in genealogy, and trace your lineage with ease using our free question-answering platform. Unlock family history, ancestral ties, and familial relationships today.
1. Understanding the Third Cousin Meaning
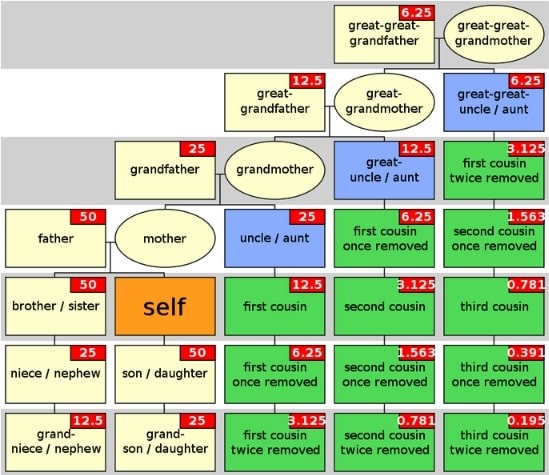
Third cousins are relatives who share a common great-great-grandparent. This means that your third cousin’s great-great-grandparent is also your great-great-grandparent. To put it simply, your third cousin is the child of your parent’s second cousin. This connection is four generations removed from both of you, making it essential to understand how family relationships extend over time.
Understanding what a third cousin is connects individuals to their extended family network. For novice genealogists, recognizing this relationship can be an invaluable starting point. By exploring how third cousins fit into the family tree, beginners can effectively use genealogical tools to trace their lineage, uncover shared ancestors, and perhaps discover unexpected family stories.
2. How To Identify A Third Cousin?
To identify a third cousin, trace your family tree back four generations. Here’s a simplified explanation:
- Shared Ancestors: You and your third cousin share great-great-grandparents.
- Parents’ Connection: Your parents and your third cousin’s parents are second cousins.
- Grandparents’ Connection: Your grandparents and your third cousin’s grandparents are first cousins.
Your third cousin is also a great-great-grandchild of your shared great-great-grandparents. One of your third cousin’s great-grandparents and one of your great-grandparents were siblings.
3. What Does The Third Cousin Relationship Entail?
The 3rd cousin relationship connects individuals to their broader family history, illustrating how extended families grow and branch out over generations. Understanding this connection is vital for genealogy enthusiasts, as it offers a clear view of family lineage and the intricate web of relationships that form our ancestral past.
4. Genetic Connection: Are Third Cousins Blood Related?
Third cousins share a genetic connection, though it’s less substantial than the DNA connection with closer relatives. When considering “Are 3rd cousins blood related,” they usually share a small amount of DNA. This amount can vary, but it’s a small percentage on average. This difference in shared DNA is due to how genes are passed down in families, which can be random. In some cases, third cousins may not share any detectable DNA due to the way genes are passed down through generations and the phenomenon of recombination.
5. Third Cousins And Marriage: Legality and Genetics
In general, marrying third cousins is legal in most places. The genetic overlap between third cousins is relatively minor, significantly reducing potential genetic risks for their descendants. While cultural norms and family traditions can shape perceptions of these unions, they are generally considered acceptable genetically.
6. Are Third Cousins Considered Family? Exploring Familial Bonds
The perception of whether third cousins are considered part of the “family” depends on factors such as family dynamics, geographical proximity, and cultural norms. In families that pay close attention to their 3rd cousin family tree, these relatives often play a role in each other’s lives, particularly in regions where families remain geographically close.
7. Influence of Older Generations
Older generations, like grandparents or great-grandparents, are often pivotal in maintaining familial bonds. With the passing of these elderly members, the connection with distant relatives like third cousins might lessen, shifting perhaps to more virtual forms of interaction, like social media.
8. Familiarity And Shared Ancestors
Families might be unaware of their third cousins, even if they reside in the same geographic area, because they lack close familial ties. This situation often leads to third cousins being virtually strangers, even though they share common ancestors.
The perception of what constitutes a near or distant relative can differ. A critical factor in this perception is whether the common ancestor is known personally. Since third cousins share great-great-grandparents, their parents, who are second cousins, might have had a personal connection with their shared great-grandparents. This generational acquaintance can significantly influence the recognition and interaction within the extended family.
9. Interaction Between Third Cousins
The interaction between third cousins can vary, ranging from regular family reunions to complete non-recognition. While geographic separation can play a role, the advent of digital communication and genealogy platforms allows for discovering and maintaining these relationships.
10. Scientific Perspective
Scientifically, third cousins are indeed family, sharing a lineage and DNA from a common ancestor. They might be unfamiliar to each other in day-to-day life. Still, the genetic link remains a testament to the extended and intricate web of family connections that span generations.
11. How Many Third Cousins Does The Average Person Have? The Prevalence of Distant Relatives
Research suggests that the average person is estimated to have about 190 third cousins. However, this number can vary based on family size and structure. The number of third cousins might be higher in larger families and lower in smaller families. This statistic provides a glimpse into the expansive nature of family connections, highlighting how an individual can be linked to a surprisingly extensive network of relatives.
12. Additional Types Of Third Cousins: Maternal and Paternal Connections
Additional types of third cousins can encompass those who share a common great-great-grandparent but through distinct familial lines or connections, such as maternal and paternal great-great-grandparents.
13. What Is A Third Cousin Once-Removed? Understanding Generational Shifts
A third cousin once-removed represents a generational shift in the family tree. This term is used when there is a one-generation difference in relation to a third cousin. For instance, the child of your third cousin is your third cousin once-removed. Similar to your parents, your third cousin would be their second cousin once-removed. Building out your family tree to confirm the lineage is essential to determine these relationships on your DNA match list, as DNA testing platforms typically don’t label “removed” relatives by default.
14. Calculating Cousins Removed: Clarifying Family Relationships
Understanding “cousins removed” might seem daunting at first, but it becomes more apparent with some calculation. To ascertain if someone is your third cousin or once-removed, start by confirming the relationship. Ensure that the closest common ancestor is a great-great-grandparent. Then, count the number of generations you are from this most recent common ancestor (MRCA) and subtract four. The difference will indicate the number of times removed.
For example, if you are six generations away from the MRCA, subtract four from six, resulting in two generations removed. In this case, you and your cousin are third cousins twice-removed.
15. What Is A Half-Third Cousin? Tracing Shared Ancestry
A half-third cousin arises when your great-great-grandparents are half-siblings, meaning you share only one great-great-grandparent. That often happens when a great-great-grandparent remarries after the death or divorce of their first spouse and has children with both partners. Their children are half-siblings, making their descendants half-cousins at various generational levels.
16. Identifying Half-Third Cousins: Uncovering Family Secrets
Identifying half-third cousins involves tracing how they fit into your family tree. It’s common to find more half-cousins than anticipated, especially since affairs and second marriages in earlier generations may not be well documented. Still, their genetic legacy can be uncovered through DNA testing.
17. Exploring The Significance of Third Cousin Relationships
Understanding third cousin relationships is valuable for genealogy enthusiasts and anyone interested in their family history. It helps in:
- Tracing Family Lineage: Discovering how different branches of your family are connected.
- Uncovering Shared Ancestors: Identifying common ancestors and their stories.
- Expanding Family Connections: Recognizing and potentially connecting with distant relatives.
18. Legal and Social Aspects of Third Cousin Relationships
- Marriage: Marrying a third cousin is legal in most places, with minimal genetic risks.
- Family Perception: Whether third cousins are considered “family” varies based on cultural norms and personal connections.
- Genetic Traits: While third cousins share some DNA, the percentage is small and can vary.
19. How to Use Genealogy Tools to Find Third Cousins
Genealogy tools and resources can significantly simplify the process of finding and understanding third cousin relationships. Here’s how to make the most of these tools:
- Online Family Trees:
- Platforms like AncestryDNA, MyHeritage, and FamilySearch allow you to build and expand your family tree. These tools help visualize relationships and identify potential third cousins.
- Tips: Start with known relatives and work backward, adding as much detail as possible. Accurate dates and locations are crucial for distinguishing between individuals with similar names.
- DNA Testing Services:
- DNA testing can confirm genetic relationships with potential third cousins. Services like 23andMe and AncestryDNA provide cousin matches based on shared DNA.
- Tips: Understand the limitations of DNA testing. While it can identify relatives, it doesn’t always specify the exact relationship. Use DNA results in conjunction with traditional genealogy research.
- Historical Records:
- Websites like GenealogyBank, Newspapers.com, and government archives offer access to historical records such as census data, birth certificates, marriage licenses, and obituaries.
- Tips: Use a variety of records to piece together family history. Census records can show family groupings, while birth and marriage records confirm relationships.
- Genealogy Software:
- Software programs like RootsMagic and Legacy Family Tree help organize and analyze genealogical data. These tools allow you to create detailed reports and charts.
- Tips: Back up your data regularly. Genealogy software can be complex, so take advantage of tutorials and user forums to learn advanced features.
- Social Media and Forums:
- Social media platforms and genealogy forums can connect you with other researchers who may have information about your family.
- Tips: Join relevant groups and participate in discussions. Share your research and ask for help when you encounter roadblocks.
- Professional Genealogists:
- If you’re struggling to make progress, consider hiring a professional genealogist. They have the expertise and resources to conduct in-depth research.
- Tips: Check the genealogist’s credentials and experience. Ask for references and discuss your research goals upfront.
20. Common Challenges In Tracing Third Cousin Relationships
Tracing third cousin relationships can be complex due to several factors:
- Incomplete Records: Historical records may be missing, inaccurate, or difficult to access.
- Common Names: Shared surnames and given names can make it challenging to distinguish between individuals.
- Migration Patterns: Families may have moved frequently, making it difficult to track them across different locations.
- Adoption and Name Changes: Adoption and legal name changes can obscure family connections.
- Lack of Family Knowledge: Family members may not have accurate information about their ancestors.
- Illegitimate Children: The existence of children born outside of marriage may not be documented.
21. FAQs About Third Cousins
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the legal status of marrying a third cousin? | Marrying a third cousin is legal in most places, as the genetic risk is minimal. |
| How much DNA do third cousins typically share? | Third cousins typically share a small amount of DNA, often less than 1%. In some cases, they may not share any detectable DNA. |
| Are third cousins considered close relatives? | The perception of closeness varies. Some families consider them part of the extended family, while others may not know them at all. |
| How do I find my third cousins? | Use online family trees, DNA testing services, and historical records to trace your lineage back to shared great-great-grandparents. |
| What is a third cousin once-removed? | A third cousin once-removed is the child of your third cousin or the parent of your third cousin. There is a one-generation difference in the relationship. |
| What is a half-third cousin? | A half-third cousin is someone who shares only one great-great-grandparent with you. This typically occurs when a great-great-grandparent remarries and has children with both spouses. |
| Why is it important to understand third cousin relationships? | Understanding these relationships helps trace family history, uncover shared ancestors, and expand your understanding of your family’s connections. |
| Can DNA testing accurately identify third cousins? | DNA testing can identify potential third cousins, but it’s important to use these results in conjunction with traditional genealogy research to confirm the relationship. |
| How many third cousins can a person have? | The average person is estimated to have around 190 third cousins, though this number can vary based on family size and structure. |
| What challenges might I face when tracing third cousin relationships? | Challenges include incomplete records, common names, migration patterns, adoption, and a lack of family knowledge. |

22. Discover Your Family Tree with WHAT.EDU.VN
Uncovering your family history is more than just a pursuit of knowledge; it’s a quest to understand your roots and connections. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide you a free platform to ask any question and receive accurate and timely answers.
Whether you’re looking to decipher your family tree or trace the branches of your family tree, WHAT.EDU.VN provides the resources to bring your family history to life.
Do you have questions about your family history? Are you struggling to understand complex relationships like third cousins? Don’t worry, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help.
23. Need Answers? Ask WHAT.EDU.VN
Are you facing challenges in finding quick, free answers to your questions? Do you feel lost and unsure where to turn for reliable information? Are you concerned about the cost of getting expert advice?
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand your difficulties. We offer a free platform where you can ask any question and receive answers from knowledgeable individuals. Our service is designed to provide you with the information you need quickly and accurately, all without any cost.
24. Take Action Now!
Ready to uncover the mysteries of your family tree? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your questions about third cousins, genealogy, or any other topic that interests you. Join our community and discover the answers you’ve been searching for.
Contact Us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Don’t let your questions go unanswered. Let what.edu.vn be your guide to knowledge and discovery.