AI Technology simulates human intelligence in machines, particularly computer systems, and is essential for automation, machine learning, and natural language processing. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide clear, accessible explanations of complex topics like AI, ensuring everyone can understand the transformative power of this technology. Discover more about the future of AI and its diverse applications.
Are you looking for answers to your questions about AI? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN for free answers and expert insights.
1. What is Artificial Intelligence (AI) Technology?
Artificial intelligence (AI) technology involves machines mimicking human cognitive functions, especially in computer systems. This includes tasks like problem-solving, learning, and decision-making. AI is not a single technology but a broad field encompassing various approaches and tools designed to enable machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence.
AI’s goal is to create systems that can perceive their environment, reason, learn, and act accordingly. This involves developing algorithms and models that allow computers to analyze data, recognize patterns, make predictions, and even generate creative content.
2. How Does AI Technology Work?
AI technology works through various methods, primarily centered around algorithms and models that enable machines to learn from data, identify patterns, and make decisions. The fundamental steps include data acquisition, pattern recognition, and decision-making.
2.1 Data Acquisition
AI systems require large amounts of data to learn effectively. This data can be structured (e.g., databases, spreadsheets) or unstructured (e.g., text, images, audio). The quality and quantity of the data are critical for training AI models.
2.2 Pattern Recognition
AI algorithms analyze data to identify correlations and patterns. Machine learning techniques, such as supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning, are used to train models to recognize these patterns.
- Supervised Learning: Models are trained on labeled data to predict outcomes or classify new data accurately.
- Unsupervised Learning: Models sort through unlabeled data to find underlying relationships or clusters.
- Reinforcement Learning: Models learn to make decisions by acting as agents and receiving feedback on their actions.
2.3 Decision-Making
Based on the patterns learned, AI systems make predictions or decisions. This can involve simple classifications or complex judgments, depending on the application.
2.4 Key Components
- Algorithms: Mathematical procedures that allow computers to solve problems.
- Models: Representations of data that enable machines to make predictions or decisions.
- Neural Networks: Complex networks of interconnected nodes (neurons) that mimic the structure of the human brain.
- Deep Learning: A subset of machine learning that uses neural networks with many layers (deep neural networks) to analyze data.
3. What are the Main Types of AI Technology?
AI can be categorized into several types based on its capabilities and functionalities. These include reactive machines, limited memory AI, theory of mind AI, and self-aware AI.
3.1 Reactive Machines
These AI systems have no memory and are task-specific. They respond to stimuli based on pre-programmed rules. A classic example is Deep Blue, the IBM chess program that defeated Garry Kasparov in the 1990s. Deep Blue could identify pieces on a chessboard and make predictions but could not use past experiences to inform future ones.
3.2 Limited Memory AI
These AI systems have memory and can use past experiences to inform future decisions. Some decision-making functions in self-driving cars are designed this way. They remember recent events and use that information to adjust their actions.
3.3 Theory of Mind AI
This refers to AI systems that can understand emotions and infer human intentions and predict behavior. This type of AI can understand that others have beliefs, desires, and intentions that affect behavior.
3.4 Self-Aware AI
In this category, AI systems have a sense of self, giving them consciousness. Machines with self-awareness understand their own current state and can reason about their own thoughts and feelings. This type of AI does not yet exist.
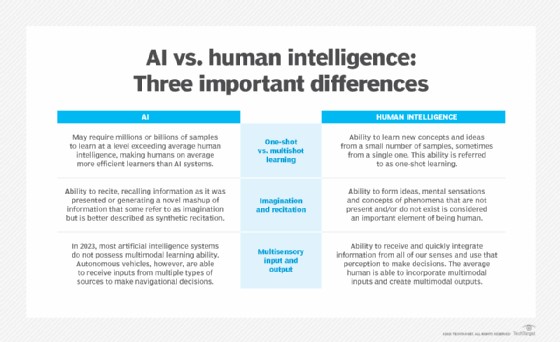
Understanding the key differences between artificial and human intelligence is crucial to effective and responsible AI use.
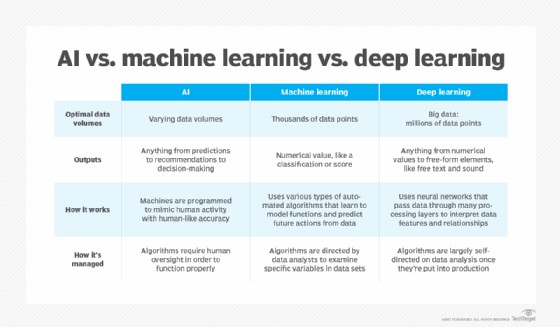
4. What are the Differences Among AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning?
AI, machine learning, and deep learning are often used interchangeably but have distinct meanings. AI is the broad concept of machines simulating human intelligence. Machine learning and deep learning are specific techniques within the field of AI.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): The overarching concept of machines simulating human intelligence. It encompasses a wide range of technologies and approaches.
- Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI that enables software to autonomously learn patterns and predict outcomes by using historical data as input.
- Deep Learning (DL): A subset of machine learning that aims to mimic the brain’s structure using layered neural networks.
5. What are the Advantages of AI Technology?
AI technology offers numerous advantages across various sectors, including increased efficiency, accuracy, and the ability to automate tasks.
5.1 Increased Efficiency
AI systems can perform tasks more quickly and efficiently than humans, especially for repetitive and detail-oriented jobs.
5.2 Improved Accuracy
AI can analyze large datasets and make predictions with greater accuracy than humans, reducing errors and improving decision-making.
5.3 Automation of Tasks
AI can automate tasks that are traditionally done by humans, freeing up human workers to focus on more creative and strategic work.
5.4 Data Processing
AI’s ability to process massive data sets gives enterprises insights into their operations they might not otherwise have noticed.
6. What are the Disadvantages of AI Technology?
Despite its advantages, AI technology also has several disadvantages, including job displacement, security vulnerabilities, environmental impact, and legal issues.
6.1 Job Displacement
AI can lead to job loss if organizations replace human workers with machines. This is a growing area of concern as AI models become more sophisticated and companies increasingly look to automate workflows using AI.
6.2 Security Vulnerabilities
AI systems are susceptible to a wide range of cyberthreats, including data poisoning and adversarial machine learning. Hackers can extract sensitive training data from an AI model or trick AI systems into producing incorrect and harmful output.
6.3 Environmental Impact
The data centers and network infrastructures that underpin the operations of AI models consume large amounts of energy and water. Consequently, training and running AI models has a significant impact on the climate.
6.4 Legal Issues
AI raises complex questions around privacy and legal liability, particularly amid an evolving AI regulation landscape that differs across regions. Using AI to analyze and make decisions based on personal data has serious privacy implications.
7. What are Examples of AI Technology in Use Today?
AI technologies enhance existing tools’ functionalities and automate various tasks and processes, affecting numerous aspects of everyday life. Prominent examples include automation, machine learning, computer vision, natural language processing, robotics, autonomous vehicles, and generative AI.
7.1 Automation
AI enhances automation technologies by expanding the range, complexity, and number of tasks that can be automated. Robotic process automation (RPA) automates repetitive, rules-based data processing tasks traditionally performed by humans.
7.2 Machine Learning
Machine learning is teaching computers to learn from data and make decisions without being explicitly programmed. Deep learning uses sophisticated neural networks to perform an advanced form of predictive analytics.
7.3 Computer Vision
Computer vision focuses on teaching machines how to interpret the visual world. By analyzing visual information such as camera images and videos using deep learning models, computer vision systems can learn to identify and classify objects and make decisions based on those analyses.
7.4 Natural Language Processing
NLP processes human language by computer programs. NLP algorithms can interpret and interact with human language, performing tasks such as translation, speech recognition, and sentiment analysis.
7.5 Robotics
Robotics involves the design, manufacturing, and operation of robots: automated machines that replicate and replace human actions, particularly those difficult, dangerous, or tedious for humans.
7.6 Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles, or self-driving cars, can sense and navigate their surrounding environment with minimal or no human input. These vehicles rely on a combination of technologies, including radar, GPS, and a range of AI and machine learning algorithms.
7.7 Generative AI
Generative AI refers to machine learning systems that can generate new data from text prompts — most commonly text and images, but also audio, video, software code, and even genetic sequences and protein structures.
8. What are the Applications of AI Technology Across Different Industries?
AI has entered a wide variety of industry sectors and research areas, including healthcare, business, education, finance and banking, law, entertainment and media, journalism, software development and IT, security, manufacturing, and transportation.
8.1 AI in Healthcare
AI is applied to improve patient outcomes and reduce systemic costs. AI-powered software can analyze CT scans and alert neurologists to suspected strokes. Online virtual health assistants and chatbots can provide general medical information, schedule appointments, and explain billing processes.
8.2 AI in Business
AI is integrated to improve efficiency, customer experience, strategic planning, and decision-making. Machine learning models power many data analytics and customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, helping companies understand how to best serve customers through personalizing offerings and delivering better-tailored marketing.
8.3 AI in Education
AI can automate aspects of grading processes, giving educators more time for other tasks. AI tools can also assess students’ performance and adapt to their individual needs, facilitating more personalized learning experiences.
8.4 AI in Finance and Banking
Banks and other financial organizations use AI to improve their decision-making for tasks such as granting loans, setting credit limits, and identifying investment opportunities. Algorithmic trading powered by advanced AI and machine learning has transformed financial markets.
8.5 AI in Law
AI automates labor-intensive tasks such as document review and discovery response. Law firms use AI and machine learning for a variety of tasks, including analytics and predictive AI to analyze data and case law, computer vision to classify and extract information from documents, and NLP to interpret and respond to discovery requests.
8.6 AI in Entertainment and Media
AI techniques are used in targeted advertising, content recommendations, distribution, and fraud detection. The technology enables companies to personalize audience members’ experiences and optimize delivery of content.
8.7 AI in Journalism
AI can streamline workflows by automating routine tasks, such as data entry and proofreading. Investigative journalists and data journalists use AI to find and research stories by sifting through large data sets using machine learning models.
8.8 AI in Software Development and IT
AI is used to automate many processes in software development, DevOps, and IT. AIOps tools enable predictive maintenance of IT environments by analyzing system data to forecast potential issues before they occur.
8.9 AI in Security
AI is used in multiple aspects of cybersecurity, including anomaly detection, reducing false positives, and conducting behavioral threat analytics. Organizations use machine learning in security information and event management (SIEM) software to detect suspicious activity and potential threats.
8.10 AI in Manufacturing
Manufacturing has been at the forefront of incorporating robots into workflows, with recent advancements focusing on collaborative robots, or cobots. These multitasking robots can take on responsibility for more tasks in warehouses, on factory floors, and in other workspaces, including assembly, packaging, and quality control.
8.11 AI in Transportation
AI technologies are used in automotive transportation to manage traffic, reduce congestion, and enhance road safety. In air travel, AI can predict flight delays by analyzing data points such as weather and air traffic conditions.
9. What is the History of AI Technology?
The concept of inanimate objects endowed with intelligence has been around since ancient times. The Greek god Hephaestus was depicted in myths as forging robot-like servants out of gold, while engineers in ancient Egypt built statues of gods that could move, animated by hidden mechanisms operated by priests.
9.1 Early Foundations
Thinkers from the Greek philosopher Aristotle to the 13th-century Spanish theologian Ramon Llull to mathematician René Descartes and statistician Thomas Bayes used the tools and logic of their times to describe human thought processes as symbols. Their work laid the foundation for AI concepts such as general knowledge representation and logical reasoning.
9.2 19th and 20th Centuries
In 1836, Cambridge University mathematician Charles Babbage and Augusta Ada King, Countess of Lovelace, invented the first design for a programmable machine, known as the Analytical Engine. The late 19th and early 20th centuries brought forth foundational work that would give rise to the modern computer.
9.3 The 1940s
Princeton mathematician John Von Neumann conceived the architecture for the stored-program computer. Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts proposed a mathematical model of artificial neurons, laying the foundation for neural networks and other future AI developments.
9.4 The 1950s
With the advent of modern computers, scientists began to test their ideas about machine intelligence. In 1950, Turing devised a method for determining whether a computer has intelligence, which he called the imitation game but has become more commonly known as the Turing test.
The modern field of AI is widely cited as beginning in 1956 during a summer conference at Dartmouth College. John McCarthy is credited with coining the term “artificial intelligence.”
9.5 The 1960s
McCarthy developed Lisp, a language originally designed for AI programming that is still used today. In the mid-1960s, MIT professor Joseph Weizenbaum developed Eliza, an early NLP program that laid the foundation for today’s chatbots.
9.6 The 1970s
Achieving AGI proved elusive, not imminent, due to limitations in computer processing and memory as well as the complexity of the problem. As a result, government and corporate support for AI research waned, leading to a fallow period lasting from 1974 to 1980 known as the first AI winter.
9.7 The 1980s
Research on deep learning techniques and industry adoption of Edward Feigenbaum’s expert systems sparked a new wave of AI enthusiasm. Expert systems were applied to tasks such as financial analysis and clinical diagnosis.
9.8 The 1990s
Increases in computational power and an explosion of data sparked an AI renaissance in the mid- to late 1990s, setting the stage for the remarkable advances in AI we see today. In 1997, Deep Blue defeated Kasparov, becoming the first computer program to beat a world chess champion.
9.9 The 2000s
Further advances in machine learning, deep learning, NLP, speech recognition, and computer vision gave rise to products and services that have shaped the way we live today. Major developments include the 2000 launch of Google’s search engine and the 2001 launch of Amazon’s recommendation engine.
9.10 The 2010s
This decade saw a steady stream of AI developments, including the launch of Apple’s Siri and Amazon’s Alexa voice assistants. In 2016, Google DeepMind’s AlphaGo model defeated world Go champion Lee Sedol.
9.11 The 2020s
The current decade has so far been dominated by the advent of generative AI, which can produce new content based on a user’s prompt. In 2022, the generative AI wave began with the launch of image generators Dall-E 2 and Midjourney, and excitement reached full force with the general release of ChatGPT that November.
These are commonly described as the four main types of AI.
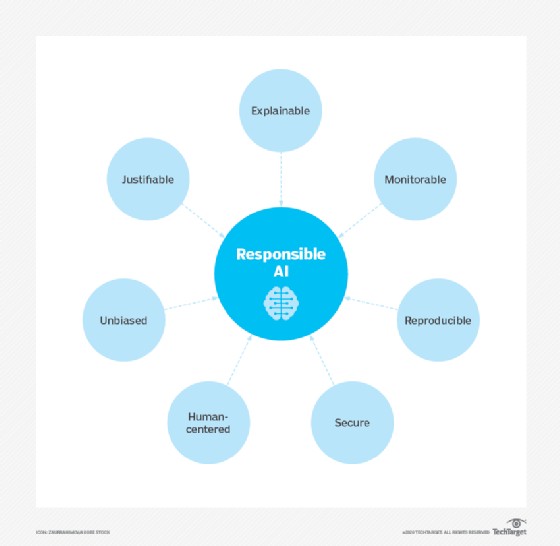
10. What are the Ethical Considerations of AI Technology?
The use of AI tools raises significant ethical questions. AI systems reinforce what they have already learned, meaning these algorithms are highly dependent on the data they are trained on. This can lead to bias, misuse, legal concerns, job displacement, and data privacy concerns.
10.1 Bias
Bias results from improperly trained algorithms and human prejudices or oversights.
10.2 Misuse
Misuse involves generative AI to produce deepfakes, phishing scams, and other harmful content.
10.3 Legal Concerns
Legal concerns include AI libel and copyright issues.
10.4 Job Displacement
Job displacement results from the increasing use of AI to automate workplace tasks.
10.5 Data Privacy Concerns
Data privacy concerns are particularly significant in fields such as banking, healthcare, and legal that deal with sensitive personal data.
These components make up responsible AI use.
FAQ about AI Technology
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What programming languages are commonly used in AI development? | Python, R, Java, C++, and Julia are popular languages among AI developers. |
| How does AI handle biased data? | AI handles biased data through careful monitoring of training processes and efforts to avoid unwanted bias, especially in complex neural networks used in deep learning. |
| What is the difference between strong AI and weak AI? | Strong AI refers to general AI with cognitive abilities on par with humans, while weak AI (narrow AI) is task-specific and cannot generalize across diverse situations. |
| How is AI used in customer service? | AI is used in customer service through virtual assistants and chatbots on corporate websites and in mobile applications to provide round-the-clock customer service and answer common questions. |
| What are the challenges in regulating AI? | The rapid evolution of AI technologies, AI’s lack of transparency, and the variety of technologies used for different purposes make it difficult to form meaningful regulations. |
| What is the role of AI in predictive maintenance? | AI is used for predictive maintenance in IT environments by analyzing system data to forecast potential issues before they occur, enabling timely interventions and reducing downtime. |
| How does AI impact the future of work? | AI is expected to automate many routine tasks, potentially leading to job displacement in some sectors but also creating new job categories that require different skills and expertise. |
| What are the privacy implications of AI? | AI raises significant privacy concerns, particularly when used to analyze and make decisions based on personal data, necessitating careful consideration of data protection regulations. |
| What are the environmental impacts of AI? | The operation of AI models requires large amounts of energy and water, contributing to a significant carbon footprint, especially for large generative models requiring extensive computing resources. |
| How is AI used in fraud detection? | AI is used in fraud detection by analyzing patterns and anomalies in financial transactions and other data to identify suspicious activities that may indicate fraudulent behavior. |
Conclusion: Embrace AI with Confidence at WHAT.EDU.VN
AI technology is a transformative force with the potential to reshape industries and improve lives. Understanding its workings, advantages, and ethical considerations is crucial for navigating this evolving landscape.
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and resources you need to stay informed and confident about AI. Whether you have questions about specific AI applications, ethical implications, or future trends, we are here to help.
Do you have questions about AI or any other topic? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today to ask your questions and receive free, expert answers. Our community of experts is ready to provide the insights you need to succeed in the age of AI.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Don’t hesitate—your answers await at what.edu.vn!