Amazon is more than just an online store; it’s a vast ecosystem. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we’re breaking down what Amazon is, its history, and its impact on the world, offering solutions and a clearer understanding. Dive in to learn about Amazon’s origins, services, and the future of this e-commerce and cloud computing titan, including cloud storage, Amazon Prime, and digital solutions.
1. What is Amazon and What Does It Do?
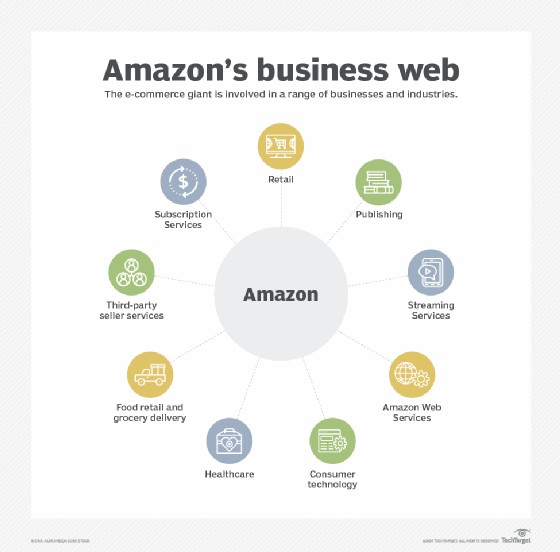
Amazon is the world’s largest online retailer, cloud service provider, and a diverse technology company. It offers e-commerce services, cloud computing, digital streaming, and artificial intelligence solutions to consumers and businesses globally.
Amazon started as an online bookstore but has expanded into a marketplace where you can buy almost anything. Beyond retail, it’s a major player in cloud computing through Amazon Web Services (AWS), providing services like data storage and computing power to businesses of all sizes. They also offer streaming services (Prime Video), smart home devices (Echo, Alexa), and much more.
2. How Did Amazon Start?
Amazon was founded by Jeff Bezos in 1994 in his garage in Bellevue, Washington. It officially opened as an online bookstore on July 16, 1995.
Bezos initially named the company Cadabra, but he later changed it to Amazon. The name Amazon was chosen because it was exotic, different, and referenced the Amazon River, reflecting Bezos’s vision for the company’s size and scale. From the beginning, Amazon’s motto was “Get Big Fast.”
3. What is Amazon Web Services (AWS)?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a comprehensive and evolving cloud computing platform that provides on-demand cloud computing services for websites and client-side applications.
AWS offers a wide array of services, including computing power, storage, databases, analytics, machine learning, and more, all accessible over the internet. Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) and Simple Storage Service (S3) are the foundational building blocks of AWS. AWS allows businesses to build and run applications, store data, and access resources without the need to invest in and manage their own infrastructure, according to the AWS website.
4. What Are the Key Milestones in Amazon’s History?
Here are some key milestones in Amazon’s history:
- 1994: Jeff Bezos founds Amazon.
- 1995: Amazon officially opens as an online bookstore.
- 2005: Amazon Prime launches, offering free two-day shipping.
- 2006: Amazon Web Services (AWS) is introduced.
- 2007: The first Amazon Kindle e-reader is released.
- 2011: Amazon debuts the Kindle Fire tablet.
- 2014: Amazon Fire TV Stick is launched.
- 2015: Amazon Alexa is rolled out to consumers.
- 2017: Amazon acquires Whole Foods Market.
- 2018: Amazon Go, a chain of cashierless grocery stores, is launched.
5. What are Amazon’s Main Products and Services?
Amazon offers a wide range of products and services across various categories. Here’s a breakdown:
Retail:
- Amazon Marketplace: E-commerce platform for third-party retailers.
- Amazon Fresh: Grocery delivery and pickup service.
- Amazon Vine: Program for manufacturers to get product reviews.
- Woot: Daily deals and limited-time offers.
- Zappos: Online retailer for shoes and clothing.
- Merch by Amazon: On-demand T-shirt printing service.
- Amazon Handmade: Platform for artisans to sell handcrafted products.
Consumer Technology:
- Amazon Kindle: E-reader for browsing, buying, and reading e-books.
- Amazon Fire Tablet: Tablet competing with Apple’s iPad.
- Amazon Fire TV: Streaming media players and digital devices.
- Amazon Alexa: Voice-controlled virtual assistant.
- Amazon Echo: Smart home device with a speaker and Alexa.
- Amazon Echo Dot: Smaller version of Amazon Echo.
- Amazon Echo Show: Amazon Echo with a touchscreen display.
- Amazon Astro: Home monitoring robot.
Subscription Services:
- Amazon Prime: Membership service with shopping and entertainment benefits.
- Amazon Prime Video: On-demand video streaming service.
- Amazon Drive: Cloud storage app.
- Twitch Prime: Premium access to Twitch, a video game streaming platform.
- Amazon Music Prime: Music streaming service.
Digital Content:
- Amazon Pay: Online transaction processing platform.
- Amazon Music Unlimited: Premium music service.
- Kindle Store: Online store for purchasing e-books.
- Amazon Appstore for Android: App store for Android devices.
AWS:
- S3: Scalable, cloud-based object storage.
- Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS): Web service for message queuing.
- Amazon EC2: Web service interface for resizable compute capacity.
- Amazon S3 Glacier: Low-cost cloud storage for data archiving and backup.
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM): Secure access management for resources.
- Amazon Redshift: Data warehouse in the cloud.
Amazon AI Services:
- Amazon SageMaker: Cloud machine learning platform.
- Amazon Lex: Service for building conversational interfaces.
- Amazon Polly: Text-to-speech service.
- Amazon Rekognition: Facial recognition and analysis platform.
- AWS DeepLens: Programmable video camera for machine learning.
- Alexa Voice Service: Programming interface for adding Alexa capabilities.
- Amazon Transcribe: Speech-to-text service.
- Amazon Translate: Cloud service for text translation.
- Alexa Skills Kit: Software development kit for building Alexa skills.
Amazon Privately Owned Brands:
- AmazonBasics: Low-budget brand for kitchen, tech, and household products.
- Amazon Elements: Health and personal care items, and nutritional supplements.
- Mama Bear: Baby products.
- Presto!: Household paper towels and toilet paper.
- Amazon Essentials: Basic clothing wear.
- Happy Belly: Snack food items.
- Goodthreads: Menswear apparel line.
6. What are Some Notable Amazon Subsidiaries and Acquisitions?
Amazon has acquired a wide range of companies to expand its reach into various industries. Some notable subsidiaries and acquisitions include:
- IMDb (1998): The Internet Movie Database, a popular source for movie, TV, and celebrity information.
- Audible (2008): A provider of audiobooks and spoken-word content.
- Zappos (2009): An online retailer of shoes and clothing.
- Twitch (2014): A video game streaming platform.
- Whole Foods Market (2017): A chain of organic grocery stores.
- Ring (2018): A home security and smart home company.
- Zoox (2020): An autonomous vehicle and robotics company.
- Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer (MGM) (2022): A film and television studio.
7. What is the Amazon Effect?
The Amazon effect refers to the disruption of the retail market due to Amazon’s size, scale, and business practices. It includes:
- Monopolistic and Anticompetitive Behavior: Concerns about Amazon outpricing local and small businesses.
- Impact on Brick-and-Mortar Stores: The decline of traditional retailers like Sears and J.C. Penney.
8. What Are Some Criticisms of Amazon?
Amazon has faced several criticisms and controversies over the years, including:
- Monopolistic and Anticompetitive Behavior: Accusations of displacing open markets with a privately controlled one.
- Unfair Treatment of Workers: Concerns about work conditions in its warehouses, including low wages and unsafe environments.
- Huge Carbon Footprint: Accusations of contributing to environmental damage through its transportation and operations.
- E-waste: Concerns about the destruction of unused or returned products, including electronics.
- Counterfeit Product Listings: Issues with counterfeit products being sold on its third-party marketplace.
- Avoiding Taxation: Criticisms for avoiding tax payments despite making huge profits.
9. What are Amazon’s Financials?
Amazon’s financial performance is closely watched by investors and analysts. Here are some key financial metrics from the first quarter of 2022:
- Net Sales: Increased 7% to $116.4 billion.
- Operating Income: Decreased to $3.7 billion.
- Net Loss: $3.8 billion, compared to a net income of $8.1 billion in the first quarter of 2021.
10. What are Some Frequently Asked Questions About Amazon?
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What Is Amazon Prime? | A subscription service that offers benefits like free shipping, streaming video, and more. |
| What is Amazon’s mission statement? | To be Earth’s most customer-centric company, where customers can find and discover anything they might want to buy online. |
| How does Amazon make money? | Primarily through online retail sales, cloud computing services (AWS), advertising, subscription services, and third-party seller fees. |
| What is the difference between Amazon and Amazon Marketplace? | Amazon sells its own products, while Amazon Marketplace allows third-party sellers to list and sell their products on Amazon’s platform. |
| What are the benefits of selling on Amazon Marketplace? | Access to a large customer base, established infrastructure, and marketing tools. |
| How does Amazon handle customer service? | Amazon offers customer service through online chat, phone, and email. They also have a comprehensive help section on their website. |
| What is Amazon’s return policy? | Amazon typically offers a 30-day return policy for most items, but this can vary depending on the product and seller. |
| How does Amazon use artificial intelligence? | Amazon uses AI in various ways, including product recommendations, fraud detection, voice assistants (Alexa), and logistics optimization. |
| What are Amazon’s sustainability efforts? | Amazon has initiatives to reduce its carbon footprint, including investing in renewable energy, electric vehicles, and sustainable packaging. |
| How does Amazon impact small businesses? | Amazon provides opportunities for small businesses to reach a wider audience but also poses challenges due to competition and marketplace fees. |

11. What is Amazon’s Impact on the Retail Industry?
Amazon has had a transformative impact on the retail industry, leading to significant shifts in consumer behavior and business models. Here’s a detailed look at its effects:
- Rise of E-commerce: Amazon’s success has fueled the growth of e-commerce, making online shopping a mainstream activity.
- Competitive Pricing: Amazon’s focus on competitive pricing has forced other retailers to lower prices, benefiting consumers but squeezing profit margins for some businesses.
- Convenience and Customer Experience: Amazon has set high standards for convenience and customer service, including fast shipping, easy returns, and personalized recommendations.
- Disruption of Traditional Retail: Many traditional brick-and-mortar retailers have struggled to compete with Amazon, leading to store closures and bankruptcies.
- Innovation in Logistics: Amazon has invested heavily in logistics and supply chain management, setting new benchmarks for delivery speed and efficiency.
- Increased Competition: Amazon’s marketplace model has increased competition among sellers, giving consumers more choices but also creating challenges for smaller businesses.
- Changing Consumer Expectations: Amazon has shaped consumer expectations around online shopping, influencing how people search for, evaluate, and purchase products.
- Growth of Third-Party Sellers: Amazon’s marketplace has enabled countless small and medium-sized businesses to reach a global audience, but it has also raised concerns about competition and counterfeit products.
- Data-Driven Insights: Amazon uses data to personalize the shopping experience, optimize pricing, and improve its supply chain, giving it a competitive advantage over retailers that lack these capabilities.
- Omnichannel Strategies: Amazon’s acquisition of Whole Foods and its expansion into physical retail stores highlight the importance of omnichannel strategies, combining online and offline channels to serve customers better.
12. What is Amazon’s Role in Cloud Computing?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the leading provider of cloud computing services, offering a wide range of on-demand resources and solutions for businesses of all sizes. Here’s an overview of Amazon’s role in cloud computing:
- Market Leadership: AWS is the dominant player in the cloud computing market, with a significant share of the global market revenue.
- Comprehensive Services: AWS offers a comprehensive suite of cloud services, including computing, storage, databases, analytics, machine learning, and more.
- Scalability and Flexibility: AWS allows businesses to easily scale their resources up or down based on demand, providing flexibility and cost savings.
- Global Infrastructure: AWS has a global network of data centers, allowing businesses to deploy applications and services closer to their customers.
- Innovation and New Technologies: AWS is constantly innovating and introducing new services, driving advancements in areas such as artificial intelligence, serverless computing, and edge computing.
- Cost-Effectiveness: AWS can be more cost-effective than traditional on-premises infrastructure, as businesses only pay for the resources they use.
- Security and Compliance: AWS provides robust security features and compliance certifications, helping businesses protect their data and meet regulatory requirements.
- Ecosystem and Partner Network: AWS has a vast ecosystem of partners, including software vendors, system integrators, and managed service providers, offering additional support and expertise.
- Democratization of Technology: AWS has democratized access to technology, allowing small and medium-sized businesses to leverage enterprise-grade infrastructure and services.
- Digital Transformation: AWS is a key enabler of digital transformation, helping businesses modernize their IT infrastructure and adopt new technologies to gain a competitive advantage.
13. What is Amazon’s Vision for the Future?
Amazon’s vision for the future is ambitious and far-reaching, encompassing various areas of innovation and growth. Here’s a look at some of the key aspects of Amazon’s future vision:
- Continued E-commerce Dominance: Amazon aims to maintain its dominance in e-commerce by expanding its product offerings, improving the customer experience, and optimizing its logistics and supply chain.
- Growth of Cloud Computing: Amazon Web Services (AWS) is expected to continue growing as more businesses migrate to the cloud and adopt cloud-native technologies.
- Expansion into New Markets: Amazon is likely to expand its presence in international markets and explore new industries, such as healthcare, finance, and energy.
- Artificial Intelligence and Automation: Amazon is investing heavily in AI and automation to improve its operations, personalize the customer experience, and develop new products and services.
- Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility: Amazon is committed to reducing its carbon footprint and promoting sustainability through initiatives such as renewable energy investments and sustainable packaging.
- Innovation in Logistics and Delivery: Amazon is exploring new technologies and methods for logistics and delivery, including drone delivery, autonomous vehicles, and last-mile optimization.
- Enhancing the Customer Experience: Amazon is focused on improving the customer experience through personalized recommendations, voice-controlled interfaces, and seamless integration of its various services.
- Investing in New Technologies: Amazon is investing in emerging technologies such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and blockchain to explore new opportunities and stay ahead of the competition.
- Building a Smart Home Ecosystem: Amazon aims to create a comprehensive smart home ecosystem with its Echo devices, Alexa voice assistant, and integration with other smart home devices and services.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Amazon will continue to leverage data to make informed decisions, optimize its operations, and personalize the customer experience.
14. How Does Amazon Use Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Amazon uses artificial intelligence (AI) extensively across its operations to enhance various aspects of its business. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how Amazon leverages AI:
- Personalized Recommendations: AI algorithms analyze customer behavior to provide personalized product recommendations, increasing sales and customer satisfaction.
- Voice Assistant (Alexa): Alexa, Amazon’s voice-controlled virtual assistant, uses AI to understand and respond to voice commands, control smart home devices, and provide information.
- Fraud Detection: AI algorithms analyze transactions to identify and prevent fraudulent activities, protecting customers and reducing financial losses.
- Logistics Optimization: AI is used to optimize logistics and supply chain management, improving delivery times, reducing costs, and minimizing disruptions.
- Image Recognition: AI-powered image recognition is used to identify products, detect objects, and analyze images for various purposes, such as quality control and product categorization.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is used to understand and analyze text data, such as customer reviews and product descriptions, to extract insights and improve customer service.
- Chatbots and Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots are used to provide automated customer service, answering questions, resolving issues, and improving customer satisfaction.
- Pricing Optimization: AI algorithms analyze market data to optimize pricing, increasing revenue and maximizing profit margins.
- Warehouse Automation: AI is used to automate tasks in warehouses, such as picking, packing, and sorting products, improving efficiency and reducing labor costs.
- Product Search and Discovery: AI is used to improve product search and discovery, helping customers find the products they need more easily and quickly.
15. What are Amazon’s Sustainability Efforts?
Amazon is committed to sustainability and has implemented various initiatives to reduce its environmental impact. Here’s an overview of Amazon’s sustainability efforts:
- Renewable Energy Investments: Amazon is investing in renewable energy projects, such as wind and solar farms, to power its operations with clean energy.
- Sustainable Packaging: Amazon is working to reduce packaging waste by using more sustainable materials, optimizing packaging sizes, and encouraging customers to recycle.
- Electric Vehicles: Amazon is deploying electric vehicles in its delivery fleet to reduce emissions and improve air quality.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Amazon has set a goal to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2040, known as the Climate Pledge.
- Waste Reduction and Recycling: Amazon is implementing waste reduction and recycling programs in its offices, warehouses, and data centers to minimize waste and conserve resources.
- Water Conservation: Amazon is implementing water conservation measures in its data centers and other facilities to reduce water consumption.
- Sustainable Forestry: Amazon is committed to sustainable forestry practices and is working to protect forests and promote responsible forest management.
- Supply Chain Sustainability: Amazon is working with its suppliers to promote sustainable practices throughout its supply chain, including reducing emissions, conserving resources, and protecting worker rights.
- Climate Pledge Fund: Amazon has established a $2 billion Climate Pledge Fund to invest in companies and technologies that are developing solutions to address climate change.
- Transparency and Reporting: Amazon is committed to transparency and regularly reports on its sustainability progress, providing stakeholders with information on its environmental performance.
Do you have more questions about Amazon? Don’t hesitate to ask them on WHAT.EDU.VN. Our community of experts is ready to provide you with quick, accurate, and free answers.
Tired of searching endlessly for answers? Need expert advice without the hefty price tag? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today, your ultimate destination for free question-and-answer services. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply curious, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to provide you with the knowledge you need, when you need it.
Ask Your Question Now!
Contact Us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: what.edu.vn