What Is An Adjective Example? Explore the world of descriptive words with WHAT.EDU.VN and enhance your understanding of grammar. We provide clear explanations and practical examples to help you master adjectives and improve your writing skills, offering linguistic precision and enhanced communication through descriptive words. Uncover adjective definition, noun modifiers, and descriptive words.
1. Adjective Definition: What Exactly Is An Adjective?
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun, providing more detail about its qualities, characteristics, or attributes. It answers questions like what kind, how many, or which one. Understanding the adjective definition is crucial for effective communication.
For example:
- The blue car (blue describes the color of the car)
- A tall building (tall describes the height of the building)
- Five apples (five specifies the number of apples)
Adjectives enhance our language by adding richness and specificity to our descriptions.
2. How To Use Adjectives Effectively
To use adjectives effectively, consider the following points:
- Placement: Adjectives usually come before the noun they modify (e.g., a beautiful flower). However, they can also follow linking verbs (e.g., the flower is beautiful).
- Variety: Use a variety of adjectives to make your writing more engaging. Avoid overusing the same adjectives.
- Specificity: Choose adjectives that accurately convey the intended meaning. Be precise in your descriptions.
- Coordinate Adjectives: Separate coordinate adjectives (adjectives that independently modify the same noun) with a comma (e.g., a long, cold winter).
- Non-Coordinate Adjectives: Do not separate non-coordinate adjectives (adjectives that form a unit of meaning) with a comma (e.g., a little old lady).
By following these guidelines, you can use adjectives to improve the clarity and impact of your writing.
3. Adjectives Modify Nouns: Enhancing Noun Descriptions
Adjectives are primarily used to modify nouns, providing additional information about their attributes. They help to paint a clearer picture for the reader. Adjectives modify nouns by specifying color, size, shape, origin, material, and many other qualities of nouns.
 An image showing an example of adjectives that modify nouns in a sentence.
An image showing an example of adjectives that modify nouns in a sentence.
Consider these examples:
- The red balloon floated in the air. (red modifies the noun balloon)
- She wore a silk dress to the party. (silk modifies the noun dress)
- He lives in a historic building downtown. (historic modifies the noun building)
- The team celebrated a major victory. (major modifies the noun victory)
In each of these sentences, the adjective enriches the description of the noun, making the image more vivid and detailed.
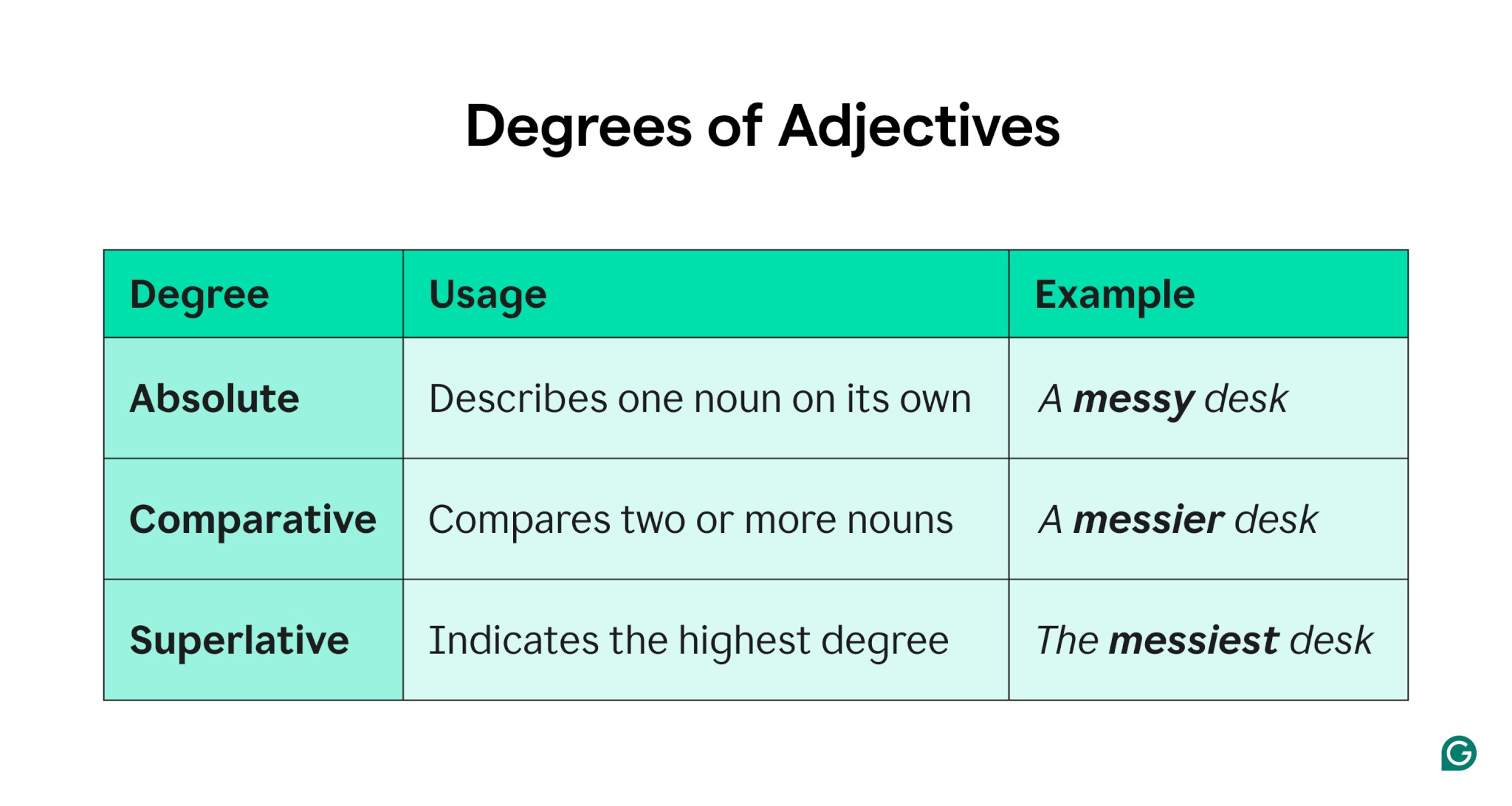
4. Degrees Of Adjectives: Absolute, Comparative, And Superlative Forms
Adjectives have three degrees: absolute, comparative, and superlative. Each form is used in different contexts to express varying levels of a quality.
4.1. Absolute Adjectives
Absolute adjectives describe a quality without making a comparison. They represent a quality in its basic form.
Examples include:
- Happy (e.g., She is a happy person.)
- Big (e.g., He lives in a big house.)
- Interesting (e.g., That is an interesting book.)
- Beautiful (e.g., The garden is beautiful.)
- Important (e.g., This is an important decision.)
4.2. Comparative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives are used to compare two things. They show which of the two has more of a particular quality. Comparative adjectives are often formed by adding -er to the end of the adjective or by using the word more before the adjective.
Examples include:
- Happier (e.g., She is happier now than before.)
- Bigger (e.g., His house is bigger than mine.)
- More interesting (e.g., This book is more interesting than that one.)
- More beautiful (e.g., The garden is more beautiful in the spring.)
- More important (e.g., This decision is more important than the last one.)
4.3. Superlative Adjectives
Superlative adjectives are used to compare three or more things. They indicate which one has the most of a particular quality. Superlative adjectives are often formed by adding -est to the end of the adjective or by using the word most before the adjective.
Examples include:
- Happiest (e.g., She is the happiest person I know.)
- Biggest (e.g., His house is the biggest in the neighborhood.)
- Most interesting (e.g., This is the most interesting book I have ever read.)
- Most beautiful (e.g., The garden is the most beautiful in the city.)
- Most important (e.g., This is the most important decision of my life.)
Understanding the degrees of adjectives allows for more precise and descriptive writing.
5. Coordinate Adjectives: Using Commas Correctly
Coordinate adjectives are adjectives that independently modify the same noun. They should be separated by a comma or the word and.
For example:
- A long, cold winter (long and cold both describe the winter independently)
- She is a smart, kind woman (smart and kind both describe the woman independently)
- He has a big, old car (big and old both describe the car independently)
To determine if adjectives are coordinate, you can try these two tests:
- Insert and between the adjectives: If the sentence still sounds natural, the adjectives are coordinate.
- Switch the order of the adjectives: If the sentence still makes sense, the adjectives are coordinate.
If either of these tests fails, the adjectives are non-coordinate and should not be separated by a comma.
6. Adjectives Vs. Adverbs: Knowing The Difference
Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns, while adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Distinguishing between the two is essential for correct usage.
Consider these examples:
- Adjective: She is a fast runner. (fast describes the noun runner)
- Adverb: She runs fast. (fast describes the verb runs)
- Adjective: He wore a colorful shirt. (colorful describes the noun shirt)
- Adverb: The artist painted colorfully. (colorfully describes the verb painted)
To differentiate, ask yourself what the word is modifying. If it describes a noun or pronoun, it’s an adjective. If it describes a verb, adjective, or adverb, it’s an adverb.
7. Nouns As Adjectives And Adjectives As Nouns
Sometimes, nouns can function as adjectives, and adjectives can function as nouns. This often depends on their placement and the context of the sentence.
7.1. Nouns As Adjectives
When a noun modifies another noun, it functions as an adjective.
For example:
- The school bus arrived late. (school is a noun, but it modifies the noun bus)
- She works in the sales department. (sales is a noun, but it modifies the noun department)
- He bought a leather jacket. (leather is a noun, but it modifies the noun jacket)
7.2. Adjectives As Nouns
Adjectives can function as nouns when they refer to a general group of people or things, often with the addition of the.
For example:
- The poor need our help. (poor is an adjective, but it refers to poor people in general)
- The rich often have different concerns. (rich is an adjective, but it refers to rich people in general)
- Only the brave dare to enter. (brave is an adjective, but it refers to brave people in general)
Understanding these shifts in function can improve your comprehension and usage of English.
8. Adjective Usage Advice: Tips For Better Writing
Here are some tips to help you use adjectives effectively in your writing:
- Use adjectives sparingly: Too many adjectives can make your writing sound cluttered and overwhelming. Choose adjectives that add significant value to your descriptions.
- Choose precise adjectives: Select adjectives that accurately convey the intended meaning. Avoid vague or generic adjectives.
- Avoid clichés: Steer clear of overused adjectives that have lost their impact. Try to find fresh and original ways to describe things.
- Consider context: Choose adjectives that are appropriate for the tone and style of your writing.
- Vary your adjectives: Use a variety of adjectives to keep your writing interesting and engaging.
By following these tips, you can use adjectives to enhance your writing without making it sound forced or unnatural.
9. Common Adjective Examples To Enhance Your Vocabulary
Here is a list of adjective examples to enhance your vocabulary:
| Category | Adjective Examples |
|---|---|
| Size | small, large, tiny, huge, immense, petite, towering |
| Color | red, blue, green, yellow, purple, orange, crimson, azure, emerald |
| Shape | round, square, triangular, oval, cylindrical, spherical, rectangular |
| Texture | smooth, rough, silky, velvety, bumpy, coarse, sleek |
| Sound | loud, soft, quiet, noisy, deafening, melodic, harmonious |
| Taste | sweet, sour, bitter, salty, savory, spicy, tangy |
| Smell | fragrant, pungent, musty, floral, smoky, earthy, acrid |
| Appearance | beautiful, ugly, attractive, handsome, stunning, plain, gorgeous |
| Personality | kind, cruel, generous, selfish, brave, timid, witty |
| Emotion | happy, sad, angry, excited, calm, anxious, joyful |
| Time | early, late, ancient, modern, recent, future, past |
| Condition | healthy, sick, broken, repaired, clean, dirty, damaged |
| Quantity | few, many, several, numerous, abundant, scarce, limited |
| Origin | American, Italian, Chinese, French, German, Spanish |
| Material | wooden, metal, plastic, paper, glass, stone, ceramic |
| Temperature | hot, cold, warm, cool, freezing, boiling, chilly |
| Difficulty | easy, hard, simple, complex, challenging, effortless |
| Importance | important, trivial, significant, crucial, minor, essential |
| Age | young, old, new, ancient, mature, youthful |
| Value | valuable, worthless, precious, cheap, expensive, priceless |
| Quality | good, bad, excellent, terrible, average, superior |
| Opinion | interesting, boring, funny, serious, exciting, dull |
| Measurement | long, short, wide, narrow, deep, shallow, tall |
| Position | high, low, top, bottom, left, right, central |
| Direction | north, south, east, west, forward, backward, sideways |
| Degree | absolute, relative, comparative, superlative, extreme |
| Intensity | intense, mild, strong, weak, bright, dim |
| State | awake, asleep, alive, dead, conscious, unconscious |
| Completeness | complete, incomplete, whole, partial, entire, lacking |
| Certainty | certain, uncertain, definite, possible, probable |
| Possibility | possible, impossible, likely, unlikely, feasible |
| Frequency | frequent, rare, occasional, constant, sporadic |
| Relevance | relevant, irrelevant, applicable, appropriate |
| Structure | organized, chaotic, structured, symmetrical |
| Order | first, last, next, previous, final |
| Attitude | positive, negative, optimistic, pessimistic |
| Behavior | polite, rude, aggressive, passive, gentle |
| Performance | efficient, inefficient, effective, productive |
| Complexity | complicated, intricate, complex, simple |
| Adaptability | flexible, rigid, adaptable, versatile |
| Capacity | capable, unable, competent, skilled |
| Control | controlled, uncontrolled, managed, supervised |
| Availability | available, unavailable, accessible, limited |
| Stability | stable, unstable, secure, shaky |
| Clarity | clear, vague, obvious, ambiguous |
| Purity | pure, impure, clean, tainted |
| Originality | original, unique, novel, conventional |
| Familiarity | familiar, strange, known, unknown |
| Naturalness | natural, artificial, genuine, synthetic |
| Reality | real, imaginary, virtual, simulated |
| Formality | formal, informal, casual, official |
| Legality | legal, illegal, lawful, illicit |
| Morality | moral, immoral, ethical, unethical |
| Sanity | sane, insane, rational, irrational |
| Health | healthy, ill, fit, infirm |
| Strength | strong, weak, robust, fragile |
| Freedom | free, captive, independent, dependent |
| Justice | just, unjust, fair, biased |
| Peace | peaceful, turbulent, serene, chaotic |
| Truth | true, false, accurate, misleading |
| Wisdom | wise, foolish, intelligent, ignorant |
| Courage | brave, cowardly, fearless, timid |
| Grace | graceful, clumsy, elegant, awkward |
| Humor | funny, serious, witty, dull |
| Beauty | beautiful, ugly, attractive, repulsive |
| Mystery | mysterious, obvious, enigmatic, clear |
| Wonder | wonderful, amazing, ordinary, typical |
| Danger | dangerous, safe, perilous, secure |
| Fortune | fortunate, unlucky, prosperous, poor |
| Power | powerful, weak, dominant, submissive |
| Fame | famous, unknown, renowned, obscure |
| Love | loving, hateful, affectionate, cold |
| Hate | hateful, loving, hostile, friendly |
| Loyalty | loyal, disloyal, faithful, treacherous |
| Trust | trustworthy, unreliable, dependable, dubious |
| Hope | hopeful, hopeless, optimistic, pessimistic |
| Fear | fearful, brave, anxious, calm |
| Grief | grieving, joyful, sorrowful, happy |
| Anger | angry, calm, furious, placid |
| Joy | joyful, sad, elated, depressed |
| Surprise | surprised, expected, astonished, predictable |
| Awe | awesome, ordinary, impressive, unremarkable |
| Comfort | comfortable, uneasy, relaxed, tense |
| Security | secure, insecure, protected, vulnerable |
| Simplicity | simple, complex, easy, difficult |
| Creativity | creative, uninspired, imaginative, dull |
| Innovation | innovative, traditional, novel, outdated |
| Efficiency | efficient, wasteful, productive, ineffective |
| Sustainability | sustainable, unsustainable, eco-friendly, harmful |
| Digitization | digital, analog, online, offline |
| Globalization | global, local, international, domestic |
| Automation | automated, manual, robotic, human-operated |
| Connectivity | connected, disconnected, networked, isolated |
| Virtualization | virtual, real, simulated, physical |
| Integration | integrated, fragmented, unified, separated |
| Scalability | scalable, limited, expandable, fixed |
| Customization | customized, standard, personalized, generic |
| Optimization | optimized, inefficient, streamlined, clunky |
| Transformation | transformed, unchanged, evolved, stagnant |
| Convergence | convergent, divergent, unified, separated |
| Disruption | disruptive, conventional, innovative, traditional |
| Resilience | resilient, fragile, robust, delicate |
| Decentralization | decentralized, centralized, distributed, hierarchical |
| Transparency | transparent, opaque, open, hidden |
| Inclusion | inclusive, exclusive, diverse, homogeneous |
| Empowerment | empowered, disempowered, autonomous, dependent |
| Collaboration | collaborative, competitive, cooperative, individualistic |
| Communication | communicative, reserved, expressive, taciturn |
| Learning | learned, ignorant, knowledgeable, uneducated |
| Growth | growing, stagnant, expanding, shrinking |
| Progress | progressive, regressive, advancing, declining |
| Development | developed, underdeveloped, emerging, declining |
| Leadership | leading, following, directing, managing |
| Influence | influential, powerless, persuasive, ineffective |
| Decision | decisive, indecisive, resolute, wavering |
| Planning | planned, spontaneous, organized, haphazard |
| Execution | executed, failed, accomplished, neglected |
| Results | successful, unsuccessful, productive, barren |
| Outcomes | positive, negative, neutral, mixed |
| Achievements | achieved, failed, attained, lost |
| Goals | ambitious, realistic, modest, unrealistic |
| Objectives | clear, vague, specific, general |
| Strategies | effective, ineffective, well-planned, poorly executed |
| Tactics | efficient, wasteful, strategic, haphazard |
| Measurements | accurate, inaccurate, precise, approximate |
| Analysis | thorough, superficial, detailed, cursory |
| Evaluation | critical, supportive, judgmental, encouraging |
| Feedback | constructive, destructive, helpful, unhelpful |
| Improvement | improved, deteriorated, enhanced, diminished |
| Innovation | innovative, traditional, groundbreaking, routine |
| Creativity | creative, uninspired, imaginative, dull |
| Adaptability | adaptable, rigid, flexible, inflexible |
| Learning | learned, ignorant, knowledgeable, uneducated |
| Knowledge | knowledgeable, ignorant, informed, uninformed |
| Skills | skilled, unskilled, competent, inept |
| Abilities | capable, unable, competent, inept |
| Talents | talented, untalented, gifted, ordinary |
| Strengths | strong, weak, resilient, fragile |
| Weaknesses | weak, vulnerable, deficient, strong |
| Potential | potential, limited, promising, bleak |
| Resources | abundant, scarce, plentiful, limited |
| Opportunities | open, limited, available, restricted |
| Challenges | difficult, easy, complex, simple |
| Risks | risky, safe, hazardous, secure |
| Rewards | rewarding, unfulfilling, satisfying, disappointing |
| Recognition | recognized, unknown, appreciated, unappreciated |
| Validation | valid, invalid, justified, unfounded |
| Support | supportive, unsupportive, helpful, hindering |
| Assistance | helpful, unhelpful, beneficial, detrimental |
| Guidance | guiding, misleading, informative, deceptive |
| Mentorship | mentoring, advising, coaching, teaching |
| Collaboration | collaborative, competitive, cooperative, individualistic |
| Networking | connected, isolated, linked, separated |
| Membership | member, non-member, participant, outsider |
| Community | communal, individualistic, collective, solitary |
| Partnership | partnered, allied, associated, detached |
| Leadership | leading, following, directing, managing |
| Management | managing, directing, overseeing, controlling |
| Ownership | owning, possessing, controlling, holding |
| Governance | governing, regulating, supervising, administering |
| Authority | authoritative, controlling, commanding, influencing |
| Responsibility | responsible, accountable, liable, answerable |
| Commitment | committed, dedicated, devoted, loyal |
| Discipline | disciplined, structured, regulated, regimented |
| Habits | habitual, customary, routine, recurring |
| Rituals | ritualistic, ceremonial, traditional, symbolic |
| Customs | customary, conventional, traditional, established |
| Traditions | traditional, cultural, ancestral, inherited |
| Norms | normal, standard, average, typical |
| Values | valued, cherished, prized, esteemed |
| Beliefs | believing, trusting, confident, certain |
| Attitudes | positive, negative, optimistic, pessimistic |
| Opinions | opinionated, biased, subjective, prejudiced |
| Perspectives | perspective, viewpoint, outlook, position |
| Standpoints | standpoint, vantage point, position, attitude |
| Interpretations | interpreting, understanding, explaining, defining |
| Meanings | meaningful, significant, important, essential |
| Implications | implied, suggested, inferred, indicated |
| Consequences | consequential, important, significant, impactful |
| Effects | effective, powerful, potent, forceful |
| Results | resulting, derived, stemming, arising |
| Outcomes | resulting, derived, stemming, arising |
| Achievements | achieved, accomplished, attained, realized |
| Goals | targeted, intended, purposed, aimed |
| Objectives | objectified, aimed, intended, proposed |
| Strategies | strategic, planned, designed, devised |
| Tactics | tactical, strategic, calculated, planned |
| Measurements | measured, calculated, assessed, evaluated |
| Analysis | analyzed, studied, examined, scrutinized |
| Evaluation | evaluated, assessed, judged, appraised |
| Feedback | constructive, critical, supportive, negative |
| Improvement | improved, enhanced, advanced, elevated |
| Innovation | innovative, creative, groundbreaking, novel |
| Creativity | creative, imaginative, resourceful, inventive |
| Adaptability | adaptable, flexible, versatile, malleable |
10. Adjective FAQs: Quick Answers To Common Questions
10.1. What Are Some Common Mistakes When Using Adjectives?
Common mistakes include:
- Misusing adjectives as adverbs (e.g., He feels badly instead of He feels bad).
- Using too many adjectives in a sentence.
- Failing to separate coordinate adjectives with a comma.
- Using vague or generic adjectives.
10.2. Can An Adjective Modify A Pronoun?
Yes, adjectives can modify pronouns. For example, in the sentence “He is smart,” the adjective smart modifies the pronoun he.
10.3. What Is A Predicate Adjective?
A predicate adjective follows a linking verb and modifies the subject of the sentence. For example, in the sentence “The sky is blue,” the adjective blue is a predicate adjective modifying the subject sky.
10.4. How Do I Identify Adjectives In A Sentence?
To identify adjectives, ask yourself which words are describing nouns or pronouns. These words are likely adjectives.
10.5. Are Numbers Considered Adjectives?
Yes, numbers are considered adjectives when they modify nouns. For example, in the phrase “three apples,” the number three is an adjective.
Do you find grammar rules perplexing and need straightforward answers? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
Are you struggling to grasp adjective usage? Do you need clarification on adjective examples, noun modifiers, and descriptive words? Do you feel overwhelmed by complex grammatical rules?
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand your challenges. Our platform provides a free, easy-to-use service that answers all your questions quickly and accurately. We connect you with knowledgeable experts who can provide clear explanations and practical examples tailored to your needs.
Here’s how WHAT.EDU.VN can help you:
- Get instant answers: No more endless searching through confusing textbooks or websites. Simply ask your question and receive a concise, reliable answer.
- Connect with experts: Our platform connects you with experienced professionals who can provide personalized guidance and support.
- Free and accessible: Our services are completely free, making quality education accessible to everyone.
- Easy to use: Our user-friendly interface makes it easy to ask questions and receive answers, regardless of your technical skills.
Don’t let grammar challenges hold you back. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply someone curious about language, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help.
Ready to experience the ease and convenience of WHAT.EDU.VN?
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your question! Let us help you unlock the power of language and achieve your goals.
Contact us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: what.edu.vn