An MSP, or managed service provider, is a company that remotely manages your information technology infrastructure and end-user systems, offering expertise and freeing you to focus on your core business. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of accessible information, providing a platform where you can get answers to all your questions, including What Is An Msp, MSP benefits, and managed IT services.
1. What is a Managed Service Provider (MSP)?
A Managed Service Provider (MSP) is a third-party company that assumes responsibility for managing and maintaining a client’s IT infrastructure and end-user systems. This encompasses a wide array of services, delivered remotely, aimed at improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enabling businesses to focus on their core competencies. MSPs provide various services, including network management, cybersecurity, cloud solutions, and data backup.
Five C-level executives weigh in on the value of MSPs to their businesses.
1.1. What are the Key Characteristics of an MSP?
- Remote Management: MSPs deliver services remotely, utilizing technology to monitor, manage, and resolve IT issues without needing on-site presence.
- Proactive Approach: MSPs emphasize proactive monitoring and maintenance to identify and resolve potential problems before they impact the business.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): MSPs operate under SLAs, which define the scope of services, performance metrics, and responsibilities of both the provider and the client.
- Scalability and Flexibility: MSPs offer scalable solutions that can adapt to the changing needs of a business.
- Expertise and Specialization: MSPs possess specialized knowledge and experience in various IT domains.
1.2. What is the Difference Between an MSP and Traditional IT Support?
| Feature | Managed Service Provider (MSP) | Traditional IT Support |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Proactive, preventative maintenance | Reactive, break-fix |
| Pricing | Predictable monthly fees | Hourly rates or project-based fees |
| Service Level | Defined in SLAs, ensuring specific performance levels | Variable, depending on the technician and issue severity |
| Scope of Service | Comprehensive IT management, including monitoring and security | Typically limited to resolving specific issues |
| Focus | Long-term IT strategy and business alignment | Short-term issue resolution |

1.3. How Has the Role of MSPs Evolved Over Time?
Initially, MSPs focused on remote monitoring and management (RMM) of servers and networks. According to a report by CompTIA, the evolution of MSPs began in the 1990s with the emergence of application service providers (ASPs), which offered remote application hosting. Today, they have expanded their scope to include cloud services, cybersecurity, and strategic IT consulting. The term “cloud service provider” and “managed service provider” are sometimes used synonymously when the provider’s service is supported by a service-level agreement (SLA) and is delivered over the internet.
2. What Services Do Managed Service Providers Offer?
MSPs offer a wide range of services tailored to meet the diverse needs of businesses. These services can be broadly categorized as follows:
2.1. Core Managed Services
- Network Management: Monitoring, maintenance, and optimization of network infrastructure, including routers, switches, and firewalls.
- Server Management: Management of physical and virtual servers, including patching, updates, and performance monitoring.
- Help Desk Support: Providing end-user support for hardware, software, and network issues.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Ensuring data is regularly backed up and can be quickly restored in the event of a disaster.
2.2. Security Services
- Managed Antivirus: Protecting systems from malware and viruses through proactive monitoring and updates.
- Firewall Management: Configuring and maintaining firewalls to prevent unauthorized access to the network.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Monitoring network traffic for malicious activity and taking steps to prevent intrusions.
- Security Audits and Compliance: Conducting regular security assessments and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
2.3. Cloud Services
- Cloud Migration: Assisting businesses in migrating their applications and data to the cloud.
- Cloud Infrastructure Management: Managing cloud-based servers, storage, and networking resources.
- Cloud Backup and Disaster Recovery: Ensuring data is backed up and can be recovered in the cloud.
- Managed Cloud Security: Providing security services for cloud-based environments.
2.4. Additional Services
- IT Consulting: Providing strategic guidance on IT planning, budgeting, and technology adoption.
- Vendor Management: Managing relationships with third-party IT vendors.
- Project Management: Overseeing IT projects, such as software implementations and infrastructure upgrades.
- Disaster Recovery Planning: Developing and implementing plans to ensure business continuity in the event of a disaster.
2.5. What is the Role of RMM and PSA Tools in MSP Service Delivery?
MSPs leverage Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) and Professional Services Automation (PSA) tools to deliver efficient and effective services.
- RMM Software: Enables MSPs to remotely monitor and manage IT systems, such as networks, servers, desktops, and mobile devices.
- PSA Tools: Enable an MSP to manage an organization’s projects, billing, assets, and inventory.
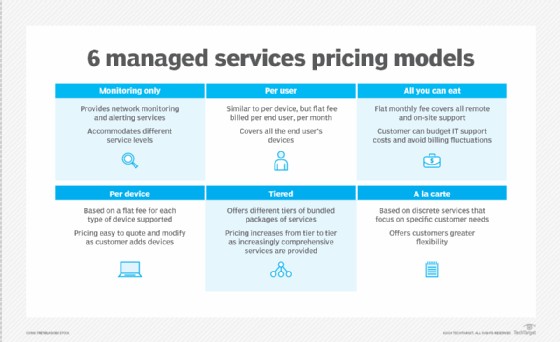
Six different pricing models for MSP services.
3. Why Should You Hire a Managed Service Provider?
Hiring an MSP offers numerous benefits, particularly for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) that may lack in-house IT expertise.
3.1. Cost Savings
- Reduced IT Costs: MSPs can help reduce IT costs by providing services at a fixed monthly rate, eliminating the need for expensive in-house IT staff.
- Predictable Budgeting: MSPs offer predictable budgeting, allowing businesses to allocate resources more effectively.
- Economies of Scale: MSPs leverage economies of scale to provide services at a lower cost than businesses could achieve on their own.
3.2. Improved Efficiency
- Focus on Core Business: MSPs allow businesses to focus on their core competencies by handling day-to-day IT tasks.
- Increased Productivity: MSPs can improve employee productivity by ensuring IT systems are running smoothly and providing timely support.
- Access to Expertise: MSPs provide access to specialized knowledge and experience in various IT domains.
3.3. Enhanced Security
- Proactive Security Measures: MSPs implement proactive security measures to protect against cyber threats.
- Compliance with Regulations: MSPs can help businesses comply with industry regulations, such as HIPAA and PCI DSS.
- Security Monitoring: MSPs provide 24/7 security monitoring to detect and respond to security incidents.
3.4. Scalability and Flexibility
- Scalable Solutions: MSPs offer scalable solutions that can adapt to the changing needs of a business.
- Flexible Service Options: MSPs provide flexible service options, allowing businesses to choose the services they need.
- Rapid Deployment: MSPs can quickly deploy new technologies and services to meet business demands.
3.5. What are Common Mistakes to Avoid When Hiring an MSP?
- Not defining clear service level agreements (SLAs): SLAs are a cornerstone of a good MSP relationship.
- Not validating the MSP’s expertise and reputation: Check references, read online reviews, and ask for case studies.
- Focusing too much on price: Cheapest isn’t always best, especially when it comes to IT.
4. How Do Managed Service Providers Work?
The engagement between an MSP and a client typically involves several key steps:
4.1. Assessment and Planning
- IT Assessment: The MSP conducts a thorough assessment of the client’s IT infrastructure, identifying strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
- Needs Analysis: The MSP works with the client to understand their business goals and IT requirements.
- Service Plan Development: The MSP develops a customized service plan that outlines the services to be provided, the service levels to be achieved, and the pricing structure.
4.2. Onboarding and Implementation
- System Setup: The MSP configures and deploys the necessary tools and technologies to monitor and manage the client’s IT infrastructure.
- Service Transition: The MSP seamlessly transitions IT management responsibilities from the client to the MSP.
- Documentation: The MSP documents all IT systems, configurations, and procedures.
4.3. Ongoing Management and Support
- Proactive Monitoring: The MSP continuously monitors IT systems for performance issues, security threats, and other potential problems.
- Incident Response: The MSP responds to incidents promptly and efficiently, minimizing downtime and disruption.
- Regular Reporting: The MSP provides regular reports on IT performance, security, and service levels.
- Service Reviews: The MSP conducts regular service reviews with the client to discuss performance, identify areas for improvement, and adjust the service plan as needed.
4.4. What are the Different Types of MSP Agreements?
- Managed Services Agreement (MSA): A comprehensive contract that outlines all the services provided by the MSP.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA): A document that defines the specific performance metrics and service levels.
- Business Associate Agreement (BAA): An agreement required when the MSP handles protected health information (PHI).
5. What Are the Different Types of Managed Service Providers?
MSPs can be categorized based on their focus, services offered, and target market:
5.1. By Focus
- Generalist MSPs: Offer a wide range of IT services to a broad range of clients.
- Specialist MSPs: Focus on a specific IT area, such as security, cloud services, or network management.
- Vertical MSPs: Specialize in serving clients in a particular industry, such as healthcare, finance, or manufacturing.
5.2. By Services Offered
- Monitoring-Only MSPs: Provide monitoring and alerting services for IT infrastructure.
- Remote Support MSPs: Offer remote troubleshooting and technical support services.
- Proactive Support MSPs: Perform preventative maintenance to prevent IT issues.
- Full-Service MSPs: Offer a comprehensive suite of IT services, including monitoring, support, security, and consulting.
5.3. By Target Market
- SMB MSPs: Focus on serving small and medium-sized businesses.
- Enterprise MSPs: Target larger organizations with complex IT requirements.
- Government MSPs: Specialize in serving government agencies.
5.4. What are the Latest Trends in the MSP Industry?
- Increased focus on cybersecurity: With cyber threats becoming more sophisticated, MSPs are placing greater emphasis on security services.
- Adoption of cloud-based solutions: MSPs are increasingly offering cloud-based services to help businesses migrate to and manage cloud environments.
- Automation and artificial intelligence: MSPs are leveraging automation and AI to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
6. What are the Challenges of Using Managed Service Providers?
While MSPs offer numerous benefits, there are also potential challenges to consider:
6.1. Dependence on Third-Party Organizations
Organizations that depend on an MSP to handle daily tasks may form a reliance on them. If the MSP fails to follow through on the SLA, the organization could experience system downtime.
6.2. Security Risks
- Data Breaches: MSPs have access to sensitive data, making them potential targets for cyberattacks.
- Compliance Issues: MSPs may not always be compliant with industry regulations, putting their clients at risk.
- Lack of Control: Clients may have limited control over the security practices of their MSP.
6.3. Communication Issues
- Response Times: It may take time for an MSP to respond to an issue.
- Language Barriers: Communication difficulties can arise if the MSP is located in a different country or region.
- Lack of Personalization: Clients may feel like they are just a number to their MSP.
6.4. Pricing Concerns
- Hidden Costs: MSPs may have hidden costs or fees that are not disclosed upfront.
- Upselling: An MSP may try and upsell an organization on technology or services they do not need.
- Lack of Transparency: Clients may not have visibility into how their MSP is spending their money.
6.5. What Questions Should You Ask a Potential MSP?
- What is your experience in our industry?
- What security measures do you have in place?
- What are your response times?
- What is your pricing structure?
- Can you provide references from current clients?
7. How Much Do Managed Service Providers Cost?
MSPs typically use one of the following pricing models:
- Per-Device Pricing: The MSP charges the customer a flat fee for each device it manages.
- Per-User Pricing: The MSP charges a flat fee for each user, accommodating users who use multiple devices.
- All-Inclusive Pricing: The MSP charges a flat fee for its IT infrastructure support and management services.
- Tiered Pricing: Organizations can choose the bundle of services that best fits their needs.
- Monitoring-Only Pricing: MSPs only offer monitoring and alerting services for an organization’s IT infrastructure.
In each of these pricing approaches, the customer pays the flat fee on a regularly scheduled basis, often monthly. Such pricing methods let MSPs sell services under a subscription model. This approach provides the MSP with a monthly recurring revenue (MRR) stream, in contrast to IT projects that tend to be one-time transactions.
MRR differs from other business models, as providers pursuing the break/fix model, for example, usually price their services on a time and materials basis. They generally bill an hourly rate for repairing a customer’s IT equipment and charge for parts or replacement gear.
7.1. What Factors Influence MSP Pricing?
- Scope of services: The more services included, the higher the price.
- Complexity of the IT environment: More complex environments require more resources and expertise, increasing costs.
- Service level agreements (SLAs): Higher SLAs with faster response times and guaranteed uptime will cost more.
- Location: MSPs in major metropolitan areas may charge more than those in smaller towns.
7.2. How Can You Negotiate a Good MSP Contract?
- Define your needs clearly: Know what services you need and what level of support you expect.
- Get multiple quotes: Compare pricing and services from different MSPs.
- Read the fine print: Understand all the terms and conditions of the contract before signing.
- Negotiate pricing and service levels: Don’t be afraid to ask for a better deal.
8. How to Choose the Right Managed Service Provider?
Choosing the right MSP is crucial for ensuring your IT needs are met effectively. Here are some key considerations:
8.1. Define Your Needs
- Assess Your IT Requirements: Identify your specific IT needs and challenges.
- Determine Your Budget: Establish a budget for managed services.
- Set Your Goals: Define your goals for outsourcing IT management.
8.2. Research Potential MSPs
- Online Research: Search for MSPs in your area and read online reviews.
- Ask for Referrals: Ask your business contacts for recommendations.
- Check Credentials: Verify the MSP’s certifications and experience.
8.3. Evaluate MSPs
- Meet with MSPs: Schedule meetings with potential MSPs to discuss your needs.
- Ask Questions: Ask MSPs about their services, pricing, and experience.
- Request Proposals: Request detailed proposals from MSPs outlining their services and pricing.
8.4. Make Your Decision
- Compare Proposals: Compare the proposals from different MSPs.
- Check References: Contact the MSP’s references to get feedback on their services.
- Negotiate Contract: Negotiate the terms of the contract with the MSP.
- Sign Contract: Sign the contract and begin the onboarding process.
8.5. What Are the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to Track When Working with an MSP?
- Uptime: The percentage of time that IT systems are operational.
- Response time: The time it takes for the MSP to respond to a support request.
- Resolution time: The time it takes for the MSP to resolve an IT issue.
- Customer satisfaction: A measure of how satisfied users are with the MSP’s services.
- Security incidents: The number of security breaches or incidents that occur.
9. Future of Managed Service Providers
The MSP industry is expected to continue to grow in the coming years, driven by the increasing complexity of IT environments and the growing need for cybersecurity.
9.1. Emerging Technologies
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): MSPs are leveraging AI to automate tasks, improve security, and enhance customer service.
- Internet of Things (IoT): MSPs are managing and securing IoT devices and networks.
- Edge Computing: MSPs are providing edge computing solutions to support low-latency applications.
- Blockchain: MSPs are using blockchain to enhance security and data integrity.
9.2. Evolving Business Models
- Co-Managed IT: MSPs are partnering with in-house IT teams to provide specialized expertise and support.
- Cloud-First MSPs: MSPs are focusing on providing cloud-based services and solutions.
- Security-Focused MSPs: MSPs are specializing in cybersecurity services.
9.3. Impact on Businesses
- Increased Agility: MSPs are enabling businesses to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
- Improved Innovation: MSPs are helping businesses adopt new technologies and innovate faster.
- Competitive Advantage: MSPs are providing businesses with a competitive advantage by improving their IT performance and security.
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand that navigating the world of IT can be daunting. That’s why we’re here to provide you with clear, concise answers to all your questions. Whether you’re wondering about cloud computing, data security, or the benefits of managed services, our platform offers a wealth of information to help you make informed decisions.
10. FAQ about Managed Service Providers
Here are some frequently asked questions about managed service providers:
10.1. What is a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP)?
A Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP) is a type of MSP that specializes in providing cybersecurity services. MSSPs offer a range of services, including:
- Managed Firewall: Configuring and maintaining firewalls to prevent unauthorized access to the network.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Monitoring network traffic for malicious activity and taking steps to prevent intrusions.
- Security Audits and Compliance: Conducting regular security assessments and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Collecting and analyzing security data to identify and respond to security incidents.
10.2. How Do I Know If I Need a Managed Service Provider?
Consider hiring an MSP if you:
- Lack in-house IT expertise.
- Are struggling to keep up with the demands of IT management.
- Are concerned about security threats.
- Want to reduce IT costs.
- Want to focus on your core business.
10.3. What are the Benefits of Using a Local MSP vs. a National MSP?
| Feature | Local MSP | National MSP |
|---|---|---|
| Personalization | More personalized service and a better understanding of local business needs | Less personalized service, may not be as familiar with local business conditions |
| Response Time | Potentially faster response times due to proximity | Response times may be slower due to geographical distance |
| Relationships | Easier to build strong relationships with the MSP team | May be more difficult to build strong relationships due to less frequent in-person interactions |
| Pricing | Pricing may be more competitive due to lower overhead costs | Pricing may be higher due to larger overhead costs and a more complex organizational structure |
| Expertise | May have less specialized expertise than a national MSP | Typically has a wider range of specialized expertise and resources |
| Scalability | May not be able to scale as quickly as a national MSP | Can typically scale more quickly to meet changing business needs |
10.4. What is the Difference Between Managed Services and Cloud Services?
Managed services refer to the outsourcing of IT management responsibilities to a third-party provider, while cloud services refer to the delivery of IT resources over the internet. MSPs often provide managed services for cloud-based environments.
10.5. How Can I Ensure My Data is Secure with a Managed Service Provider?
- Choose a reputable MSP with a strong security track record.
- Review the MSP’s security policies and procedures.
- Ensure the MSP has the necessary security certifications.
- Implement strong data encryption.
- Regularly audit the MSP’s security practices.
- Request that the MSP undergo regular security audits by a third party.
- Ensure that the MSP has a comprehensive data breach response plan in place.
- Implement a data loss prevention (DLP) solution to protect sensitive data.
- Regularly back up your data to a secure location.
- Implement multi-factor authentication for all user accounts.
- Provide security awareness training to your employees.
- Stay informed about the latest security threats and vulnerabilities.
- Maintain a strong security posture by implementing a layered security approach.
In conclusion, a managed service provider can be a valuable asset for businesses of all sizes, offering cost savings, improved efficiency, enhanced security, and scalability. By understanding the different types of MSPs, the services they offer, and the challenges of using them, you can make an informed decision about whether an MSP is right for your business.
Ready to explore how a managed service provider can transform your IT landscape? Do you have more questions about MSPs or other IT-related topics? Visit what.edu.vn today to ask your questions and receive expert answers from our community of knowledgeable professionals. Your path to IT clarity starts here. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States or Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890.