What Is An Oracle, and how does it bridge the gap between blockchains and the real world? WHAT.EDU.VN provides a simple solution for understanding this technology and its critical role in decentralized applications, answering your questions and exploring off-chain data integration. Discover the definition of oracles, explore its various types, and learn how it enhances smart contract capabilities through price feeds and data validation, paving the way for advanced decentralized finance solutions and real-world data application.
1. Understanding the Core: What Is an Oracle?
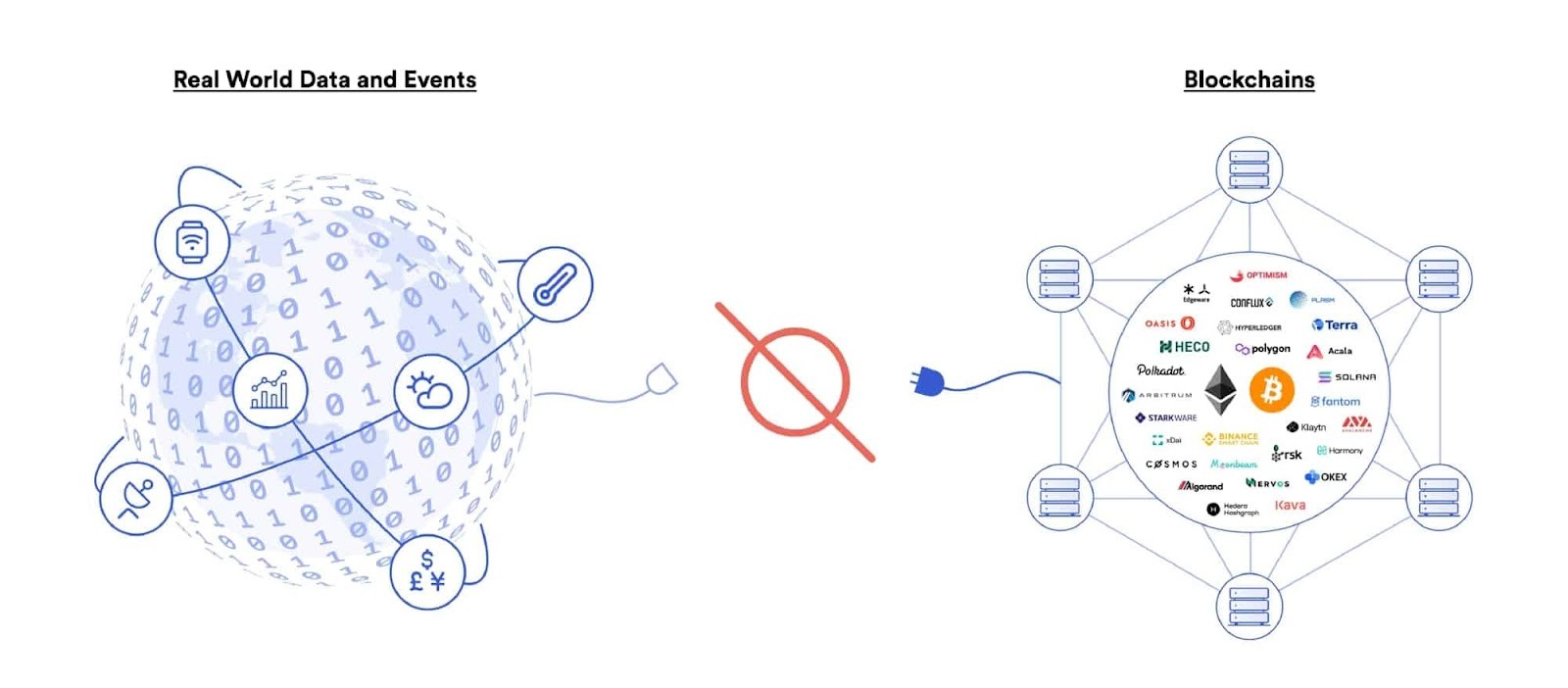
An oracle acts as a vital bridge connecting blockchains to the outside world, also called off-chain. Blockchains, by design, are isolated environments, unable to directly access data or systems external to their network. This isolation ensures security and consensus but limits their ability to interact with real-world events and data. Oracles solve this problem by securely fetching external data and transmitting it to the blockchain, enabling smart contracts to react to real-world information. This integration is essential for expanding the capabilities of smart contracts and supporting a wide range of decentralized applications.
2. The Oracle Problem: Bridging Blockchains to Reality
The “oracle problem” refers to the inherent limitation of smart contracts: their inability to natively interact with external data and systems. Blockchains maintain security by remaining isolated from external systems. This isolation ensures transaction validity, prevents double-spending, and mitigates downtime. However, this also means smart contracts cannot directly access real-world data, such as prices, weather, or event outcomes. Oracles act as a secure middleware, bridging this gap by fetching off-chain data and delivering it on-chain for smart contracts to use. This bridge is necessary because most smart contract applications, especially in DeFi, require real-world data to function effectively.
Blockchains cannot connect to real-world data and events on their own.
3. Why Oracles Matter: Expanding Smart Contract Capabilities
Oracles are essential because they expand the types of digital agreements that blockchains can support. By providing a universal gateway to off-chain resources, oracles enable smart contracts to interact with the real world, enhancing their functionality and applicability.
Major industries benefit from combining oracles and smart contracts:
- Finance: Accessing asset prices
- Insurance: Utilizing weather information
- Gaming: Generating randomness
- Supply Chain: Integrating IoT sensor data
- Government: Verifying identities
4. Centralized vs. Decentralized Oracles: Choosing the Right Approach
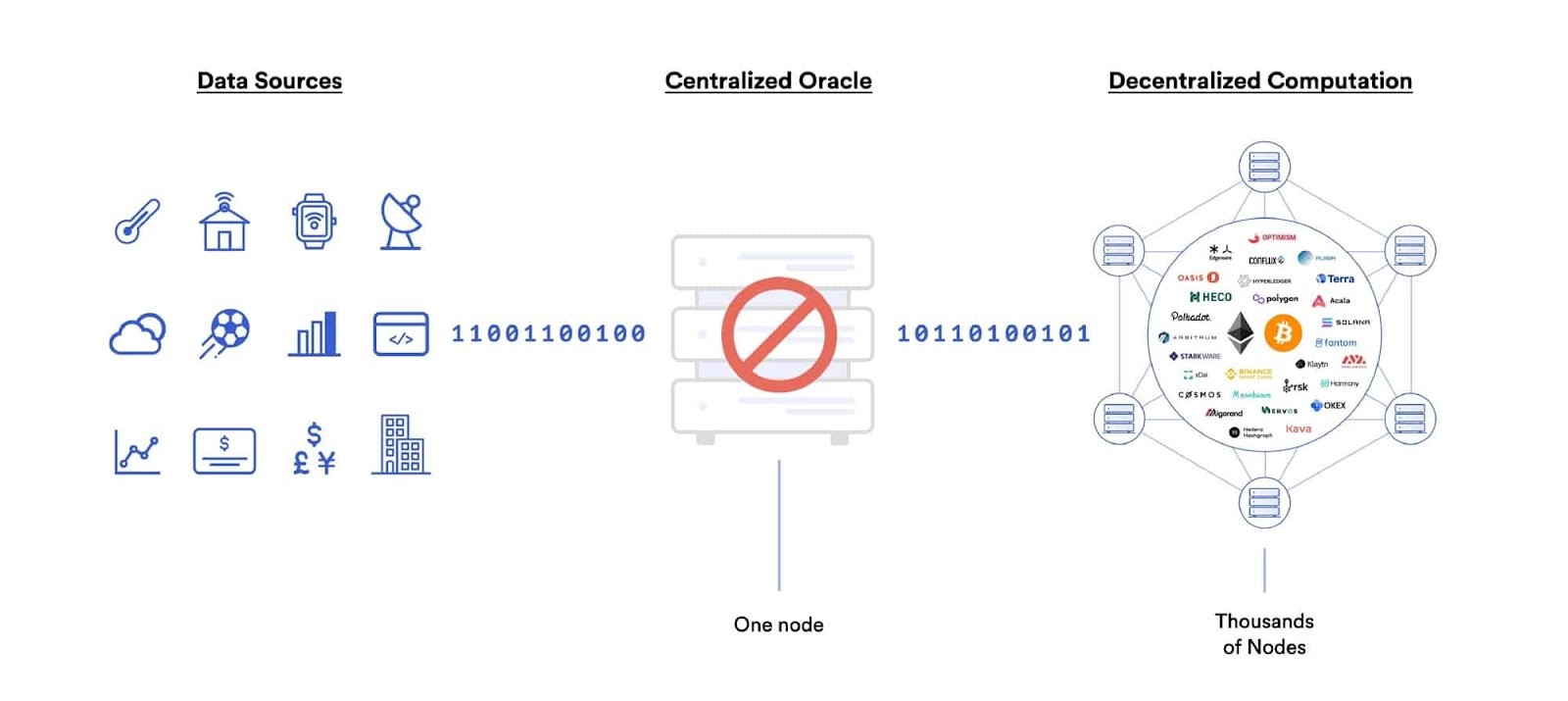
- Centralized Oracles: Involve a single entity providing data to a smart contract, creating a single point of failure. If the oracle goes offline or is corrupted, the smart contract will not have access to data or may execute improperly.
- Decentralized Oracles (DONs): Combine multiple independent oracle node operators and data sources to achieve end-to-end decentralization. DONs eliminate single points of failure, ensuring data accuracy and reliability.
Centralized oracles are a single point of failure
5. Decentralized Oracle Networks (DONs): Enhancing Security and Reliability
Decentralized Oracle Networks (DONs) are crucial for preventing data manipulation, inaccuracies, and downtime. By combining multiple independent oracle node operators and data sources, DONs establish end-to-end decentralization.
Benefits of DONs:
- Data Accuracy: Aggregating data from multiple sources ensures higher accuracy.
- Reliability: Eliminating single points of failure prevents downtime.
- Security: Protecting against data manipulation and corruption.
6. Exploring Hybrid Smart Contracts: Combining On-Chain and Off-Chain Resources
Decentralized Oracle Networks (DONs) enable the creation of hybrid smart contracts, where on-chain code and off-chain infrastructure are combined to support advanced decentralized applications (dApps) that react to real-world events and interoperate with traditional systems. This approach is essential for building applications that require both the security of a blockchain and access to real-world data.
7. Chainlink Price Feeds: A Practical Example of Decentralization
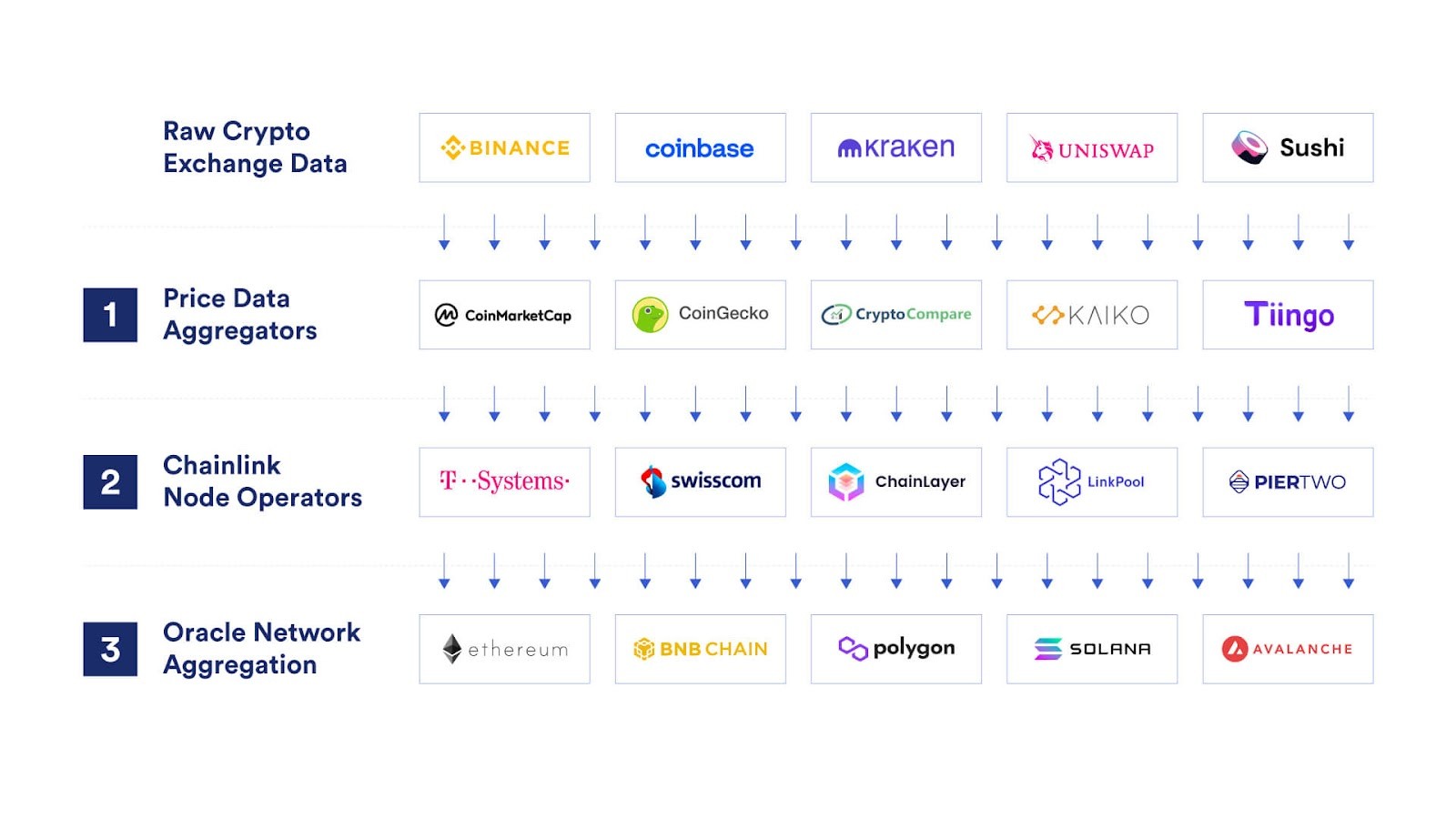
Many services, such as Chainlink Price Feeds, incorporate three layers of decentralization:
- Data Source Level: Aggregating data from multiple independent sources.
- Node Operator Level: Using multiple independent node operators.
- Oracle Network Level: Decentralizing the network itself.
Chainlink Price Feeds secure billions of dollars across smart contract ecosystems, ensuring smart contracts can safely rely on data inputs during their execution.
Chainlink Price Feeds deploy three layers of decentralized aggregation
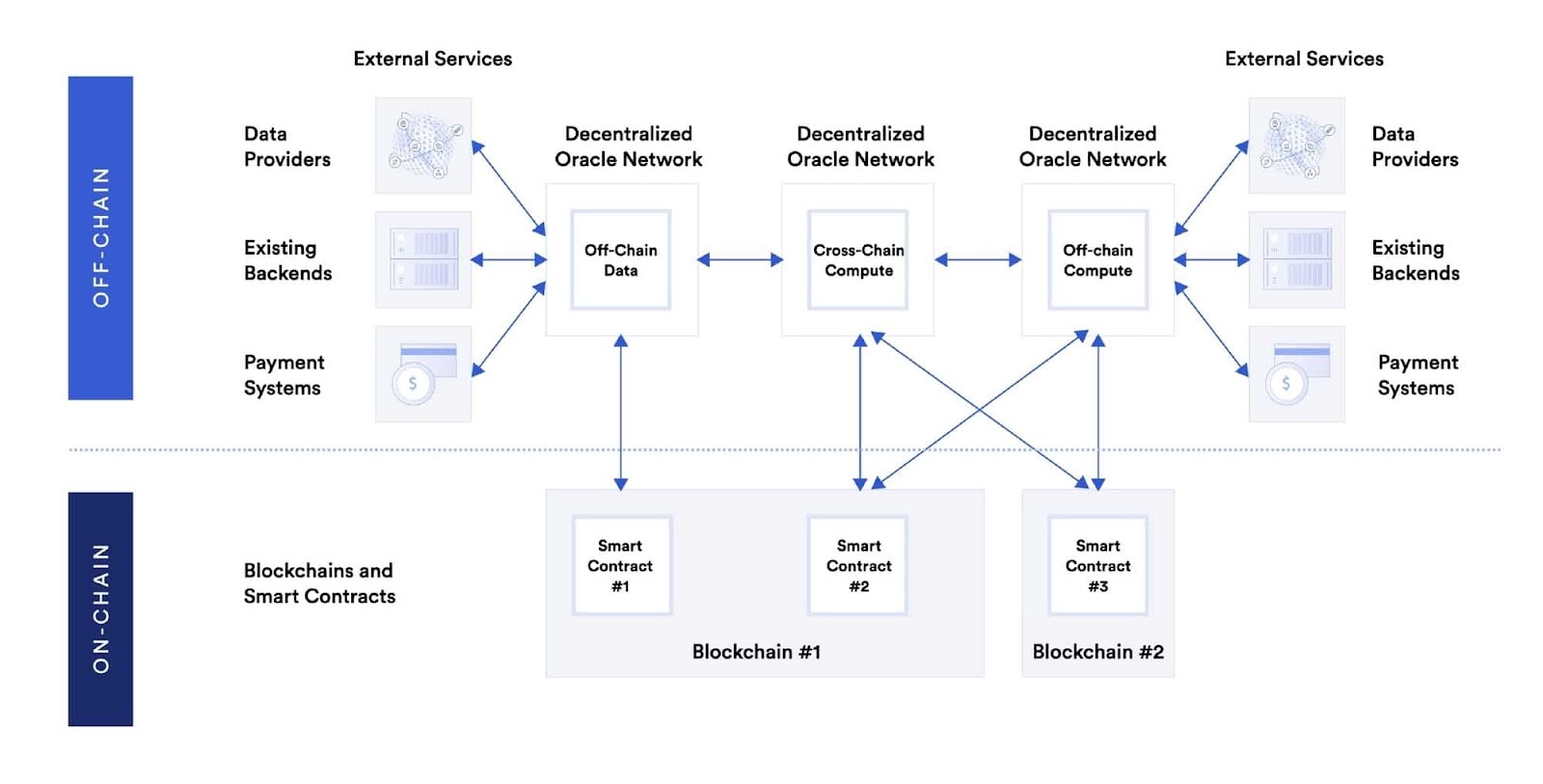
8. Types of Blockchain Oracles: Adapting to Different Needs
Given the wide range of off-chain resources, blockchain oracles come in many forms. Each type involves some combination of fetching, validating, computing upon, and delivering data to a destination.
8.1. Input Oracles
Fetch data from the real world (off-chain) and deliver it onto a blockchain network for smart contract consumption. Used to power Chainlink Price Feeds, providing DeFi smart contracts with on-chain access to financial market data.
8.2. Output Oracles
Allow smart contracts to send commands to off-chain systems, triggering them to execute certain actions. Examples include informing a banking network to make a payment or pinging an IoT system to unlock a car door once the on-chain rental payment is made.
8.3. Cross-Chain Oracles
Read and write information between different blockchains, enabling interoperability for moving data and assets between blockchains. Useful for using data on one blockchain to trigger an action on another or bridging assets cross-chain so they can be used outside the native blockchain.
8.4. Compute-Enabled Oracles
Use secure off-chain computation to provide decentralized services that are impractical to do on-chain due to technical, legal, or financial constraints. This includes using Chainlink Automation to trigger the running of smart contracts when predefined events take place or using a verifiable randomness function to provide a tamper-proof and provably fair source of randomness to smart contracts.
Different types of oracles enable the creation of hybrid smart contracts
9. Oracle Reputation: Ensuring Reliability and Accuracy
Reputation is key to choosing between oracle service providers. Blockchain oracle systems allow users and developers to monitor and filter oracles based on parameters they deem important. Since oracles sign and deliver their data onto an immutable public blockchain ledger, their historical performance can be analyzed and presented through interactive dashboards.
Reputation frameworks provide transparency into the accuracy and reliability of each oracle network and individual oracle node operator. Users can then make informed decisions about which oracles they want to service their smart contracts.
10. Blockchain Oracle Use Cases: Real-World Applications
Smart contract developers use oracles to build more advanced decentralized applications across a wide range of use cases. Here are some of the most common applications:
10.1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi relies heavily on price oracles to access financial data about assets and markets. Decentralized money markets use price oracles to determine borrowing capacity and check for undercollateralization. Synthetic asset platforms use price oracles to peg the value of tokens to real-world assets. Automated market makers (AMMs) use price oracles to concentrate liquidity and improve capital efficiency.
10.2. Dynamic NFTs and Gaming
Oracles enable non-financial use cases, such as dynamic NFTs that change based on external events like time or weather. Compute oracles generate verifiable randomness for assigning randomized traits to NFTs or selecting random winners in NFT drops. On-chain gaming applications use verifiable randomness to create engaging gameplay experiences like random loot boxes or randomized matchmaking.
10.3. Insurance
Insurance smart contracts use input oracles to verify the occurrence of insurable events during claims processing, accessing physical sensors, web APIs, satellite imagery, and legal data. Output oracles provide a way to make payouts on claims using other blockchains or traditional payment networks.
10.4. Enterprise
Cross-chain oracles offer enterprises a secure blockchain middleware that allows them to connect their backend systems to any blockchain network. This enables enterprises to read/write to any blockchain and perform complex logic on how to deploy assets and data across chains.
10.5. Sustainability
Hybrid smart contracts are advancing environmental sustainability by creating better incentives for green practices through advanced verification techniques. Oracles supply smart contracts with environmental data from sensors, satellite imagery, and advanced ML computation, allowing smart contracts to dispense rewards to people practicing reforestation or engaging in conscious consumption. Oracles are also supporting many new forms of carbon credits to offset the impacts of climate change.
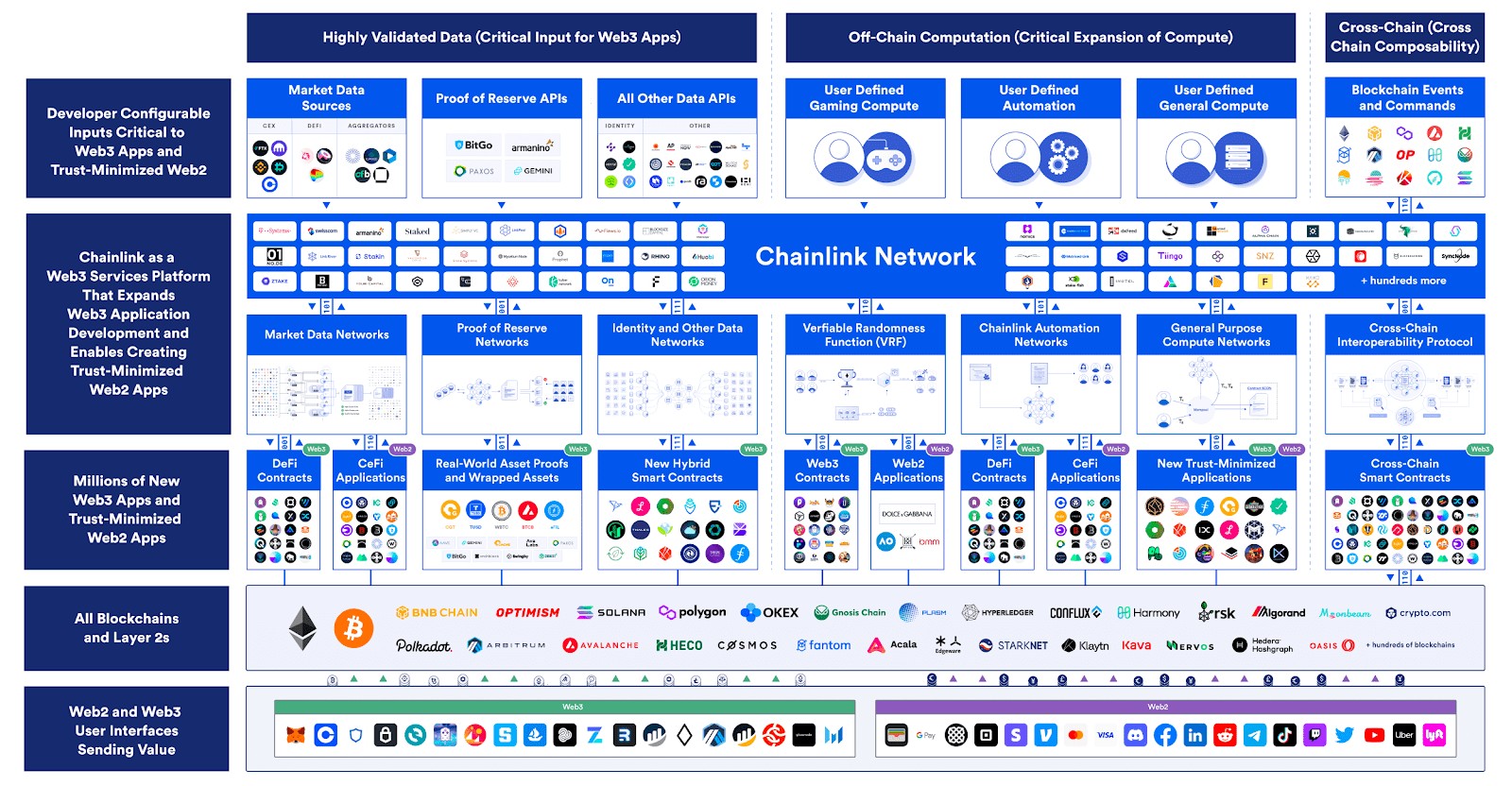
Chainlink’s growing collection of decentralized oracle services
11. The Future of Oracles: Redefining Value Exchange
Oracles extend the capabilities of blockchain networks by providing access to the external resources required to harness useful and advanced hybrid smart contract use cases beyond simple tokenization. Oracle-powered hybrid smart contracts are redefining the way society exchanges value and enforces contractual agreements.
12. FAQs About Oracles
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the main function of an oracle in blockchain? | An oracle’s main function is to bridge the gap between a blockchain and the real world by providing external data to smart contracts. |
| Why are oracles necessary for smart contracts? | Oracles are necessary because smart contracts cannot inherently access off-chain data. They enable smart contracts to interact with real-world events and data, expanding their functionality. |
| What are the risks associated with using centralized oracles? | Centralized oracles introduce a single point of failure, making smart contracts vulnerable to data manipulation, inaccuracies, and downtime. If the oracle is compromised, the smart contract may execute improperly. |
| How do decentralized oracles enhance security? | Decentralized oracles combine multiple independent node operators and data sources, eliminating single points of failure and ensuring data accuracy and reliability. This multi-layered approach enhances the security of smart contracts. |
| What types of data can oracles provide to smart contracts? | Oracles can provide various types of data, including price feeds, weather information, event outcomes, IoT sensor data, and verifiable randomness. This data enables smart contracts to support a wide range of use cases. |
| What is a hybrid smart contract? | A hybrid smart contract combines on-chain code with off-chain infrastructure to support advanced decentralized applications. Oracles enable the creation of hybrid smart contracts by providing the necessary external data and computation. |
| How do cross-chain oracles facilitate interoperability? | Cross-chain oracles read and write information between different blockchains, enabling the transfer of data and assets. This facilitates interoperability and allows smart contracts to interact with multiple blockchain networks. |
| What role do compute-enabled oracles play in blockchain? | Compute-enabled oracles use secure off-chain computation to provide decentralized services that are impractical to perform on-chain. This includes verifiable randomness, data privacy, and automated execution of smart contracts. |
| How is oracle reputation assessed? | Oracle reputation is assessed based on historical performance, accuracy, reliability, and transparency. Reputation frameworks provide users with the ability to monitor and filter oracles based on these parameters. |
| What are some real-world use cases for oracles? | Real-world use cases for oracles include decentralized finance (DeFi), dynamic NFTs, gaming, insurance, enterprise solutions, and sustainability initiatives. Oracles enable smart contracts to interact with real-world data, enhancing their functionality and applicability across various industries. |
| How do oracles support decentralized finance (DeFi)? | Oracles provide DeFi applications with accurate and reliable price feeds, enabling functions like lending, borrowing, and trading. They ensure that smart contracts have the data needed to execute financial transactions securely and efficiently. |
| In what ways do oracles enhance sustainability efforts? | Oracles supply smart contracts with environmental data from sensors, satellite imagery, and advanced machine learning, enabling the automation of incentives for green practices. This helps to verify and reward actions that support sustainability goals. |
| Can oracles provide verifiable randomness for blockchain games? | Yes, compute-enabled oracles can provide verifiable randomness, ensuring that the outcomes of blockchain games are fair and unpredictable. This enhances the integrity and user experience of on-chain gaming applications. |
| How do oracles assist in the execution of insurance smart contracts? | Oracles verify the occurrence of insurable events by accessing external data sources, ensuring that claims are processed accurately and efficiently. They also facilitate payouts through other blockchains or traditional payment networks. |
| What are the key benefits of using decentralized oracle networks? | Decentralized oracle networks (DONs) offer enhanced security, reliability, and data accuracy compared to centralized oracles. By distributing the data source and validation process across multiple independent entities, DONs eliminate single points of failure and improve the overall robustness of smart contracts. |
13. Ask Your Questions on WHAT.EDU.VN
Still have questions about oracles or other blockchain technologies? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN to ask your questions and receive free, expert answers from our community of knowledgeable professionals. Don’t let confusion hold you back – empower yourself with the information you need to succeed.
Call to Action
Ready to dive deeper into the world of oracles and decentralized technology? Have questions about a specific project or concept? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your questions for free. Our community is here to help you understand the complexities of blockchain and smart contracts, ensuring you have the knowledge you need to thrive.
Contact Us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Let what.edu.vn be your guide to mastering oracles and the exciting world of decentralized technology!