Are you curious about the function of a catalytic converter in your vehicle? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we simplify complex topics like this, offering clear explanations and expert insights. A catalytic converter is an essential component of your car’s exhaust system, playing a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions. Let’s explore its purpose, function, and significance in maintaining air quality. With this comprehensive guide, you’ll gain a solid understanding of emission control, exhaust system components, and automotive pollution reduction.
1. What Is a Catalytic Converter?
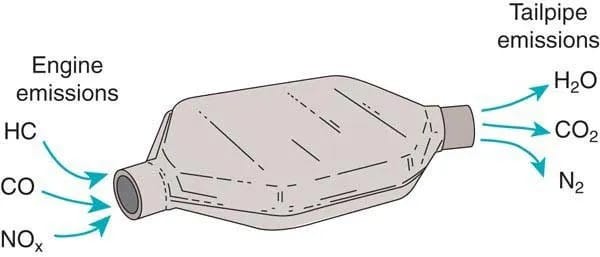
A catalytic converter is a key component in a vehicle’s exhaust system designed to minimize the emission of toxic pollutants. It achieves this by transforming hazardous combustion gases into less harmful substances, such as water vapor and carbon dioxide. This conversion occurs through chemical reactions prompted by exposing the fumes to specific chemicals and metals within the converter.
The primary role of a catalytic converter is to reduce the amount of air pollution caused by vehicles. It’s designed to convert harmful gases like hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances. Understanding the importance of this device can help you appreciate its role in environmental protection.
2. What Does the Catalytic Converter Do?
The primary purpose of a catalytic converter is to use a catalyst-filled chamber to convert harmful compounds from an engine’s emissions into safer gases like steam. The converter splits up unsafe molecules in the gases produced by a car before they are released into the atmosphere.
Located on the underside of a vehicle, the catalytic converter resembles a large metal box with two pipes extending from it. It utilizes these pipes and the catalyst to render the gases safe for expulsion. Gases enter through the “input” pipe connected to the vehicle’s engine and pass over the catalyst. This process triggers a chemical reaction that breaks down the pollutants. The resulting, less harmful gases then exit through the second pipe, or “output,” which connects to the car’s tailpipe.
2.1. Core Purpose of Catalytic Converters
The main goal of catalytic converters in automotive systems is to lower the emission of harmful pollutants from an engine’s exhaust gases, thereby making them more environmentally friendly. The effectiveness and reliability of these converters are crucial not only for maintaining vehicle performance but also for contributing to efforts aimed at reducing air pollution.
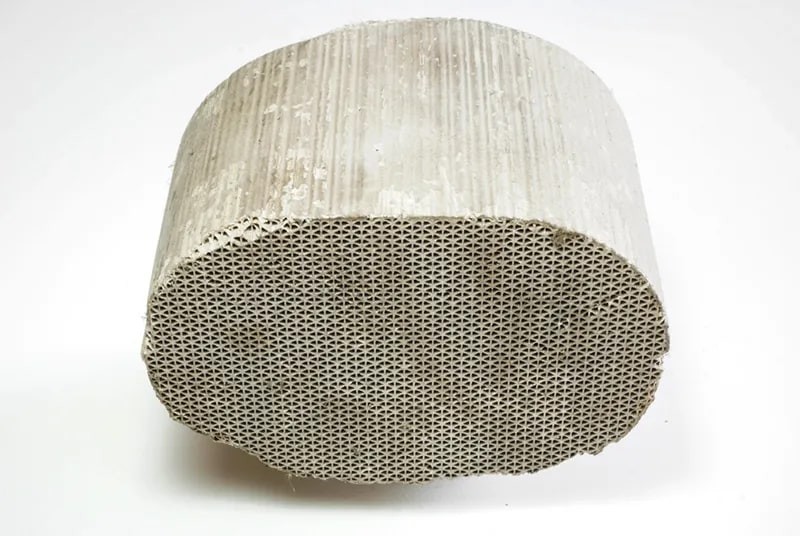
3. What Is Inside a Catalytic Converter?
The catalyst inside a catalytic converter is typically made from platinum or similar metals like rhodium or palladium. Gases flow through a ceramic honeycomb structure within the converter’s housing. This structure is lined with metals that perform specific jobs to reduce emissions. There are two main types of catalysts that may be found in a car:
- Reduction Catalysts: These help reduce nitrogen oxide pollution by removing oxygen. Nitrogen oxides are broken down into nitrogen and oxygen gases, which are harmless on their own.
- Oxidation Catalysts: These are used to change carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide by adding oxygen in an opposite process.
An oxygen (O2) sensor is also located near the catalytic converter, which tells the car’s electronic control unit (ECU) how much oxygen is present in the exhaust gases. This helps the vehicle run on a more efficient air/fuel ratio, ensuring the engine provides the converter with enough oxygen to complete the oxidation process.
4. What Are the Different Types of Catalytic Converters?
As mentioned earlier, there are two primary types of catalysts – reduction and oxidation – used within an exhaust system to manage specific gases.
Depending on the vehicle’s year and type of catalytic converter, a reduction catalyst may not always be present. Here are the two main types of car converters:
- Two-Way: Two-way catalytic converters were used in vehicles in the United States until 1981. They only feature oxidation catalysts, which help convert carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide. Hydrocarbons (unburned and partially burned fuel) are changed to carbon dioxide and water.
- Three-Way: Since 1981, the three-way catalytic converter has been standard. It performs the same functions as the two-way converter but includes a reduction catalyst. As mentioned, this catalyst is used to convert nitrogen oxides to nitrogen and oxygen gases.
Diesel engines use two-way catalysts, and the converters are specifically designed to work with diesel exhausts. The converters for these types of engines target particulates known as soluble organic fractions, which are made from hydrocarbons bound to soot.
5. Who Invented the Catalytic Converter?
The history of the catalytic converter dates back to the end of the 19th century, when some prototypes were developed in France. In the mid-1950s, Eugene Houdry, a French mechanical engineer, received a patent for his research to develop catalytic converters for gasoline engines.
Houdry’s development of the catalytic converter stemmed from his concerns about the impact of smokestack and automobile exhaust on air pollution. Having seen the results of studies in Los Angeles, he began working on converters for smokestacks.
Catalytic converters were further developed after emissions control regulations began in the early 1960s. The first production catalytic converter was created in 1973 at Engelhard Corporation, and widespread use of the part began around 1975.
6. How Can You Prevent Catalytic Converter Theft?
Catalytic converters are often targeted by thieves because they contain valuable precious metals. Thefts are more common on vehicles with higher ground clearance, making the part easier to access.
Regardless of your vehicle type, here are some steps to help prevent theft:
- Park in well-lit areas close to building entrances if a secure garage isn’t available.
- Weld the catalytic converter to the vehicle frame, making it harder to remove.
- Consider buying an aftermarket part, such as a metal cage, that can be installed to cover the converter.
- Install a car alarm with a vibration alert sensor.
- Engrave your vehicle identification number (VIN) on the converter to make selling the part more difficult and alert you if it’s stolen.
7. What Are the Signs of Catalytic Converter Issues?
What happens when a catalytic converter fails? Given its role in a vehicle’s exhaust system, several symptoms can arise when it begins to wear out.
Some signs to watch out for include:
- Declining Fuel Efficiency: A clogged catalytic converter can reduce airflow through your engine. To compensate, your engine might burn more fuel, leading to a noticeable drop in fuel efficiency.
- Check Engine Light: A check engine light can indicate various issues. Cars manufactured after 1996 have a diagnostic system that tests the catalytic converter. If the converter malfunctions, the air-to-fuel ratio sensors might trigger the warning light.
- Rotten Egg Smell: Internal damage to the catalytic converter can hinder its ability to convert exhaust gases, resulting in a sulfuric “rotten egg” smell.
- Engine Starting Issues: Exhaust gases must escape. A clogged catalytic converter can prevent this, increasing exhaust pressure and causing your car to sputter or stall when starting.
- Poor Acceleration: Trapped exhaust and increased pressure from a clogged converter can cause acceleration problems. You might notice jerking or stalling when trying to accelerate.
- Failed Emissions Test: Many states require regular vehicle emissions testing, and a failing grade could indicate a problem with your catalytic converter, possibly accompanied by the symptoms mentioned above.
8. Catalytic Converter FAQs
8.1. Why Do People Steal Catalytic Converters?
Catalytic converters are targeted for theft due to the valuable precious metals they contain. Typically, they include platinum, palladium, and rhodium, which can be sold to metal dealers.
8.2. What’s Inside Catalytic Converters?
A standard catalytic converter typically contains 3 to 7 grams of platinum, 2 to 7 grams of palladium, and 1 to 2 grams of rhodium.
8.3. How Much Is a Catalytic Converter Worth?
A recycler will pay between $50 and $250 for a catalytic converter, with some from hybrid vehicles fetching $800 to $1,500. Keep in mind that replacing a stolen catalytic converter can cost around $2,000, highlighting the importance of taking preventive measures.
8.4. How Long Does a Catalytic Converter Typically Last?
A catalytic converter typically lasts between 70,000 and 100,000 miles. However, its lifespan can vary based on vehicle type, usage patterns, and maintenance habits.
8.5. Can a Catalytic Converter Be Cleaned or Repaired?
Catalytic converters can often be cleaned, but repairing them is generally not feasible due to their construction and materials. Cleaning involves using specific chemical treatments to remove carbon and other deposits.
This process can restore some functionality, especially if the converter isn’t heavily damaged. However, physical damage or severe clogging, often caused by internal melting or breakdown, usually requires replacement of the catalytic converter.
Understanding catalytic converters is crucial for vehicle maintenance and environmental stewardship. Have more questions about your car or other topics? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN for fast, free answers to all your questions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Catalytic Converters
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the main function of a catalytic converter in a car? | Converts harmful pollutants from the engine’s exhaust into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide and water. |
| Where is the catalytic converter located in a vehicle? | Typically located underneath the vehicle, part of the exhaust system between the engine and the tailpipe. |
| What precious metals are typically found inside a catalytic converter? | Platinum, palladium, and rhodium are the primary precious metals used due to their catalytic properties. |
| How does a catalytic converter help reduce air pollution? | By facilitating chemical reactions that convert harmful gases into less harmful ones before they are released into the atmosphere. |
| What are the symptoms of a failing catalytic converter? | Reduced fuel efficiency, check engine light, rotten egg smell, issues starting the engine, and poor acceleration. |
| How can I prevent my catalytic converter from being stolen? | Park in well-lit areas, weld the converter to the frame, install a protective cage, and engrave the VIN on the converter. |
| How long does a catalytic converter usually last? | Typically lasts between 70,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on vehicle usage and maintenance. |
| Is it possible to clean a catalytic converter? | Yes, cleaning is possible, but repair is generally not feasible. Cleaning can remove deposits and restore some functionality if the damage is not severe. |
| What is the difference between a two-way and a three-way converter? | Two-way converters oxidize carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons, while three-way converters also reduce nitrogen oxides. |
| Why are catalytic converters more frequently stolen from hybrid cars? | Hybrid cars’ catalytic converters are often more valuable due to less frequent use, which means they contain a higher concentration of precious metals. |

For all your questions, remember that WHAT.EDU.VN is here to provide fast, free, and reliable answers.
Have questions about catalytic converters or any other topic? Don’t struggle to find answers alone. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today, where you can ask questions for free and receive prompt, reliable responses from knowledgeable experts. Our platform is designed to provide quick and easy access to information, helping you understand complex topics with ease. Whether it’s about automotive technology, environmental science, or any other subject, WHAT.EDU.VN is your go-to resource. Don’t hesitate—ask your question now and experience the convenience of free expert advice. Visit what.edu.vn at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or reach us via WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Your answers are just a question away!