Consciousness, the essence of your experiences, from the taste of your morning coffee to the sting of a paper cut, has puzzled thinkers for centuries, but WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help you understand it better. It encompasses every sensation, thought, and emotion you experience. Let’s explore the scientific quest to understand consciousness, its neural basis, and the leading theories attempting to demystify this fundamental aspect of existence, unlocking a deeper understanding of subjective experience and the neural correlates of consciousness.
1. What Is Consciousness and Why Is It So Difficult to Define?
Consciousness is the state of being aware of oneself and one’s surroundings, but this simple definition belies its complexity. The difficulty in defining consciousness stems from its subjective nature; it’s a personal experience that is hard to quantify or objectively measure. Each individual’s conscious experience, often referred to as qualia, is unique and difficult to convey to others, making a universal definition elusive. This is why understanding the nature of awareness remains one of the greatest challenges in science and philosophy, with many still questioning, what is the nature of consciousness?
2. What Are Qualia, and How Do They Relate to Consciousness?
Qualia are the subjective, qualitative properties of experiences. They are the ‘what it is like’ aspects of consciousness. Examples include the redness of red, the pain of a headache, or the taste of chocolate. Qualia are inherently personal and cannot be fully captured by physical descriptions or objective measurements. The existence and nature of qualia are central to many debates about consciousness, with some arguing that they are essential to understanding conscious experience, while others deny their existence or importance.
3. What Are the Neuronal Correlates of Consciousness (NCC)?
The neuronal correlates of consciousness (NCC) are the minimal set of neuronal mechanisms jointly sufficient for any specific conscious experience. In simpler terms, NCC refers to the specific brain activity that directly corresponds to a conscious perception or experience. Identifying the NCC is a key goal in consciousness research, as it could reveal the neural basis of subjective awareness.
3.1 What Brain Regions Are Most Closely Associated with Consciousness?
Research suggests that the posterior hot zone, encompassing the parietal, occipital, and temporal regions of the cerebral cortex, plays a significant role in generating conscious experiences. These areas are involved in processing sensory information, such as vision, hearing, and touch.
3.1.1 Why Are These Regions More Important Than Others, Like the Cerebellum?
The cerebellum, despite containing a large number of neurons, appears to be less relevant to conscious experience due to its uniform, parallel circuitry and lack of complex feedback loops. Unlike the cerebral cortex, the cerebellum operates primarily as a feed-forward system with limited interaction between its computational modules. This suggests that complex feedback and integration of information are crucial for consciousness.
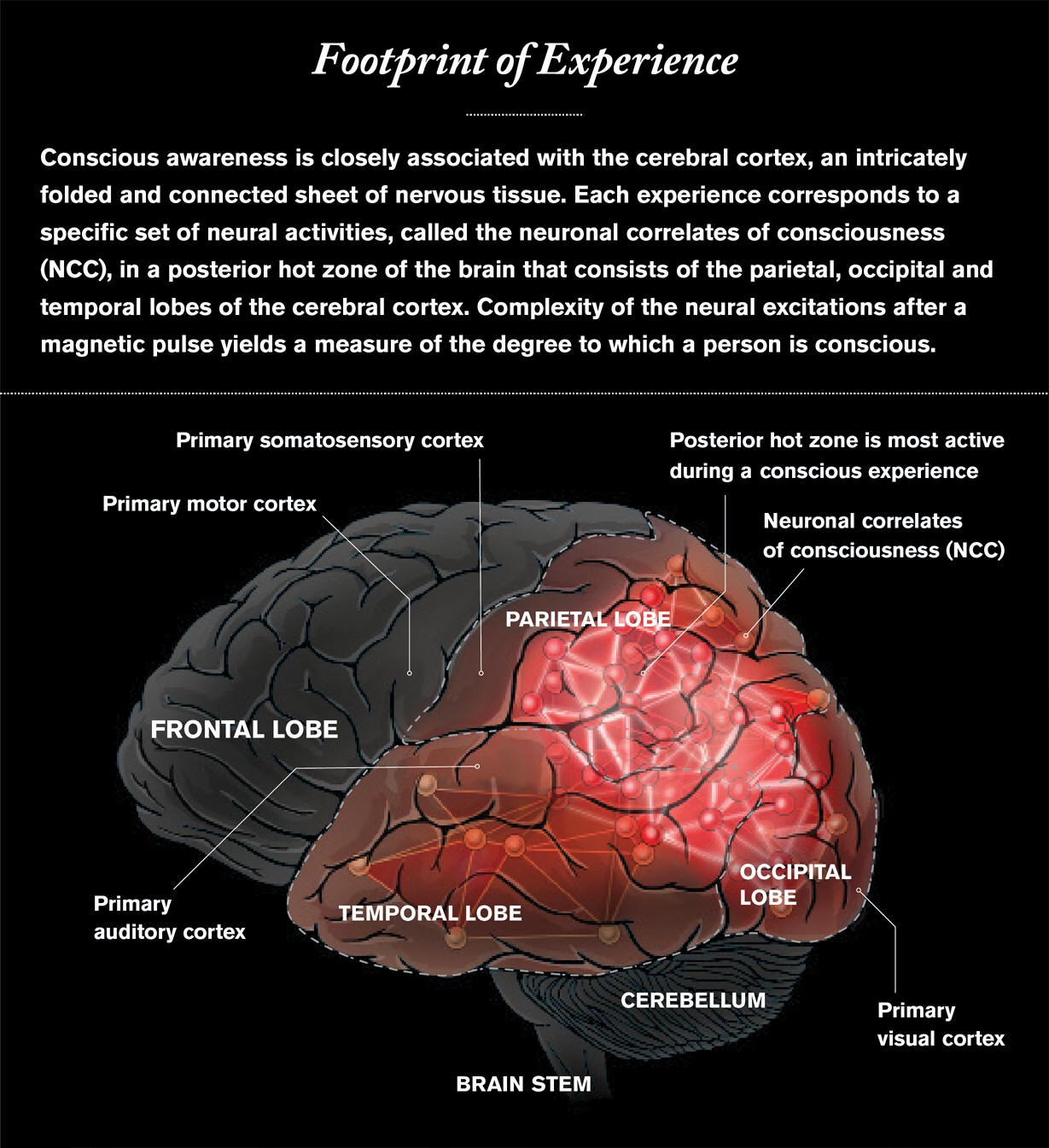 Brain regions associated with consciousness
Brain regions associated with consciousness
4. How Do Brain Injuries and Lesions Affect Consciousness?
Brain injuries and lesions can provide valuable insights into the neural basis of consciousness. Damage to specific brain regions can lead to the loss of certain conscious experiences, such as the ability to recognize faces or perceive motion. Studies of patients with lesions in the posterior cortex have revealed the importance of these areas for generating subjective content.
4.1 What Happens to Consciousness After a Spinal Cord Injury?
A complete severing of the spinal cord typically results in paralysis and loss of bodily sensations below the level of the injury. However, individuals with spinal cord injuries often retain their ability to experience life in all its variety, including seeing, hearing, smelling, feeling emotions, and remembering. This suggests that the spinal cord is not essential for generating consciousness.
4.2 Can Someone Be Conscious Without Being Able to Communicate?
Yes, individuals in a minimally conscious state may exhibit some signs of non-reflexive behavior, indicating some level of awareness, even if they cannot communicate effectively. Techniques like “zap and zip” have revealed that some patients in a vegetative state, who appear to be unconscious, may still have brain activity patterns similar to those of conscious individuals. This highlights the importance of developing reliable methods for detecting consciousness in non-communicative patients.
5. What Is the “Zap and Zip” Technique, and How Does It Measure Consciousness?
The “zap and zip” technique, pioneered by Giulio Tononi and Marcello Massimini, involves sending an intense pulse of magnetic energy into the skull to induce a brief electric current in the neurons underneath. The resulting brain activity is recorded using electroencephalogram (EEG) sensors.
5.1 How Does This Technique Determine if Someone Is Conscious?
The complexity of the brain’s response to the magnetic pulse is analyzed using an algorithm that compresses the data, similar to “zipping” computer files. The resulting “perturbational complexity index” provides an estimate of the brain’s complexity. Higher complexity scores are associated with consciousness, while lower scores are observed in deeply sleeping or anesthetized individuals.
6. What Are the Major Theories of Consciousness?
Several theories attempt to explain the nature of consciousness, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The two most popular theories are:
6.1 Global Neuronal Workspace (GNW) Theory
GNW theory, proposed by Bernard J. Baars, Stanislas Dehaene, and Jean-Pierre Changeux, suggests that consciousness arises when information is globally broadcast to multiple cognitive systems in the brain. This global broadcasting allows different parts of the brain to access and process the information, leading to conscious awareness.
6.1.1 How Does GNW Explain Unconscious Processing?
According to GNW, unconscious processing involves information that is localized to specific sensory-motor systems and not globally broadcast. For example, when you type quickly without consciously thinking about each keystroke, the information is localized to the brain circuits connecting your eyes to your finger movements.
6.1.2 Does GNW Imply That Computers Can Be Conscious?
GNW posits that computers of the future, with sufficient cognitive sophistication and the ability to globally broadcast information, could potentially be conscious. This is because the theory focuses on the type of information processing, rather than the specific hardware or biological substrate.
6.2 Integrated Information Theory (IIT)
Integrated Information Theory (IIT), developed by Giulio Tononi, posits that consciousness is intrinsic causal power associated with complex mechanisms. It states that any complex and interconnected system whose structure encodes a set of cause-and-effect relationships will have some level of consciousness.
6.2.1 What Is Φ (Phi) in IIT, and How Is It Measured?
Φ (Phi) is a single nonnegative number that quantifies the level of consciousness in a system, according to IIT. It is derived from the complexity of the underlying interconnected structure. A system with a Φ of zero does not have any conscious experience, while a system with a higher Φ has more intrinsic causal power and is more conscious.
6.2.2 Does IIT Imply That a Brain Simulation Can Be Conscious?
IIT predicts that a sophisticated simulation of a human brain running on a digital computer cannot be conscious. This is because the simulation lacks the actual causal power and interconnectedness of the physical brain. Consciousness, according to IIT, must be built into the structure of the system, not merely simulated.
7. What Is the Relationship Between Consciousness and the Physical World?
The relationship between consciousness and the physical world, often referred to as the mind-body problem, is one of the most enduring questions in philosophy and science. How can subjective experiences arise from physical matter?
7.1 Is Consciousness an Illusion?
Some philosophers and scientists argue that consciousness is an illusion, denying the existence of qualia or claiming that they can never be meaningfully studied by science. However, this view is not widely accepted, as most scholars recognize consciousness as a given and seek to understand its relationship to the objective world.
7.2 How Can Science Study Subjective Experience?
Despite the subjective nature of consciousness, science can study it by searching for its physical footprints, such as the neuronal correlates of consciousness. By identifying the specific brain activity that corresponds to conscious experiences, researchers hope to gain a better understanding of the neural basis of awareness.
8. What Are the Ethical Implications of Consciousness Research?
Consciousness research raises important ethical considerations, particularly in the context of patients with impaired or altered states of consciousness.
8.1 How Should We Treat Patients Who May Be Conscious but Unable to Communicate?
Establishing whether a patient is experiencing life is a grave challenge, particularly for those unable to communicate. Techniques like “zap and zip” can help identify patients who may be conscious but unable to communicate, ensuring that they receive appropriate care and consideration.
8.2 What Are the Implications of Machine Consciousness for Artificial Intelligence?
If machines were to become conscious, it would raise profound ethical questions about their rights and treatment. Understanding the conditions under which a physical system can have experiences is crucial for navigating the ethical landscape of artificial intelligence.
9. What Are Some Unanswered Questions About Consciousness?
Despite significant progress in consciousness research, many fundamental questions remain unanswered.
9.1 Why Do Certain Neurons Give Rise to Consciousness and Not Others?
It is still unclear why specific neurons or brain regions are crucial for generating conscious experiences, while others are not. Understanding the unique properties of these neurons may provide insights into the neural mechanisms of consciousness.
9.2 Why Do Different Sensations Feel Different?
The qualitative differences between different sensations, such as the blueness of the sky and the screech of a violin, are not fully understood. Exploring the neural coding of these sensations may shed light on why they feel so different.
9.3 What Is the Function of Consciousness?
The purpose of consciousness is still a matter of debate. Does it serve a specific function, or is it simply a byproduct of complex brain activity? Understanding the function of consciousness may provide clues to its origins and nature.
10. How Can I Learn More About Consciousness?
If you’re curious about exploring more about this fascinating subject, there are many resources available, including books, articles, and online courses. Some researchers are actively seeking answers to these questions. Consider reaching out to them!
10.1 Where Can I Find Reliable Information About Consciousness Research?
Reputable sources of information about consciousness research include scientific journals, university websites, and science news outlets. Be sure to critically evaluate the information you find and consult multiple sources.
10.2 How Can WHAT.EDU.VN Help Me Understand Consciousness?
WHAT.EDU.VN provides a platform for asking questions and receiving answers from knowledgeable individuals, offering a valuable resource for exploring the mysteries of consciousness. If you have any questions about consciousness, don’t hesitate to ask on WHAT.EDU.VN. Our community of experts is here to help you unravel the complexities of the mind and explore the nature of awareness. Contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890. Website: WHAT.EDU.VN.
The quest to understand consciousness is an ongoing journey, with new discoveries and theories constantly emerging. By exploring the scientific, philosophical, and ethical dimensions of consciousness, we can gain a deeper appreciation for this fundamental aspect of existence. Remember, if you’re struggling to find answers, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help. Ask your questions and get free, reliable answers from our community. Uncover the mysteries of consciousness with us today!
Navigating the complexities of consciousness can be challenging. If you’re seeking clarity and understanding, WHAT.EDU.VN is your go-to resource for free answers and expert insights. Don’t hesitate to ask your questions and embark on a journey of discovery with us!
FAQ: Consciousness
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the difference between consciousness and awareness? | Consciousness generally refers to the state of being aware of oneself and one’s surroundings, while awareness is a broader term that can include being aware of specific stimuli or information. Consciousness often implies a higher level of self-awareness and subjective experience. |
| Can animals be conscious? | The question of animal consciousness is a complex and debated topic. Many scientists believe that at least some animals, particularly mammals and birds, exhibit signs of consciousness, such as self-recognition, problem-solving abilities, and emotional responses. However, the extent and nature of animal consciousness are still under investigation. |
| What is an altered state of consciousness? | An altered state of consciousness is any state that deviates from normal waking consciousness. This can include sleep, dreaming, meditation, hypnosis, drug-induced states, and certain medical conditions. Altered states of consciousness often involve changes in perception, thought, emotion, and self-awareness. |
| How does anesthesia affect consciousness? | Anesthesia typically induces a temporary loss of consciousness by disrupting the neural processes that support awareness. Anesthetic drugs can affect various brain regions and neurotransmitter systems, leading to a reduced level of brain activity and a disconnection between different parts of the brain. |
| What is the role of attention in consciousness? | Attention plays a crucial role in consciousness by selecting and filtering information for conscious processing. Attention can be thought of as a spotlight that highlights certain stimuli or thoughts, allowing them to enter conscious awareness. Without attention, much of the information we receive would remain unconscious. |
| Is there a single “consciousness center” in the brain? | No, there is no single “consciousness center” in the brain. Instead, consciousness appears to arise from the coordinated activity of multiple brain regions, including the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and reticular formation. These regions work together to integrate and process information, giving rise to subjective experience. |
| How do dreams relate to consciousness? | Dreams are a form of altered consciousness that occurs during sleep. While dreaming, we experience vivid sensory and emotional experiences, even though we are not aware of our external surroundings. The neural mechanisms underlying dreaming are not fully understood, but they likely involve the activation of brain regions associated with perception, emotion, and memory. |
| Can meditation enhance consciousness? | Some studies suggest that meditation can enhance certain aspects of consciousness, such as attention, self-awareness, and emotional regulation. Meditation practices may promote changes in brain activity and connectivity, leading to a greater capacity for mindfulness and present-moment awareness. |
| What is the “hard problem” of consciousness? | The “hard problem” of consciousness, coined by philosopher David Chalmers, refers to the difficulty of explaining how subjective experiences arise from physical processes. It is relatively easy to explain how the brain processes information or generates behavior, but it is much harder to explain why these processes are accompanied by subjective feelings or qualia. |
| How can I contribute to consciousness research? | While direct participation in research studies may require specialized training, you can contribute to consciousness research by supporting scientific organizations, raising awareness about the importance of consciousness research, and critically evaluating information about consciousness from various sources. You can also ask questions and engage in discussions on platforms like what.edu.vn. |
If you’re still curious and have more questions, remember that WHAT.EDU.VN is here to provide you with free and reliable answers. Our community of experts is ready to help you explore the depths of consciousness and unravel its mysteries. Don’t hesitate – ask your questions now and embark on a journey of discovery!