Electronic dance music, commonly known as EDM music, is a genre that has exploded in popularity. Are you looking to understand What Is Edm Music and its nuances? WHAT.EDU.VN is here to offer a comprehensive guide, providing clarity and insights into EDM. Discover the world of electronic sounds, dance rhythms, and synthesized beats that define EDM music. Uncover its creation, various forms, and the exciting world of electronic dance music.
1. Defining Electronic Dance Music (EDM)
Electronic Dance Music (EDM) is essentially any form of music produced electronically with digital (computers) and analog equipment, designed to be danced to. It’s characterized by synthesizers, drum machines, processed samples, and recordings, creating a distinct “electronic nature” sound.
- Electronic Production: Utilizes digital and analog equipment.
- Dance-Oriented: Designed for dancing and rhythmic movement.
- Synthesized Sounds: Prominent use of synthesizers and drum machines.
- Precise and Loud: Aims for a full, clear, and impactful sound.
1.1. The Essence of EDM Sound
EDM’s sound is distinct because of the complete control producers have over it. Unlike acoustic genres that require extensive audio engineering to achieve clarity, EDM allows for precise manipulation of every element. You can place a kick drum exactly on the beat, enhance synth sounds, and replace vocal samples with ease. This level of control results in EDM tunes that sound inherently bigger and cleaner, from the initial idea to the final product.
1.2. Dance vs. Electronic Music Debate
It’s worth noting that some people differentiate electronic and dance music, arguing that not all electronic music is necessarily made for clubs. However, for simplicity, EDM can be considered a broad umbrella genre, similar to rock, jazz, or hip-hop. Spotify, for instance, has a Dance/Electronic category, highlighting this inclusive view. Making this kind of music requires dedication and mastery, dispelling the myth that it’s as simple as ‘pressing a button’.
2. A Brief History of Electronic Music
Electronic music traces its roots back to Musique Concrete, a French term for musical collage. This early form involved arranging samples of recorded sounds into a musical piece using primitive technology. As synthesizers were developed, they began to be integrated into this form, laying the groundwork for what would become EDM.
- Musique Concrete: Early form of electronic music using recorded sound samples.
- Synthesizer Development: The creation of synthesizers allowed for new sonic possibilities.
- House Music Origins: Influenced by disco, funk, soul, and jazz, pioneering a danceable electronic sound.
2.1. The Rise of House Music
House music, with its distinct electronic sound driven by drum machines, synths, and samples, emerged as one of the first forms of “danceable” electronic music. Characterized by its 4-on-the-floor rhythm, house music paved the way for numerous subgenres, including UK garage, trance, techno, and more. Although the term EDM didn’t exist yet, it was simply known as “dance music.”
2.2. The Shift to Digital and Proliferation of Subgenres
In the following decades, electronic dance music transitioned from analog equipment to computers, making it more accessible and affordable. This shift led to a proliferation of EDM subgenres such as jungle, garage, hip-hop, techno, trance, electro house, progressive, and eurodance.
2.3. EDM’s Mainstream Adoption
In the last 10-15 years, EDM has moved from being a niche genre to gaining widespread recognition and appreciation. No longer confined to clubs, it has become a mainstream phenomenon. This is where the term “EDM” gained traction, serving as a simple way to describe any electronic music suitable for dancing. If you’ve ever wondered ‘what is EDM’ after a rave, you’re part of this evolution.
3. The Diverse Subgenres of EDM
Electronic dance music encompasses a wide range of subgenres, each with its unique characteristics and appeal. Understanding these subgenres can help you appreciate the breadth and depth of EDM.
- Future Bass: Known for its melodic and emotive soundscapes.
- Big Room House: Characterized by energetic builds and impactful drops.
- Hybrid Trap: Combines elements of trap and other genres for a dynamic sound.
- Dubstep: Features heavy basslines and syncopated rhythms.
- Electronic Pop: Blends electronic sounds with pop structures and melodies.
- Future House: Infuses house music with futuristic sounds and elements.
3.1. Exploring Additional EDM Subgenres
Beyond the most popular subgenres, EDM offers a deep dive into various styles such as deep house, trance, drum & bass, hardstyle, and garage. The list continues to expand, sometimes leading to more niche classifications like “hyper jazzstep” or “hardcore breakbeat trance.”
3.2. The Importance of Genre Exploration
If you’re interested in creating EDM, exploring different genres can help you find your niche. Attending events like Tomorrowland, where big room house and trap are common, can provide inspiration. However, it’s essential not to limit yourself and to bring your unique imprint to your chosen style.
3.3. Navigating the Ever-Changing Subgenre Landscape
Subgenres evolve, gain popularity, and sometimes fade away. New ones emerge regularly, so it’s best not to get too caught up in labels. The key is to create music that resonates with you, regardless of the term used.
4. EDM: Commercial or Comprehensive?
A common debate within electronic music communities revolves around the definition of EDM. Does it encompass all electronic dance music, or does it refer specifically to the popular, commercially successful variety heard on the radio and top Spotify playlists? Can artists as diverse as Martin Garrix, Carl Cox, and Goldie be categorized under the same umbrella?
- Purist View: Argues that subgenres like “real deep house” or “old school jungle” are distinct from EDM.
- Inclusive View: Considers EDM as a broad term for any electronic music designed for dancing.
4.1. The Evolution of the EDM Term
Before the term EDM became popular, umbrella terms such as “electronica,” “electronic music,” and “dance music” were commonly used. Around 2010-2011, EDM emerged as a handy and marketable term as genres like big room, trap, and future bass gained prominence.
4.2. Resistance and Acceptance
Producers and DJs who had been in the scene for a while sometimes resisted the term EDM because the new breed of electronic music differed significantly from what they were accustomed to. However, genres were evolving and creating new sounds, making it all EDM—electronic dance music.
4.3. A Parallel to Other Genres
The situation is similar to metal and punk music, which have different aesthetics but are both considered “rock.” While more and more musical genres adopt electronic technology, the defining factor of EDM remains its primarily electronic sounds designed for the dance floor. This encompasses everything from Chicago house to tearout dubstep.
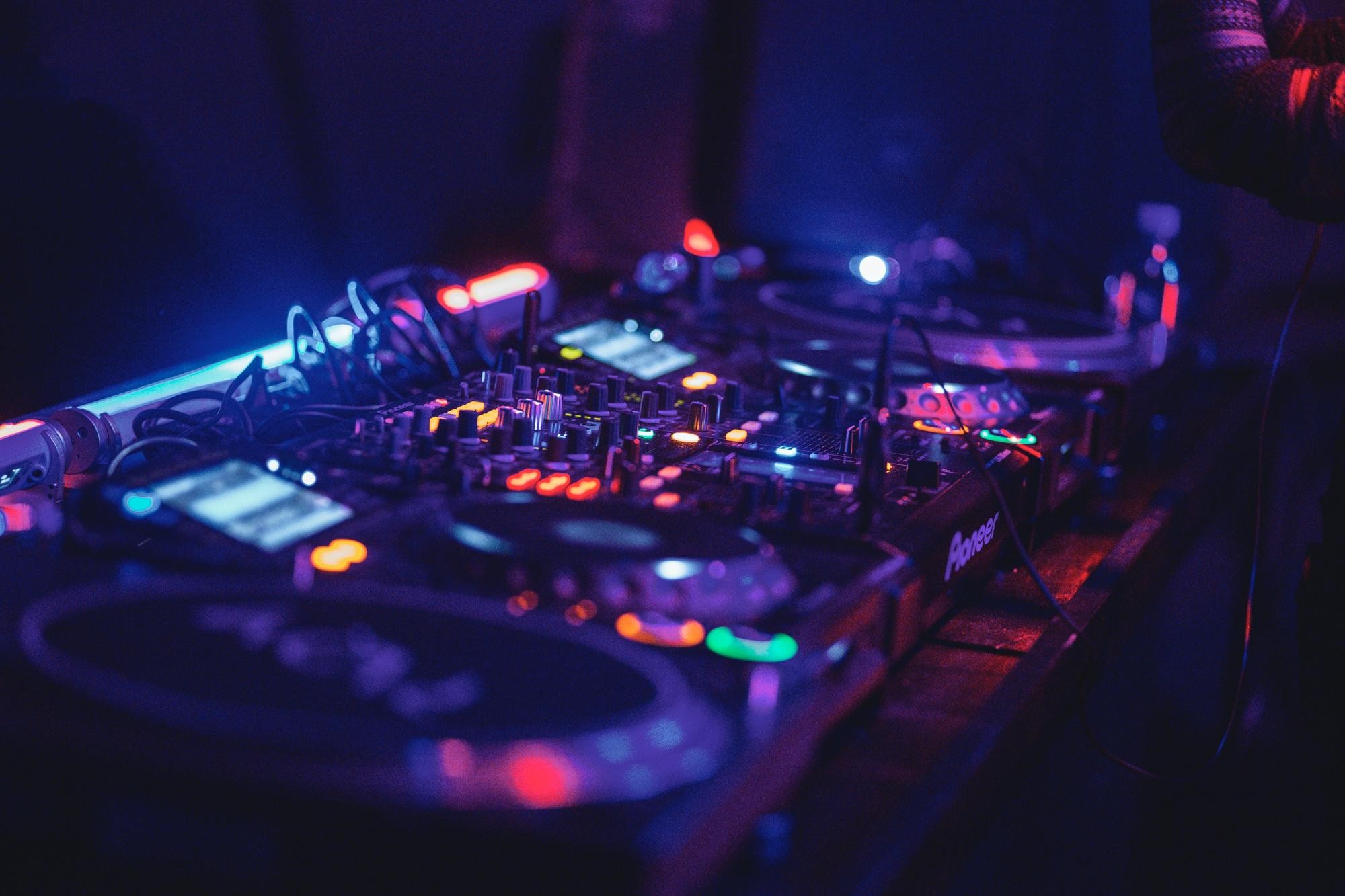
5. The Process of Creating EDM
Electronic dance music is primarily created on a computer by an electronic music producer. These producers may also be DJs, but it’s not a requirement. Computers offer the flexibility to create and manipulate any recorded or created sound. This is good news for aspiring producers, as you likely already have a suitable computer.
- Producer Role: Electronic music producers create EDM using computers.
- Computer Flexibility: Computers offer the tools to manipulate and create sounds.
- Accessibility: You don’t need a high-spec computer to get started.
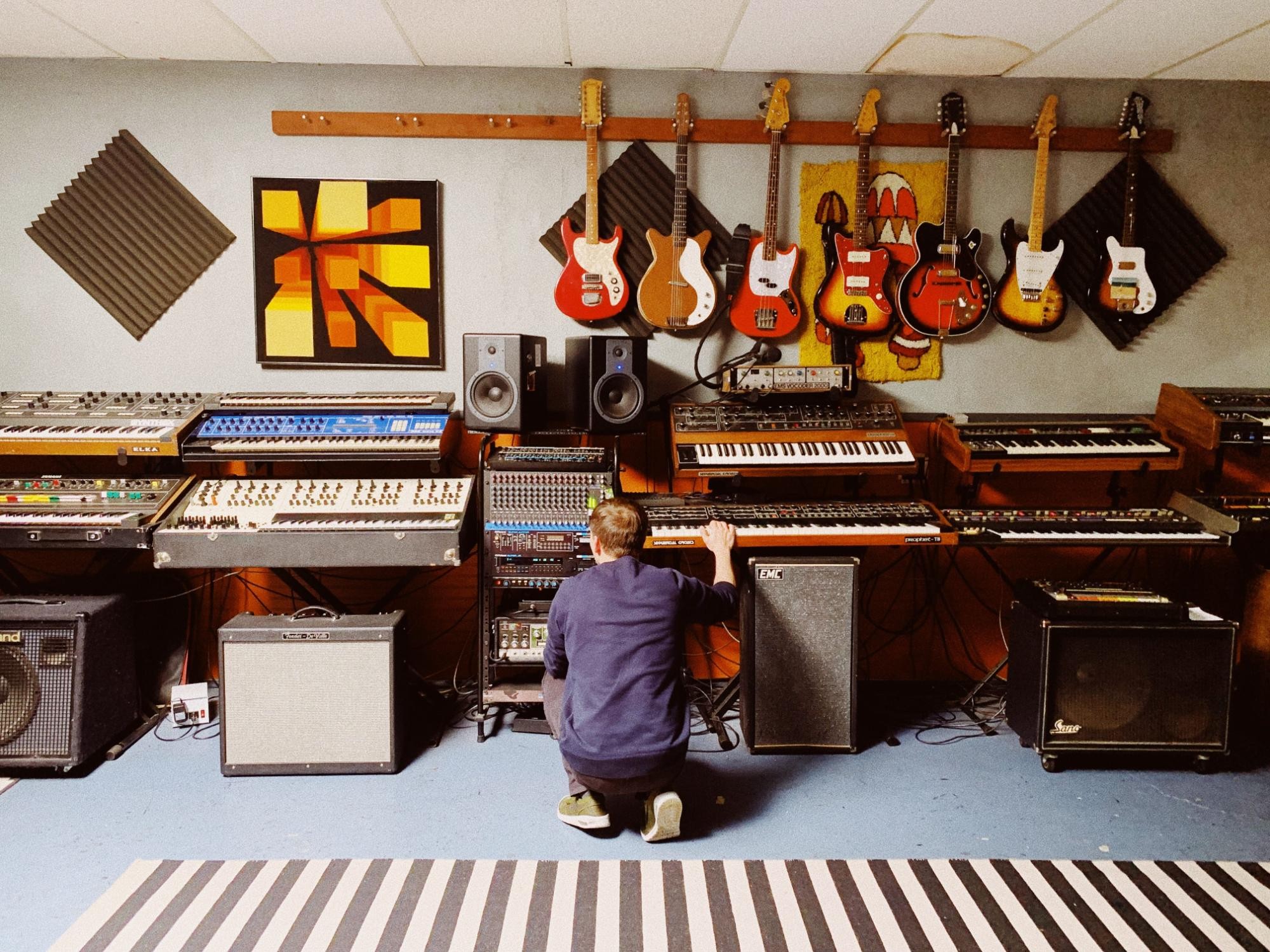
5.1. Essential Studio Equipment
The minimum viable studio consists of a laptop/desktop, headphones, and a DAW (digital audio workstation). You’ll also need good samples and maybe a few plugins and resources. With this setup, you can produce tracks that rival those heard at major festivals.
5.2. The Importance of Education
If you want to learn electronic music production effectively, quality education is essential. This can include structured courses that offer comprehensive knowledge and helpful support. Consider platforms like WHAT.EDU.VN for guidance and learning resources. Structured courses ensure you learn in the right order, with no knowledge gaps, and have access to answers to your questions.
5.3. Overcoming the Learning Curve
Learning electronic music production requires overcoming common mistakes and focusing on fundamental techniques. Shiny techniques are less important than a solid foundation. With the right education, you’ll save time, headaches, and disappointment.
6. Essential Elements of EDM Production
To fully grasp what is EDM music, it’s essential to understand the key elements that go into its production. These elements combine to create the unique and captivating sound that defines the genre.
- Rhythm and Beat: The backbone of EDM, typically featuring a 4/4 time signature.
- Basslines: Deep, resonant basslines that drive the energy of the track.
- Melody: Catchy and memorable melodies that hook the listener.
- Harmony: Chord progressions that create emotional depth and texture.
- Sound Design: Synthesized sounds and samples that give EDM its electronic edge.
6.1. Rhythm and Beat
The rhythmic structure of EDM is usually based on a 4/4 time signature, providing a consistent and danceable beat. This foundation allows for complex layering of other elements, creating a dynamic and engaging sound.
6.2. Basslines
Basslines in EDM are often deep and resonant, providing the low-end frequencies that drive the energy of the track. These basslines can range from simple and repetitive to complex and evolving, depending on the subgenre.
6.3. Melody
Catchy and memorable melodies are crucial for hooking the listener and making the track stand out. These melodies are often created using synthesizers and can be manipulated to create a wide range of emotions.
6.4. Harmony
Chord progressions add emotional depth and texture to EDM tracks. These harmonies can range from simple major and minor chords to more complex and dissonant voicings, depending on the desired mood.
6.5. Sound Design
Sound design is where EDM truly shines, utilizing synthesized sounds and samples to create unique and captivating textures. This element is crucial for giving EDM its electronic edge and distinguishing it from other genres.
7. The Role of Technology in EDM
Technology is at the heart of what is EDM music, driving its creation and evolution. From hardware synthesizers to advanced software plugins, technology provides the tools for producers to craft their sound.
- DAWs (Digital Audio Workstations): The primary software used for producing EDM.
- Synthesizers: Instruments for creating a wide range of electronic sounds.
- Plugins: Software that enhances and manipulates audio.
- Sampling: The process of using pre-recorded sounds in a new composition.
7.1. DAWs (Digital Audio Workstations)
DAWs like Ableton Live, Logic Pro, and FL Studio are essential for EDM production, providing a platform for recording, editing, and mixing audio. These programs offer a wide range of tools and features for creating complex and layered tracks.
7.2. Synthesizers
Synthesizers are used to create a vast array of electronic sounds, from melodic leads to deep basslines. Modern synthesizers often come in software form, offering endless possibilities for sound design.
7.3. Plugins
Plugins enhance and manipulate audio, adding effects like reverb, delay, and distortion. They can also be used for more complex tasks like equalization and compression, shaping the overall sound of the track.
7.4. Sampling
Sampling involves using pre-recorded sounds in a new composition. This technique is widely used in EDM to create unique textures and rhythms, often transforming familiar sounds into something entirely new.
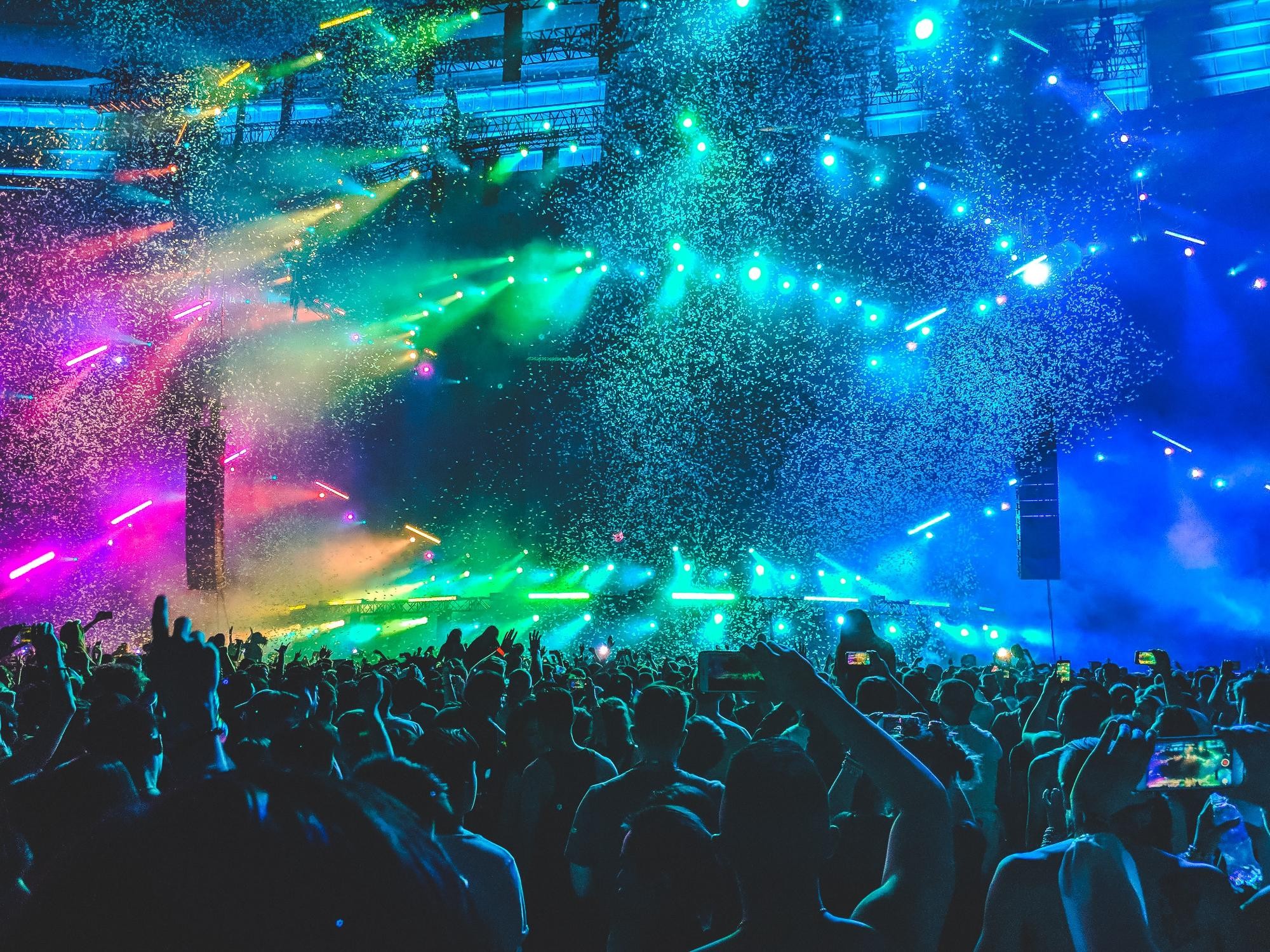
8. The Impact of EDM on Culture
EDM has had a significant impact on culture, influencing fashion, art, and social trends. Its rise in popularity has led to the creation of massive music festivals and a global community of fans.
- Music Festivals: Large-scale events that showcase EDM artists.
- Global Community: A worldwide network of EDM fans and producers.
- Fashion and Art: EDM-inspired styles and aesthetics.
- Social Trends: The influence of EDM on dance and social culture.
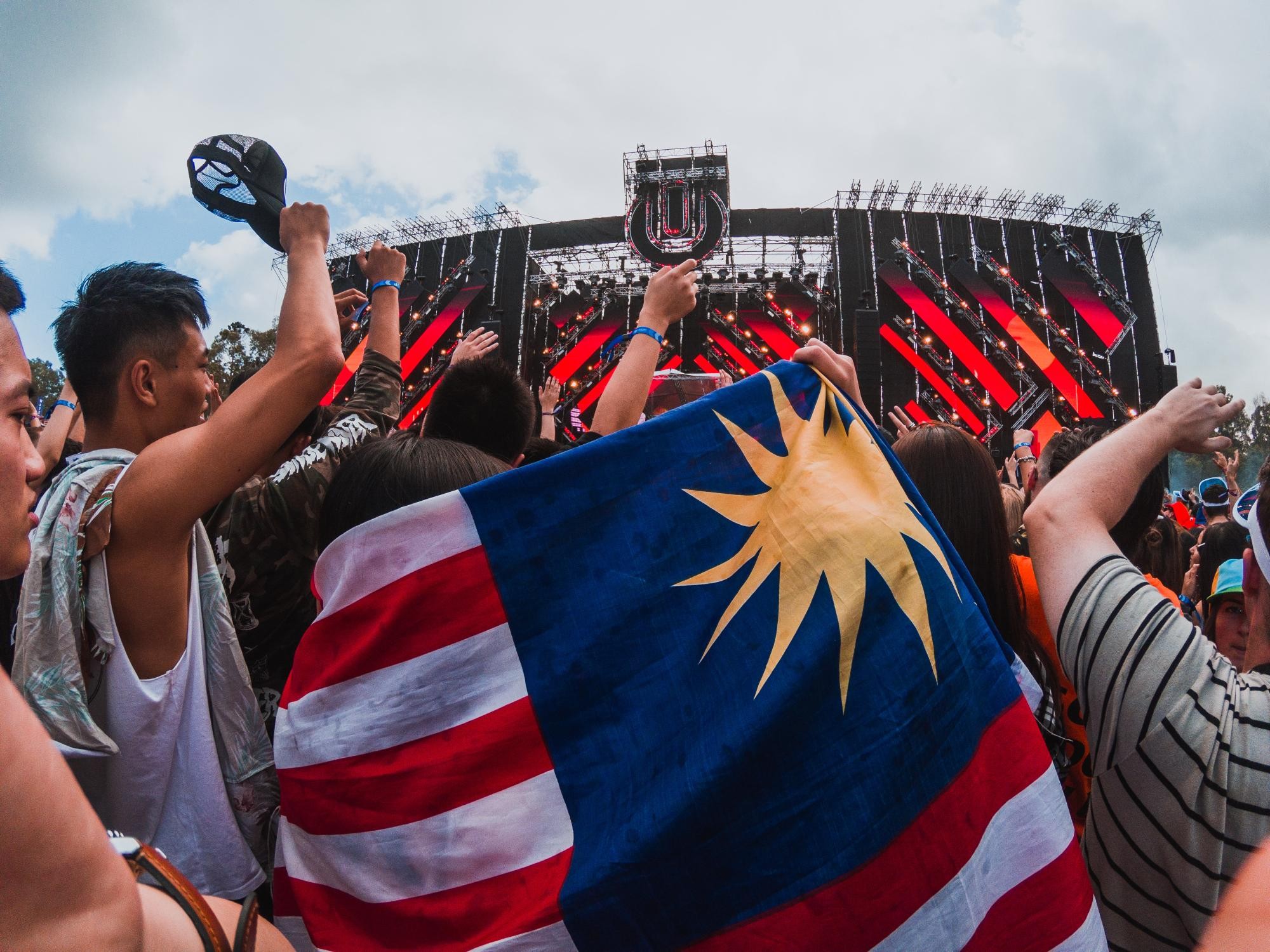
8.1. Music Festivals
Music festivals like Tomorrowland, Electric Daisy Carnival, and Ultra Music Festival are major events that showcase EDM artists and attract fans from around the world. These festivals offer immersive experiences with stunning visuals and high-energy performances.
8.2. Global Community
The global community of EDM fans and producers is a diverse and passionate group. Online forums, social media groups, and meetups provide opportunities for collaboration and connection.
8.3. Fashion and Art
EDM has influenced fashion and art, with vibrant colors, futuristic designs, and bold statements becoming popular. These aesthetics reflect the energy and innovation of the genre.
8.4. Social Trends
EDM has also impacted social trends, influencing dance and social culture. Its infectious rhythms and high-energy performances encourage movement and expression, creating a sense of unity and excitement.
9. Common Misconceptions About EDM
Despite its popularity, EDM is often misunderstood. Clearing up these misconceptions can help people appreciate the genre and its contributions to music.
- It’s Just Noise: EDM is often criticized for being repetitive and lacking substance.
- Anyone Can Make It: The perception that EDM production is easy and requires no skill.
- It All Sounds the Same: The belief that all EDM tracks are indistinguishable from one another.
9.1. It’s Just Noise
EDM is often criticized for being repetitive and lacking substance. However, the repetition in EDM is intentional, creating a hypnotic and danceable rhythm. The best EDM tracks feature intricate layering and subtle changes that keep the listener engaged.
9.2. Anyone Can Make It
The perception that EDM production is easy and requires no skill is a common misconception. While the tools for making EDM are accessible, mastering the art of sound design, mixing, and arrangement takes time and dedication.
9.3. It All Sounds the Same
The belief that all EDM tracks are indistinguishable from one another is also untrue. With its diverse subgenres and unique artistic expressions, EDM offers a wide range of sounds and styles. Exploring different artists and subgenres can reveal the richness and variety of the genre.
10. Finding Your Path in EDM
Whether you’re a listener, dancer, or aspiring producer, finding your path in EDM involves exploration, education, and engagement with the community. Discovering what resonates with you and pursuing your passion can lead to a fulfilling experience.
- Explore Subgenres: Discover the diverse sounds of EDM by exploring different subgenres.
- Attend Events: Immerse yourself in the EDM culture by attending music festivals and club nights.
- Learn Production: Acquire the skills and knowledge to create your own EDM tracks.
- Connect with the Community: Engage with other fans and producers online and in person.
10.1. Explore Subgenres
Start your journey by exploring the various subgenres of EDM. From the melodic sounds of future bass to the hard-hitting beats of dubstep, there’s something for everyone to discover.
10.2. Attend Events
Immerse yourself in the EDM culture by attending music festivals and club nights. These events offer the opportunity to experience the energy of live performances and connect with other fans.
10.3. Learn Production
If you’re interested in creating your own EDM tracks, consider learning the basics of music production. Online courses, tutorials, and workshops can provide the skills and knowledge you need to get started.
10.4. Connect with the Community
Engage with other fans and producers online and in person. Online forums, social media groups, and meetups provide opportunities for collaboration, feedback, and support.
Unlock Your EDM Potential with WHAT.EDU.VN
Are you ready to delve deeper into what is EDM music and explore its endless possibilities? Whether you’re curious about its history, eager to learn production techniques, or simply looking to connect with fellow enthusiasts, WHAT.EDU.VN is your go-to resource. We offer free guidance and answers to all your questions.
Don’t let confusion hold you back! Ask your questions on WHAT.EDU.VN and receive prompt, accurate answers from knowledgeable community members. No matter how simple or complex your query, we’re here to help you understand and appreciate the world of EDM.
Need Instant Answers?
Visit WHAT.EDU.VN now and ask your questions for free. Connect with a community of experts and enthusiasts ready to share their knowledge. Your journey into EDM begins here!
Contact Us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About EDM Music
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What exactly does EDM stand for? | EDM stands for Electronic Dance Music. It is a broad term encompassing various genres of electronic music made for dancing. |
| What are the main characteristics of EDM? | EDM typically features synthesized sounds, strong beats, and is designed for dancing. Common elements include basslines, melodies, and electronic sound design. |
| Who are some famous EDM artists? | Famous EDM artists include David Guetta, Skrillex, Marshmello, Calvin Harris, and The Chainsmokers, among many others. |
| What equipment is needed to make EDM? | You’ll need a computer, a DAW (Digital Audio Workstation), headphones, and possibly plugins and samples to get started. |
| How do I start learning EDM production? | Start with online tutorials, courses, and practice. Experiment with different sounds and techniques to develop your style. |
| What are some popular EDM festivals? | Popular EDM festivals include Tomorrowland, Electric Daisy Carnival (EDC), Ultra Music Festival, and Creamfields. |
| How has EDM influenced pop music? | EDM has greatly influenced pop music by incorporating electronic sounds, beats, and production techniques, resulting in hybrid genres. |
| Can EDM be considered a serious art form? | Yes, EDM is a serious art form that requires creativity, technical skill, and musical knowledge to produce high-quality tracks. |
| What makes EDM different from other genres? | EDM’s unique sound comes from its heavy reliance on electronic instruments, synthesizers, and drum machines, creating a distinct sonic landscape. |
| Where can I find free resources to learn EDM? | Websites like WHAT.EDU.VN, YouTube tutorials, and free sample packs online can help you get started without spending money. |





Still have questions? The world of EDM is vast and always evolving, but understanding its fundamentals can open up a world of musical enjoyment and creativity. Whether you’re looking to deepen your knowledge, explore new subgenres, or even start producing your own tracks, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to support you. Don’t hesitate to ask your questions and connect with our community.
The Ultimate Call to Action
Ready to explore the world of EDM and get your questions answered for free? Visit what.edu.vn now and dive into our community of experts and enthusiasts. Whether you’re curious about the history, production techniques, or the latest trends, we’re here to guide you every step of the way. Don’t miss out—ask your questions today and unlock the secrets of EDM music!