Are you looking to find out What Is Gmt Right Now? WHAT.EDU.VN provides you with the current Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) and helps you understand its significance. Discover the current GMT time, convert time zones, and explore related time standards like UTC to ensure you’re always on time, bridging global connections and eliminating any timing confusion with time conversions and up-to-date information on time zones.
1. Understanding GMT (Greenwich Mean Time)
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the mean solar time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London. It was established in 1884 as the prime meridian for timekeeping, serving as the baseline for time zones worldwide. Today, while Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is the primary time standard, GMT remains a significant reference point.
1.1. How GMT Originated
GMT’s origins trace back to the need for a standard time for navigation and astronomy. The Royal Observatory, founded in 1675, played a crucial role in these advancements. As the British Empire expanded, GMT became increasingly important for coordinating global activities, especially with the advent of railways and telegraphs.
1.2. The Role of the Royal Observatory
The Royal Observatory in Greenwich was not only a center for astronomical observations but also a hub for developing accurate timekeeping methods. The transit circle, installed in 1851, allowed astronomers to precisely measure the time when the sun crossed the meridian, establishing GMT as a reliable time standard.
1.3. GMT as the Prime Meridian
In 1884, the International Meridian Conference in Washington, D.C., formally adopted GMT as the prime meridian, or zero degrees longitude. This decision standardized global time zones, making it easier to coordinate international communications and travel.
2. The Difference Between GMT and UTC
Although often used interchangeably, GMT and Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) are not exactly the same. UTC is based on atomic clocks, while GMT is based on the Earth’s rotation. This difference leads to slight variations over time, which are corrected by leap seconds in UTC.
2.1. UTC: The Modern Time Standard
UTC is the primary time standard used today. It’s maintained by the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM) and is more accurate than GMT because it relies on atomic clocks. These clocks measure time based on the frequency of atomic vibrations, providing a highly stable and precise time reference.
2.2. Why UTC Is More Accurate Than GMT
The Earth’s rotation is not perfectly uniform; it can be affected by various factors, such as tidal forces and movements within the Earth’s core. These irregularities mean that GMT can drift slightly over time. UTC, using atomic clocks, avoids these issues and remains consistent.
2.3. Leap Seconds: Keeping UTC Aligned
To keep UTC aligned with the Earth’s rotation, leap seconds are occasionally added. These adjustments ensure that UTC remains within 0.9 seconds of GMT. The International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) determines when leap seconds are necessary.
3. Why Knowing the Current GMT Time Is Important
Knowing the current GMT time is essential for many activities, from international business to coordinating scientific research. It serves as a universal reference point, allowing people in different time zones to communicate and collaborate effectively.
3.1. International Business and Communication
In the world of international business, knowing GMT is crucial for scheduling meetings and coordinating projects across different time zones. It helps ensure that everyone is on the same page, regardless of their location.
3.2. Aviation and Navigation
Aviation and navigation rely heavily on GMT (often referred to as Zulu time in aviation) for flight planning, air traffic control, and maritime operations. Using a standard time reference reduces the risk of errors and improves safety.
3.3. Scientific Research and Data Synchronization
Scientists often use GMT/UTC to timestamp data and coordinate experiments across different locations. This standardization is vital for ensuring the integrity and comparability of research findings.
4. How to Find the Current GMT Time
Finding the current GMT time is easier than ever, thanks to the internet. Numerous websites and tools provide real-time GMT updates, allowing you to stay synchronized no matter where you are.
4.1. Online Time Converters and Websites
Websites like WHAT.EDU.VN offer real-time GMT updates and time zone converters. These tools allow you to quickly find the current GMT time and convert it to your local time zone.
4.2. Smartphone Apps and World Clocks
Many smartphone apps and world clock applications provide GMT time. These apps often include features like alarms and meeting planners, making it easy to coordinate with people in different time zones.
4.3. Setting Your Computer or Phone to GMT
You can also set your computer or phone to display GMT. This can be useful if you frequently need to reference GMT or work with international teams. Most operating systems allow you to add additional time zones to your display.
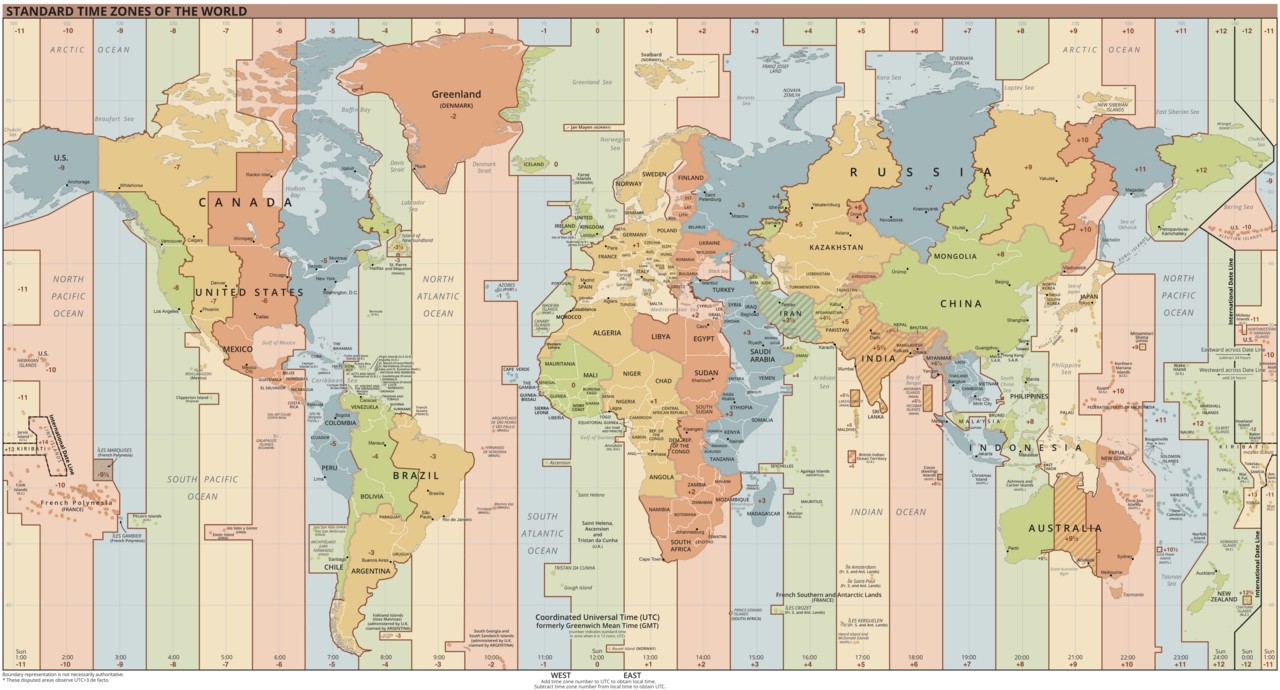 World Time Zones Map
World Time Zones Map
5. GMT Time Zones Around the World
GMT is the basis for many time zones around the world. Understanding how different regions relate to GMT can help you quickly calculate the time in various locations.
5.1. Countries That Use GMT
Several countries and regions use GMT as their standard time, particularly in West Africa. These include:
- Ghana
- Ivory Coast
- Burkina Faso
- Mali
- Togo
5.2. Calculating Time Differences From GMT
To calculate the time in a different location, you need to know its time zone offset from GMT. For example, New York City is GMT-4 during standard time and GMT-5 during daylight saving time. So, if it’s 12:00 GMT, it would be 08:00 in New York during standard time.
5.3. Daylight Saving Time and GMT
Daylight Saving Time (DST) can affect the time difference between GMT and local time. During DST, many regions move their clocks forward by an hour, changing their offset from GMT. Always check whether a region is observing DST when calculating time differences.
6. Common Uses of GMT in Various Fields
GMT is not just a time standard; it’s a critical tool in many fields, from broadcasting to logistics. Its universal nature makes it indispensable for coordinating activities across borders and time zones.
6.1. Broadcasting and Media
Broadcasting companies often use GMT to schedule programming and coordinate live broadcasts across different regions. This ensures that viewers around the world can tune in at the correct time.
6.2. Logistics and Shipping
Logistics and shipping companies rely on GMT to track shipments and coordinate deliveries across different time zones. Accurate timekeeping is essential for ensuring that goods arrive on schedule.
6.3. Computer Systems and Networking
In computer systems and networking, GMT/UTC is used to synchronize clocks and log events. This standardization is vital for maintaining the integrity of data and coordinating distributed systems.
7. Converting GMT to Other Time Zones
Converting GMT to other time zones is a common task for many people, whether for scheduling meetings or planning travel. Understanding the process and using the right tools can make this task much easier.
7.1. Using Online Time Zone Converters
Online time zone converters are a quick and easy way to convert GMT to other time zones. Simply enter the GMT time and the desired time zone, and the converter will do the rest. WHAT.EDU.VN offers a reliable and user-friendly time zone converter.
7.2. Manual Calculation Methods
If you prefer to calculate time zone differences manually, you need to know the GMT offset for the target time zone. Add or subtract the offset from the GMT time to find the local time. Remember to account for Daylight Saving Time if applicable.
7.3. Popular Time Zone Conversions
Some popular time zone conversions include:
- GMT to EST (Eastern Standard Time): GMT-5
- GMT to PST (Pacific Standard Time): GMT-8
- GMT to CET (Central European Time): GMT+1
- GMT to JST (Japan Standard Time): GMT+9
8. GMT and Its Impact on Global Culture
GMT has had a significant impact on global culture, shaping how we perceive and organize time. Its adoption as a standard time reference has facilitated international collaboration and communication.
8.1. The Standardization of Time
The adoption of GMT as the prime meridian and standard time reference led to the standardization of time zones worldwide. This standardization has made it easier to coordinate activities across different regions and cultures.
8.2. The Concept of Universal Time
GMT has contributed to the concept of universal time, the idea that there is a single, global time that everyone can reference. This concept is essential for many aspects of modern life, from international business to scientific research.
8.3. Cultural Differences in Time Perception
Despite the standardization of time zones, cultural differences in time perception persist. Some cultures prioritize punctuality, while others are more flexible. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective cross-cultural communication.
9. Frequently Asked Questions About GMT
9.1. What is GMT Used For?
GMT is used as a reference point for time zones around the world. It helps in coordinating international business, aviation, scientific research, and more.
9.2. Is GMT the Same as Zulu Time?
Yes, in aviation and military contexts, GMT is often referred to as Zulu time. This terminology helps avoid confusion when coordinating activities across different time zones.
9.3. How Does Daylight Saving Time Affect GMT?
Daylight Saving Time (DST) affects the time difference between GMT and local time. During DST, many regions move their clocks forward by an hour, changing their offset from GMT.
9.4. Where Can I Find the Most Accurate GMT Time?
You can find the most accurate GMT time on websites like WHAT.EDU.VN, which provide real-time updates based on atomic clocks.
9.5. Why Is It Important to Know GMT?
Knowing GMT is important for coordinating international activities, scheduling meetings, and ensuring accurate timekeeping in various fields.
10. The Future of Timekeeping: Beyond GMT and UTC
While GMT and UTC have served as the backbone of global timekeeping for decades, the future may hold new advancements and standards. Exploring these possibilities can provide insights into how we might manage time in the years to come.
10.1. The Potential for New Time Standards
As technology advances, there may be opportunities to develop even more precise and reliable time standards. These new standards could address some of the limitations of GMT and UTC, such as the need for leap seconds.
10.2. The Role of Quantum Clocks
Quantum clocks, which use the quantum properties of atoms to measure time, are showing promise as the next generation of timekeeping devices. These clocks could offer unprecedented accuracy and stability, potentially revolutionizing fields like telecommunications and navigation.
10.3. Adapting to a Globalized World
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the need for accurate and standardized timekeeping will only grow. Future time standards will need to adapt to the challenges of a globalized world, ensuring seamless coordination across different regions and cultures.
11. Real-Life Examples of GMT Usage
To further illustrate the importance of GMT, let’s look at some real-life examples of how it is used in various sectors.
11.1. International News Broadcasting
News organizations often use GMT to coordinate the timing of their broadcasts. For example, a news program might be scheduled to air at 18:00 GMT, allowing viewers in different time zones to tune in at the same relative time.
11.2. Global Financial Markets
Financial markets around the world rely on GMT to synchronize trading activities. This ensures that trades are executed at the correct time and that market data is consistent across different exchanges.
11.3. Coordinating Disaster Relief Efforts
In the event of a natural disaster, aid organizations use GMT to coordinate relief efforts across different time zones. This helps ensure that resources are deployed efficiently and that assistance reaches those who need it most.
12. The Science Behind Timekeeping
Understanding the science behind timekeeping can provide a deeper appreciation for the complexities of GMT and UTC.
12.1. The History of Time Measurement
The history of time measurement dates back to ancient civilizations, who used the sun, moon, and stars to track the passage of time. Over the centuries, more sophisticated methods were developed, including sundials, water clocks, and mechanical clocks.
12.2. Atomic Clocks and Their Precision
Atomic clocks are the most accurate timekeeping devices ever created. They use the frequency of atomic vibrations to measure time with incredible precision, achieving accuracy to within a few seconds per billion years.
12.3. The Role of Leap Seconds
Leap seconds are added to UTC to keep it aligned with the Earth’s rotation. These adjustments are necessary because the Earth’s rotation is not perfectly uniform and can be affected by various factors.
13. Resources for Staying Updated on GMT
To stay updated on GMT and time zone changes, here are some useful resources:
13.1. Official Timekeeping Organizations
Organizations like the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM) and the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) provide authoritative information on time standards and leap seconds.
13.2. Online Time Zone Databases
Online time zone databases, such as the IANA Time Zone Database, offer comprehensive information on time zones around the world, including GMT offsets and Daylight Saving Time rules.
13.3. Educational Websites and Articles
Websites like WHAT.EDU.VN provide educational articles and resources on GMT, UTC, and timekeeping. These resources can help you deepen your understanding of time and its significance.
14. How to Use GMT Effectively in Your Daily Life
Integrating GMT into your daily life can help you stay organized and connected, especially if you work or communicate with people in different time zones.
14.1. Scheduling International Meetings
When scheduling international meetings, always specify the time in GMT or UTC. This will help avoid confusion and ensure that everyone knows exactly when the meeting will take place.
14.2. Planning Travel Across Time Zones
When planning travel across time zones, use a time zone converter to adjust your schedule and avoid jet lag. Try to gradually adjust your sleep schedule in the days leading up to your trip.
14.3. Coordinating With Remote Teams
If you work with a remote team, use GMT to coordinate tasks and deadlines. This will help ensure that everyone is on the same page and that projects are completed on time.
15. Debunking Common Myths About GMT
There are several common myths about GMT that are worth debunking.
15.1. Myth: GMT Is Always the Same as London Time
While GMT is based on the time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, it is not always the same as the local time in London. During Daylight Saving Time, London observes British Summer Time (BST), which is GMT+1.
15.2. Myth: GMT Is Obsolete
Despite the widespread use of UTC, GMT is not obsolete. It remains an important reference point for time zones around the world and is still used in many contexts.
15.3. Myth: Time Zones Are Always Integer Hour Offsets
While most time zones are integer hour offsets from GMT, there are some exceptions. For example, Nepal Standard Time (NPT) is GMT+5:45.
16. Exploring the Cultural Significance of Time
Time is not just a scientific concept; it also has deep cultural significance. Different cultures perceive and value time in different ways.
16.1. Polychronic vs. Monochronic Cultures
Some cultures are polychronic, meaning they view time as flexible and fluid. Others are monochronic, meaning they view time as linear and structured. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective cross-cultural communication.
16.2. The Importance of Punctuality
In some cultures, punctuality is highly valued, while in others, it is less important. Being aware of these cultural norms can help you avoid misunderstandings and build stronger relationships.
16.3. Time and Spirituality
Time also plays a significant role in many spiritual traditions. Practices like meditation and mindfulness encourage individuals to be present in the moment and appreciate the passage of time.
17. Advanced Timekeeping Concepts
For those who want to delve deeper into the world of timekeeping, here are some advanced concepts to explore:
17.1. Sidereal Time
Sidereal time is based on the Earth’s rotation relative to the stars, rather than the sun. It is used by astronomers to track the position of celestial objects.
17.2. Terrestrial Time
Terrestrial Time (TT) is a time scale used for astronomical calculations. It is more uniform than UTC and is not subject to leap seconds.
17.3. Barycentric Dynamical Time
Barycentric Dynamical Time (TDB) is a time scale used for calculating the motion of objects in the solar system. It is based on the center of mass of the solar system.
18. Resources for Further Learning
To continue your journey into the world of timekeeping, here are some valuable resources:
18.1. Books on Time and Timekeeping
There are many excellent books on the history, science, and cultural significance of time. Some popular titles include “A Brief History of Time” by Stephen Hawking and “Longitude” by Dava Sobel.
18.2. Online Courses and Tutorials
Online learning platforms like Coursera and edX offer courses on timekeeping, astronomy, and physics. These courses can provide a more in-depth understanding of the concepts discussed in this article.
18.3. Museums and Observatories
Visiting museums and observatories can be a great way to learn more about timekeeping. The Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, is a particularly popular destination for those interested in the history of GMT.
19. Staying Ahead of Time: Tips and Tricks
Here are some additional tips and tricks for staying ahead of time:
19.1. Use Multiple Time Zones on Your Devices
Most computers and smartphones allow you to display multiple time zones. This can be helpful if you frequently communicate with people in different locations.
19.2. Set Reminders and Alarms in GMT
When scheduling tasks or meetings, set reminders and alarms in GMT. This will help you stay on track, regardless of your current location.
19.3. Invest in a High-Quality Watch
A high-quality watch can be a valuable tool for timekeeping. Look for a watch with a GMT function or the ability to display multiple time zones.
20. Call to Action: Your Questions Answered
Do you have any questions about GMT, time zones, or timekeeping? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN to ask your questions and get free answers from our experts. We’re here to help you stay on time and stay connected.
If you’re finding it difficult to get quick, free answers to your questions, don’t know who to ask, or are worried about consultation costs, WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help. We provide a free platform where you can ask any question and receive fast, accurate answers. Connect with a community of knowledgeable individuals ready to assist you. Visit us today at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. You can also visit our website at what.edu.vn for more information.
