Are you wondering, What Is Half Of 1/4 Cup? The answer is simple: Half of 1/4 cup is equal to 2 tablespoons. This guide from WHAT.EDU.VN will explain the conversion, provide helpful tips for measuring, and offer some real-world examples. You’ll discover valuable culinary insights, precise measurements, and practical baking tips.
1. Understanding the Basics of Cup Measurements
Before diving into calculating half of 1/4 cup, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals of cup measurements. Understanding these basics will make halving or adjusting recipes much easier. Let’s explore the foundational conversions and relationships within cup measurements.
-
What is a Cup?
A cup is a standard unit of volume, primarily used in cooking and baking. It is part of both the US customary and metric systems, though the exact volume can vary slightly. In the US, one cup is defined as 8 fluid ounces, which is approximately 237 milliliters. This measurement is crucial for ensuring consistent results in your culinary endeavors.
-
Breaking Down a Cup
To effectively work with fractions of a cup, it’s helpful to understand how a cup can be divided into smaller units:
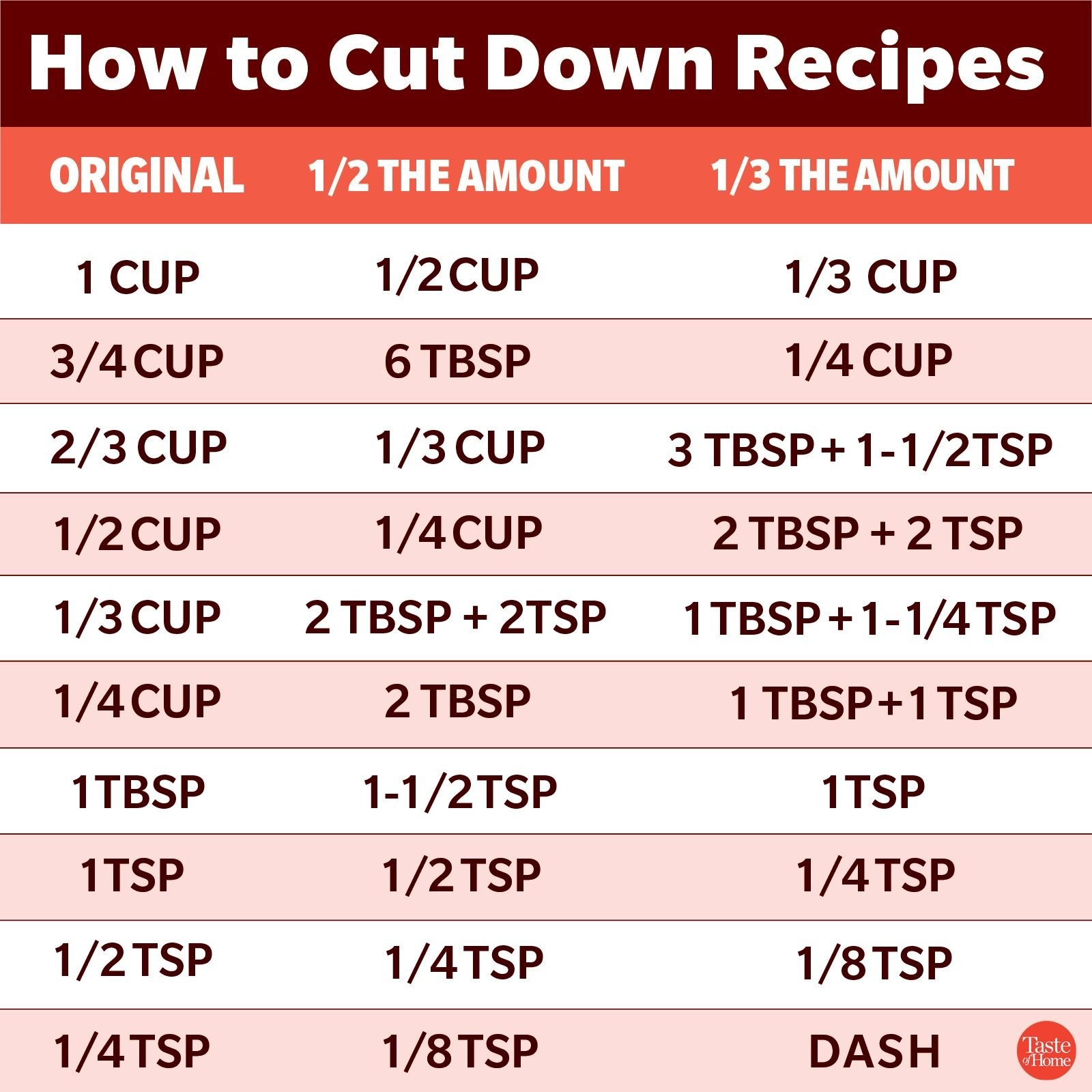
- 1 cup = 8 fluid ounces
- 1 cup = 16 tablespoons (tbsp)
- 1 cup = 48 teaspoons (tsp)
These conversions are useful when a recipe calls for amounts less than a full cup, or when you need to scale a recipe up or down.
-
Common Cup Fractions
Recipes often use fractions of a cup, so knowing their equivalent measurements is beneficial:
- 1/2 cup = 4 fluid ounces = 8 tablespoons
- 1/3 cup = Approximately 2.67 fluid ounces = 5 tablespoons + 1 teaspoon
- 1/4 cup = 2 fluid ounces = 4 tablespoons
-
Importance of Accurate Measurements
In cooking, particularly in baking, accurate measurements are critical. Even slight variations can affect the outcome of a dish. Using the correct measuring tools and understanding the conversions ensures that your recipes turn out as expected. For example, when baking a cake, the precise ratio of wet to dry ingredients is vital for the cake’s texture and rise.
-
Measuring Techniques
Different ingredients require different measuring techniques for accuracy:
- Liquids: Use a liquid measuring cup. Pour the liquid in and check the measurement at eye level to ensure accuracy.
- Dry Ingredients: Use dry measuring cups. Spoon the ingredient into the cup until it’s overflowing, then level it off with a flat edge, like a knife.
- Solid Fats: For ingredients like shortening or butter, pack them firmly into the measuring cup and level off.
-
Metric vs. US Customary Units
It’s important to be aware of the differences between metric and US customary units. While a US cup is approximately 237 ml, a metric cup is exactly 250 ml. This difference can be significant when converting recipes from one system to another. Always specify which system you are using to avoid confusion.
-
Tools for Measuring
Having the right measuring tools is essential for accuracy. A basic set should include:
- Liquid measuring cups (usually glass or plastic with a handle and spout)
- Dry measuring cups (typically a set of nested cups in standard sizes)
- Measuring spoons
For even greater precision, consider using a kitchen scale, especially when baking.
-
Practical Application
Understanding these basic principles allows you to easily adjust recipes, convert measurements, and ensure consistent results in your cooking and baking. Whether you’re halving a recipe or converting from metric to US units, a solid grasp of these fundamentals will prove invaluable.
2. Calculating Half of 1/4 Cup
Now, let’s focus on the primary question: What is half of 1/4 cup? This section provides a step-by-step breakdown to calculate this measurement, along with practical examples and tips.
-
Step-by-Step Calculation
To find half of 1/4 cup, you can use the following methods:
-
Fraction Method:
- Start with the fraction: 1/4 cup
- Divide by 2 (or multiply by 1/2): (1/4) ÷ 2 = (1/4) × (1/2) = 1/8 cup
-
Tablespoon Conversion:
- 1/4 cup is equal to 4 tablespoons.
- Divide 4 tablespoons by 2: 4 tbsp ÷ 2 = 2 tablespoons
-
Fluid Ounce Conversion:
- 1/4 cup is equal to 2 fluid ounces.
- Divide 2 fluid ounces by 2: 2 fl oz ÷ 2 = 1 fluid ounce
-
-
The Answer: 2 Tablespoons
Therefore, half of 1/4 cup is equal to 1/8 cup, which is equivalent to 2 tablespoons or 1 fluid ounce. This conversion is crucial for precise cooking and baking.
 Two tablespoons in a measuring spoon.
Two tablespoons in a measuring spoon.
Alternative text: Measuring two tablespoons, equivalent to half of a quarter cup, essential for precise cooking.
-
Practical Examples
To illustrate this further, consider the following examples:
-
Example 1: Cake Recipe
- A cake recipe calls for 1/4 cup of oil. You want to make a smaller cake, so you halve the recipe. You will need 2 tablespoons of oil.
-
Example 2: Salad Dressing
- A salad dressing recipe requires 1/4 cup of vinegar. To make a smaller batch, you need to use half of that amount, which is 2 tablespoons of vinegar.
-
Example 3: Cookie Dough
- A cookie dough recipe calls for 1/4 cup of melted butter. If you want to make fewer cookies, you’ll use 2 tablespoons of melted butter.
-
-
When to Use This Measurement
Knowing that half of 1/4 cup is 2 tablespoons is especially useful in situations like:
- Reducing Recipe Sizes: When you want to make a smaller portion of a recipe.
- Adjusting Flavors: When experimenting with flavors and you want to add a small amount of an ingredient.
- Dietary Control: When you’re carefully monitoring your ingredient intake for dietary reasons.
-
Tips for Accurate Measurement
To ensure accuracy when measuring 2 tablespoons:
- Use the Right Tools: Use standard measuring spoons.
- Level Off: When measuring dry ingredients, fill the tablespoon and level it off with a straight edge.
- Check Consistency: Ensure your ingredients are properly mixed or melted, as needed.
-
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Eyeballing: Avoid estimating the amount, as this can lead to inconsistencies in your recipes.
- Using Incorrect Spoons: Kitchen spoons are not always the same size as measuring spoons. Always use standard measuring spoons for accuracy.
-
Advanced Techniques
For more advanced baking or cooking, consider using a kitchen scale for precise measurements, especially when halving or doubling recipes.
3. Converting Measurements to Tablespoons and Teaspoons
Understanding how to convert cup measurements to tablespoons and teaspoons is crucial for precise cooking and baking. This section provides a comprehensive guide to these conversions, making it easier to adjust recipes and measure ingredients accurately.
-
Why Convert to Tablespoons and Teaspoons?
Converting to smaller units like tablespoons and teaspoons is particularly useful when:
- A recipe calls for a small fraction of a cup.
- You need to scale down a recipe.
- You want to measure ingredients with greater precision.
-
Basic Conversions
Here are the essential conversions you should know:
- 1 cup = 16 tablespoons
- 1 tablespoon = 3 teaspoons
-
Converting Fractions of a Cup
To convert fractions of a cup to tablespoons and teaspoons, follow these steps:
-
1/2 Cup:
- 1/2 cup = (1/2) * 16 tablespoons = 8 tablespoons
- 8 tablespoons = 8 * 3 teaspoons = 24 teaspoons
-
1/3 Cup:
- 1/3 cup = Approximately 5.33 tablespoons
- This is often rounded to 5 tablespoons + 1 teaspoon (since 0.33 tbsp is roughly 1 tsp)
-
1/4 Cup:
- 1/4 cup = (1/4) * 16 tablespoons = 4 tablespoons
- 4 tablespoons = 4 * 3 teaspoons = 12 teaspoons
-
1/8 Cup:
- 1/8 cup = (1/8) * 16 tablespoons = 2 tablespoons
- 2 tablespoons = 2 * 3 teaspoons = 6 teaspoons
-
-
Quick Reference Chart
| Cup Measurement | Tablespoons | Teaspoons |
|---|---|---|
| 1 cup | 16 tbsp | 48 tsp |
| 3/4 cup | 12 tbsp | 36 tsp |
| 2/3 cup | 10.67 tbsp (approx. 10 tbsp + 2 tsp) | 32 tsp |
| 1/2 cup | 8 tbsp | 24 tsp |
| 1/3 cup | 5.33 tbsp (approx. 5 tbsp + 1 tsp) | 16 tsp |
| 1/4 cup | 4 tbsp | 12 tsp |
| 1/8 cup | 2 tbsp | 6 tsp |
| 1 tablespoon | N/A | 3 tsp |
-
Practical Examples
-
Example 1: Reducing a Recipe
- A recipe calls for 1/3 cup of sugar, but you want to use half that amount.
- Half of 1/3 cup = (1/2) * (1/3) = 1/6 cup
- Convert 1/6 cup to tablespoons: (1/6) * 16 tbsp = Approximately 2.67 tbsp
- This is roughly 2 tablespoons + 2 teaspoons
-
Example 2: Measuring Small Quantities
- You need 1/8 cup of vanilla extract.
- 1/8 cup = 2 tablespoons
- This is easier to measure using tablespoons rather than trying to estimate 1/8 cup.
-
-
Tips for Accurate Conversion
- Use Standard Measuring Tools: Always use standard measuring cups, tablespoons, and teaspoons for accuracy.
- Level Dry Ingredients: When measuring dry ingredients, level off the spoon or cup with a flat edge to ensure you have the correct amount.
- Consistency is Key: Ensure your ingredients are properly mixed or melted before measuring.
-
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Approximating Too Much: While rounding is sometimes necessary, avoid excessive approximation, as it can affect the outcome of your recipe.
- Using Non-Standard Utensils: Kitchen spoons and forks are not the same size as measuring spoons. Always use standard measuring tools.
-
Advanced Techniques
For complex recipes, consider using a kitchen scale for even greater precision. This is particularly helpful when converting between volume and weight measurements.
4. How to Halve an Egg
Halving an egg might seem challenging, but it’s a useful skill when you need to reduce a recipe that calls for just one egg. This section provides practical methods to accurately halve an egg, ensuring your recipes turn out perfectly.
-
Why Halve an Egg?
There are several reasons why you might need to halve an egg:
- Reducing Recipe Size: When you want to make a smaller portion of a recipe.
- Dietary Adjustments: When you are trying to reduce cholesterol or calories.
- Baking Precision: Sometimes, the right texture requires a precise amount of egg.
-
Method 1: The Whisk and Eyeball Technique
This is the simplest method for halving an egg:
- Crack the Egg: Crack the egg into a small bowl.
- Whisk: Whisk the egg thoroughly until the yolk and white are fully combined.
- Estimate Half: Pour approximately half of the whisked egg mixture into your recipe.
- Save the Rest: The remaining half can be saved for another use, such as an omelet or another baking project.
-
Method 2: The Weighing Technique
For more precise measurement, use a kitchen scale:
- Weigh the Bowl: Place a small bowl on your kitchen scale and tare (zero) the scale.
- Crack the Egg: Crack the egg into the bowl.
- Record the Weight: Note the total weight of the egg.
- Calculate Half: Divide the total weight by two to find half the weight.
- Pour Half: Pour out the egg until the scale reads half the original weight.
-
Tips for Accuracy
- Use a Precise Scale: If using the weighing method, ensure your kitchen scale is accurate.
- Whisk Thoroughly: When whisking, make sure the yolk and white are fully combined for an even distribution.
- Estimate Carefully: If eyeballing, try to be as precise as possible when pouring out half the egg.
-
When to Use Each Method
- Whisk and Eyeball: Best for recipes where a slight variation in egg quantity won’t significantly impact the outcome, such as in some pancake or scrambled egg recipes.
- Weighing Technique: Ideal for baking recipes where precise measurements are crucial, such as cakes, cookies, or custards.
-
Practical Examples
-
Example 1: Small Batch Baking
- A cookie recipe calls for one egg, but you only want to make a few cookies. Use the weighing method to halve the egg accurately.
-
Example 2: Reducing Cholesterol
- You’re making scrambled eggs and want to reduce the cholesterol. Halve the egg using the whisk and eyeball method.
-
-
What to Do with the Remaining Egg
- Store Properly: If you have leftover whisked egg, store it in an airtight container in the refrigerator and use it within 24 hours.
- Use in Other Dishes: Add it to omelets, frittatas, or use it as an egg wash for pastries.
-
Alternatives to Halving an Egg
If halving an egg seems too complicated, consider these alternatives:
- Use Egg Replacers: Products like flaxseed meal mixed with water can mimic the binding properties of an egg.
- Adjust Other Ingredients: In some recipes, you can slightly adjust other liquid ingredients to compensate for using a whole egg instead of half.
5. Tips for Reducing and Scaling Recipes
Scaling recipes down or up is a common need in the kitchen, whether you’re cooking for fewer people, using different pan sizes, or adjusting ingredient quantities. This section offers essential tips for accurately reducing and scaling recipes to achieve consistent results.
-
Why Scale Recipes?
There are several reasons to scale recipes:
- Adjusting Servings: Cooking for a smaller or larger group.
- Using Different Pan Sizes: Adapting a recipe to fit the pan you have.
- Ingredient Availability: Modifying a recipe based on the amount of ingredients on hand.
-
Basic Principles of Scaling
- Maintain Ratios: The key to scaling recipes successfully is maintaining the correct ratio of ingredients.
- Accurate Measurements: Use precise measuring tools to ensure the scaled ingredients match the intended proportions.
-
Steps for Reducing a Recipe
-
Determine the Scaling Factor:
- Divide the desired yield by the original yield. For example, if you want to halve a recipe, the scaling factor is 1/2 or 0.5.
-
Multiply Each Ingredient:
- Multiply the amount of each ingredient by the scaling factor.
- Example: If a recipe calls for 1 cup of flour and you’re halving it, multiply 1 cup by 0.5 to get 1/2 cup of flour.
-
Adjust Cooking Time:
- Smaller quantities may require less cooking time. Check the dish frequently to prevent overcooking.
-
-
Steps for Increasing a Recipe
-
Determine the Scaling Factor:
- Divide the desired yield by the original yield. For example, if you want to double a recipe, the scaling factor is 2.
-
Multiply Each Ingredient:
- Multiply the amount of each ingredient by the scaling factor.
- Example: If a recipe calls for 1/2 cup of sugar and you’re doubling it, multiply 1/2 cup by 2 to get 1 cup of sugar.
-
Adjust Cooking Time:
- Larger quantities may require more cooking time. Monitor the dish and adjust the cooking time accordingly.
-
-
Specific Ingredient Considerations
-
Spices and Seasonings:
- When scaling down, reduce spices and seasonings conservatively, as they can easily overpower a smaller dish.
- When scaling up, increase spices gradually, tasting as you go to avoid over-seasoning.
-
Liquids:
- Adjust liquids proportionally to maintain the correct consistency.
-
Eggs:
- Scaling eggs can be tricky. Use the methods described earlier for halving eggs, or consider using egg replacers.
-
Yeast:
- For baking recipes, adjust yeast carefully, as it is crucial for leavening. Use a kitchen scale for precise measurements.
-
-
Example: Scaling a Cookie Recipe
Original Recipe (Makes 24 Cookies):
- 1 cup butter
- 1/2 cup sugar
- 2 cups flour
- 1 egg
- 1 tsp vanilla extract
Scaled Recipe (Makes 12 Cookies – Halved):
- 1/2 cup butter
- 1/4 cup sugar
- 1 cup flour
- 1/2 egg (use the methods described earlier)
- 1/2 tsp vanilla extract
-
Adjusting Cooking Time and Temperature
- Cooking Time: Smaller quantities generally require less cooking time, while larger quantities require more.
- Temperature: Maintain the original temperature unless the recipe specifies otherwise.
- Monitoring: Always monitor the dish closely to prevent overcooking or undercooking.
-
Using Online Recipe Scalers
- There are many online tools and apps that can help you scale recipes automatically. These tools can be particularly useful for complex recipes with multiple ingredients.
-
Tips for Success
- Read the Recipe Carefully: Understand the purpose of each ingredient before scaling.
- Start Small: When scaling for the first time, start with a small adjustment to see how the recipe turns out.
- Take Notes: Keep track of your adjustments and the results, so you can refine your scaling techniques over time.
6. Common Cooking Measurement Conversions
Having a grasp of common cooking measurement conversions can save time and ensure accuracy in the kitchen. This section provides a handy reference guide to essential conversions that every home cook should know.
-
Why Learn Measurement Conversions?
- Recipe Adjustments: Easily scale recipes up or down to suit your needs.
- International Recipes: Convert measurements between metric and US customary units.
- Ingredient Substitutions: Make informed substitutions when you don’t have a specific ingredient on hand.
-
Basic Units of Measurement
- Volume: Measures the amount of space a substance occupies. Common units include cups, tablespoons, teaspoons, fluid ounces, milliliters, and liters.
- Weight: Measures the heaviness of a substance. Common units include ounces, pounds, grams, and kilograms.
-
Essential Volume Conversions
-
Cups to Fluid Ounces:
- 1 cup = 8 fluid ounces
- 1/2 cup = 4 fluid ounces
- 1/4 cup = 2 fluid ounces
- 1/8 cup = 1 fluid ounce
-
Cups to Tablespoons and Teaspoons:
- 1 cup = 16 tablespoons
- 1 cup = 48 teaspoons
- 1/2 cup = 8 tablespoons
- 1/4 cup = 4 tablespoons
- 1 tablespoon = 3 teaspoons
-
Milliliters to Fluid Ounces and Cups:
- 1 fluid ounce = Approximately 29.57 milliliters
- 1 cup (US) = Approximately 237 milliliters
- 1 cup (Metric) = 250 milliliters
-
-
Essential Weight Conversions
-
Ounces to Pounds:
- 1 pound = 16 ounces
-
Ounces to Grams:
- 1 ounce = Approximately 28.35 grams
-
Grams to Kilograms:
- 1 kilogram = 1000 grams
-
-
Temperature Conversions
-
Fahrenheit to Celsius:
- °C = (°F – 32) * 5/9
-
Celsius to Fahrenheit:
- °F = (°C * 9/5) + 32
-
-
Quick Reference Chart
| Measurement | US Customary | Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | 1 cup | Approximately 237 ml (US) / 250 ml (Metric) |
| 1 fluid ounce | Approximately 29.57 ml | |
| 1 tablespoon | Approximately 14.79 ml | |
| 1 teaspoon | Approximately 4.93 ml | |
| Weight | 1 pound | Approximately 453.59 grams |
| 1 ounce | Approximately 28.35 grams |
-
Practical Examples
-
Example 1: Converting a Recipe from US to Metric
- A recipe calls for 1 cup of milk (US). You need to convert this to milliliters.
- 1 cup (US) = Approximately 237 ml
-
Example 2: Adjusting Oven Temperature
- A recipe requires baking at 350°F. You need to convert this to Celsius.
- °C = (350 – 32) * 5/9 = Approximately 177°C
-
-
Tips for Accurate Conversions
- Use Conversion Charts: Keep a conversion chart handy in your kitchen.
- Use Online Tools: Utilize online conversion calculators for quick and accurate results.
- Be Mindful of Units: Always double-check the units you are converting from and to.
-
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Mixing Up US and Metric Cups: Remember that US and metric cups have slightly different volumes.
- Incorrect Temperature Conversions: Use the correct formulas to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius.
7. Adjusting Recipes for Different Pan Sizes
Adapting recipes to fit different pan sizes is a common challenge in baking. Whether you have a smaller or larger pan than the recipe calls for, understanding how to adjust the ingredients and cooking time will help you achieve the best results. This section provides a comprehensive guide to adjusting recipes for various pan sizes.
-
Why Adjust for Pan Size?
- Consistent Results: Using the correct pan size ensures that your baked goods cook evenly and have the right texture.
- Preventing Overflow: A pan that is too small can cause the batter to overflow during baking.
- Avoiding Underbaking: A pan that is too large can result in a thin, dry, and overcooked product.
-
Understanding Pan Volume
-
Importance of Volume: The volume of a pan is crucial for determining how a recipe will bake. Volume is the amount of space inside the pan.
-
Measuring Pan Volume:
- Rectangular or Square Pans: Measure the length, width, and height of the pan in inches. Multiply these dimensions to find the volume in cubic inches.
- Round Pans: Measure the diameter and height of the pan. Use the formula V = πr²h, where r is the radius (half of the diameter) and h is the height.
-
-
Common Pan Sizes and Volumes
| Pan Type | Dimensions | Approximate Volume |
|---|---|---|
| 9×13 inch Rectangular | 9″ x 13″ x 2″ | Approximately 234 cubic inches |
| 8×8 inch Square | 8″ x 8″ x 2″ | Approximately 128 cubic inches |
| 9 inch Round | 9″ diameter x 2″ | Approximately 254 cubic inches |
| 8 inch Round | 8″ diameter x 2″ | Approximately 201 cubic inches |
| Loaf Pan | 9″ x 5″ x 3″ | Approximately 135 cubic inches |
-
Steps for Adjusting Recipes
-
Calculate Pan Volume:
- Measure the volume of both the original pan size (as specified in the recipe) and the pan you intend to use.
-
Determine Scaling Factor:
- Divide the volume of your pan by the volume of the original pan. This will give you the scaling factor.
-
Adjust Ingredients:
- Multiply each ingredient by the scaling factor to determine the new quantities.
-
Adjust Cooking Time:
- Monitor the baking process closely, as the cooking time may need to be adjusted based on the pan size.
-
-
Example: Adjusting a Cake Recipe
Original Recipe:
- Cake recipe designed for a 9-inch round pan (Volume ≈ 254 cubic inches)
- You want to use an 8-inch round pan (Volume ≈ 201 cubic inches)
Steps:
- Scaling Factor: 201 / 254 ≈ 0.79
- Adjust Ingredients: Multiply each ingredient by 0.79.
- Adjust Cooking Time: Start checking for doneness about 10-15 minutes earlier than the original recipe suggests.
-
Adjusting Cooking Time and Temperature
- Smaller Pans: May require slightly less cooking time. Check for doneness frequently.
- Larger Pans: May require slightly more cooking time. Monitor the edges to prevent overbrowning.
- Temperature: Generally, maintain the same temperature unless the recipe indicates otherwise.
-
Specific Considerations
- Cakes: For layer cakes, ensure the batter is evenly distributed between pans.
- Brownies and Bars: Adjust the baking time to prevent overcooking the edges.
- Casseroles: Ensure the filling is evenly spread in the pan for uniform cooking.
-
Tips for Success
- Use Accurate Measurements: Precise measurements are crucial for successful adjustments.
- Monitor Closely: Keep a close eye on the baking process, especially when trying a new adjustment.
- Test with a Skewer: Use a skewer or toothpick to check for doneness in the center of the baked good.
8. The Role of Accurate Measurements in Baking Success
Accurate measurements are fundamental to achieving consistent and successful results in baking. This section highlights the importance of precision, the impact of inaccurate measurements, and provides guidelines for measuring ingredients correctly.
-
Why Accuracy Matters in Baking
- Chemical Reactions: Baking involves precise chemical reactions between ingredients. Accurate measurements ensure these reactions occur as expected.
- Texture and Consistency: The ratio of wet to dry ingredients, the amount of leavening agents, and the proportion of fats and sugars all contribute to the final texture and consistency of baked goods.
- Flavor Balance: Precise measurements ensure the right balance of flavors, preventing one ingredient from overpowering the others.
-
Impact of Inaccurate Measurements
- Dry and Crumbly Cakes: Too much flour or not enough liquid can result in a dry, crumbly cake.
- Dense and Heavy Breads: Incorrect yeast measurements can lead to dense, heavy breads that don’t rise properly.
- Flat Cookies: Too much butter or sugar can cause cookies to spread too thin and become flat.
- Inconsistent Results: Variations in measurements can lead to inconsistent results, making it difficult to replicate successful recipes.
-
Measuring Tools for Accuracy
-
Dry Measuring Cups:
- Use nested cups for measuring dry ingredients like flour and sugar.
- Spoon the ingredient into the cup until it is overflowing, then level off with a flat edge (e.g., a knife).
- Avoid packing the ingredient into the cup unless the recipe specifies.
-
Liquid Measuring Cups:
- Use clear glass or plastic cups with measurement markings on the side.
- Place the cup on a level surface and pour the liquid in, checking the measurement at eye level.
- Avoid lifting the cup to check the measurement, as this can lead to inaccurate readings.
-
Measuring Spoons:
- Use standard measuring spoons for small quantities of both dry and liquid ingredients.
- Level off dry ingredients with a flat edge.
-
Kitchen Scale:
- A kitchen scale is the most accurate tool for measuring ingredients, especially in baking.
- Use the tare function to zero out the weight of the bowl or container before adding the ingredient.
-
-
Measuring Techniques for Different Ingredients
-
Flour:
- Lightly spoon flour into the measuring cup, then level off.
- Avoid scooping directly from the bag, as this can pack the flour and result in too much being used.
-
Sugar:
- Granulated Sugar: Spoon into the measuring cup and level off.
- Brown Sugar: Pack firmly into the measuring cup and level off.
-
Liquids:
- Pour liquids into a liquid measuring cup and check at eye level.
- For viscous liquids like honey or molasses, spray the measuring cup with non-stick spray for easy release.
-
Fats:
- Butter: Cut into tablespoons or use sticks with measurement markings.
- Shortening: Pack firmly into the measuring cup and level off.
- Oil: Pour into a liquid measuring cup and check at eye level.
-
-
Tips for Ensuring Accuracy
- Use Standard Measuring Tools: Always use standard measuring cups, spoons, and scales.
- Check Expiration Dates: Ensure ingredients like baking powder and yeast are fresh.
- Read the Recipe Carefully: Pay attention to specific instructions, such as whether to pack or level ingredients.
- Double-Check Measurements: Before adding ingredients, double-check that you have measured them correctly.
-
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Eyeballing Measurements: Avoid estimating amounts, as this can lead to inconsistent results.
- Using the Wrong Tools: Use the appropriate measuring tools for dry and liquid ingredients.
- Ignoring Instructions: Follow the recipe’s instructions for measuring ingredients, such as sifting flour or packing brown sugar.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Cooking Measurements
This section addresses common questions related to cooking measurements, providing concise answers and helpful tips to enhance your culinary skills.
Volume Measurements
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| How many tablespoons are in 1/2 cup? | There are 8 tablespoons in 1/2 cup. |
| How many teaspoons are in 1 tablespoon? | There are 3 teaspoons in 1 tablespoon. |
| What is the difference between a fluid ounce and an ounce? | A fluid ounce is a unit of volume, while an ounce is a unit of weight. They are not interchangeable. |
| How many milliliters are in a US cup? | There are approximately 237 milliliters in a US cup. |
Weight Measurements
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| How many ounces are in a pound? | There are 16 ounces in a pound. |
| How many grams are in an ounce? | There are approximately 28.35 grams in an ounce. |
| What is the best way to measure dry ingredients by weight? | Use a kitchen scale for accurate measurements. Tare the scale with the bowl, then add the ingredient until you reach the desired weight. |
| How do I convert grams to pounds? | Divide the number of grams by 453.59 to get the equivalent in pounds. |
Temperature Measurements
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| How do I convert Fahrenheit to Celsius? | Use the formula: °C = (°F – 32) * 5/9 |
| How do I convert Celsius to Fahrenheit? | Use the formula: °F = (°C * 9/5) + 32 |
| What is the freezing point of water in Fahrenheit and Celsius? | The freezing point of water is 32°F and 0°C. |
| What is the boiling point of water in Fahrenheit and Celsius? | The boiling point of water is 212°F and 100°C. |
Recipe Adjustments
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| How can I halve a recipe that calls for one egg? | Whisk the egg in a bowl and use half of the mixture, or weigh the egg and use half the weight. |
| How do I adjust cooking time when scaling a recipe? | Smaller quantities usually require less cooking time, while larger quantities require more. Monitor the dish closely. |
| What should I do if I don’t have the exact pan size specified in a recipe? | Adjust the recipe for different pan sizes by measuring the volume of the original and substitute pans to ensure even baking. |
| Is it okay to substitute ingredients in a recipe? | Yes, but be mindful of how substitutions might affect the taste and texture of the final product. |
General Cooking Tips
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Why is it important to use standard measuring tools? | Standard measuring tools ensure consistent and accurate results in your recipes. |
| How should I measure flour for baking? | Lightly spoon the flour into the measuring cup, then level off with a flat edge. Avoid packing the flour. |
| What is the best way to measure sticky liquids like honey? | Spray the measuring cup with non-stick spray for easy release and accurate measurement. |
| How often should I calibrate my kitchen scale? | Calibrate your kitchen scale regularly, especially if you use it frequently, to ensure accuracy. |
10. Leveraging WHAT.EDU.VN for Your Culinary Questions
Are you seeking instant answers to your burning culinary questions? Look no further than WHAT.EDU.VN! Our platform is designed to provide you with fast, free, and reliable answers from a community of knowledgeable experts.
-
Why Use WHAT.EDU.VN?
- Free Answers: Get your questions answered without any cost.
- Quick Responses: Receive prompt responses to your inquiries.
- Expert Advice: Connect with a community of experts who are passionate about sharing their knowledge.
- Easy to Use: Our platform is user-friendly, making it simple to ask questions and find answers.
-
How what.edu.vn Can Help You
