Human-computer interaction (HCI) is the study of how people interact with computers and the design of technology to make that interaction better, and WHAT.EDU.VN is here to answer all your questions about it. We offer free answers to your questions, focusing on user-centered design, usability, and accessibility, so you can get the information you need without worrying about costs or complex research. Join our community and ask your questions today to explore the world of user experience, interface design, and interaction design.
1. What Is Human-Computer Interaction (HCI)?
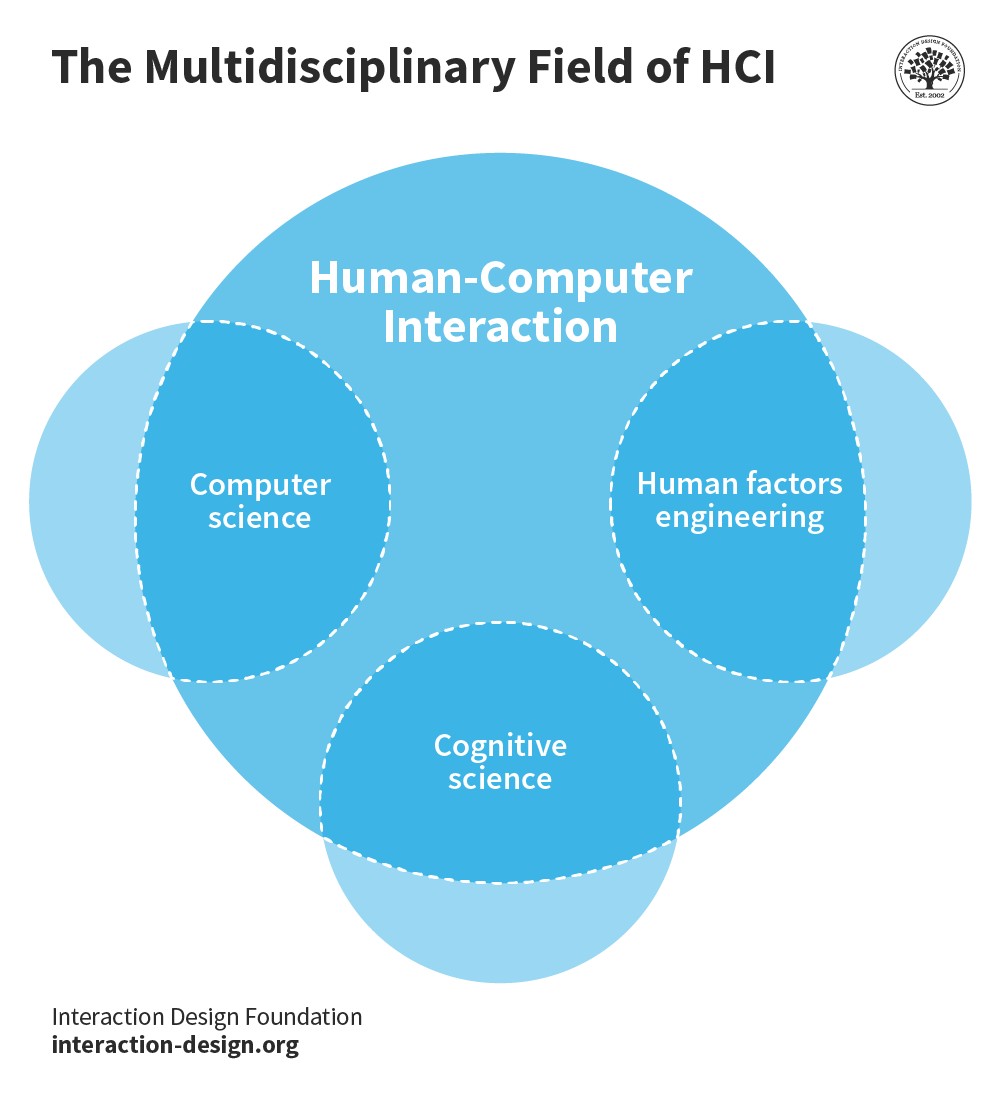
Human-computer interaction (HCI) is a multidisciplinary field that focuses on the design, evaluation, and implementation of interactive computing systems for human use and the study of major phenomena surrounding them. It aims to make computer technology more usable, accessible, and desirable to people. In essence, HCI seeks to bridge the gap between humans and computers, ensuring that technology serves human needs and capabilities effectively.
HCI is not just about making computers easy to use; it’s about understanding how people think, feel, and behave when they interact with technology. By understanding these factors, HCI professionals can design interfaces and systems that are intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable to use. This field incorporates aspects of computer science, cognitive psychology, design, and engineering to create technology that truly meets the needs of its users.
Want to learn more about HCI and get your questions answered for free? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today.
2. What Are the Key Principles of Human-Computer Interaction?
The key principles of HCI guide the design and evaluation of interactive systems. These principles ensure that technology is user-centered, efficient, and effective. Here are some of the fundamental principles:
- User-Centered Design: This principle emphasizes that the design process should revolve around the needs and preferences of the users. User research, testing, and feedback are essential components of user-centered design.
- Usability: Usability refers to the ease with which users can achieve their goals when using a system. Key aspects of usability include learnability, efficiency, memorability, errors, and satisfaction.
- Accessibility: Accessibility ensures that technology is usable by people with a wide range of abilities and disabilities. This includes providing alternative input methods, clear visual design, and compatibility with assistive technologies.
- Utility: Utility refers to the extent to which a system provides the functionality that users need. A system may be usable but lack the necessary features to be truly useful.
- Learnability: Learnability is the ease with which new users can begin effective interaction and achieve maximal performance.
- Efficiency: Efficiency measures the speed at which users can accomplish tasks once they have learned the system.
- Memorability: Memorability is the ease with which users can remember how to use the system after a period of not using it.
- Errors: Minimizing errors involves reducing the number of errors users make, as well as providing effective error recovery mechanisms.
- Satisfaction: Satisfaction refers to the overall pleasantness of using the system. A satisfying system is enjoyable and motivates users to continue using it.
3. What Are the Main Goals of Human-Computer Interaction?
The main goals of HCI are to improve the interaction between humans and computers by making systems:
- Usable: Easy to learn and use.
- Safe: Protecting users from harm and data loss.
- Effective: Enabling users to achieve their goals.
- Efficient: Allowing users to perform tasks quickly and with minimal effort.
- Enjoyable: Providing a satisfying and engaging experience.
- Accessible: Usable by people with a wide range of abilities and disabilities.
According to research from Stanford University’s Human-Computer Interaction Group in 2023, systems designed with these goals in mind lead to increased productivity, reduced errors, and higher user satisfaction.
Want to learn more and ask your questions? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN for free answers and expert insights.
4. What Are the Core Components of Human-Computer Interaction?
HCI involves several core components that work together to create effective and user-friendly systems. These components include:
- The User: Understanding the user is central to HCI. This involves studying their cognitive abilities, physical capabilities, emotions, and cultural background.
- The Computer: This includes hardware, software, and any other technology that users interact with. HCI professionals need to understand the capabilities and limitations of computer technology.
- The Interaction: This refers to the way the user and the computer communicate and work together. The interaction should be intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable.
- The Context: The context in which the interaction takes place is also important. This includes the physical environment, the social setting, and the task that the user is trying to accomplish.
5. What Disciplines Contribute to the Field of HCI?
HCI is a multidisciplinary field that draws on knowledge and techniques from a wide range of disciplines, including:
- Computer Science: Provides the technical foundation for building interactive systems.
- Cognitive Psychology: Offers insights into how people perceive, think, and learn, which are essential for designing user-friendly interfaces.
- Human Factors Engineering: Focuses on designing systems that are compatible with human physical and cognitive capabilities.
- Design: Contributes principles and methods for creating visually appealing and effective interfaces.
- Sociology: Provides an understanding of how technology affects social interactions and group dynamics.
- Anthropology: Offers insights into how people use technology in different cultural contexts.
- Linguistics: Helps in designing effective communication between users and computers, such as natural language interfaces.
According to a 2024 study by MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL), the integration of these diverse disciplines is crucial for advancing the field of HCI.
6. What Are the Key Areas of Research in Human-Computer Interaction?
HCI research covers a broad range of topics aimed at improving the design, evaluation, and understanding of interactive systems. Key areas of research include:
- Usability Testing: Evaluating the ease of use of a system by observing users as they perform tasks.
- Interface Design: Creating effective and appealing user interfaces that facilitate interaction.
- Interaction Techniques: Developing new ways for users to interact with computers, such as gesture recognition, voice control, and virtual reality.
- Accessibility: Ensuring that technology is usable by people with disabilities through assistive technologies and inclusive design practices.
- User Modeling: Creating models of user behavior and cognition to inform the design of adaptive and personalized systems.
- Computer-Supported Cooperative Work (CSCW): Studying how technology can support collaboration and communication among groups of people.
- Human-Robot Interaction (HRI): Investigating the interaction between humans and robots, including the design of robot interfaces and behaviors.
- Affective Computing: Developing systems that can recognize, interpret, and respond to human emotions.
- Ubiquitous Computing: Designing technology that is seamlessly integrated into the environment and available whenever and wherever it is needed.
7. How Does HCI Relate to User Experience (UX) Design?
HCI and UX design are closely related fields that share the common goal of creating user-centered technology. While HCI is a broad, multidisciplinary field that encompasses the study of human-computer interaction, UX design is a more focused practice that emphasizes the overall experience of using a product or service.
In many ways, HCI can be seen as the scientific foundation for UX design. HCI research provides insights into user behavior, cognition, and emotion that inform the design decisions made by UX professionals. UX designers apply these insights to create interfaces and interactions that are intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable.
Some key differences between HCI and UX design include:
- Focus: HCI is more research-oriented, while UX design is more practice-oriented.
- Scope: HCI covers a broader range of topics than UX design, including social and organizational computing, accessibility, and human-robot interaction.
- Methods: HCI researchers use a variety of methods, including experiments, surveys, and ethnographic studies, while UX designers rely more on usability testing, user interviews, and A/B testing.
Despite these differences, HCI and UX design are complementary fields that benefit from each other’s knowledge and expertise. UX designers often draw on HCI research to inform their design decisions, while HCI researchers use UX design practices to validate their theories and findings.
Do you have questions about the relationship between HCI and UX design? Ask them on WHAT.EDU.VN and get free, expert answers.
8. What Are Some Common Methods Used in HCI?
HCI professionals use a variety of methods to design, evaluate, and improve interactive systems. Some common methods include:
- Usability Testing: Involves observing users as they interact with a system to identify usability problems and measure performance.
- User Interviews: Gathering qualitative data about user needs, preferences, and experiences through structured or semi-structured interviews.
- Surveys: Collecting quantitative data from a large number of users through questionnaires or online surveys.
- Ethnographic Studies: Observing users in their natural environment to understand how they use technology in real-world contexts.
- Heuristic Evaluation: Evaluating a system against a set of established usability principles or heuristics to identify potential problems.
- Cognitive Walkthrough: Simulating a user’s problem-solving process to identify potential cognitive obstacles.
- A/B Testing: Comparing two versions of a design to see which performs better in terms of user engagement, conversion rates, or other metrics.
- Eye Tracking: Measuring where users look on a screen to understand their attention patterns and identify areas of interest or confusion.
9. What Are the Career Opportunities in Human-Computer Interaction?
HCI offers a wide range of career opportunities in various industries and settings. Some common job titles in HCI include:
- UX Designer: Designs the overall experience of using a product or service, including the user interface, interaction design, and information architecture.
- UX Researcher: Conducts research to understand user needs, behaviors, and preferences, and uses these insights to inform design decisions.
- Usability Analyst: Evaluates the usability of a system and recommends improvements based on user feedback and testing.
- Interaction Designer: Focuses on the design of interactive behaviors and interfaces, ensuring that they are intuitive and efficient.
- Information Architect: Organizes and structures information within a system to make it easy for users to find what they need.
- HCI Researcher: Conducts research on human-computer interaction topics in academia or industry.
- Accessibility Specialist: Ensures that technology is accessible to people with disabilities by applying accessibility guidelines and standards.
HCI professionals work in a variety of industries, including:
- Software Development: Designing user interfaces for desktop, web, and mobile applications.
- Web Design: Creating user-friendly and engaging websites.
- Gaming: Designing interactive experiences for video games.
- Healthcare: Developing medical devices and software that are safe and effective for healthcare professionals and patients.
- Education: Designing educational software and online learning platforms.
- Government: Creating accessible and user-friendly government services and websites.
- Automotive: Designing in-car interfaces and systems.
10. What Are the Current Trends in Human-Computer Interaction?
The field of HCI is constantly evolving to keep pace with new technologies and changing user needs. Some current trends in HCI include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to create more intelligent and personalized user interfaces, such as chatbots, virtual assistants, and recommendation systems.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): VR and AR technologies are creating new opportunities for immersive and interactive experiences.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT is connecting everyday objects to the internet, creating new challenges and opportunities for HCI design.
- Wearable Technology: Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, are becoming increasingly popular, requiring new approaches to interface design and interaction.
- Voice User Interfaces (VUIs): Voice-controlled devices, such as smart speakers and voice assistants, are becoming more common, requiring new approaches to interaction design.
- Accessibility: There is a growing awareness of the importance of accessibility in HCI design, with a focus on creating technology that is usable by people with disabilities.
- Ethical Considerations: As technology becomes more powerful and pervasive, there is increasing concern about the ethical implications of HCI design, such as privacy, bias, and security.
According to a 2025 forecast by Gartner, these trends will continue to shape the field of HCI in the coming years, driving innovation and creating new opportunities for HCI professionals.
11. How Can I Get Started in Human-Computer Interaction?
If you’re interested in pursuing a career in HCI, there are several steps you can take to get started:
- Get an Education: Consider pursuing a degree in computer science, psychology, design, or a related field. Many universities offer specialized programs in HCI or UX design.
- Learn the Fundamentals: Familiarize yourself with the key concepts, principles, and methods of HCI. There are many books, articles, and online resources available to help you learn the basics.
- Gain Practical Experience: Look for opportunities to work on HCI projects, either through internships, volunteer work, or personal projects. This will give you valuable hands-on experience and help you build your portfolio.
- Network with Professionals: Attend HCI conferences, workshops, and meetups to connect with other professionals in the field. This can help you learn about job opportunities and get advice from experienced practitioners.
- Build a Portfolio: Create a portfolio of your HCI projects to showcase your skills and experience to potential employers.
12. What Are Some Examples of Successful Human-Computer Interaction?
Successful HCI is evident in many technologies and applications we use daily. Here are a few examples:
- Smartphones: Modern smartphones have intuitive touch interfaces, voice control, and personalized features, making them easy to use for a wide range of tasks.
- Websites: Well-designed websites have clear navigation, accessible content, and responsive layouts, providing a seamless user experience across different devices.
- ATM Machines: ATM machines have simple interfaces with clear instructions, allowing users to easily withdraw cash, deposit checks, and perform other banking transactions.
- GPS Navigation Systems: GPS navigation systems have intuitive maps, voice guidance, and real-time traffic updates, making it easy for drivers to find their way.
- Gaming Consoles: Modern gaming consoles have user-friendly controllers, immersive graphics, and online multiplayer capabilities, providing engaging and enjoyable gaming experiences.
13. How Does HCI Address Accessibility for Users with Disabilities?
HCI plays a crucial role in ensuring that technology is accessible to people with disabilities. By applying accessibility principles and guidelines, HCI professionals can create systems that are usable by people with a wide range of abilities. Some key strategies for addressing accessibility in HCI include:
- Providing Alternative Input Methods: Allowing users to interact with a system using alternative input methods, such as speech recognition, eye tracking, or switch devices.
- Designing for Visual Impairments: Creating interfaces with high contrast, large font sizes, and screen reader compatibility.
- Designing for Auditory Impairments: Providing visual alternatives for auditory information, such as captions for videos and transcripts for audio recordings.
- Designing for Motor Impairments: Creating interfaces that can be used with limited motor skills, such as large touch targets and single-switch access.
- Following Accessibility Standards: Adhering to accessibility standards such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) to ensure that systems meet established accessibility criteria.
14. What Role Does Culture Play in Human-Computer Interaction?
Culture plays a significant role in human-computer interaction, influencing how people perceive, interpret, and interact with technology. Cultural factors can affect everything from the visual design of interfaces to the way information is organized and presented. Some key considerations for cultural sensitivity in HCI include:
- Language: Providing interfaces in multiple languages to accommodate users from different linguistic backgrounds.
- Symbols and Icons: Using symbols and icons that are culturally appropriate and easily understood by users from different cultures.
- Color: Selecting colors that have positive connotations in different cultures, avoiding colors that may be offensive or have negative meanings.
- Layout: Designing layouts that are consistent with cultural norms, such as reading direction (left-to-right or right-to-left).
- Values: Respecting cultural values and beliefs when designing interfaces, avoiding content that may be offensive or disrespectful.
15. How Does Human-Computer Interaction Contribute to the Development of New Technologies?
HCI is a driving force behind the development of new technologies. By understanding human needs, behaviors, and preferences, HCI professionals can identify opportunities for innovation and guide the design of new products and services. HCI contributes to the development of new technologies in several ways:
- Identifying User Needs: HCI research helps to identify unmet user needs and pain points that can be addressed by new technologies.
- Guiding Design Decisions: HCI principles and methods provide guidance for making design decisions that are user-centered and effective.
- Evaluating Prototypes: HCI testing methods allow designers to evaluate prototypes and refine their designs based on user feedback.
- Promoting Adoption: By creating technologies that are usable, accessible, and enjoyable, HCI helps to promote the adoption and acceptance of new technologies.
Do you have more questions about how HCI impacts new technologies? Ask them on WHAT.EDU.VN and get free, insightful answers.
16. What Is the Future of Human-Computer Interaction?
The future of HCI is bright, with many exciting possibilities on the horizon. As technology continues to evolve, HCI will play an increasingly important role in shaping the way we interact with computers and the world around us. Some key trends that are likely to shape the future of HCI include:
- More Natural User Interfaces: Interfaces that are more natural, intuitive, and seamlessly integrated into our lives, such as brain-computer interfaces and gesture-based interfaces.
- Personalized and Adaptive Systems: Systems that are tailored to individual user needs and preferences, adapting to our behavior and learning from our interactions.
- Ubiquitous and Pervasive Computing: Technology that is seamlessly integrated into the environment, available whenever and wherever it is needed.
- Increased Focus on Ethics and Social Impact: A greater emphasis on the ethical implications of HCI design, ensuring that technology is used for good and that its benefits are shared by all.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Closer collaboration between HCI professionals and experts from other fields, such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and neuroscience, to create more innovative and impactful technologies.
The field of HCI is constantly evolving, and there are always new challenges and opportunities to explore. By staying informed, embracing new technologies, and focusing on the needs of users, HCI professionals can help to create a future where technology empowers people and improves lives.
Don’t let your questions about HCI go unanswered. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and get free, expert advice.
17. How Can Human-Computer Interaction Improve the Healthcare Industry?
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) has the potential to significantly improve the healthcare industry by enhancing the usability, efficiency, and safety of medical devices, software, and systems. Here are some key ways HCI can make a difference:
- Improved Electronic Health Records (EHRs): HCI principles can help design EHR systems that are more intuitive and user-friendly for healthcare professionals. This includes streamlining data entry, improving information retrieval, and reducing cognitive overload, ultimately leading to better patient care.
- Enhanced Medical Device Interfaces: Medical devices, such as infusion pumps, ventilators, and monitoring systems, often have complex interfaces. HCI can help simplify these interfaces, reduce errors, and improve the overall usability of these critical devices.
- Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring: HCI can play a crucial role in designing telemedicine platforms and remote monitoring systems that are easy to use for both patients and healthcare providers. This includes ensuring that video conferencing, data sharing, and remote monitoring tools are accessible and effective.
- Patient Engagement Tools: HCI can help create patient engagement tools, such as mobile apps and online portals, that empower patients to take a more active role in their own healthcare. These tools can provide patients with access to their medical records, educational resources, and communication channels with their healthcare providers.
- Training and Simulation Systems: HCI can be used to design training and simulation systems that help healthcare professionals develop and maintain their skills. These systems can provide realistic and interactive training scenarios that improve clinical performance and reduce errors.
18. How Can Human-Computer Interaction Be Applied to Improve Education?
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) can be effectively applied to improve education by enhancing the design of learning technologies, creating more engaging and effective learning experiences, and supporting diverse learners. Here are some specific applications:
- Interactive Learning Platforms: HCI principles can guide the design of interactive learning platforms that are engaging, intuitive, and personalized. This includes creating interfaces that are easy to navigate, providing feedback that is timely and relevant, and adapting the learning content to meet the individual needs of each student.
- Educational Games and Simulations: HCI can be used to design educational games and simulations that are both fun and effective. These games can provide students with opportunities to learn by doing, explore complex concepts, and develop problem-solving skills.
- Assistive Technologies: HCI can play a crucial role in developing assistive technologies for students with disabilities. This includes creating software and hardware that support students with visual impairments, hearing impairments, learning disabilities, and other special needs.
- Online Learning Environments: HCI principles can help design online learning environments that are accessible, engaging, and effective. This includes ensuring that online courses are easy to navigate, providing opportunities for interaction and collaboration, and supporting diverse learning styles.
- Teacher Support Tools: HCI can be used to create teacher support tools that help teachers plan lessons, assess student progress, and communicate with parents. These tools can streamline administrative tasks, improve communication, and free up teachers to focus on teaching.
19. How Can Human-Computer Interaction Help in Environmental Sustainability?
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) can contribute significantly to environmental sustainability by promoting eco-friendly behaviors, optimizing resource consumption, and enhancing environmental awareness. Here’s how HCI can be applied:
- Smart Home and Energy Management Systems: HCI can help design smart home and energy management systems that provide users with real-time feedback on their energy consumption and encourage them to adopt more sustainable behaviors. These systems can also automate energy-saving tasks, such as turning off lights and adjusting thermostats.
- Sustainable Transportation Systems: HCI can be used to design sustainable transportation systems that encourage the use of public transportation, cycling, and walking. This includes creating mobile apps that provide users with information on public transportation schedules, bike routes, and walking paths.
- Eco-Friendly Product Design: HCI can play a role in designing eco-friendly products that are both sustainable and user-friendly. This includes considering the environmental impact of materials, manufacturing processes, and product lifecycles.
- Waste Reduction and Recycling Systems: HCI can help design waste reduction and recycling systems that are easy to use and encourage people to recycle. This includes creating clear and intuitive interfaces for recycling bins and providing users with information on what can be recycled.
- Environmental Monitoring and Awareness Tools: HCI can be used to create environmental monitoring and awareness tools that provide users with information on environmental issues, such as air quality, water pollution, and climate change. These tools can help raise awareness and encourage people to take action to protect the environment.
20. What Ethical Considerations Are Important in Human-Computer Interaction?
Ethical considerations are paramount in Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) to ensure that technology is developed and used in a responsible and beneficial manner. Here are some key ethical considerations:
- Privacy: HCI professionals must respect user privacy and protect their personal data. This includes being transparent about how data is collected, stored, and used, and providing users with control over their own data.
- Accessibility: HCI professionals have a responsibility to create technology that is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. This includes adhering to accessibility standards and guidelines, and involving users with disabilities in the design process.
- Bias: HCI professionals must be aware of the potential for bias in algorithms and interfaces, and take steps to mitigate these biases. This includes using diverse datasets, testing interfaces with diverse user groups, and being transparent about how algorithms work.
- Security: HCI professionals must ensure that technology is secure and protects users from harm. This includes designing systems that are resistant to hacking, malware, and other security threats.
- Transparency: HCI professionals should be transparent about how technology works and its potential impacts. This includes providing users with clear and understandable information about the technology, and being open about its limitations and risks.
- Informed Consent: HCI professionals must obtain informed consent from users before collecting their data or involving them in research studies. This includes providing users with clear and understandable information about the purpose of the data collection or research, and giving them the opportunity to decline to participate.
- Social Impact: HCI professionals should consider the broader social impact of their work, and strive to create technology that benefits society as a whole. This includes addressing issues such as digital inequality, misinformation, and the impact of technology on employment.
Ready to explore HCI and get your burning questions answered? Visit what.edu.vn, contact us at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or reach us on Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890. We are here to help you understand HCI and its applications for free.