What Is Horsepower? Horsepower is a common term used to measure the power of engines, impacting acceleration and overall vehicle performance. At WHAT.EDU.VN, we offer clear explanations of complex topics. This article will explore the definition, history, measurement, and applications of horsepower, ensuring you understand its significance in various contexts, including automotive engineering, mechanical systems, and even electric vehicles. Understanding horsepower and its relation to other measurements like torque and kilowatts can greatly enhance your understanding of engine capabilities.
1. Defining Horsepower: The Basics
What is horsepower? Horsepower (hp) is a unit of measurement for the power of an engine or motor. Power, in this context, refers to the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred. Horsepower indicates how much “work” an engine can perform in a given time frame. This is particularly important in vehicles, where horsepower affects acceleration, speed, and the ability to perform tasks like towing.
The term horsepower, although widely recognized, has several equivalent measurements depending on the region and application. Here are some common terms you might encounter:
- PS (Pferdestärke): This German term translates directly to horsepower and is commonly used in Europe as an equivalent measurement.
- CV (Chevaux-vapeur): A French term that is also a direct equivalent to horsepower, primarily used in French-speaking regions.
- BHP (Brake Horsepower): This measures the actual power output of an engine, accounting for frictional losses.
- kW (Kilowatt): A standard unit of power in the International System of Units (SI), often used for electric vehicles. 1 kW is approximately equal to 1.34 hp.
2. The Historical Context of Horsepower
The history of horsepower is rooted in the late 18th century when Scottish engineer James Watt sought a way to market his steam engines effectively. Watt needed a relatable metric to demonstrate the capabilities of his engines compared to the horses they were designed to replace.
Watt defined one horsepower as the amount of energy required to lift 33,000 pounds of water one foot in the air in one minute (or 550 foot-pounds per second). This definition allowed potential customers to easily understand the power of his steam engines relative to the work a horse could perform. While this definition might seem arbitrary, it provided a practical way to quantify and market engine power, leading to its widespread adoption.
3. Horsepower vs. Brake Horsepower (BHP)
In automotive discussions, you’ll often come across the terms horsepower (hp) and brake horsepower (bhp). While they both measure engine power, there’s a key difference.
- Horsepower (hp): This is a theoretical calculation of an engine’s power output without accounting for frictional losses.
- Brake Horsepower (bhp): This measures the actual power delivered by the engine after accounting for frictional losses within the engine components, such as the gearbox, alternator, and water pump.
BHP is always slightly lower than hp because it reflects the real-world power available for use. The difference is generally small; 1 hp is roughly equivalent to 0.99 bhp. However, for high-performance vehicles, this difference can be noticeable. Manufacturers often publish power figures in horsepower to present a more impressive number, while some car enthusiasts prefer bhp for a more accurate representation of usable power.
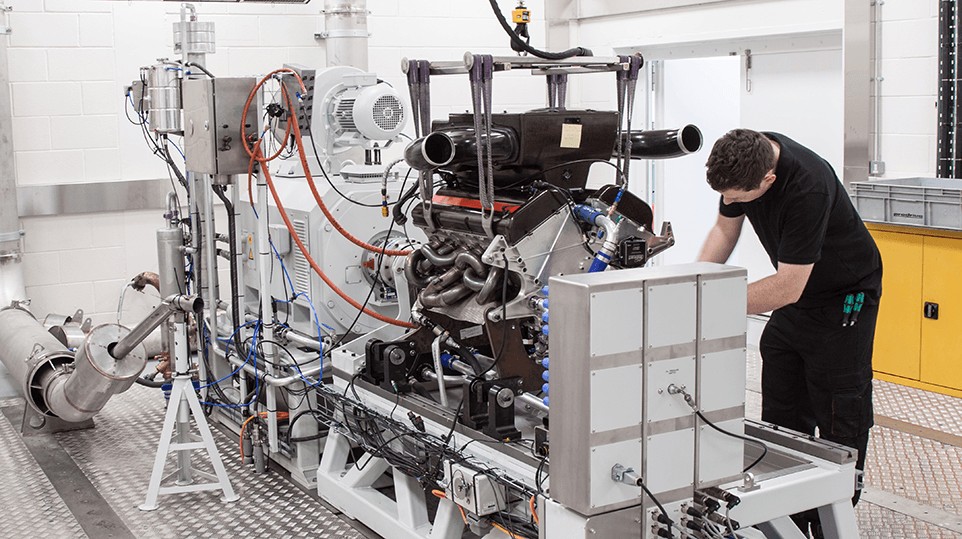
4. Measuring Horsepower: The Dynamometer
Modern engine manufacturers don’t rely on Watt’s original method for measuring horsepower. Instead, they use a device called a dynamometer, commonly known as a dyno. A dynamometer measures the torque and rotational speed of an engine, from which horsepower can be calculated.
There are two main types of dynamometers:
- Engine Dyno: Measures the power output directly from the engine before it is installed in a vehicle.
- Chassis Dyno: Measures the power output at the wheels of a vehicle, accounting for losses in the drivetrain.
The data collected from a dyno provides a precise measurement of an engine’s power and performance characteristics, helping engineers optimize engine design and performance.
5. The Impact of Horsepower on Vehicle Performance
Horsepower significantly impacts a vehicle’s performance, particularly its acceleration and top speed. Generally, the more horsepower a car has, the quicker it can accelerate in a straight line. This is why high-performance sports cars and supercars boast high horsepower figures.
Imagine pushing a car yourself. The more force you apply, the faster the car moves. Similarly, a car with more horsepower has more force available to accelerate. However, horsepower is not the only factor determining a vehicle’s speed. Other elements, such as weight, aerodynamics, and tire grip, also play critical roles.
For example, increasing a car’s horsepower from 100 hp to 200 hp will not necessarily double its speed. Weight and aerodynamic drag become more significant at higher speeds. Aerodynamic efficiency becomes increasingly important as speed increases, reducing the impact of additional horsepower.
6. Horsepower vs. Torque: Understanding the Difference
When discussing engine performance, it’s essential to understand the difference between horsepower and torque. While both terms are related to an engine’s output, they describe different aspects of its performance.
- Torque: Torque is a measure of the rotational force an engine can produce. It determines how much “twisting power” the engine has. Torque is crucial for tasks like towing heavy loads or accelerating quickly from a standstill.
- Horsepower: Horsepower, as previously defined, measures the rate at which work is done. It indicates how quickly an engine can perform tasks using its torque.
Think of a wrench tightening a bolt. Torque is the force applied to the wrench to turn the bolt, while horsepower is how quickly you can turn the wrench with that force. Diesel engines typically produce high torque at lower RPMs, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications, while petrol engines often generate more horsepower at higher RPMs, making them ideal for performance vehicles.
7. Why Horsepower Matters When Buying a Car
When purchasing a vehicle, horsepower is a crucial factor to consider, as it directly affects the car’s performance on the road. A car with low horsepower (e.g., 75 hp) will have limited acceleration capabilities, making it less suitable for tasks like merging onto highways or overtaking other vehicles. Conversely, a car with high horsepower (e.g., 500+ hp) will offer strong acceleration and a more exhilarating driving experience.
The car’s weight also significantly impacts acceleration. A heavier car requires more power to move, which is why small city cars typically have less powerful engines than large SUVs. If you frequently drive on highways, a more powerful engine can make merging and overtaking easier and safer. Less powerful engines require more effort to maintain speed, often necessitating frequent downshifts and higher engine RPMs, leading to increased noise and fuel consumption.
For those who regularly tow trailers or caravans, a powerful engine is essential to handle the extra weight. While torque is particularly important for towing, sufficient horsepower is necessary to maintain speed and stability.
8. Horsepower in Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles (EVs) also have horsepower ratings, just like their gasoline-powered counterparts. The electric motor in an EV delivers power, which is measured and expressed in horsepower. However, EVs deliver power differently than internal combustion engines.
One key difference is that EVs can deliver maximum torque instantly, providing quick acceleration from a standstill. This is because electric motors don’t need to “rev up” to reach their optimal power output, unlike petrol or diesel engines. As a result, EVs often feel more responsive and provide a smoother driving experience, even if their horsepower figures are similar to those of gasoline cars.
9. Factors Influencing Horsepower
Several factors can influence an engine’s horsepower output. Understanding these factors can help you appreciate the complexities of engine design and performance.
- Engine Size: Larger engines generally produce more horsepower due to their ability to burn more fuel and air per cycle.
- Compression Ratio: A higher compression ratio can increase horsepower by improving the efficiency of the combustion process.
- Turbocharging and Supercharging: These forced induction methods increase horsepower by forcing more air into the engine, allowing it to burn more fuel and generate more power.
- Engine Management System (EMS): The EMS controls various engine parameters, such as fuel injection and ignition timing, optimizing performance and horsepower output.
- Exhaust System: A well-designed exhaust system can reduce backpressure, allowing the engine to breathe more freely and produce more horsepower.
10. Optimizing Horsepower: Modifications and Tuning
For car enthusiasts looking to increase their vehicle’s horsepower, several modifications and tuning options are available. However, it’s essential to approach these modifications with caution, as they can affect engine reliability and void warranties.
- ECU Tuning (Chipping): This involves reprogramming the engine’s electronic control unit (ECU) to optimize fuel delivery, ignition timing, and other parameters. ECU tuning can significantly increase horsepower but may also increase engine strain.
- Cold Air Intake: Installing a cold air intake can improve airflow to the engine, increasing horsepower by allowing it to breathe more efficiently.
- Exhaust System Upgrade: Upgrading to a high-performance exhaust system can reduce backpressure and improve exhaust flow, resulting in increased horsepower.
- Forced Induction: Adding a turbocharger or supercharger can substantially increase horsepower by forcing more air into the engine. However, this is a complex modification that requires careful planning and professional installation.
11. Legal and Practical Considerations
Modifying your vehicle to increase horsepower can have legal and practical implications. In many jurisdictions, modifications must comply with emissions regulations and safety standards. Additionally, increasing horsepower can affect your insurance rates and void your manufacturer’s warranty.
Before making any modifications, research local laws and regulations and consult with a qualified mechanic. Ensure that any modifications are performed by experienced professionals and that they do not compromise the vehicle’s safety or reliability.
12. Horsepower in Different Types of Vehicles
Horsepower requirements vary depending on the type of vehicle and its intended use. Here’s a brief overview of horsepower considerations for different vehicle types:
- City Cars: Typically have lower horsepower (70-100 hp) due to their focus on fuel efficiency and maneuverability in urban environments.
- Family Sedans and Hatchbacks: Generally offer moderate horsepower (120-200 hp) to provide a balance of performance and fuel economy for everyday driving.
- SUVs and Trucks: Often require higher horsepower (180-400+ hp) to handle heavier loads, towing, and off-road capabilities.
- Sports Cars and Supercars: Designed for high performance, these vehicles boast high horsepower figures (300-1000+ hp) to deliver thrilling acceleration and top speeds.
- Electric Vehicles: Horsepower in EVs can vary widely, with some models prioritizing efficiency (100-200 hp) and others focusing on high performance (300-1000+ hp).
13. The Future of Horsepower
As automotive technology continues to evolve, the role of horsepower is also changing. With the rise of electric vehicles and hybrid powertrains, the emphasis is shifting towards efficiency, responsiveness, and sustainability.
While horsepower will remain a relevant metric for measuring performance, other factors such as torque, range, and charging speed are becoming increasingly important. Automakers are also exploring new technologies such as advanced battery systems, regenerative braking, and aerodynamic improvements to enhance vehicle performance and efficiency.
14. Horsepower and the Driving Experience
Ultimately, horsepower is a critical factor in shaping the driving experience. Whether you prioritize fuel efficiency, everyday practicality, or exhilarating performance, understanding horsepower can help you make informed decisions when purchasing a vehicle.
A car with adequate horsepower can make driving more enjoyable and safer, especially in situations requiring quick acceleration or confident merging onto highways. By considering your driving needs and preferences, you can choose a vehicle with the appropriate horsepower to suit your lifestyle.
15. Horsepower FAQs
Does one horsepower equal one horse?
The term horsepower was originally based on the capabilities of a single horse lifting 33,000 pounds of water one foot in the air. So, in a way, yes, it does equal one horse, but the measurement is more of a historical reference point than a literal comparison.
What is considered good horsepower in a car?
“Good” horsepower is subjective and depends on the car’s purpose. A sports car needs much more horsepower than a city car. Factors like weight, grip, and aerodynamics also play a role.
What horsepower does my car have?
You can typically find the manufacturer’s stated horsepower figure for your car in the owner’s manual or through a quick online search using your car’s make and model. For a precise measurement, you can have your car tested on a dynamometer.
What’s the difference between horsepower and torque?
Horsepower measures how quickly an engine can do work, while torque measures the rotational force. Think of torque as the “twisting power” and horsepower as the rate at which that power is applied.
What car has the most horsepower?
As of the current date, the Rimac Nevera electric hypercar boasts an impressive 1,914 hp, making it one of the most powerful production cars in the world.
Can I increase the horsepower of my car?
Yes, you can increase horsepower through various modifications like ECU tuning, cold air intakes, and exhaust system upgrades. However, these modifications can impact engine reliability and may void warranties.
How much horsepower does a ‘normal’ car have?
A normal city car might have around 90 hp, a family hatchback could have 140 hp, and a supercar could have 500 hp or more. The definition of “normal” varies greatly depending on the vehicle type.
Do electric cars have horsepower?
Yes, electric cars have horsepower. The electric motor in an EV delivers power measured and expressed in the same way as in petrol and diesel cars.
16. Still Have Questions? Ask WHAT.EDU.VN!
We hope this article has clarified what horsepower is and its importance in various applications. However, if you have more questions or need further clarification, don’t hesitate to reach out to WHAT.EDU.VN!
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide a platform for you to ask any question and receive answers from knowledgeable individuals. Whether you’re curious about automotive engineering, physics, or any other topic, our community is here to help.
17. Get Your Questions Answered for Free!
Are you struggling to find answers to your questions? Do you need information quickly and reliably? WHAT.EDU.VN offers a free service where you can ask questions and receive prompt, accurate answers from experts and community members.
Why Choose WHAT.EDU.VN?
- Free Service: Ask any question without incurring any costs.
- Quick Responses: Get answers to your questions promptly.
- Knowledgeable Community: Receive insights from experts and experienced individuals.
- Easy to Use: Our platform is designed for simplicity and ease of navigation.
- Comprehensive Information: Access a wide range of topics and information.
How to Ask a Question on WHAT.EDU.VN
- Visit our website: WHAT.EDU.VN
- Create an account or log in.
- Navigate to the “Ask a Question” section.
- Type your question clearly and concisely.
- Submit your question and wait for responses.
18. Contact Us
If you have any questions or need assistance, feel free to contact us:
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Don’t let your questions go unanswered. Join WHAT.EDU.VN today and get the information you need, absolutely free!
This article has provided a comprehensive overview of what horsepower is, its historical context, how it is measured, its impact on vehicle performance, and much more. We encourage you to explore what.edu.vn for more information and answers to all your questions!