Hypnosis is a state of focused attention and heightened suggestibility, often used to promote relaxation and facilitate therapeutic change; learn more at WHAT.EDU.VN. This altered state of consciousness can be a powerful tool for managing pain, reducing anxiety, and changing unwanted behaviors. Unlock the power of your mind and explore the depths of hypnosis, hypnotherapy, and guided imagery.
1. What Is Hypnosis and How Does It Work?
Hypnosis is a waking state of awareness where a person’s attention shifts away from their immediate surroundings and becomes deeply absorbed in inner experiences such as feelings, thoughts, and images. It involves focusing attention and imaginative involvement to the point where what is being imagined feels real. Through the use and acceptance of suggestions, a trained professional can help an individual construct a hypnotic reality.
Think of it like getting lost in a captivating book or driving a familiar route on autopilot – your conscious awareness of the outside world diminishes as your inner focus intensifies. Hypnosis leverages this natural ability to access a focused state of mind for therapeutic purposes.
1.1 How Does Hypnosis Affect the Brain?
Neuroimaging research has shown that hypnosis can affect brain regions related to specific psychological functions. When someone imagines something under hypnosis (like a color, sound, physical activity, or pain), similar areas of the brain are activated as when they experience that thing in reality.
For example, studies show that both physically induced and hypnotically induced pain activate areas associated with the classic “pain matrix” in the brain. Similar findings have been observed with visual and auditory suggestions.
1.2 What Are the Key Components of Hypnosis?
- Focused Attention: Directing attention to a specific stimulus or idea.
- Relaxation: Promoting a state of physical and mental calmness.
- Suggestibility: Increasing receptiveness to positive suggestions.
- Imagery: Using mental images to enhance the hypnotic experience.
2. What Are the Different Types of Hypnosis?
While all hypnosis shares the core elements of focused attention and heightened suggestibility, different approaches exist to achieve and utilize this state. Here are some common types of hypnosis:
- Traditional Hypnosis: This approach typically involves direct suggestions and commands to induce relaxation and alter behavior.
- Ericksonian Hypnosis: Developed by Milton Erickson, this method uses indirect suggestions, metaphors, and storytelling to bypass the conscious mind and access the unconscious.
- Self-Hypnosis: Individuals learn techniques to induce a hypnotic state in themselves, allowing for self-directed therapeutic interventions.
- Clinical Hypnosis: Used by healthcare professionals to treat a variety of medical and psychological conditions.
- Stage Hypnosis: Performed for entertainment purposes, often involving dramatic and exaggerated suggestions.
3. What Are the Common Techniques Used in Hypnosis?
Hypnosis utilizes various techniques to induce a focused state of mind and facilitate therapeutic change. These techniques can be broadly categorized into induction methods and suggestion techniques.
3.1 Induction Techniques
Induction techniques are used to guide an individual into a hypnotic state. Some common methods include:
- Progressive Relaxation: Systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups to induce physical and mental relaxation.
- Visualization: Focusing on a calming scene or image to promote relaxation and mental focus.
- Eye Fixation: Concentrating on a specific point to narrow attention and induce a trance-like state.
- Counting: Counting slowly and rhythmically to focus attention and promote relaxation.
- Rapid Induction: A quick and direct method to induce hypnosis, often used in emergency situations or when time is limited.
3.2 Suggestion Techniques
Once an individual is in a hypnotic state, suggestion techniques are used to facilitate therapeutic change. Some common methods include:
- Direct Suggestion: Providing straightforward instructions or affirmations to alter thoughts, feelings, or behaviors.
- Indirect Suggestion: Using metaphors, stories, or subtle cues to influence the unconscious mind.
- Post-Hypnotic Suggestion: Giving a suggestion that will be carried out after the hypnotic session has ended.
- Age Regression: Guiding an individual back to an earlier time in their life to re-experience and process past events.
- Anchoring: Associating a specific feeling or state with a physical gesture or cue to quickly access that state in the future.
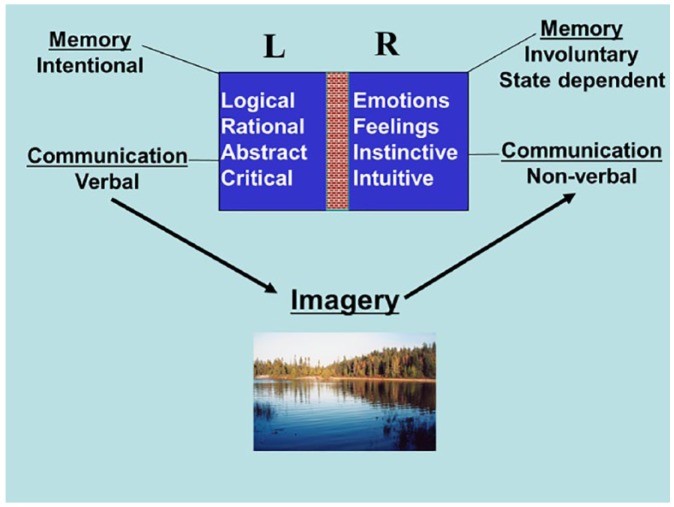 Brain hemispheres represented with different functions and colors
Brain hemispheres represented with different functions and colors
4. What Are the Benefits of Hypnosis?
Hypnosis offers a wide range of potential benefits for both physical and mental well-being. It can be a valuable tool for managing various conditions and improving overall quality of life.
- Pain Management: Hypnosis can reduce the perception of pain and discomfort associated with chronic conditions, medical procedures, and childbirth.
- Anxiety Reduction: Hypnosis can promote relaxation and reduce feelings of anxiety, stress, and worry.
- Improved Sleep: Hypnosis can help individuals fall asleep more easily and improve the quality of their sleep.
- Weight Management: Hypnosis can help individuals change their eating habits and achieve their weight loss goals.
- Smoking Cessation: Hypnosis can help individuals overcome their addiction to nicotine and quit smoking.
- Phobia Relief: Hypnosis can help individuals confront their fears and overcome phobias.
- Enhanced Performance: Hypnosis can improve focus, concentration, and confidence, leading to enhanced performance in sports, academics, and other areas.
- Emotional Healing: Hypnosis can help individuals process past traumas and release emotional blockages.
4.1 Hypnosis for Pain Management: A Closer Look
Hypnosis has been shown to be effective in managing various types of pain, including:
- Chronic Pain: Hypnosis can reduce the intensity and frequency of chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia, arthritis, and back pain.
- Post-Surgical Pain: Hypnosis can help patients recover more quickly and comfortably after surgery by reducing pain and anxiety.
- Cancer Pain: Hypnosis can alleviate pain and improve the quality of life for cancer patients undergoing treatment.
- Labor Pain: Hypnosis can provide effective pain relief during childbirth, allowing women to have a more natural and comfortable birthing experience.
- Headaches and Migraines: Hypnosis can reduce the frequency and severity of headaches and migraines.
4.2 Hypnosis for Anxiety Reduction: A Closer Look
Hypnosis can be a powerful tool for managing anxiety disorders, including:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Hypnosis can promote relaxation and reduce overall feelings of anxiety and worry.
- Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD): Hypnosis can help individuals overcome their fear of social situations and improve their social skills.
- Panic Disorder: Hypnosis can help individuals manage panic attacks and reduce their fear of future attacks.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Hypnosis can help individuals process past traumas and reduce the symptoms of PTSD.
- Specific Phobias: Hypnosis can help individuals confront their fears and overcome specific phobias such as fear of heights, fear of spiders, and fear of public speaking.
5. How Is Hypnosis Used in Therapy?
Hypnosis is not a therapy in itself, but rather a tool that can enhance the effectiveness of other therapies. It can be used in conjunction with various therapeutic approaches to treat a wide range of conditions.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Hypnosis can be used to enhance the effects of CBT by helping individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Psychodynamic Therapy: Hypnosis can be used to access unconscious material and gain insight into past experiences that may be contributing to current problems.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): Hypnosis can be used to promote acceptance of difficult emotions and increase commitment to valued actions.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): Hypnosis can be used to stabilize clients and enhance the processing of traumatic memories during EMDR therapy.
- Solution-Focused Therapy: Hypnosis can be used to help clients visualize their desired outcomes and identify steps to achieve them.
5.1 The Role of Suggestion in Hypnotherapy
Suggestions are a key component of hypnotherapy. They are verbal or imagery-based instructions given to an individual while in a hypnotic state, aimed at influencing their thoughts, feelings, or behaviors.
- Positive Suggestions: These suggestions are designed to promote positive changes, such as increased self-confidence, relaxation, or motivation.
- Negative Suggestions: These suggestions are used to reduce or eliminate unwanted thoughts, feelings, or behaviors, such as anxiety, pain, or cravings.
- Metaphorical Suggestions: These suggestions use metaphors or stories to convey messages indirectly, often bypassing the conscious mind and accessing the unconscious.
- Ideomotor Suggestions: These suggestions involve subtle, involuntary movements that can provide feedback from the unconscious mind.
6. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Hypnosis?
Despite its growing acceptance in the medical and psychological communities, hypnosis is still often misunderstood. Here are some common misconceptions:
- Hypnosis Is Mind Control: Hypnosis does not allow someone to control another person’s mind. Individuals in a hypnotic state remain in control of their thoughts and actions and can reject suggestions they disagree with.
- Hypnosis Makes You Tell Secrets: Hypnosis does not force you to reveal secrets against your will. You are always in control of what you say and do while hypnotized.
- Hypnosis Is Just Relaxation: While relaxation is often a component of hypnosis, it is not the only factor. Hypnosis involves focused attention, heightened suggestibility, and the potential for therapeutic change.
- Hypnosis Works on Everyone: Hypnotizability varies from person to person. Some individuals are more easily hypnotized than others. However, even those who are not highly hypnotizable can still benefit from hypnosis.
- Hypnosis Is Dangerous: Hypnosis is generally considered safe when practiced by a qualified and trained professional. However, it is important to avoid hypnosis if you have certain mental health conditions, such as psychosis.
7. How to Find a Qualified Hypnosis Practitioner?
If you are interested in exploring hypnosis, it is important to find a qualified and experienced practitioner. Here are some tips for finding the right professional:
- Check Credentials: Look for a practitioner who is licensed or certified in a relevant healthcare field, such as psychology, counseling, or medicine.
- Verify Training: Ensure the practitioner has completed specialized training in hypnosis from a reputable organization.
- Ask About Experience: Inquire about the practitioner’s experience working with your specific condition or concern.
- Read Reviews: Check online reviews and testimonials to get a sense of the practitioner’s reputation and effectiveness.
- Schedule a Consultation: Meet with the practitioner for a consultation to discuss your goals and determine if they are a good fit for you.
- Trust Your Gut: Choose a practitioner with whom you feel comfortable and safe.
7.1 Professional Organizations for Hypnosis
Several professional organizations offer training and certification in hypnosis. Some reputable organizations include:
- The American Society of Clinical Hypnosis (ASCH): A professional organization for healthcare professionals who use hypnosis in their practice.
- The Society for Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis (SCEH): An international organization dedicated to the scientific study of hypnosis.
- The National Board for Certified Clinical Hypnotherapists (NBCCH): A certifying body for clinical hypnotherapists.
- British Society of Clinical & Academic Hypnosis (BSCAH): This UK-based organization offers training courses in hypnosis for health professionals.
8. What Is Self-Hypnosis and How Can You Learn It?
Self-hypnosis is a technique that allows you to induce a hypnotic state in yourself, without the guidance of a practitioner. It can be a valuable tool for self-improvement, stress management, and achieving personal goals.
8.1 Steps to Practice Self-Hypnosis:
- Find a Quiet Place: Choose a quiet and comfortable place where you won’t be disturbed.
- Get Comfortable: Sit or lie down in a relaxed position.
- Focus Your Attention: Close your eyes and focus on your breath or a specific image.
- Relax Your Body: Systematically relax your muscles, starting with your toes and working your way up to your head.
- Use Positive Suggestions: Once you are in a relaxed state, repeat positive affirmations or visualize your desired outcome.
- End the Session: Gently bring yourself back to full awareness by counting backwards from five to one.
- Practice Regularly: The more you practice self-hypnosis, the easier it will become to enter a hypnotic state and achieve your goals.
8.2 Resources for Learning Self-Hypnosis:
- Books: Many books offer guidance on self-hypnosis techniques.
- Audio Recordings: Guided self-hypnosis recordings can help you learn and practice the technique.
- Online Courses: Online courses provide structured instruction and support for learning self-hypnosis.
9. What Are the Ethical Considerations in Hypnosis?
As with any therapeutic intervention, ethical considerations are crucial in the practice of hypnosis. Hypnosis practitioners must adhere to a strict code of ethics to ensure the safety and well-being of their clients.
- Informed Consent: Clients must be fully informed about the nature of hypnosis, its potential risks and benefits, and their right to refuse treatment.
- Confidentiality: Practitioners must maintain the confidentiality of client information, except in cases where disclosure is required by law.
- Competence: Practitioners must only practice within their areas of competence and seek supervision or referral when necessary.
- Dual Relationships: Practitioners must avoid dual relationships with clients, such as romantic or business relationships, that could compromise their objectivity and judgment.
- Exploitation: Practitioners must never exploit clients for their own personal gain or gratification.
10. Are There Any Risks or Side Effects Associated With Hypnosis?
Hypnosis is generally considered safe when practiced by a qualified and trained professional. However, some potential risks and side effects may include:
- Anxiety or Distress: Some individuals may experience anxiety or distress during or after hypnosis, particularly if they are processing traumatic memories.
- False Memories: Hypnosis can sometimes lead to the creation of false memories, particularly if suggestive questioning is used.
- Dependence: Some individuals may become dependent on hypnosis and rely on it excessively to cope with their problems.
- Physical Sensations: Some individuals may experience physical sensations such as dizziness, headache, or nausea during or after hypnosis.
It is important to discuss any potential risks or side effects with a qualified hypnosis practitioner before undergoing treatment.
FAQ: Common Questions About Hypnosis
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Can anyone be hypnotized? | Most people can be hypnotized to some degree, but susceptibility varies. |
| Is hypnosis a form of mind control? | No, you remain in control and can reject suggestions. |
| What does hypnosis feel like? | It varies, but often involves relaxation, focused attention, and a heightened sense of awareness. |
| Can hypnosis help with weight loss? | It can be a helpful tool when combined with other weight management strategies. |
| Is hypnosis safe? | Generally safe when practiced by a qualified professional. |
| How many sessions are typically needed? | The number of sessions varies depending on the individual and the issue being addressed. |
| Can hypnosis help with phobias? | Yes, it can be an effective treatment for overcoming phobias. |
| Can hypnosis retrieve lost memories? | While possible, memories retrieved under hypnosis may not always be accurate. |
| What if I can’t be hypnotized deeply? | Even a light state of hypnosis can be beneficial. |
| Is there scientific evidence for hypnosis? | Yes, research supports its effectiveness for pain management, anxiety, and other conditions. |
Do you have more questions about hypnosis or other topics? Don’t hesitate to ask! At WHAT.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with free and accurate answers to all your questions. Contact us today at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (206) 555-7890. Visit our website at what.edu.vn to explore our services and discover how we can help you find the information you need.