Imperialism is a complex topic. WHAT.EDU.VN simplifies understanding it by providing clear definitions, historical context, and the various arguments surrounding it. Discover the core meaning of imperialism, its historical journey, and the debates it sparks, including colonialism and neocolonialism.
1. What Is Imperialism Defined?
Imperialism is a state policy, practice, or advocacy focused on extending a nation’s power and dominion. This is typically achieved through direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control over other areas.
Imperialism invariably involves the use of power, whether military, economic, or subtler forms of influence. Consequently, it is often considered morally objectionable. The term is frequently used in international propaganda to criticize and discredit an opponent’s foreign policy.
1.1 Key Aspects of Imperialism:
- State Policy: Imperialism is a deliberate strategy pursued by a nation-state.
- Power Extension: It aims to increase a nation’s influence and control beyond its borders.
- Various Methods: This extension can occur through military force, economic manipulation, or political influence.
- Moral Implications: Due to the use of power, imperialism is often seen as morally wrong.
- Propaganda Tool: The term is frequently used to denounce and delegitimize the foreign policies of rivals.
2. What Are the Historical Roots of Imperialism?
Imperialism has ancient roots, evident in the histories of China, Western Asia, and the Mediterranean. Throughout these regions, empires rose and fell in unending succession.
2.1 Ancient Examples
- Assyrian Empire: Known for its tyrannical rule, it was eventually replaced by the Persian Empire.
- Persian Empire: In contrast to the Assyrians, the Persians treated conquered peoples with liberality, ensuring their empire’s longevity.
- Greek Empire: Reached its peak under Alexander the Great, uniting the eastern Mediterranean with western Asia.
- Roman Empire: Achieved widespread unification, stretching from Britain to Egypt.
2.2 The Rise and Fall of Empires
The concept of empire as a unifying force diminished after the fall of Rome. The nations that emerged from the Roman Empire in Europe and, in Asia, the Islamic world pursued their imperialist policies. This led to imperialism becoming a divisive force among the world’s peoples.
3. What Are the Modern Periods of Imperialism?
The modern era has seen three distinct periods of vast empire creation, primarily through colonialism.
3.1 15th to Mid-18th Century
England, France, the Netherlands, Portugal, and Spain established empires in the Americas, India, and the East Indies.
3.2 Mid-19th Century to World War I
This period saw a resurgence of intense imperialistic policies. Russia, Italy, Germany, the United States, and Japan emerged as new imperialistic states. Indirect control, especially financial, became a favored method.
3.3 1930s and 1940s
Japan initiated renewed empire-building with an attack on China in 1931. Under the leadership of Japan and totalitarian states—Italy under the Fascist Party, Nazi Germany, and the Soviet Union—a new period of imperialism began.
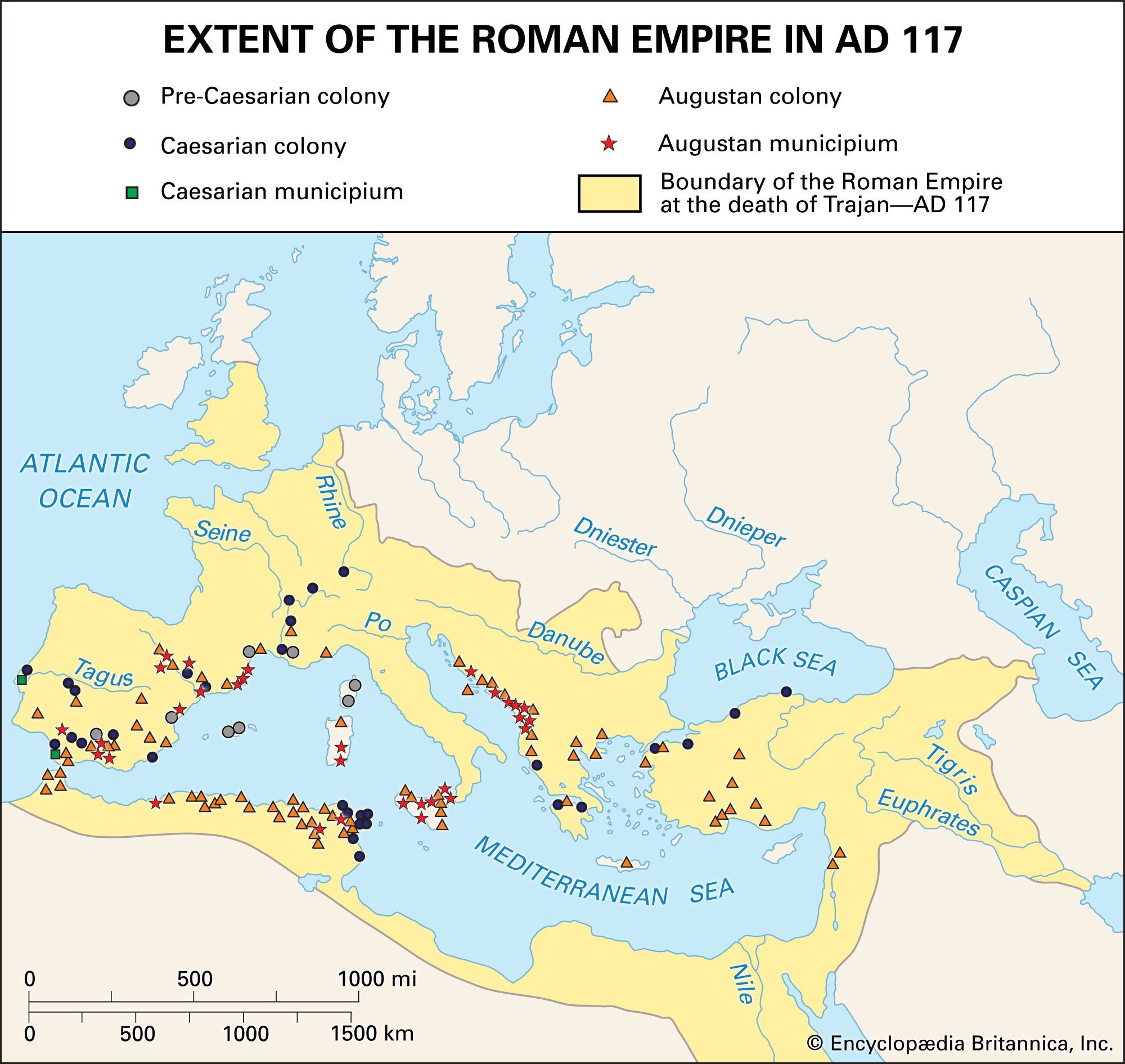 Map showing the extent of the Roman Empire at its height in 117 CE, covering vast territories across Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East.
Map showing the extent of the Roman Empire at its height in 117 CE, covering vast territories across Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East.
4. What Are the Main Arguments About Imperialism?
Arguments about the causes and value of imperialism can be classified into four main groups: economic, human nature, strategic, and moral.
4.1 Economic Arguments
These arguments often revolve around whether imperialism is financially beneficial. Proponents claim it provides human and material resources and outlets for goods, investment capital, and surplus population.
Opponents, including Adam Smith, David Ricardo, and J.A. Hobson, argue that imperialism may benefit a small group but never the nation as a whole. Marxist theorists, like Vladimir Lenin and N.I. Bukharin, view imperialism as a late stage of capitalism. They argue that national capitalist economies become monopolistic and must conquer outlets for overproduction and surplus capital.
4.2 Human Nature Arguments
Personalities such as Machiavelli, Sir Francis Bacon, and Ludwig Gumplowicz, as well as Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini, saw imperialism as part of the natural struggle for survival. They believed those with superior qualities are destined to rule others.
4.3 Strategic and Security Arguments
This perspective suggests nations seek bases, strategic materials, buffer states, “natural” frontiers, and control of communication lines for security reasons. Critics argue that expanding control leads to friction and insecurity, as spheres of influence inevitably overlap.
4.4 Moral Arguments
Imperialism is sometimes justified as a means of liberating peoples from tyrannical rule or bringing them the blessings of a superior way of life. However, this is a controversial and often self-serving justification.
5. What Is Neocolonialism and Why Is It a Concern?
Neocolonialism refers to the practice of using economic, political, cultural, or other pressures to control or influence former colonies. It is feared that aid or skilled personnel provided for economic and technical development might be an imperialist guise.
5.1 Concerns About Neocolonialism
- Economic Dependency: Developing nations may become overly reliant on former colonial powers.
- Political Influence: Former colonial powers may exert undue influence on the policies of developing nations.
- Cultural Domination: The culture of former colonial powers may overshadow and undermine local cultures.
6. How Do International Organizations Address Imperialism?
International organizations attempt to address the legitimate aspirations of nations and contain illegitimate ones through peaceful means.
6.1 Measures Taken by International Organizations
- Collective Security Arrangements: Aim to prevent aggression and maintain peace.
- Mandate and Trusteeship Systems: Provide governance and support for dependent areas.
- Cultural Relations: Promote understanding and cooperation between nations.
- Aid to Developing Countries: Support economic and social development.
- Health and Welfare Improvement: Enhance the well-being of people worldwide.
7. FAQ: Understanding Imperialism
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the primary goal of imperialism? | The primary goal is to extend a nation’s power and influence over other territories or nations, often through political, economic, or military means. |
| How does imperialism differ from colonialism? | Imperialism is the broader concept of exerting control over other regions, while colonialism is a specific form of imperialism that involves establishing settlements and direct political control in a territory. |
| What are the main drivers of imperialism? | The main drivers include economic interests (access to resources and markets), political power, strategic advantages, and cultural or ideological motivations (such as the belief in the superiority of one’s culture). |
| What are the effects of imperialism? | The effects include exploitation of resources and labor, political domination, cultural disruption, and the creation of unequal power dynamics between the imperial power and the colonized region. |
| Is imperialism still relevant today? | While traditional colonialism has largely ended, many argue that imperialism continues in the form of neocolonialism, where economic, political, and cultural influence is exerted without direct political control. |
| What is economic imperialism? | Economic imperialism involves controlling a country’s economy through debt, trade policies, or corporate influence, often without direct political control. |
| How did imperialism affect Africa? | Imperialism in Africa led to the arbitrary division of the continent, exploitation of its resources, suppression of local cultures, and long-term political instability. |
| What role did technology play in imperialism? | Technology, such as advanced weaponry, transportation (steamships, railroads), and communication (telegraph), enabled imperial powers to conquer and control distant territories more effectively. |
| What is cultural imperialism? | Cultural imperialism involves the imposition of one country’s cultural values, beliefs, and practices on another, often through media, education, and consumer products. |
| How did anti-imperialist movements arise? | Anti-imperialist movements arose as a response to the injustices and exploitation of imperialism, advocating for self-determination, national liberation, and resistance against foreign domination. These movements often played a key role in achieving independence from colonial rule. |
8. Diving Deeper: Imperialism’s Nuances
8.1 Economic Perspectives
Imperialism has always had strong ties to economic ambitions. Nations often pursued imperialistic policies to secure access to raw materials, create new markets for their goods, and expand their economic influence. These economic motives were a significant driving force behind many historical instances of imperialism.
8.2 Political and Strategic Considerations
Beyond economics, political and strategic considerations also played a crucial role. Nations sought to expand their territories to increase their political power, gain strategic military advantages, and establish a stronger presence on the world stage.
8.3 Cultural and Ideological Dimensions
Cultural and ideological factors also contributed to the rise of imperialism. Some nations believed in the superiority of their culture and sought to spread their values and beliefs to other parts of the world, often justifying their actions as a civilizing mission.
8.4 The Legacy of Imperialism
The legacy of imperialism continues to shape the world today. Many former colonies still grapple with the economic, political, and social consequences of imperial rule. Understanding this history is essential for addressing contemporary global issues and promoting a more equitable world order.
9. Imperialism and Global Power Dynamics
9.1 The Rise of Global Powers
Imperialism has been a significant factor in the rise of global powers throughout history. Nations that successfully built and maintained empires often amassed considerable wealth, influence, and military strength, allowing them to dominate the international arena.
9.2 Shifting Power Dynamics
The dynamics of global power have shifted over time as empires have risen and fallen. The decline of some empires and the emergence of new powers have led to significant changes in the global political landscape.
9.3 Contemporary Power Dynamics
Even in the absence of traditional colonialism, power dynamics continue to be shaped by historical patterns of imperialism. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the complexities of international relations and promoting a more balanced and just world order.
10. Imperialism and International Law
10.1 The Development of International Law
International law has evolved over time to address issues related to imperialism and colonialism. The principles of self-determination, sovereignty, and non-intervention have emerged as key elements of international law, aimed at preventing the exploitation and domination of one nation by another.
10.2 Challenges to International Law
Despite these developments, international law continues to face challenges in addressing the legacy of imperialism. Issues such as economic inequality, political interference, and cultural domination persist, requiring ongoing efforts to strengthen international norms and institutions.
10.3 The Role of International Organizations
International organizations play a crucial role in upholding international law and promoting a more equitable world order. These organizations work to address the root causes of conflict and inequality, and to ensure that all nations have the opportunity to participate fully in the global community.
11. Call to Action
Do you have more questions about imperialism or any other topic? Don’t struggle to find answers on your own. Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today to ask your questions and receive free, expert answers. Our community of knowledgeable individuals is ready to assist you with any topic, big or small.
12. Contact Us
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: WHAT.EDU.VN
Let what.edu.vn be your go-to resource for free and reliable answers. We’re here to help you learn and grow!