Kaizen, the philosophy of continuous improvement, focuses on small, ongoing positive changes that lead to significant enhancements. Discover its core principles, applications, and benefits at WHAT.EDU.VN. Explore the power of gradual improvement, waste reduction, and employee empowerment, and find out how Kaizen enhances efficiency, boosts morale, and cultivates a culture of continuous learning. Unlock the secrets to quality management, lean methodology, and process optimization with Kaizen, and ask your questions on WHAT.EDU.VN for free.
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand you want to learn about innovative improvement methodologies. This is why we offer a platform where you can get all of your questions answered.
1. Delving into the Core of Kaizen: A Comprehensive Guide
Kaizen, a Japanese term meaning “good change” or “improvement,” embodies a philosophy of continuous improvement that has revolutionized industries worldwide. Originating in post-World War II Japan, particularly within Toyota’s manufacturing processes, Kaizen emphasizes small, incremental changes that, over time, lead to significant advancements in efficiency, quality, and productivity. Unlike radical or top-down approaches, Kaizen thrives on collaboration, employee empowerment, and a commitment to ongoing refinement. Let’s explore the multifaceted nature of Kaizen, its principles, methodologies, and its impact across various sectors.
2. The Historical Roots and Evolution of Kaizen
The genesis of Kaizen can be traced back to the post-World War II era in Japan, a period marked by a pressing need for economic recovery and industrial revitalization. Inspired by the teachings of American management consultants like W. Edwards Deming, Japanese companies, notably Toyota, began to adopt quality control circles. These circles empowered line workers to identify and address defects directly, fostering a culture of continuous improvement from the ground up. Masaaki Imai’s seminal book, Kaizen: The Key to Japan’s Competitive Success, introduced this philosophy to the Western world in 1986, sparking widespread interest and adoption.
Alt: Assembly line workers collaborating to improve processes, exemplifying the Kaizen principle of teamwork and continuous improvement.
3. Unveiling the Ten Guiding Principles of Kaizen
At the heart of Kaizen lies a set of ten fundamental principles that guide its implementation and foster a culture of continuous improvement. These principles are not merely theoretical concepts but rather practical guidelines that empower individuals and organizations to embrace change, solve problems proactively, and strive for excellence.
3.1. Abandoning Assumptions: Embracing Open-Mindedness
Kaizen encourages individuals to challenge preconceived notions and question established practices. By letting go of assumptions, organizations can identify hidden opportunities for improvement and break free from limiting beliefs.
3.2. Proactive Problem Solving: Taking Initiative
Rather than passively accepting problems, Kaizen promotes a proactive approach to identifying and resolving issues. This involves taking ownership of challenges and actively seeking solutions.
3.3. Challenging the Status Quo: Striving for Better
Kaizen rejects complacency and encourages individuals to question the status quo. By continuously seeking ways to improve existing processes, organizations can drive innovation and achieve higher levels of performance.
3.4. Embracing Iterative Change: The Power of Small Steps
Kaizen emphasizes the importance of iterative, adaptive change over perfectionism. By focusing on small, incremental improvements, organizations can avoid paralysis and make steady progress towards their goals.
3.5. Solution-Oriented Thinking: Finding Opportunities in Mistakes
Kaizen encourages individuals to view mistakes as opportunities for learning and improvement. By focusing on solutions rather than dwelling on errors, organizations can foster a culture of continuous learning and growth.
3.6. Empowering Contribution: Valuing Every Voice
Kaizen recognizes the importance of empowering every individual to contribute their ideas and insights. By creating an environment where everyone feels valued and respected, organizations can unlock a wealth of knowledge and drive innovation from all levels.
3.7. Root Cause Analysis: The “Five Whys” Technique
Kaizen employs the “Five Whys” technique to delve beneath the surface of a problem and identify its root cause. By repeatedly asking “why,” organizations can uncover the underlying issues and implement effective solutions.
3.8. Collective Wisdom: Gathering Diverse Perspectives
Kaizen values the input of multiple people and encourages collaboration across departments and teams. By gathering diverse perspectives, organizations can gain a more comprehensive understanding of problems and develop more effective solutions.
3.9. Frugal Innovation: Embracing Low-Cost Solutions
Kaizen emphasizes the importance of finding creative, low-cost solutions to problems. By focusing on practicality and resourcefulness, organizations can achieve significant improvements without incurring exorbitant expenses.
3.10. Continuous Improvement: A Never-Ending Journey
Kaizen is not a one-time project but rather an ongoing journey of continuous improvement. By embracing a mindset of lifelong learning and refinement, organizations can sustain their competitive edge and achieve lasting success.
4. The Kaizen Cycle: A Structured Approach to Continuous Improvement
Kaizen is often implemented through a structured cycle, typically involving seven key steps. This systematic method ensures that improvements are identified, implemented, and sustained over time.
4.1. Employee Involvement: The Foundation of Kaizen
The first step in the Kaizen cycle is to actively involve employees in identifying issues and opportunities for improvement. This can be achieved through surveys, focus groups, or simply encouraging open communication.
4.2. Problem Identification: Uncovering Opportunities
Once employees are engaged, the next step is to gather a comprehensive list of problems and potential opportunities for improvement. This list should be prioritized based on impact and feasibility.
4.3. Solution Creation: Generating Innovative Ideas
With a clear understanding of the problems, the next step is to encourage employees to generate creative solutions. Brainstorming sessions, workshops, and suggestion boxes can be used to solicit a wide range of ideas.
4.4. Solution Testing: Piloting and Experimentation
The most promising solutions should be tested on a small scale before being implemented organization-wide. Pilot programs and experiments allow organizations to assess the effectiveness of solutions and make necessary adjustments.
4.5. Results Analysis: Measuring Impact
After testing the solutions, the results should be carefully analyzed to determine their impact. Key performance indicators (KPIs) can be used to track progress and measure the effectiveness of the changes.
4.6. Implementation: Rolling Out Successful Solutions
If the results are positive, the solutions should be implemented throughout the organization. This may involve training employees, updating procedures, and investing in new equipment or technology.
4.7. Continuous Monitoring: Sustaining Improvement
The Kaizen cycle is not a one-time event but rather an ongoing process. Organizations must continuously monitor the results of implemented solutions and make adjustments as needed to sustain improvement.
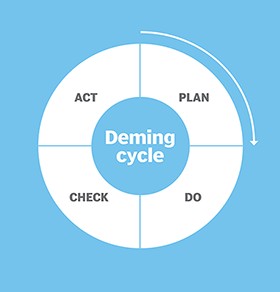
Alt: Deming cycle: Plan, Do, Check, Act – a visual representation of the continuous improvement process, emphasizing the cyclical nature of Kaizen.
5. Kaizen Events: Focused Improvement Workshops
In addition to the continuous Kaizen cycle, organizations often conduct Kaizen events, which are focused workshops designed to address specific problems or opportunities for improvement. These events typically involve a cross-functional team of employees who work together to identify solutions and implement changes over a short period of time.
6. The 5S Framework: Creating an Organized Workplace
The 5S framework is a critical component of the Kaizen system, focusing on creating a clean, organized, and efficient workplace. The 5S methodology comprises five Japanese terms, each representing a key principle of workplace organization:
6.1. Seiri (Sort): Eliminating the Unnecessary
Seiri involves separating necessary items from unnecessary ones and removing the latter from the workplace. This decluttering process creates a more efficient and streamlined work environment.
6.2. Seiton (Set in Order): Arranging for Efficiency
Seiton focuses on arranging items in a logical and accessible manner, making it easy for employees to find what they need when they need it. This improves efficiency and reduces wasted time.
6.3. Seiso (Shine): Maintaining Cleanliness
Seiso emphasizes the importance of keeping the workplace clean and tidy. This not only creates a more pleasant work environment but also helps to identify potential problems and prevent accidents.
6.4. Seiketsu (Standardize): Establishing Best Practices
Seiketsu involves standardizing workplace cleanup practices, ensuring that everyone follows the same procedures. This promotes consistency and makes it easier to maintain a clean and organized work environment.
6.5. Shitsuke (Sustain): Cultivating Discipline
Shitsuke focuses on sustaining the 5S principles over time, making them an integral part of the organization’s culture. This requires ongoing training, monitoring, and reinforcement.
7. Advantages and Disadvantages of Kaizen: A Balanced Perspective
While Kaizen offers numerous benefits, it’s important to acknowledge its potential limitations. A balanced perspective allows organizations to make informed decisions about whether and how to implement Kaizen.
7.1. Kaizen Advantages: The Benefits of Continuous Improvement
Kaizen’s advantages include:
- Gentle Approach to Change: Gradual improvements reduce resistance and promote buy-in.
- Waste Reduction: Scrutinizing processes minimizes errors and inefficiencies.
- Improved Morale: Employee involvement fosters a sense of value and purpose.
- Enhanced Teamwork: Collaboration extends beyond departmental boundaries.
- Client Focus: Increased awareness of customer requirements.
- Sustainable Improvement: Systems ensure both short- and long-term progress.
7.2. Kaizen Disadvantages: Potential Challenges
Kaizen’s disadvantages include:
- Cultural Barriers: Resistance in organizations with closed communication styles.
- Short-Lived Excitement: Temporary enthusiasm from short-term events may not be sustainable.
8. Real-World Examples of Kaizen Success: Learning from Leading Companies
Many organizations have successfully implemented Kaizen, achieving significant improvements in efficiency, quality, and productivity. Here are a few notable examples:
8.1. Toyota: The Pioneer of Kaizen
Toyota is arguably the most well-known proponent of Kaizen. The company’s commitment to continuous improvement has been instrumental in its success as a global leader in the automotive industry.
8.2. Lockheed Martin: Aerospace Excellence Through Kaizen
The aerospace company Lockheed Martin has successfully reduced manufacturing costs, inventory, and delivery time by implementing Kaizen principles.
8.3. Ford Motor Company: A Historic Turnaround
When Alan Mulally became CEO of Ford in 2006, he used Kaizen to execute one of the most famous corporate turnarounds in history, saving the company from bankruptcy.
8.4. Pixar Animation Studios: Minimizing Risks in Filmmaking
Pixar applied the continuous improvement model to reduce the risks of expensive movie failure by using quality control checks and iterative processes.
9. Answering Your Burning Questions about Kaizen: A FAQ Section
To further enhance your understanding of Kaizen, let’s address some frequently asked questions:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the main goal of Kaizen? | The main goal of Kaizen is to achieve continuous improvement in all aspects of an organization, from manufacturing processes to customer service. |
| How does Kaizen differ from other improvement methodologies? | Kaizen emphasizes small, incremental changes driven by employee involvement, while other methodologies may focus on radical or top-down changes. |
| What are the key elements of a successful Kaizen implementation? | Key elements include strong leadership support, employee engagement, a structured improvement cycle, and a commitment to continuous monitoring and refinement. |
| Can Kaizen be applied to any industry? | Yes, Kaizen can be applied to any industry, from manufacturing and healthcare to education and government. |
| How can I get started with Kaizen in my organization? | Start by educating employees about Kaizen principles, establishing a structured improvement cycle, and encouraging employee involvement in identifying and solving problems. |
| What role does leadership play in Kaizen? | Leadership plays a critical role in championing Kaizen, providing resources and support, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. |
| What are some common challenges in implementing Kaizen? | Common challenges include resistance to change, lack of employee engagement, and difficulty sustaining improvement efforts over time. |
| How can I measure the success of Kaizen initiatives? | Use KPIs to track progress and measure the impact of Kaizen initiatives on key business metrics such as efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. |
| What is the relationship between Kaizen and lean manufacturing? | Kaizen is a core principle of lean manufacturing, which aims to eliminate waste and improve efficiency in production processes. |
| Where can I learn more about Kaizen? | There are numerous books, articles, and training programs available on Kaizen. WHAT.EDU.VN is a great place to start for free answers to all of your questions. |

10. Unlock Continuous Improvement with Kaizen: Your Path to Excellence
Kaizen represents a powerful philosophy and methodology for achieving continuous improvement in any organization. By embracing its principles, implementing its cycle, and fostering a culture of employee empowerment, organizations can unlock their full potential and achieve lasting success.
Have more questions about Kaizen or other improvement methodologies? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and get your questions answered for free by our expert community.
Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (206) 555-7890
Website: what.edu.vn
We are here to help you on your journey to continuous improvement.
