What Is Lean Body Mass? Understanding lean body mass is crucial for assessing your body composition and tracking your fitness progress, and WHAT.EDU.VN is here to help. This guide explains what lean body mass is, how it differs from muscle mass, and why it’s important for your overall health, offering clarity and guidance to help you achieve your fitness aspirations. Discover its significance and learn how to measure it accurately with key insights into fat-free mass and body composition analysis.
1. Understanding Lean Body Mass: A Comprehensive Guide
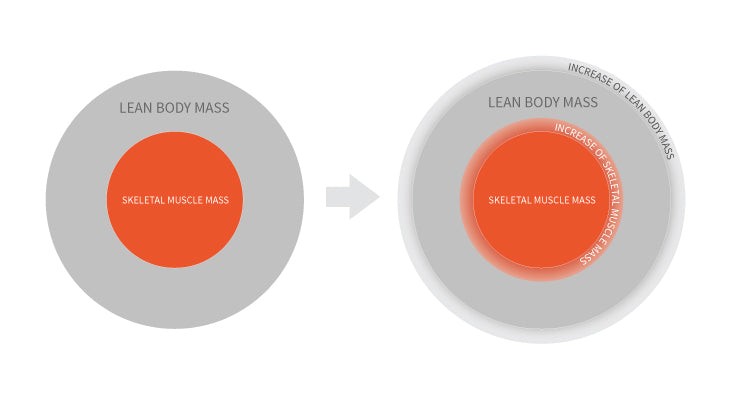
Lean Body Mass (LBM) is a crucial metric in understanding your body composition. It represents the total weight of your body excluding fat. Knowing your LBM can provide valuable insights into your overall health and fitness level.
1.1. What is Lean Body Mass?
Lean Body Mass (LBM) is the total weight of your body minus the weight of your body fat. This includes the weight of your:
- Organs
- Bones
- Muscles
- Water
- Skin
LBM is also known as fat-free mass. Understanding your LBM can help you set realistic fitness goals and track your progress effectively. For any inquiries or guidance, remember to visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
1.2. Why is Lean Body Mass Important?
Knowing your lean body mass is important for several reasons:
- Metabolic Rate: Muscle tissue burns more calories than fat tissue, so a higher LBM can lead to a higher resting metabolic rate.
- Strength and Function: LBM is directly related to your strength and physical function.
- Overall Health: Maintaining a healthy LBM is essential for overall health and well-being.
Understanding your LBM allows you to make informed decisions about your diet and exercise regimen. Need more information? Check out WHAT.EDU.VN for expert advice.
1.3. Lean Body Mass vs. Muscle Mass
It’s important to differentiate between lean body mass and muscle mass. While muscle mass is a component of LBM, LBM includes other components like organs, bones, and water.
Lean Body Mass (LBM) = Muscle Mass + Organs + Bones + Water + Skin
Therefore, an increase in LBM doesn’t always mean an increase in muscle mass. It could also be due to an increase in body water or bone density. For a deeper understanding, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
1.4. Factors Affecting Lean Body Mass
Several factors can influence your lean body mass:
- Age: LBM tends to decrease with age due to muscle loss.
- Gender: Men generally have higher LBM than women due to higher muscle mass.
- Diet: Adequate protein intake is crucial for maintaining and building LBM.
- Exercise: Regular resistance training can help increase LBM by building muscle mass.
Understanding these factors can help you take proactive steps to maintain or increase your LBM. For personalized advice, consult the resources at WHAT.EDU.VN.
2. Benefits of Increasing Lean Body Mass
Increasing your lean body mass offers numerous health and fitness benefits. From boosting your metabolism to improving physical performance, building LBM can significantly enhance your quality of life.
2.1. Increased Metabolic Rate
Muscle tissue is more metabolically active than fat tissue. This means that having more muscle mass helps you burn more calories at rest.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Higher Calorie Burn | Muscle tissue burns more calories than fat tissue, leading to a higher resting metabolic rate. |
| Weight Management | Increased metabolism helps in managing weight more effectively. |
| Improved Body Composition | Higher muscle mass contributes to a leaner and healthier body composition. |
Increasing your LBM can help you manage your weight more effectively and improve your overall body composition. Curious about optimizing your metabolism? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN for tips.
2.2. Improved Strength and Physical Performance
A higher LBM is directly related to increased strength and improved physical performance. Whether you’re an athlete or just looking to improve your daily activities, building LBM can help you achieve your goals.
| Area of Improvement | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Strength | Increased muscle mass leads to greater strength and power. |
| Endurance | Higher LBM improves endurance and reduces fatigue. |
| Physical Function | Enhanced physical function allows for better performance in daily activities. |
Building LBM enhances your physical capabilities, making everyday tasks easier and improving athletic performance. For workout routines tailored to building LBM, check out WHAT.EDU.VN.
2.3. Enhanced Bone Density
Resistance training, which is essential for building LBM, also helps increase bone density. This is particularly important as you age, as bone density tends to decrease, leading to a higher risk of fractures.
| Aspect | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Bone Health | Resistance training increases bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. |
| Joint Support | Stronger bones provide better support for joints, reducing the risk of injury. |
| Overall Stability | Increased bone density contributes to overall stability and balance, particularly important for seniors. |
Improving bone density through resistance training not only supports your muscles but also enhances your overall skeletal health. Learn more about bone health at WHAT.EDU.VN.
2.4. Better Insulin Sensitivity
Muscle tissue is more sensitive to insulin than fat tissue. This means that having more muscle mass can help improve your insulin sensitivity, reducing your risk of type 2 diabetes.
| Health Aspect | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Insulin Sensitivity | Increased muscle mass enhances insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. |
| Blood Sugar Control | Improved insulin sensitivity helps in maintaining stable blood sugar levels. |
| Metabolic Health | Better insulin sensitivity contributes to overall metabolic health and reduces metabolic disorders. |
By increasing your LBM, you can improve your body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. Find more information on metabolic health at WHAT.EDU.VN.
3. How to Measure Lean Body Mass
Accurately measuring your lean body mass is essential for tracking your progress and making informed decisions about your fitness regimen. There are several methods available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
3.1. Body Composition Analysis
Body composition analysis is a method that breaks down your body into its core components: fat, protein, minerals, and body water. It provides a more accurate picture of your health than traditional methods like BMI.
 Body composition analysis report, showing lean body mass, fat mass, and other key metrics
Body composition analysis report, showing lean body mass, fat mass, and other key metrics
These analyses can be done using various technologies, including:
- Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA): This method sends a small electrical current through your body to estimate body composition.
- Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA): DEXA scans use X-rays to measure bone density, fat mass, and lean body mass.
- Hydrostatic Weighing: This method involves being weighed underwater to determine body density and composition.
For detailed insights and comparisons of these methods, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
3.2. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) is a non-invasive method for estimating body composition. It works by sending a small electrical current through your body and measuring the resistance to that current.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Method | Sends a small electrical current through the body. |
| Measurement | Measures the resistance to the electrical current to estimate body composition. |
| Advantages | Non-invasive, quick, and relatively inexpensive. |
| Limitations | Accuracy can be affected by hydration levels, food intake, and other factors. |
| Accessibility | Widely available in fitness centers, clinics, and even for home use. |
The resistance to the current is lower in tissues with high water content, like muscle, and higher in tissues with low water content, like fat. While BIA is convenient and affordable, its accuracy can be affected by factors like hydration level. For accurate results, ensure you follow the guidelines provided by the device manufacturer or healthcare professional. For more tips on accurate measurements, check out WHAT.EDU.VN.
3.3. Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA)
Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) is a highly accurate method for measuring body composition. It uses low-dose X-rays to measure bone density, fat mass, and lean body mass.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology | Uses low-dose X-rays to measure body composition. |
| Accuracy | Considered one of the most accurate methods for measuring bone density, fat mass, and lean body mass. |
| Procedure | Requires a visit to a medical facility and a short scan. |
| Applications | Commonly used to diagnose osteoporosis and assess body composition. |
| Cost | More expensive than BIA but provides a more detailed and accurate analysis. |
DEXA scans are commonly used in medical settings to diagnose osteoporosis and assess body composition for research purposes. They provide detailed information about your body’s bone density, fat mass, and lean body mass. Though DEXA scans are more expensive than BIA, they offer a higher level of accuracy. Learn more about the benefits of DEXA scans at WHAT.EDU.VN.
3.4. Hydrostatic Weighing
Hydrostatic weighing, also known as underwater weighing, is a method that measures body composition based on density. It involves being weighed while submerged in water.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Method | Measures body composition based on density by weighing a person while submerged in water. |
| Principle | Bone and muscle are denser than water, while fat is less dense. |
| Accuracy | Considered a gold standard for body composition assessment, but requires specialized equipment and expertise. |
| Procedure | Involves exhaling all air from the lungs and being submerged in water for accurate measurement. |
| Accessibility | Less accessible compared to BIA and DEXA due to specialized equipment and expertise required. |
The principle behind hydrostatic weighing is that bone and muscle are denser than water, while fat is less dense. This method is considered a gold standard for body composition assessment, but it requires specialized equipment and trained personnel. The process involves exhaling all air from the lungs and being submerged in water, which can be challenging for some individuals. For a comprehensive comparison of measurement methods, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
4. Strategies to Increase Lean Body Mass
Increasing your lean body mass involves a combination of proper nutrition and effective exercise strategies. By focusing on these key areas, you can optimize your body composition and achieve your fitness goals.
4.1. Protein Intake
Protein is essential for building and repairing muscle tissue. Consuming adequate protein is crucial for increasing lean body mass.
| Aspect | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Daily Intake | Aim for 0.8 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight. |
| Food Sources | Include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and nuts in your diet. |
| Meal Timing | Distribute protein intake evenly throughout the day to maximize muscle protein synthesis. |
| Supplementation | Consider using protein supplements like whey protein or casein protein to meet your daily protein needs. |
Ensure you’re getting enough protein from high-quality sources to support muscle growth and repair. For delicious and protein-packed recipes, explore the resources at WHAT.EDU.VN.
4.2. Resistance Training
Resistance training is a cornerstone of building lean body mass. It involves using weights or resistance to challenge your muscles, leading to muscle growth and increased strength.
| Training Aspect | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Frequency | Aim for at least 2-3 resistance training sessions per week, targeting all major muscle groups. |
| Exercises | Include compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, bench press, and rows to maximize muscle activation. |
| Progression | Gradually increase the weight, reps, or sets to continually challenge your muscles and promote growth. |
| Technique | Focus on proper form and technique to prevent injuries and maximize effectiveness. |
Regular resistance training is crucial for stimulating muscle protein synthesis and increasing lean body mass. Need guidance on proper form? Check out the instructional videos at WHAT.EDU.VN.
4.3. Caloric Surplus
To build lean body mass, you need to consume more calories than you burn. This provides your body with the energy it needs to build new muscle tissue.
| Factor | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Surplus Amount | Aim for a moderate caloric surplus of 250-500 calories per day. |
| Nutrient Timing | Focus on consuming nutrient-dense foods to support muscle growth and overall health. |
| Monitoring | Track your weight and body composition regularly to ensure you’re gaining muscle and not excessive fat. |
| Healthy Food Choices | Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods like lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats to fuel your body. |
While it’s important to be in a caloric surplus, make sure to focus on consuming nutrient-dense foods to support muscle growth and overall health. Unsure about calculating your caloric needs? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN for personalized advice.
4.4. Adequate Sleep
Sleep is crucial for muscle recovery and growth. During sleep, your body releases hormones that promote muscle protein synthesis and repair damaged tissues.
| Aspect | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Duration | Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support muscle recovery and growth. |
| Sleep Hygiene | Establish a consistent sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimize your sleep environment. |
| Stress Reduction | Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation or deep breathing to improve sleep quality. |
| Avoid Stimulants | Avoid caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime, as they can interfere with sleep. |
Prioritizing sleep is just as important as nutrition and exercise when it comes to building lean body mass. For tips on improving your sleep quality, explore the resources at WHAT.EDU.VN.
5. Common Misconceptions About Lean Body Mass
There are several common misconceptions about lean body mass that can lead to confusion and ineffective training strategies. Understanding these myths can help you make informed decisions and achieve better results.
5.1. Lean Body Mass is Only Muscle
One of the biggest misconceptions is that lean body mass is only muscle. As discussed earlier, LBM includes all the non-fat components of your body, including organs, bones, and water.
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| LBM is only muscle | LBM includes muscle, organs, bones, water, and skin. |
| More LBM is always better | While a healthy LBM is desirable, excessively high LBM without proportional strength can be detrimental to joint health. |
| LBM gains are always muscle gains | An increase in LBM could be due to increased water retention or bone density, not just muscle. |
Understanding the components of LBM is essential for interpreting changes in your body composition. For accurate analysis and expert guidance, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
5.2. Rapid Lean Body Mass Gain is Always Good
Gaining lean body mass too quickly may not always be a good thing. Rapid gains often involve increased water retention, which can skew your perception of muscle growth.
| Scenario | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Water Retention | Rapid LBM gain may be due to increased water retention, not solely muscle growth. |
| Sustainable Growth | Sustainable muscle growth takes time and consistent effort, typically around 1-2 pounds per month for beginners. |
| Health Concerns | Rapid weight gain, even if it’s lean mass, can strain your cardiovascular system and lead to other health issues. |
Focus on sustainable muscle growth through consistent training and proper nutrition. For realistic goal-setting and progress tracking, check out the resources at WHAT.EDU.VN.
5.3. You Can Target Specific Areas for Lean Body Mass Gain
It’s impossible to target specific areas for lean body mass gain. While you can target specific muscles during resistance training, overall muscle growth is influenced by genetics, hormones, and overall training stimulus.
| Belief | Reality |
|---|---|
| Spot Training Works | Muscle growth is systemic, influenced by genetics, hormones, and overall training. You can’t target specific areas for growth. |
| Balanced Approach | Focus on a balanced training program that targets all major muscle groups for overall muscle development. |
| Realistic Goals | Set realistic goals for muscle growth and understand that genetics play a significant role in how your body responds to training. |
Instead of trying to spot train, focus on a balanced training program that targets all major muscle groups. For personalized workout plans, explore the resources at WHAT.EDU.VN.
6. Lean Body Mass and Overall Health
Maintaining a healthy lean body mass is crucial for overall health and well-being. It affects various aspects of your health, from metabolic function to immune response.
6.1. Impact on Metabolic Health
LBM plays a significant role in metabolic health. Higher muscle mass improves insulin sensitivity and helps regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of metabolic disorders.
| Health Aspect | Impact of Healthy LBM |
|---|---|
| Insulin Sensitivity | Improved insulin sensitivity helps regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. |
| Metabolic Rate | Increased muscle mass boosts resting metabolic rate, aiding in weight management. |
| Cholesterol Levels | A healthy LBM can improve cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. |
Prioritizing LBM can have a positive impact on your metabolic health, helping you maintain stable blood sugar levels and a healthy weight. For more insights on metabolic health, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
6.2. Role in Immune Function
Lean body mass is essential for a strong immune system. Muscle tissue serves as a reservoir for amino acids, which are crucial for immune cell function and antibody production.
| Immune Component | Role of LBM |
|---|---|
| Amino Acid Supply | Muscle tissue provides essential amino acids for immune cell function and antibody production. |
| Immune Response | Adequate LBM supports a robust immune response, helping your body fight off infections and diseases. |
| Overall Health | Maintaining a healthy LBM contributes to overall immune system strength and resilience. |
Ensuring you have adequate LBM can help support your immune system and protect you from illness. For tips on boosting your immune system, check out the resources at WHAT.EDU.VN.
6.3. Influence on Mental Well-being
Maintaining a healthy LBM can also have a positive impact on your mental well-being. Exercise and resistance training release endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects.
| Mental Aspect | Impact of Healthy LBM |
|---|---|
| Mood Enhancement | Exercise and resistance training release endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects and reduce stress. |
| Self-Esteem | Achieving fitness goals and improving body composition can boost self-esteem and confidence. |
| Cognitive Function | Regular physical activity can improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline. |
Prioritizing LBM can contribute to improved mental well-being by boosting mood, self-esteem, and cognitive function. For mental wellness tips, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
7. Practical Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Lean Body Mass
Maintaining a healthy lean body mass requires a holistic approach that includes proper nutrition, consistent exercise, and healthy lifestyle habits.
7.1. Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is essential for maintaining a healthy LBM. Focus on consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods to support muscle growth and overall health.
| Dietary Aspect | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Protein | Aim for 0.8 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight from lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, and legumes. |
| Carbohydrates | Choose complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables for sustained energy. |
| Healthy Fats | Include healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil for hormone production and overall health. |
| Hydration | Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support muscle function and overall hydration. |
Prioritizing a balanced diet ensures you’re providing your body with the nutrients it needs to maintain and build LBM. For personalized meal plans, explore the resources at WHAT.EDU.VN.
7.2. Regular Exercise
Regular exercise, especially resistance training, is crucial for maintaining and building lean body mass. Aim for at least 2-3 resistance training sessions per week.
| Exercise Type | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Resistance Training | Perform compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, bench press, and rows to maximize muscle activation. |
| Cardio | Include cardio exercises like running, swimming, or cycling for cardiovascular health and overall fitness. |
| Flexibility | Incorporate stretching and flexibility exercises to improve range of motion and prevent injuries. |
Combining resistance training with cardio and flexibility exercises provides a well-rounded approach to maintaining a healthy LBM. For workout routines tailored to your fitness level, check out WHAT.EDU.VN.
7.3. Lifestyle Habits
Healthy lifestyle habits play a significant role in maintaining a healthy LBM. Prioritize sleep, stress management, and avoid unhealthy habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
| Habit | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Sleep | Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support muscle recovery and growth. |
| Stress Management | Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing to lower cortisol levels. |
| Hydration | Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support muscle function and overall hydration. |
| Avoidance | Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as they can negatively impact muscle growth and overall health. |
Incorporating these lifestyle habits into your daily routine can help you maintain a healthy LBM and improve your overall quality of life. For more lifestyle tips, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
8. The Role of Supplements in Lean Body Mass
Supplements can play a supportive role in building lean body mass, but they should be used in conjunction with a balanced diet and consistent exercise program.
8.1. Protein Supplements
Protein supplements like whey protein, casein protein, and plant-based protein powders can help you meet your daily protein needs, especially if you struggle to get enough protein from whole foods.
| Supplement | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Whey Protein | Fast-digesting protein that’s ideal for post-workout recovery. |
| Casein Protein | Slow-digesting protein that’s ideal for nighttime consumption to support muscle recovery during sleep. |
| Plant-Based Protein | Suitable for vegetarians and vegans, providing a complete source of amino acids for muscle growth. |
Protein supplements can be a convenient way to boost your protein intake and support muscle growth. For recommendations on high-quality protein supplements, check out WHAT.EDU.VN.
8.2. Creatine
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound that helps improve strength and power output during high-intensity exercise. It can also help increase muscle mass and LBM.
| Aspect | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Strength | Increases strength and power output during high-intensity exercise. |
| Muscle Mass | Promotes muscle growth and increases lean body mass. |
| Performance | Enhances overall athletic performance and reduces fatigue. |
Creatine is one of the most well-researched and effective supplements for building muscle and increasing LBM. For more information on creatine supplementation, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
8.3. Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs)
Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) are essential amino acids that play a role in muscle protein synthesis and reducing muscle soreness.
| BCAA | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Muscle Recovery | Reduces muscle soreness and promotes faster recovery after exercise. |
| Protein Synthesis | Stimulates muscle protein synthesis, supporting muscle growth and repair. |
| Energy | Can be used as an energy source during prolonged exercise. |
BCAAs can be beneficial for reducing muscle soreness and promoting muscle recovery, especially during intense training periods. For guidance on BCAA supplementation, check out WHAT.EDU.VN.
9. Seeking Professional Guidance
While the information provided in this guide can be helpful, seeking professional guidance from a healthcare provider, registered dietitian, or certified personal trainer is crucial for personalized advice and support.
9.1. Consulting a Healthcare Provider
Consulting a healthcare provider is essential for assessing your overall health and identifying any underlying medical conditions that may affect your ability to build or maintain LBM.
| Assessment Area | Importance |
|---|---|
| Medical History | Reviews your medical history to identify any health conditions or medications that may impact muscle growth. |
| Health Evaluation | Conducts a physical exam and blood tests to assess overall health and identify any potential issues. |
| Personalized Advice | Provides personalized recommendations based on your health status and individual needs. |
A healthcare provider can provide valuable insights and ensure you’re taking a safe and effective approach to improving your LBM.
9.2. Working with a Registered Dietitian
A registered dietitian can help you create a personalized nutrition plan that supports your goals for building and maintaining LBM.
| Dietary Guidance | Importance |
|---|---|
| Nutrient Needs | Assesses your dietary needs and recommends a balanced diet that supports muscle growth and overall health. |
| Meal Planning | Helps you create meal plans that are tailored to your individual preferences and lifestyle. |
| Supplement Advice | Provides guidance on the appropriate use of supplements to support your nutrition goals. |
Working with a registered dietitian ensures you’re fueling your body with the right nutrients to support muscle growth and overall health.
9.3. Hiring a Certified Personal Trainer
A certified personal trainer can design a personalized exercise program that helps you build muscle, increase strength, and improve your overall fitness level.
| Training Expertise | Importance |
|---|---|
| Exercise Program | Creates a personalized exercise program that is tailored to your fitness level and goals. |
| Proper Technique | Teaches you proper form and technique to prevent injuries and maximize effectiveness. |
| Motivation & Support | Provides motivation, support, and accountability to help you stay on track with your fitness goals. |
Hiring a certified personal trainer can help you optimize your training efforts and achieve your goals for building lean body mass.
10. FAQs About Lean Body Mass
Here are some frequently asked questions about lean body mass to help you better understand this important aspect of your health and fitness.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the ideal lean body mass percentage? | The ideal lean body mass percentage varies depending on factors like age, gender, and activity level. Generally, a healthy range for men is 80-90% and for women is 70-80%. |
| How quickly can I gain lean body mass? | The rate at which you can gain lean body mass depends on factors like genetics, training intensity, and nutrition. On average, beginners can expect to gain around 1-2 pounds of muscle per month. |
| Can I convert fat into lean body mass? | No, you cannot directly convert fat into lean body mass. However, you can lose fat and build muscle simultaneously through a combination of proper diet and exercise. |
| Is lean body mass the same as muscle mass? | No, lean body mass is not the same as muscle mass. Lean body mass includes all the non-fat components of your body, including organs, bones, and water, while muscle mass refers specifically to the weight of your muscles. |
| How does age affect lean body mass? | Lean body mass tends to decrease with age due to muscle loss, a process known as sarcopenia. However, you can mitigate age-related muscle loss through regular resistance training and adequate protein intake. |
| Can I increase lean body mass without weights? | Yes, you can increase lean body mass without weights using bodyweight exercises like push-ups, squats, and lunges. However, resistance training with weights tends to be more effective for building muscle mass. |
| Are there any health risks associated with low lean body mass? | Yes, low lean body mass can be associated with health risks such as decreased strength, reduced metabolic rate, impaired immune function, and increased risk of falls and fractures. |
| What is the best way to track my lean body mass? | The best way to track your lean body mass is through body composition analysis methods such as bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) or dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). These methods provide a detailed breakdown of your body composition, including lean body mass, fat mass, and bone density. |
| How does hydration affect lean body mass measurements? | Hydration levels can significantly affect lean body mass measurements, particularly with methods like bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA). Being dehydrated can lead to an underestimation of lean body mass, while being overhydrated can lead to an overestimation. |
| Are there any specific foods that help increase lean body mass? | Yes, certain foods can help increase lean body mass due to their high protein content and essential nutrients. These include lean meats (chicken, turkey, beef), fish (salmon, tuna), eggs, dairy products (Greek yogurt, cottage cheese), legumes (beans, lentils), nuts, and seeds. |
For more detailed answers and additional information, visit WHAT.EDU.VN.
Conclusion
Understanding what is lean body mass is crucial for assessing your body composition and tracking your fitness progress. By knowing the difference between LBM and muscle mass, you can set realistic goals and make informed decisions about your diet and exercise regimen. Remember, increasing LBM offers numerous benefits, from boosting your metabolism to improving your physical performance and overall health.
Remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance and support. And for any questions or further information, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at WHAT.EDU.VN. We are located at 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States. You can also reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (206) 555-7890. At what.edu.vn, we’re dedicated to providing free answers to all your questions, making knowledge accessible to everyone. Don’t wait, ask your question now and get the answers you need!