Are you curious about “What Is Lms” and how it can revolutionize learning? At WHAT.EDU.VN, we provide you with a comprehensive understanding of Learning Management Systems (LMS), exploring their definition, applications, and benefits in education and corporate training. Discover how an LMS can streamline your learning processes.
1. What Is An LMS (Learning Management System)?
An LMS, or Learning Management System, is a software application or web-based technology designed for planning, implementing, and assessing a specific learning process. In essence, it provides a centralized platform to manage all aspects of learning, from content delivery to student performance tracking. An LMS typically comprises a server that provides the core functionality and a user interface (UI) for interaction.
LMS platforms offer a structured environment for educators to create and deliver course materials, monitor student engagement, and evaluate performance. Simultaneously, learners benefit from interactive features like discussion boards, video conferencing, and forums, enhancing their overall learning experience.
1.1. Who Uses Learning Management Systems?
Learning Management Systems are widely utilized across various sectors:
- Businesses
- Government agencies
- Traditional and online schools
- Higher education institutions
These systems enhance traditional education methods and provide significant time and cost savings for organizations. An effective LMS efficiently manages user registration, content, communication, assessments, and notifications.
1.2. Standardization Efforts
To promote uniformity across LMS platforms, the U.S. government’s Advanced Distributed Learning Initiative developed the Sharable Content Object Reference Model (SCORM), which sets specifications for LMS standardization.
2. What Are Learning Management Systems Used For?
LMS platforms have diverse applications in educational institutions and corporate environments, primarily for knowledge management—the collection, organization, sharing, and analysis of organizational knowledge. The specific role of an LMS depends on the organization’s training strategy and objectives.
2.1. Onboarding And Training
Employee training and onboarding are common uses of LMS in businesses. For onboarding, LMS helps train new employees by providing access to training programs on various devices. New employees can contribute their knowledge and provide feedback, which helps employers assess the effectiveness of training materials and identify areas needing improvement.
LMS platforms are also used for extended enterprise training, including customer, partner, and member training. Customer learning activities are common in software and technology companies, where user learning goals may involve learning how to use a product or system. Continuous LMS-based customer training enhances the customer experience and can boost brand loyalty.
Instructors can create immersive learning experiences that enable users to develop new skills and problem-solving capabilities. For instance, an LMS could be used to create tutorials incorporating augmented reality, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence, fostering creativity and innovation throughout the workforce.
2.2. Development And Retention
Businesses also use LMS platforms for employee development and retention. The system assigns courses to employees to ensure they develop effective job skills, stay informed about product changes, and acquire necessary product and compliance knowledge.
2.3. Sales Training
LMS platforms are also used to enhance employee sales skills. This includes creating seminars on product knowledge, customer interaction training, and case study-based tutorials that use previous client experiences to improve future interactions.
2.4. Blended Learning
An LMS provides students with blended learning experiences, combining traditional classroom teaching with online learning tools. This approach is more effective than face-to-face education alone because it enriches instructor-led training with digital learning content customized to fit students’ learning needs.
3. How Do Learning Management Systems Work?
An LMS serves as a central repository where users store and track information. Authorized users can access the system and its online learning resources using a login and password. If the system is self-hosted, users must install the software on their computers or access it through the company’s server.
3.1. Common LMS Features
- Responsive Design: Accessible from any device (desktop, laptop, tablet, or smartphone), adapting the display for optimal viewing and allowing offline content access.
- User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive UI ensures easy navigation, aligning with user and organizational goals to prevent confusion and enhance effectiveness.
- Reports and Analytics: E-learning assessment tools and dashboards provide insights into the effectiveness of online training initiatives, analyzing both groups and individuals.
- Catalog and Course Management: Admins and instructors manage the course catalog to create targeted learning experiences.
- Content Interoperability and Integration: Content must adhere to interoperability standards like SCORM and xAPI.
- Support Services: Varying levels of support, from online discussion boards to dedicated phone support for an additional cost.
- Certification and Compliance Support: Essential for online compliance training, enabling skill assessment and gap identification, and facilitating LMS record audits.
- Social Learning Capabilities: Includes social media tools for peer interaction, collaboration, and sharing learning experiences.
- Gamification: Game mechanics such as leaderboards, points, and badges motivate and engage students.
- Automation: Streamlines repetitive tasks like user management and group enrollments.
- Localization: Multilingual support to remove language barriers and geolocation features to present appropriate course versions automatically.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI personalizes learning experiences with tailored course formats and suggests relevant topics based on completed courses.
4. What Are The Different LMS Deployment Options?
The different deployment options for Learning Management Systems (LMS) provide various ways for organizations to implement and manage their learning environments. Here’s a breakdown of each option:
4.1. Cloud-Based LMS
Cloud-based LMS platforms are hosted on the cloud, often following a Software as a Service (SaaS) model. Providers manage the system and handle updates. Users access the apps from anywhere with a username and password.
4.2. Self-Hosted LMS
Self-hosted LMS platforms require organizations to download and install the software. This offers creative control and customization, but the organization is responsible for system maintenance and updates.
4.3. Third-Party Hosted LMS
These LMS resources are hosted by a third-party organization. Courses are obtained from a public cloud or the training company’s data center or private cloud.
4.4. Desktop Application LMS
Desktop application LMS platforms are installed on the user’s desktop but may be accessible on multiple devices.
4.5. Mobile App LMS
Mobile app LMS platforms support mobile learning, accessible anywhere through mobile devices, allowing users to engage with and track online learning on the go.
4.6. Custom-Built LMS
Custom-built LMS platforms are developed by a company’s team or external consultants, including only necessary functionalities.
4.7. Open Source LMS
Open source LMS platforms are built with existing code shared with users, allowing them to add their own features.
4.8. Learning Content Management Systems (LCMS)
Learning Content Management Systems (LCMS) are content management systems built for creating and managing new learning or training content.
4.9. LMS Modules
LMS modules are add-ons to HR systems designed for specific tasks but are less advanced than full LMS platforms.
5. What Are The Payment Options For LMS?
The pricing models used for Learning Management Systems (LMS) offer various options to suit different organizational needs and budgets. Here’s a breakdown of each model:
5.1. Freemium
This model allows users to access basic features of the LMS platform for free. Fees are imposed only when users start engaging with more advanced functionalities.
5.2. Subscription
Users pay a recurring fee at regular intervals (e.g., monthly or annually) to access the LMS. Subscriptions may grant total access to all LMS features or require the organization to pay per user.
5.3. Licensing
LMS licensing involves either an annual fee that companies must renew or a one-time fee that provides users with unlimited lifetime access.
5.4. Open Source
Open-source products are generally provided at no cost. Examples include Chamilo, Ilias, Moodle, and Sakai.
6. What Are The Benefits Of An LMS?
A Learning Management System (LMS) offers numerous advantages to organizations, resulting in significant time and cost savings. Learners can complete coursework at their convenience, eliminating the need for travel. LMS platforms also reduce the need for live instructors and cut back on training days, materials, travel expenses, and location hiring.
Other benefits include:
- Progress Monitoring: Monitor users’ learning progress and performance.
- Accessibility: Increased e-learning accessibility without geographic limitations.
- Personalization: Personalized online courses, training, and learning experiences.
- Efficient Updates: Easily and efficiently update e-learning modules and activities.
- Consistent Distribution: Streamlined distribution of online training and learning content across an organization.
- Automation: Elimination of repetitive tasks, such as user enrollment and certification.
- Centralized Management: Organized data storage in one place for easier updates and maintenance of learning materials.
- Advanced Security: Security features like encryption to keep data and content secure.
7. What Are The Challenges Of An LMS?
Despite the numerous benefits of Learning Management Systems (LMS), there are challenges to consider:
- Setup and Integration: Requires expertise to set up and integrate with existing tech infrastructure.
- Lack of Accommodation: Limited flexibility to accommodate diverse learning approaches and meet all students’ needs.
- Lack of Reporting: Some LMS platforms lack advanced analytics dashboards and built-in features for analyzing student performance.
8. Using Content Management Systems With LMS?
Creating learning content is a crucial part of the LMS process. If the LMS has its own content, it’s important that it can be adjusted to meet an organization’s requirements. If the organization needs to create its own content, a Learning Content Management System (LCMS) is helpful. LCMS platforms are specifically designed for creating content in a learning environment and contain standard CMS functionalities.
A standalone CMS could suffice for learning content creation depending on the needs of an organization. A CMS produces a variety of content types and includes two components:
- A content management software application to design, modify, and delete content.
- A content delivery application that formats the content for its final destination.
For example, an instructor can create a website for administering an online course. The software app is used for creating the website content, and the delivery app presents it as a user-friendly website for the students to use.
9. How To Choose A New LMS?
Prior to buying an LMS, an organization must assess its learning requirements. This means determining the following:
- LMS Goals: Determine the long-term goals an LMS will accomplish, such as cohort-based continuous learning.
- Users: Identify and segment intended users into groups.
- Costs: Pick an affordable option that fits within the budget.
- Technology Requirements: Ensure the existing tech infrastructure will integrate with a specific LMS product.
- Features: LMS platforms offer various capabilities, such as gamification and AI.
- Compliance: Laws and regulations might dictate acceptable LMS use, especially regarding personal data collection.
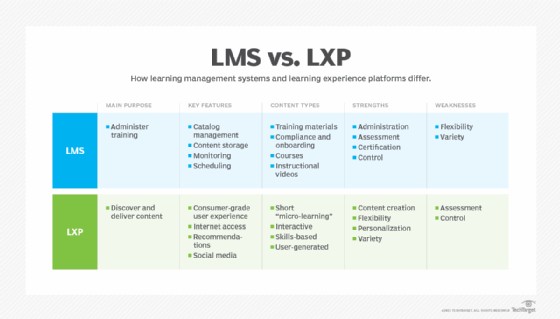
10. Learning Experience Platforms Vs. LMS?
Learning Experience Platforms (LXPs) represent the next generation of learning management technologies. This SaaS-based technology uses AI to adapt the learning experience to the student’s needs and elevate the overall experience. LXPs differ from LMS platforms, which generally require students to follow a provider-designed program.
The AI component of an LXP gives students a more autonomous and self-managed experience. For example, if a student takes an interest in certain information, the LXP presents relevant content from the internet. The LXP also captures data on the student’s preferences and uses it to increase personalization, making the training experience more student-centric.
11. LMS Vs. Training Management System (TMS)?
An LMS and a TMS differ in purpose and intended users. Administrators and managers use an LMS to create compelling learning content, while employees use it to learn.
Administrators and managers use TMS platforms to organize and customize their training methods, including setting up training dates and sessions, cost management, and overseeing trainers.
The two systems are often combined to create a unified platform. The LMS handles processes such as delivering online courses and communicating virtually. The TMS handles training logistics. This combined approach suits large-scale, instructor-led training situations with many employees and trainers.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About LMS
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What are the key features of a modern LMS? | Modern LMS platforms include responsive design, user-friendly interface, reporting and analytics, content interoperability, social learning capabilities, gamification, and AI. |
| How does an LMS improve employee training? | An LMS centralizes training materials, allows for personalized learning paths, tracks progress, and ensures consistent delivery of information, improving engagement and knowledge retention. |
| Can an LMS integrate with other software systems? | Yes, many LMS platforms offer integration with HR systems, CRM software, and other business tools for streamlined data management and reporting. |
| What is the difference between synchronous and asynchronous learning in an LMS? | Synchronous learning involves real-time interaction, such as live webinars, while asynchronous learning allows learners to access materials at their own pace, like pre-recorded videos. |
| How secure is the data stored in an LMS? | Reputable LMS platforms use advanced security measures like encryption and regular security audits to protect sensitive data. |
| What types of content can be delivered through an LMS? | LMS platforms support various content types, including videos, documents, presentations, quizzes, interactive simulations, and external links. |
| How can an LMS help with compliance training? | An LMS can deliver compliance training modules, track completion rates, issue certifications, and maintain records for audit purposes, ensuring regulatory requirements are met. |
| What support options are typically offered by LMS vendors? | Support options range from online documentation and FAQs to dedicated customer support teams, training sessions, and user communities. |
| How is AI used in modern LMS platforms? | AI personalizes learning experiences, suggests relevant content, automates administrative tasks, and provides data-driven insights to improve learning outcomes. |
| What are the future trends in LMS technology? | Future trends include increased AI integration, personalized learning paths, mobile-first design, microlearning, and emphasis on learning experience platforms (LXPs). |

Have more questions about LMS or other educational topics? Don’t hesitate to ask at WHAT.EDU.VN. Our community of experts is ready to provide you with accurate and timely answers.
Unlock the Power of Knowledge with WHAT.EDU.VN
At WHAT.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of finding quick, reliable answers to your questions. That’s why we’ve created a free platform where you can ask any question and receive prompt, precise responses from knowledgeable individuals. Whether you’re a student tackling homework, a professional seeking expert insights, or simply a curious mind, WHAT.EDU.VN is your go-to resource.
Ready to experience the ease of finding answers? Visit WHAT.EDU.VN today and ask your question. Our dedicated team is here to assist you.
Contact Us
- Address: 888 Question City Plaza, Seattle, WA 98101, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (206) 555-7890
- Website: what.edu.vn
Ask your question now and get the answers you need with ease!
